Non invasive genetic test
What is noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and what disorders can it screen for?: MedlinePlus Genetics
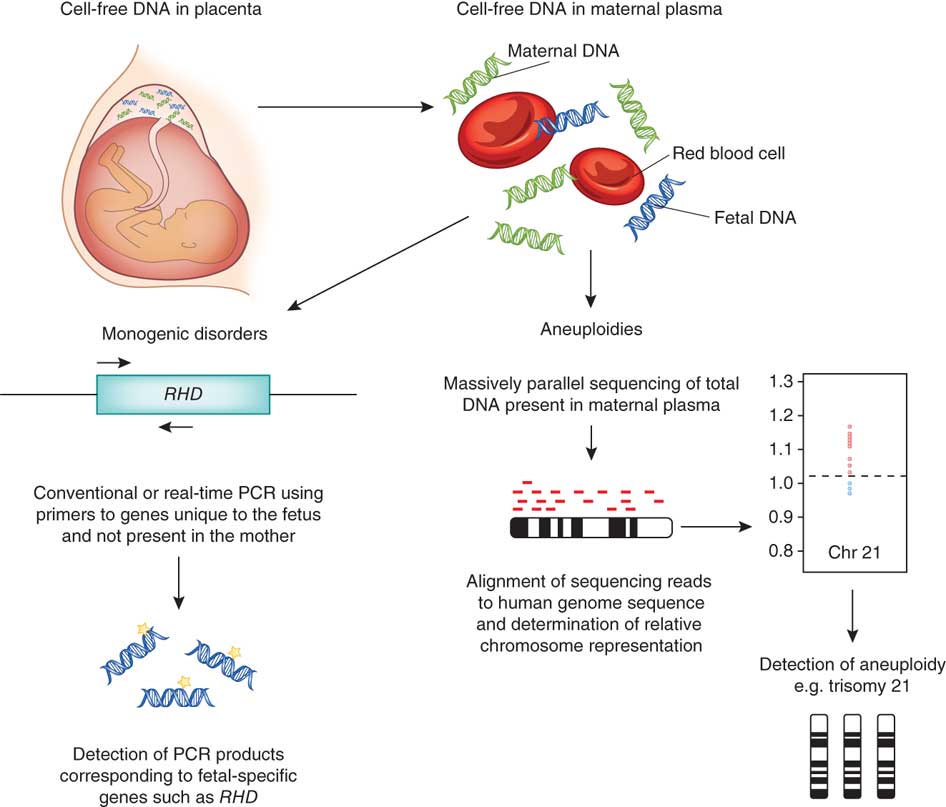
Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT), sometimes called noninvasive prenatal screening (NIPS), is a method of determining the risk that the fetus will be born with certain genetic abnormalities. This testing analyzes small fragments of DNA that are circulating in a pregnant woman’s blood. Unlike most DNA, which is found inside a cell’s nucleus, these fragments are free-floating and not within cells, and so are called cell-free DNA (cfDNA). These small fragments usually contain fewer than 200 DNA building blocks (base pairs) and arise when cells die off and get broken down and their contents, including DNA, are released into the bloodstream.
During pregnancy, the mother’s bloodstream contains a mix of cfDNA that comes from her cells and cells from the placenta. The placenta is tissue in the uterus that links the fetus and the mother’s blood supply. These cells are shed into the mother’s bloodstream throughout pregnancy. The DNA in placental cells is usually identical to the DNA of the fetus. Analyzing cfDNA from the placenta provides an opportunity for early detection of certain genetic abnormalities without harming the fetus.
NIPT is most often used to look for chromosomal disorders that are caused by the presence of an extra or missing copy (aneuploidy) of a chromosome. NIPT primarily looks for Down syndrome (trisomy 21, caused by an extra chromosome 21), trisomy 18 (caused by an extra chromosome 18), trisomy 13 (caused by an extra chromosome 13), and extra or missing copies of the X chromosome and Y chromosome (the sex chromosomes). The accuracy of the test varies by disorder.
NIPT may include screening for additional chromosomal disorders that are caused by missing (deleted) or copied (duplicated) sections of a chromosome. NIPT is beginning to be used to test for genetic disorders that are caused by changes (variants) in single genes. As technology improves and the cost of genetic testing decreases, researchers expect that NIPT will become available for many more genetic conditions.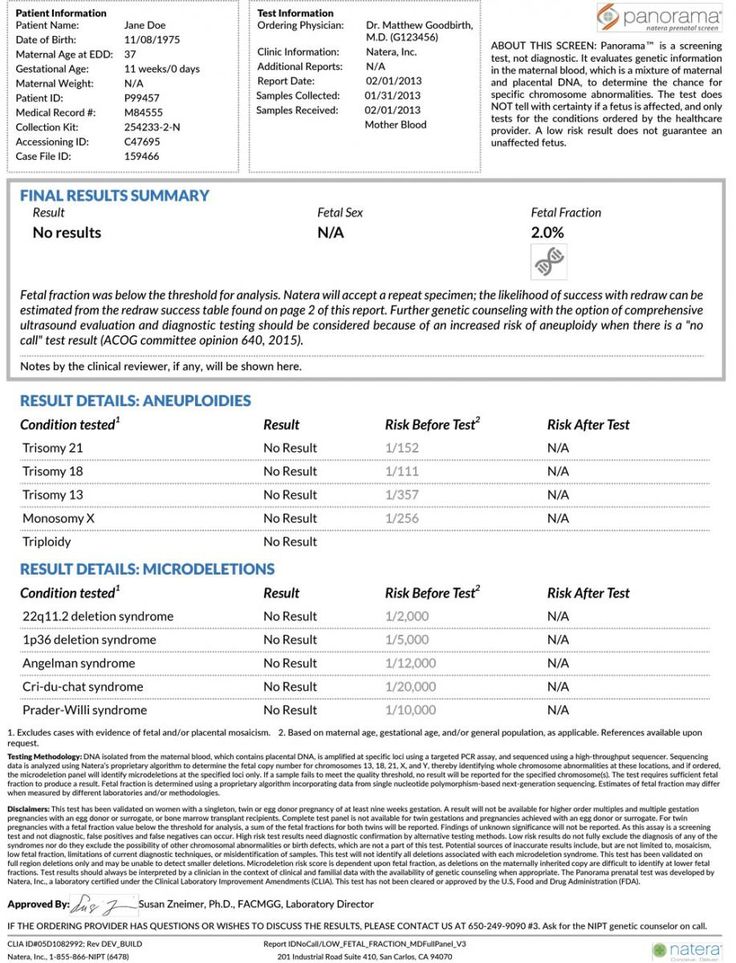
NIPT is considered noninvasive because it requires drawing blood only from the pregnant woman and does not pose any risk to the fetus. NIPT is a screening test, which means that it will not give a definitive answer about whether or not a fetus has a genetic condition. The test can only estimate whether the risk of having certain conditions is increased or decreased. In some cases, NIPT results indicate an increased risk for a genetic abnormality when the fetus is actually unaffected (false positive), or the results indicate a decreased risk for a genetic abnormality when the fetus is actually affected (false negative). Because NIPT analyzes both fetal and maternal cfDNA, the test may detect a genetic condition in the mother.
There must be enough fetal cfDNA in the mother’s bloodstream to be able to identify fetal chromosome abnormalities. The proportion of cfDNA in maternal blood that comes from the placenta is known as the fetal fraction. Generally, the fetal fraction must be above 4 percent, which typically occurs around the tenth week of pregnancy. Low fetal fractions can lead to an inability to perform the test or a false negative result. Reasons for low fetal fractions include testing too early in the pregnancy, sampling errors, maternal obesity, and fetal abnormality.
Low fetal fractions can lead to an inability to perform the test or a false negative result. Reasons for low fetal fractions include testing too early in the pregnancy, sampling errors, maternal obesity, and fetal abnormality.
There are multiple NIPT methods to analyze fetal cfDNA. To determine chromosomal aneuploidy, the most common method is to count all cfDNA fragments (both fetal and maternal). If the percentage of cfDNA fragments from each chromosome is as expected, then the fetus has a decreased risk of having a chromosomal condition (negative test result). If the percentage of cfDNA fragments from a particular chromosome is more than expected, then the fetus has an increased likelihood of having a trisomy condition (positive test result). A positive screening result indicates that further testing (called diagnostic testing, because it is used to diagnose a disease) should be performed to confirm the result.
Committee Opinion No. 640: Cell-Free DNA Screening For Fetal Aneuploidy. Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Sep;126(3):e31-7. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001051. PubMed: 26287791.
Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Sep;126(3):e31-7. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001051. PubMed: 26287791.
Dondorp W, de Wert G, Bombard Y, Bianchi DW, Bergmann C, Borry P, Chitty LS, Fellmann F, Forzano F, Hall A, Henneman L, Howard HC, Lucassen A, Ormond K, Peterlin B, Radojkovic D, Rogowski W, Soller M, Tibben A, Tranebjærg L, van El CG, Cornel MC. Non-invasive prenatal testing for aneuploidy and beyond: challenges of responsible innovation in prenatal screening. Summary and recommendations. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 Apr 1. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.56. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed: 25828867.
Goldwaser T, Klugman S. Cell-free DNA for the detection of fetal aneuploidy. Fertil Steril. 2018 Feb;109(2):195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.12.019. PubMed: 29447662.
Gregg AR, Skotko BG, Benkendorf JL, Monaghan KG, Bajaj K, Best RG, Klugman S, Watson MS. Noninvasive prenatal screening for fetal aneuploidy, 2016 update: a position statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med. 2016 Oct;18(10):1056-65. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.97. Epub 2016 Jul 28. PubMed: 27467454.
Genet Med. 2016 Oct;18(10):1056-65. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.97. Epub 2016 Jul 28. PubMed: 27467454.
Rose NC, Kaimal AJ, Dugoff L, Norton ME; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics; Committee on Genetics; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Screening for Fetal Chromosomal Abnormalities: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 226. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Oct;136(4):e48-e69. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004084. PubMed: 32804883.
Skrzypek H, Hui L. Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal aneuploidy and single gene disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017 Jul;42:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Feb 28. PubMed: 28342726.
How are genetic conditions diagnosed?: MedlinePlus Genetics
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
A doctor may suspect a diagnosis of a genetic condition on the basis of a person's physical characteristics and family history, or on the results of a screening test.
Genetic testing is one of several tools that doctors use to diagnose genetic conditions. The approaches to making a genetic diagnosis include:
A physical examination: Certain physical characteristics, such as distinctive facial features, can suggest the diagnosis of a genetic disorder. A geneticist will do a thorough physical examination that may include measurements such as the distance around the head (head circumference), the distance between the eyes, and the length of the arms and legs. Depending on the situation, specialized examinations such as nervous system (neurological) or eye (ophthalmologic) exams may be performed. The doctor may also use imaging studies including x-rays, computerized tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to see structures inside the body.
Personal medical history: Information about an individual's health, often going back to birth, can provide clues to a genetic diagnosis. A personal medical history includes past health issues, hospitalizations and surgeries, allergies, medications, and the results of any medical or genetic testing that has already been done.

Family health history: Because genetic conditions often run in families, information about the health of family members can be a critical tool for diagnosing these disorders. A doctor or genetic counselor will ask about health conditions in an individual's parents, siblings, children, and possibly more distant relatives. This information can give clues about the diagnosis and inheritance pattern of a genetic condition in a family.
Laboratory tests, including genetic testing: Molecular, chromosomal, and biochemical genetic or genomic testing are used to diagnose genetic disorders. Other laboratory tests that measure the levels of certain substances in blood and urine can also help suggest a diagnosis.
Genetic testing is currently available for many genetic conditions. However, some conditions do not have a genetic test; either the genetic cause of the condition is unknown or a test has not yet been developed. In these cases, sequencing the entire genome may result in locating the responsible genetic variant. Additionally, a combination of the approaches listed above may be used to make a diagnosis. Even when genetic testing is available, the tools listed above are used to narrow down the possibilities (known as a differential diagnosis) and choose the most appropriate genetic tests to pursue.
Additionally, a combination of the approaches listed above may be used to make a diagnosis. Even when genetic testing is available, the tools listed above are used to narrow down the possibilities (known as a differential diagnosis) and choose the most appropriate genetic tests to pursue.
A diagnosis of a genetic disorder can be made anytime during life, from before birth to old age, depending on when the features of the condition appear and the availability of testing. Sometimes, having a diagnosis can guide treatment and management decisions. A genetic diagnosis can also suggest whether other family members may be affected by or at risk of a specific disorder. Even when no treatment is available for a particular condition, having a diagnosis can help people know what to expect and may help them identify useful support and advocacy resources.
What is NIPT and how much does it cost?
Victoria Zorina
loves tests
Author profile
In Russia, pregnant women get two free screenings for fetal chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome.
However, there is another fetal health screening called the non-invasive prenatal test, or NIPT. This test is paid - it costs from 25,000 R. In some cases, it helps to clarify the child's condition without puncturing the amniotic sac or uterine wall. I'll tell you how it is carried out and who really needs it. nine0003
See a doctor
Our articles are written with love for evidence-based medicine. We refer to authoritative sources and go to doctors with a good reputation for comments. But remember: the responsibility for your health lies with you and your doctor. We don't write prescriptions, we make recommendations. Relying on our point of view or not is up to you.
What is NIPT
A non-invasive prenatal test is a method that determines the risk of having a baby with certain genetic abnormalities. nine0003
What is NIPT and what diseases can it detect - Medline
Summary of NIPT recommendations - American Academy of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Non-invasive prenatal testing, NIPT - Australian Public Health
including piercing the fetal bladder, where the child is.
Research method. Material for research — maternal venous blood. Her plasma contains the extracellular DNA of the mother herself and the child, mainly fragments of placental DNA, which are usually identical to the DNA of the fetus. All living organisms have extracellular DNA, it is shorter than those molecules in the cell nucleus, and its function is not yet fully known. nine0003
The necessary fragments of genetic material are extracted from the blood in the laboratory and analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities - Down syndrome and others. The test can be done from about the tenth week of pregnancy.
Extracellular DNA and pregnancy - article on the site "Biomolecule"
NIPT works like this: they calculate the percentage of DNA for each fetal chromosome. Thus, it is possible to detect chromosomal disorders associated with the presence of an extra copy of a chromosome or the absence of one of the copies. nine0003
For example, if the amount of extracellular DNA is higher than normal for chromosomes of the 21st, 18th or 13th pairs, then the fetus has an increased likelihood of the corresponding trisomies - Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome or Patau.
NIPT is a screening procedure and may be prescribed by an OB/GYN or geneticist. A woman can also take the test of her own free will; this does not require a referral. In Russia, NIPT is not paid from the compulsory health insurance fund - it will not be possible to do a test for free.
But there is an exception: in Moscow, from 2020, it is possible to do a test at the expense of compulsory medical insurance if the risk of chromosomal pathology according to combined screening is in the range of 1:100 - 1:2500 and the pregnant woman has a Moscow residence permit. It can also be offered to pregnant women aged 35 years and older due to age-related risks. nine0003
Order of the Moscow Health Department No. 199
Is it necessary to confirm the diagnosis with an invasive test. If any non-invasive test showed that a pregnant woman has a high risk of having a child with chromosomal abnormalities, this does not mean that there really is a violation.
NIPT also does not make a diagnosis, but only assesses the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities. Don't decide to terminate a pregnancy based on test results alone. nine0052
Don't decide to terminate a pregnancy based on test results alone. nine0052
/list/down-syndrome/
10 awkward questions about Down syndrome
In Western countries, it is used as an additional screening test. None of the current NIPT tests are FDA-approved in the United States. The organization warns that there is a possibility of false results, and that a high risk for NIPT needs to be confirmed with a diagnostic test.
Diagnostic tests include invasive tests, such as amniocentesis, an analysis of amniotic fluid, for which you need to pierce the fetal bladder. The decision to conduct an invasive test is made by the woman. Some laboratories, such as Genomed, perform invasive testing free of charge if NIPT has shown the presence of a chromosomal abnormality. nine0003
Your choice after positive screening - Public Health England English
An invasive test is also recommended if free screening and NIPT show different results.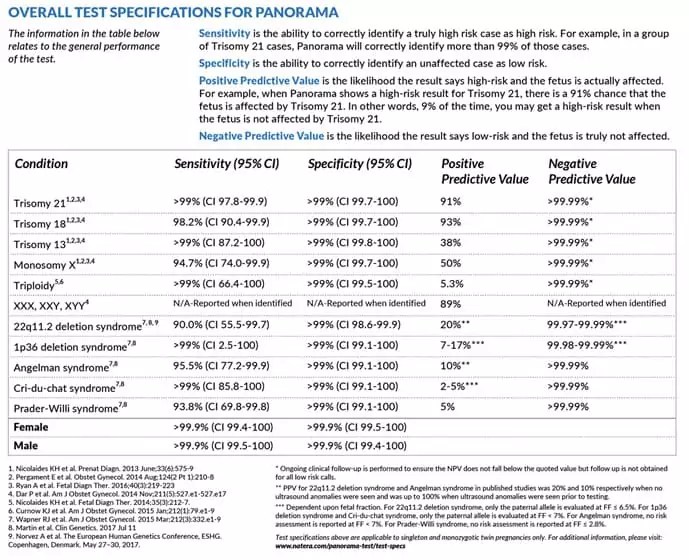
Invasive prenatal diagnosis — Mosgorzdrav
Is the test safe for the child. NIPT uses maternal venous blood, so it is completely safe for the fetus, like other blood tests. Unlike invasive tests - amniocentesis, cordocentesis, chorionbiopsy - NIPT does not require piercing the amniotic sac, umbilical vein, or uterine wall. nine0003
How NIPT differs from combined prenatal screening according to OMS
During the combined screening prescribed by OMS, ultrasound and a biochemical blood test for some compounds are done.
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation on assistance in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2020
For example, in the first trimester it is the PAPP-A protein, which is often below normal in case of chromosomal abnormalities, and the hCG hormone. Such screening is done at 10-13 weeks of pregnancy. In the 19-21st week of pregnancy, a second screening is carried out. nine0003
The woman also fills out a special questionnaire to help clarify the risks. For example, indicates whether she smokes. This also includes age-related risks. The risk level is calculated based on all the data received: the ultrasound picture, the results of the blood test and the answers to the questionnaire.
For example, indicates whether she smokes. This also includes age-related risks. The risk level is calculated based on all the data received: the ultrasound picture, the results of the blood test and the answers to the questionnaire.
Combination screening can only approximate the likelihood of a chromosomal abnormality. A non-invasive prenatal test will estimate the probability more accurately - for example, for Down syndrome, the accuracy can reach 9nine%. But, of course, he can be wrong.
/analiz-hgch/
HCG blood test: when and how much it costs
NIPT does not replace mandatory screenings. In the UK, from June 1, 2021, it is offered to pregnant women with a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities based on the results of combined screenings. And only if all the tests showed a high risk, an invasive study is done.
In what cases it is worth doing NIPT
Yulia Tarasova
Geneticist, network of clinics "Mother and Child"
NIPT is an excellent tool for assessing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities. Combined prenatal screening detects nine out of ten cases of Down syndrome, while there is a high probability of a false positive result. NIPT makes it possible to identify the very tenth case, avoiding unnecessary invasive diagnostic procedures.
Combined prenatal screening detects nine out of ten cases of Down syndrome, while there is a high probability of a false positive result. NIPT makes it possible to identify the very tenth case, avoiding unnecessary invasive diagnostic procedures.
In general, NIPT would replace combined prenatal screening were it not for the cost. This method has no other drawbacks, and you don’t even need to donate blood on an empty stomach. nine0003
However, NIPT also has limitations: even the most expanded panel does not reveal all possible genetic pathologies. Also, this test is not needed if abnormalities are detected by the results of ultrasound: it will lead to a loss of time, money and a false sense of security in case of a good result.
In this situation, you need to go to a geneticist and plan an invasive test: its diagnostic capabilities are wider, the time for obtaining the result is shorter, and this is the only way to make a diagnosis.
When choosing between the standard and extended NIPT panel, remember that the stated high test reliability only applies to the common chromosomal abnormalities included in the standard panel.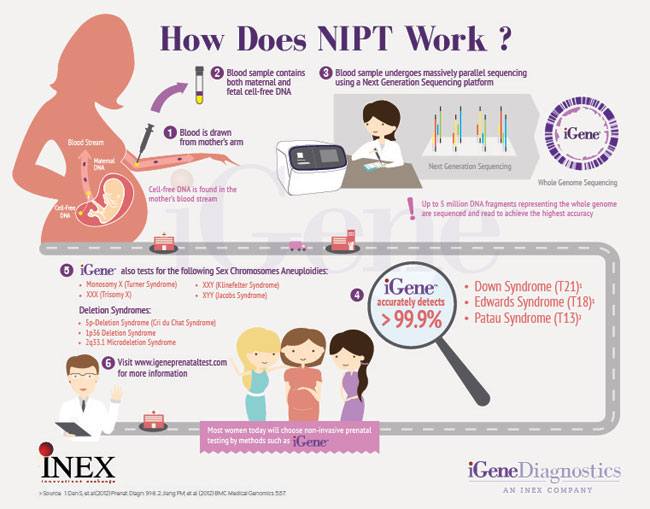 These are Down, Edwards and Patau syndromes. Other pathologies are determined with less accuracy, false positive results are more common, and the cost of the test is higher. nine0003
These are Down, Edwards and Patau syndromes. Other pathologies are determined with less accuracy, false positive results are more common, and the cost of the test is higher. nine0003
Accuracy of the non-invasive prenatal test
The accuracy of NIPT in test instructions is estimated to be up to 99%, especially for Down syndrome. However, studies show different data. Let me remind you that this is a screening test, and it cannot be reliable in all 100% of cases.
Clinical benefit of extended NIPT for chromosomal abnormalities - Journal of the Association of Reproduction and Genetics
Non-invasive prenatal screening in multiple pregnancies - American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Thus, in a study involving 2139 pregnant women who underwent NIPT, all 100% of cases of Down, Edwards and Patau syndromes were identified. In another study, women with multiple pregnancies had five out of five cases of Down syndrome, one in one case of Patau syndrome, and a case of Edwards syndrome was false negative.
The same study cites an analysis of 11 other studies showing NIPT accuracy of 95% for Down syndrome, 82% for Edwards syndrome, and 80% for Patau syndrome. nine0003
NIPT, like other laboratory tests, has two characteristics.
Sensitivity indicates how well the test detects children with chromosomal disorders. According to some data, the sensitivity of the test for Down syndrome is about 99%, which means that 1% of the tested fetuses that have a pathology will be considered healthy by the test.
The specificity of indicates how well the test excludes healthy people. According to studies, the specificity of the test for trisomy reaches 99% and above, which means that he considers 1% of healthy fetuses to be sick.
/list/genetics/
13 important questions for geneticist Irina Zhegulina
Can NIPT analysis fail? NIPT may fail only for technical reasons: due to an unsuccessful blood test or laboratory error. In this case, you can request a second test for free.
In this case, you can request a second test for free.
What can be learned with NIPT
What fetal chromosomal abnormalities can be detected. nine0030 NIPT detects many chromosomal pathologies with high accuracy. All tests, except for those specialized for individual diseases, determine:
- Down syndrome - trisomy for the 21st pair of chromosomes, that is, three chromosomes instead of two.
- Edwards syndrome - trisomy on the 18th pair of chromosomes.
- Patau syndrome - trisomy on the 13th pair of chromosomes.
Some tests can also detect other chromosomal abnormalities, see the specific test for a complete list. Among them:
- Klinefelter's syndrome - extra sex X chromosomes in boys;
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome - one X chromosome instead of two in girls;
- triploidy - the presence of three instead of two paired sets of chromosomes in cells;
- microdeletion - the absence of sections of one or another chromosome, for example, crying cat, Angelman, Prader-Willi syndromes.

Can NIPT detect genetic mutations. NIPT tests are available for certain monogenic syndromes caused by mutations in a child. For example, the Vistara test in Genomed reveals the likelihood of frequent mutations associated with 25 monogenic diseases. But it does not detect chromosomal mutations like regular NIPT, it is carried out in addition to it. The cost of such a panel is 75,000-80,000 R.
/pay-for-childbirth/
“Duplicate any tests if in doubt”: how much does it cost to bear a child
Also, some laboratories offer to determine the risk of a child developing hereditary diseases associated with mother’s mutations, such as cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria, galactosemia and others. This is an additional service - a genetic test for the mother along with NIPT. If pregnancy occurred as a result of IVF with a donor egg, such a panel is useless: you need to take blood from a donor woman. nine0003
Is it possible to determine the sex of the child and in what cases. In most singleton pregnancies, the sex of the baby can be determined if there is enough genetic material in the blood for testing.
In most singleton pregnancies, the sex of the baby can be determined if there is enough genetic material in the blood for testing.
Sex is determined by the presence or absence of a male Y chromosome. If it is, the woman is pregnant with a boy, if not, with a girl. With twin pregnancy, an accurate sex determination is not always possible: in the absence of a Y-chromosome in the DNA of the fetus, it can be assumed that both children are female, if present, at least one of the male fetuses. In the case of identical twins, both will be of the same sex. Parents may opt out of gender determination through NIPT. nine0003
In what cases should NIPT be done? An analysis for monogenic syndromes - phenylketonuria, galactosemia, cystic fibrosis, spinal muscular atrophy, hearing loss and others - is recommended to be performed before pregnancy, not only for the expectant mother, but also for the father.
If it turns out that both parents are carriers of a genetic mutation, they should consider in vitro fertilization with preimplantation diagnostics of embryos for monogenic diseases.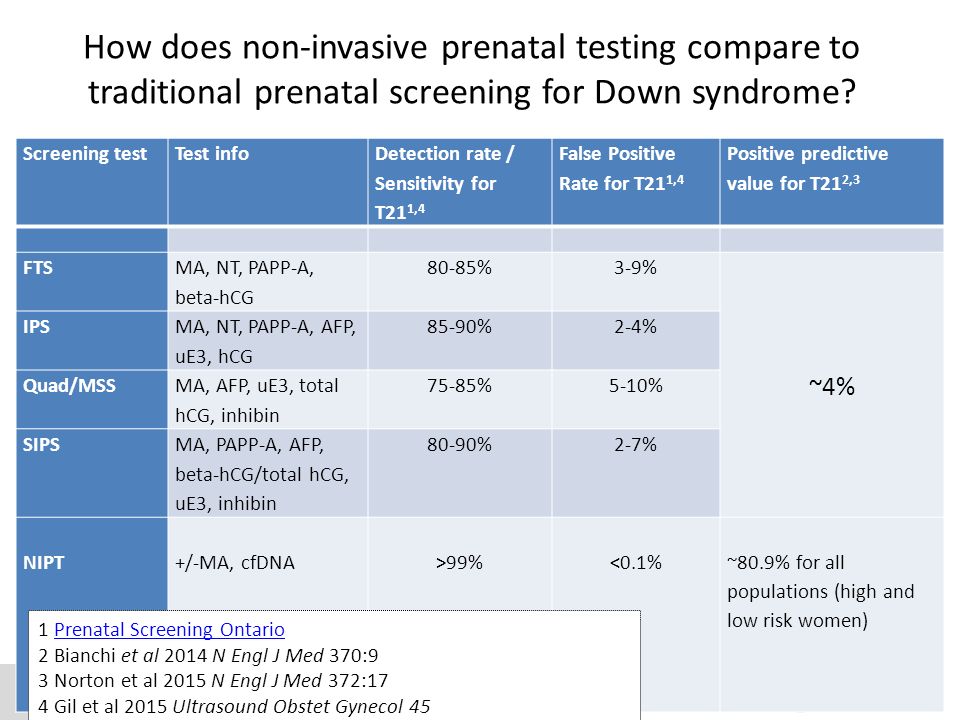 nine0003
nine0003
Contraindications for NIPT: when it is better not to test
Main contraindications for NIPT:
- More than two fetuses in the uterus - the percentage of DNA of each fetus will be less than needed for testing.
- In the past, the woman had a bone marrow transplant, stem cells or donor organs - a high probability of an incorrect result.
- Maternal obesity - with a BMI over 30, the proportion of fetal DNA in the blood may be too small, and the test will be inaccurate. nine0144
- A woman has an oncological disease - the probability of a mistake also increases.
- Signs of fetal chromosomal abnormalities are visible on ultrasound, in this case there is no point in doing NIPT, it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis with an invasive test.
Can NIPT be done in multiple pregnancies? NIPT is done for single or twin pregnancies. If a woman is expecting triplets or more children, the analysis is not carried out - the probability of errors is high.
NIPT can also be performed during pregnancy resulting from IVF, in vitro fertilization, including a donor egg. nine0003
/guide/eko/
How much does IVF cost
What to look for when choosing a test
NIPT tests from different laboratories differ in several parameters that may be important.
List of diseases. The cost of the test often depends on this indicator. The cheapest way to take a test is only for Down syndrome - it costs 15,000-20,000 R. All other tests also determine Edwards and Patau syndromes, and many of them also other chromosomal abnormalities. If you are tested not only for the most common trisomies, the price approximately doubles. nine0003
Test takes 8-12 business days on average.
/list/raz-plunut/
Find out the origin and possible diseases: where to take genetic tests
Additional services. NIPT fees may include consultations with a geneticist before or after the test. Sometimes, in combination with NIPT, a genetic test of the mother is done for the carriage of genes for certain diseases.
Sometimes, in combination with NIPT, a genetic test of the mother is done for the carriage of genes for certain diseases.
Types of non-invasive prenatal tests
In Russia, you can take several types of NIPT, I will tell you about the most popular ones. nine0003
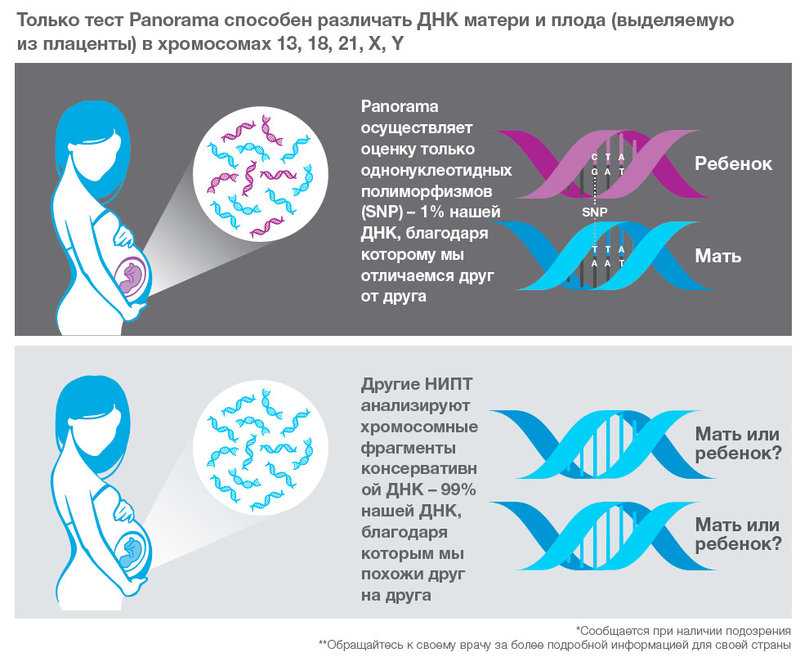
Panorama. The most famous test in the world with a large database of clinical data and the only one that distinguishes fetal DNA from maternal DNA. Because of this, it is considered the most accurate.
Panorama NIPT was developed by the American laboratory Natera and exists in two versions, basic and advanced.
Description Panorama
The basic set includes, for example, Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, Jacobs syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome, as well as X-chromosome trisomy and triploidy. nine0003
The expanded set also includes microdeletions: 1p36, cat's cry syndromes, Angelman, Prader-Willi. Another test determines the sex of the fetus. The results are analyzed in the USA. Completion time is 12 business days.
The results are analyzed in the USA. Completion time is 12 business days.
Prenetix. This test was developed by the Swiss laboratory Roche, outside of Russia it is called Harmony.
Description Harmony
List of diseases: Down syndrome, Edwards, Patau, Shereshevsky-Turner, Klinefelter. The test also determines the gender of the baby. nine0003
Description of NIPS "Genomeda"
Analysis of the results is carried out in Russia. Completion time is 12 business days.
NIPS "Genomeda". The NIPS test was developed in Russia by the Genomed laboratory. Defines the same disorders as Panorama, except for triploidy. The extended version includes the determination of genetic mutations in the mother. The analysis of the results is carried out in Russia. Completion time is eight business days.
Description of Veracity
Veracity and Veragene. nine0030 Tests from the NIPD Genetics laboratory located in Cyprus.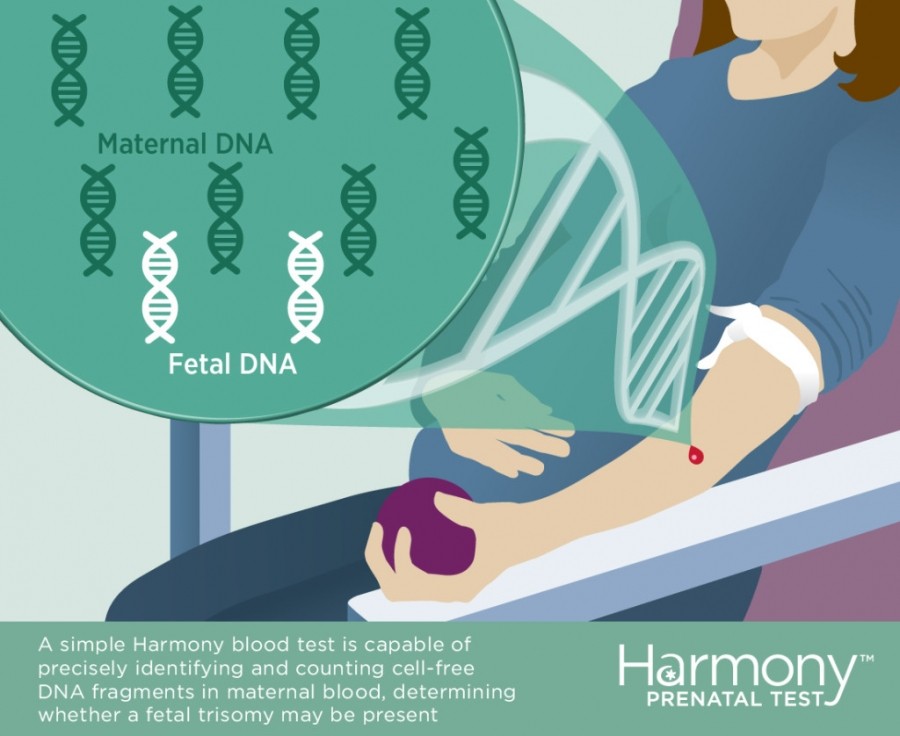 The Veracity test includes 3-12 chromosomal disorders, including Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, microdeletions.
The Veracity test includes 3-12 chromosomal disorders, including Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, microdeletions.
The Veragene test includes the determination of 112 diseases, including hereditary ones - cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria. It also determines the sex of the fetus. The analysis of the results is carried out in Cyprus. Completion time is 12 business days.
How much does NIPT cost and where can I take it? I will give prices in some clinics and laboratories in Moscow, in other regions prices may vary slightly. nine0003
How much does NIPT cost in Moscow
| Laboratory name | Test name | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| "Genomed" | "Genomed" | 17,000—34,000 R |
| Panorama | 28,000—37,000 R | |
| KDL | "Genomed" | 17 894—35 788 Р |
| Progen | Panorama | 23,000—44,000 R |
| Veracity | 24,000—30,500 R | |
| Veragene | 45 000 R | |
| Genetico | Prenetix | 24,900—34,000 R |
| ZIR | Prenetix | 29 990 Р |
| Mother and Child | Veracity, Evogen | 28 000-111 700 R |
Laboratory "Genomed"
Test "Genomed"
17 000-34 000 R
Panorama
28 000–37 000 R
Laboratory KDL 9000 9000 9000 –35 788 R
Laboratory "Strand"
Panorama
23 000-44 000 R
Test Veracy
24 000-30 500 500 R
VERAGENE
45 000 R 9000 9000 Laboratory of GENETICO
Test PreNETIX
24 900-34 000 R
Laboratory CIR
Test Prenetix
29 990 R
Laboratory Mother and Child Tests Veracity, Evogen 9000 000 000 -1111111111111111111111111111111111 700 Р
How to prepare for NIPT
The non-invasive prenatal test does not require special training. You do not need to refuse food or prescribed medications.
You do not need to refuse food or prescribed medications.
How is the study. nine0030 Venous blood is taken from a pregnant woman for analysis, the procedure takes several minutes. After taking the test, you need to keep the bandage on your arm for about half an hour, just like after a regular blood test.
How soon the results will be. The turnaround time for an NIPT test is 8 to 12 business days from the time a woman has had her blood sample taken.
Test results usually contain the phrases "low risk" or "high risk" for each chromosomal disorder, a risk calculation, and the sex of the fetus if the woman has not refused to know it. nine0003
/list/obstetrics-gynecology/
“Pregnancy is not a disease, it does not need to be treated”: 19 important questions for obstetrician Oksana Bogdashevskaya
This is what the Prenetix test result looks like. Source: "Laboratory TsIR"Remember
- The NIPT test is taken from 9-10 weeks of pregnancy by one or two children.

- Material for analysis - venous blood, the test is safe for mother and child.
- The test detects chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, including Down syndrome. nine0144
- If there is a high risk of a chromosomal abnormality, an invasive test such as amniotic fluid, cord blood, or chorion biopsy is recommended.
- The average cost of NIPT in Russia is about 30,000 rubles.
Health news, interviews with doctors and instructions for patients - in our telegram channel. Subscribe to keep abreast of what is happening: @t_zdorov.
Non-invasive prenatal genetic test | CPS Medica
nine0460- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) nine0143 Pregnancy management and prenatal diagnosis
- cervical dysplasia
- Treatment of varicocele nine0144
- Videocolposcopy
- Pregnancy management programs nine0144
- IVF according to compulsory medical insurance for residents of the regions
- Expert ultrasound 3D/4D during pregnancy nine0144
- Non-invasive prenatal genetic test
- Preimplantation genetic testing nine0144
- IVF under CHI for residents of St.
 Petersburg
Petersburg - IVF according to compulsory medical insurance in the Leningrad region nine0144
- Infertility treatment
- ultrasonic cavitation nine0144
- Transfer of embryos into the uterus
- Intrauterine insemination nine0144
- PGD/PGT
- Screening ultrasound in the third trimester nine0144
- Perinatal/reproductive psychologist
- Erosion of the cervix (ectopia) nine0144
- Treatment of submucosal fibroids
- Implatest - Endometrial Receptivity Study nine0144
- Gynecologist-endocrinologist appointment
- Colposcopy nine0144
- Reception of a mammologist
- Endometrial polyp nine0144
- Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst
- Fetal cardiotocography (fetal CTG) nine0144
- Hysteroscopy
- Office hysteroscopy nine0144
- Office diagnostic hysteroscopy
- Office hysteroscopy with endometrial biopsy nine0144
- Laboratory diagnostics
- Day hospital nine0144
- Follicle puncture
- Stimulation of superovulation nine0144
- Preeclampsia
- Ultrasound examination of folliculogenesis with biophysical profile of the uterus nine0144
- Hysteroresectoscopy
- Hysterosalpingography nine0144
- Fallopian tube laparoscopy
- Laparoscopy in gynecology nine0144
- Laser vaporization of the cervix
- Treatment of endometriosis nine0144
- Treatment of an ovarian cyst
- Laparoscopy of uterine fibroids nine0144
- Non-developing pregnancy
- Pathology of the endometrium nine0144
- Pathology of the cervix
- Treatment of the endometrial polyp nine0144
- Polyp of the cervix
- Preventive examination by a gynecologist nine0144
- radio wave surgery
- polycystic ovary syndrome nine0144
- Ultrasound hysterosalpinography (USGSG)
- human papillomavirus nine0144
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis
- Frozen pregnancy nine0144
Sign up
8 812 565-18-40
An expert approach to happiness! nine0003
Our branches
Assisted reproductive technologies
Obstetrics
and gynecology Fetal Medicine Center
Urology
and andrology
Assisted Reproductive Technologies obstetrics and gynecology Center for Fetal Medicine Urology and Andrology nine0003
Saint-Petersburg, Torez avenue, 72
Center for Reproduction and Family Planning Medica in St. PetersburgServicesNon-invasive prenatal genetic test
PetersburgServicesNon-invasive prenatal genetic test
A laboratory diagnostic method that allows you to identify the presence of chromosomal diseases in a child, such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome and others. This study of fetal DNA isolated from the mother's venous blood is absolutely safe! The accuracy of the method reaches 99.9%!
Enroll
Price: from 30 240₽
To take the test, a woman just needs to come to the clinic and donate blood from a vein - just like for conventional tests. NIPT is indicated already in early pregnancy, starting at 9-10 weeks. The only condition is that the KTP indicator (coccyx-parietal size of the fetus) should be from 32 mm. Since CTE is determined during an ultrasound examination, a non-invasive test is done after it. Readiness of the result after taking a blood test - from 12 days. nine0003
Read more
About direction
The Genetics Department of the Medica Family Planning Center has the capacity to conduct a wide range of research in the field of reproductive genetics, including various options for preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
Cost of services
Full price list for referral servicesGeneticist, initial appointment
2 700 ₽
Enroll
Geneticist, follow-up visit
2 200 ₽
Enroll
NIPT Targeted test for 13, 18, 21, X, Y chromosomes.
30 240 RUB nine0003
Enroll
Blood sampling from a peripheral vein (in adults)
Enroll
Video
Embryo biopsy
Oocyte vitrification and delayed motherhood program - childbirth (,) cannot be (,) delayed 18+
Reproductologist Elena Tanchuk about indications for ART (assisted reproductive technologies)
Human papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical cancer - diagnosis, treatment, prevention. Samoilova Svetlana Gennadievna
Samoilova Svetlana Gennadievna
Treatment of infertility in different age periods. Yusupova Oksana Nikolaevna CPS Medica 18+
Hormonal contraceptives COCs - truth and myths. Kovaleva Natalia Sergeevna CPS Medica 18+
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) at the Center for Reproduction and Family Planning Medica
The female factor in infertility. Tanchuk Elena Valerievna. Reproduction Center Medica 18+
Frozen pregnancies - why pregnancy does not develop. Bokach Olga Mikhailovna
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) - types, transmission, diagnosis. Sheikhov Magomedsadiq 18+
How to plan a healthy pregnancy. Yusupova Oksana Nikolaevna
Yusupova Oksana Nikolaevna
Cryopreservation of germ cells and embryos. Kozhevnikov Igor Valerievich
Treatment of infertility in different age periods. Yusupova Oksana Nikolaevna CPS Medica 18+
The menstrual cycle - the norm and pathology. Danielyan Roza Martunovna. CPS Medica. 18+
Male fertility - when should a man start to worry and anti-age therapy CPS Medica 18+
Reproduction doctor's appointment - we plan pregnancy correctly. Pisaroglo Maria Ivanovna. CPS Medica
Psychosomatics of infertility - all diseases are caused by nerves. Konon Ksenia Mikhailovna. CPS Medica 18+
Reproductologist Elena Tanchuk about indications for assisted reproductive technologies (ART)
PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome). Danielyan Roza Martunovna. Reproduction Center Medica 18+
Danielyan Roza Martunovna. Reproduction Center Medica 18+
Testosterone and its effect on the human body. Kudryavtsev Artemy Alexandrovich. CPS Medica 18+
Ultrasound screening of pregnant women - why and how often. Ten Natalya Alekseevna. CPS Medica
Successful embryo implantation during natural pregnancy and after IVF. Konon Xenia Mikhailovna.18+
Endometriosis. Zakharova Oksana Vadimovna Center for Reproduction and Family Planning Medica 18+
The episode of the broadcast of the hysteroscopy operation in the 'Center for Reproduction and Family Planning 'Medica'
Erectile dysfunction - diagnosis, treatment, prevention. Sheikhov Magomedsadyk Gasanovich. 18+
Sheikhov Magomedsadyk Gasanovich. 18+
03/27/2021
The lifestyle of the father and his age affect the health of the child
Age, addiction to alcohol and other bad habits of the father can cause birth defects in the unborn child.
Read more
03/20/2021
Expertise on contraception
In developed countries, about 40% of adolescents aged 15-19years have sexual experience.
Read more
02/15/2021
10 questions about IVF
In a couple of years, the world's first "test-tube baby" - Lisa Brown - will be 40 years old.
Read more
01/14/2021
Together against cancer nine0003
February 4th is World Cancer Day.
Read more
All articles
Address
Family Planning Center "MEDICA"
Address:
Torez Ave., 72 (hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 2nd floor)
nine0785 Specific
lakes
nine0785 Pl.