Newborn baby drink water
When can babies drink water?
When can babies drink water? | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
If your baby is under 6 months old, they only need to drink breastmilk or infant formula. From 6 months of age, you can give your baby small amounts of water, if needed, in addition to their breastmilk or formula feeds.
Why is water not suitable for babies younger than 6 months?
Before 6 months, breastmilk or formula is both food and drink for your baby. It is all they need, even in hot weather. Giving your baby water may mean they drink less breastmilk or formula. This can put them at risk of not getting enough milk or formula to grow properly. Giving your baby a lot of water or excessively diluted formula over a short time can also make them very unwell.
When can I give water to my baby?
If your baby is around 6 months old, you can offer small amounts of cooled boiled tap water but you should not replace their breastmilk or formula feeds. Breastmilk or formula should still be their main drink up to 12 months of age.
After 12 months, their main drink should be water and cow's milk or breastmilk. You can offer water or milk in a cup. There's no need to boil tap water once your baby has reached 12 months.
If your baby has just started on solids, start with a few sips of water from a cup when they are eating. This is so they can learn about drinking from a cup and it can also help prevent constipation due to the increased bulk of their poo. The aim is to get them used to drinking from a cup as this will be their main way of drinking from 12 months on.
What about in hot weather?
In hot weather, it is important to offer more frequent breastfeeds or bottle-feeds if your baby is under 6 months. Do not offer water unless recommended by a doctor.
Your baby may want to drink more than usual but for shorter periods. If you breastfeed, you should also make sure you drink enough water.
To make breastfeeding more comfortable for you and your baby in hot weather:
- place a towel, sheet or pillowcase between yourself and your baby
- lie down to breastfeed to reduce skin contact
Your baby is properly hydrated (getting enough fluids) if they have 6 to 8 pale wet nappies over 24 hours.
What if my baby has a fever?
If your baby has a fever, is under 6 months and is breastfed, you may need to offer extra breastfeeds. If they are under 6 months and formula-fed, you can offer smaller amounts of formula more frequently. Do not offer water unless advised by a doctor.
If your baby is older than 6 months, continue to breastfeed or bottle feed. You can offer water in between feeds. The most important thing to check is whether your child is getting enough fluids.
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and support.
What about other drinks?
Fruit juice, soft drinks and cordial are not suitable for babies under 12 months old.
Caffeinated drinks such as tea, coffee and energy drinks — and, of course, alcohol — are not suitable for children of any age.
Sources:
Australian Breastfeeding Association (Keeping baby cool in the heat), National Health and Medical Research Council (Infant Feeding Guidelines), NSW Health (Babies and children in hot weather), Raising Children Network (Fever), Raising Children Network (Healthy drinks for kids and teenagers), Royal Children's Hospital (Guide to foods for baby’s first year), World Health Organization (Why can’t we give water to a breastfeeding baby before 6 months, even when it is hot?)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.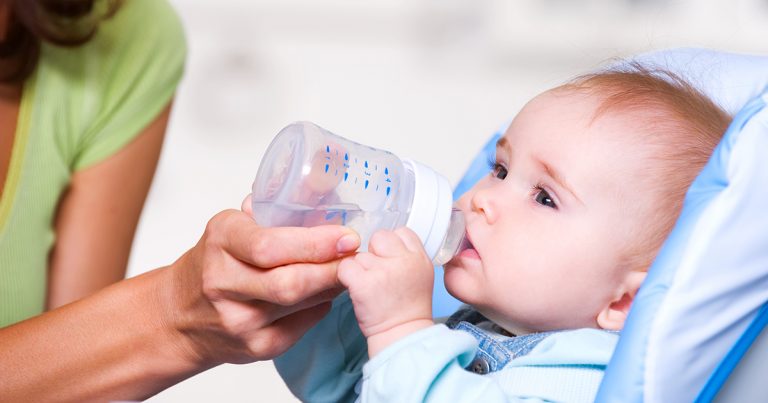
Last reviewed: July 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Healthy drinks for kids
- Feeding your baby with formula
- Breastfeeding your baby
- Balancing introducing solids with milk feeds
Need more information?
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Why Can't Babies Have Water? About the Risks and When It's OK
It’s a bright, sunny day outside, and your whole family is feeling the heat and guzzling water. Your newborn surely needs some hydration, too, right?
Yes, but not of the H2O variety. Your little one — if under 6 months old — should be receiving both nutrition and hydration from breast milk or formula, not water.
You probably know this, but you might not know why. It’s because babies’ bodies aren’t suited for water until several months after birth. Tiny tummies and developing kidneys put them at risk for both nutrient loss and water intoxication. Here’s the scoop.
Baby tummies are quite small. In fact, at birth, a baby’s belly only holds about 1 to 2 teaspoons, or 5 to 10 milliliters (mL)! Clearly, it does empty fast — which is why your babe needs so many feedings in a 24-hour period — but you want to fill that little tummy with nutrient-rich breast milk or formula.
So it makes sense that one risk of giving your baby water is that you’ll be filling their belly with a really quite useless substance (at least to a baby) and leaving no room for those vitamins, minerals, fat, and calories so crucial for growth and development. This can cause serious problems.
Baby’s tummy does grow over the first 6 months of life, but it’s pretty gradual. By the time they’re 1 month old, their stomach capacity is about 2. 7 to 5 ounces (80 to 150 mL). By 6 months — when you can introduce little sips of water — they can generally hold about 7 ounces (207 mL) at a time.
7 to 5 ounces (80 to 150 mL). By 6 months — when you can introduce little sips of water — they can generally hold about 7 ounces (207 mL) at a time.
Even between 6 months and 1 year of age, the amount of water you give your baby should be very limited. It’s more for them to get the taste and experience of water rather than for any real medical purpose like hydration. After all, formula and breast milk are very hydrating — and also give your little one what they need to grow and thrive.
Another very serious risk of giving babies water before they’re ready is water intoxication.
Hold the front door. Water — toxic?
Absolutely. In fact, water can be toxic to anyone if drunk in large quantities. But unsurprisingly, “large” is very relative to size and age here. An adult with healthy kidneys, for example, would have to drink several liters in a short period of time to get to the point of water intoxication.
That said, it does happen to people, particularly soldiers and athletes, who tend to be in situations where they can become dehydrated quickly and then overcompensate.
In short, when the kidneys are given more water than they can handle, the excess water ends up in your bloodstream. This dilutes the fluid in your bloodstream and lowers the concentration of important electrolytes, like sodium. Too much dilution and you’re at risk for hyponatremia, which literally means too little (hypo) salt in the blood (natremia).
And baby kidneys can’t handle as much water as adult kidneys — not by a long shot. In addition to being much smaller than an adult’s kidneys, a baby’s kidneys are also not as developed. So they can’t process as much water at a time.
So giving a baby younger than 6 months even a moderate amount of water in a short period of time can lead to hyponatremia, which at its most dangerous can cause brain swelling and even death. In fact, because the brain is still developing as well, the swelling can happen more easily in an infant with hyponatremia than in an adult with hyponatremia.
A dangerous equation
Remember: Tiny tummy + immature kidneys + developing brain = Avoid giving babies water until they are 6 months of age
The thing is, most parents aren’t filling bottles with water and giving them to their infants.
The risk comes from things that you might not even give a second thought.
For example, while many swimming schools don’t offer lessons to babies under 6 months, some will start them as young as 4 months. There’s nothing inherently wrong with introducing a baby to the pool if it’s done safely — but without the proper precautions, babies can swallow pool water and experience water intoxication as a result.
Another seemingly harmless act that can lead to trouble is diluting formula or breast milk. Going back to our hydration scenario, it might seem to make sense to mix more water into your baby’s formula powder on a hot day. But don’t do this — it deprives baby of nutrients and can also lead to them getting more water than their kidneys can handle.
Because formula and breast milk are calorie rich, they stay in the body longer rather than overwhelming the kidneys. As a nice side effect, staying in the body longer also means they’re good at keeping your little one hydrated — no extra water needed.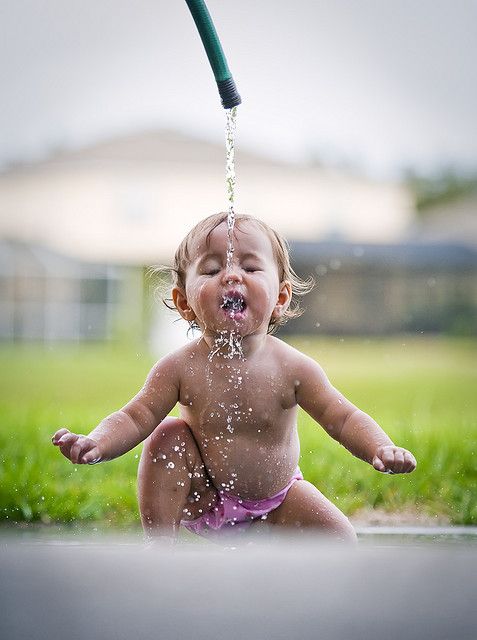
At around 6 months of age, it’s OK to introduce small amounts of water — we’re talking on the teaspoon or tablespoon scale, not the full-bottle scale. It’s a good time to start introducing the concept that thirst can be quenched with water, but your baby’s main source of hydration (not to mention nutrition) should continue to be breast milk or formula.
Most babies will see water as a sort of novelty at this age and still prefer their milk. Some might even balk at the taste and make a face, especially if they were expecting something else! That’s OK — this will change.
By 1 year old, your baby — who’s just about a toddler, if you can believe it! — can have water in larger quantities as they want it, along with cow’s milk and a nutritious diet.
Related: When can baby drink water?
Talk to your pediatrician if you have any concerns about your baby’s hydration or their readiness for water. Depending on if your baby was born prematurely or has certain health conditions, your timeline for introducing water may vary.
In addition, if your baby shows any of these signs of water intoxication, head to the hospital immediately:
- inconsolable crying
- vomiting
- lethargy
- seizures
- tremors
Fortunately, parents are usually aware — by word of mouth or from their pediatrician — that they shouldn’t give young babies water. But now you also know the why behind the guideline.
when, how much and what kind of water to give a newborn and children with breastfeeding and artificial?
Does a newborn baby need water? This question worries many young mothers, while the recommendations of doctors differ: some believe that the baby does not need any additional fluid, while others argue that the child needs water. Let's try to figure out how and when to give your baby water and how water for newborns differs from ordinary drinking water.
Breast milk is both food and drink for the baby, since it is 90% water and in the first weeks of life it is able to maintain the fluid balance at the required level. Mother's milk helps the process of digestion, as it contains all the enzymes necessary for this. Moreover, the mother's body is able to very accurately adapt to the needs of the child, adjusting the composition of milk depending on the situation. For example, if a baby needs more fluid, he will breastfeed more often and, as a result, receive more unsaturated foremilk, which quenches thirst and restores electrolyte balance.
Mother's milk helps the process of digestion, as it contains all the enzymes necessary for this. Moreover, the mother's body is able to very accurately adapt to the needs of the child, adjusting the composition of milk depending on the situation. For example, if a baby needs more fluid, he will breastfeed more often and, as a result, receive more unsaturated foremilk, which quenches thirst and restores electrolyte balance.
It may seem that the child does not need water, but this is not so: there are situations when it is indispensable. Indeed, up to three months, babies should be given water only on the recommendation of a doctor. Babies older than four months can be fed quite calmly - contrary to popular belief, this does not lead to the child's refusal to breastfeed, and even more so to his exhaustion. If the baby drinks water with pleasure, there are no contraindications for this. But the lack of fluid for the baby is very dangerous - adults should not forget that the metabolic rate in newborns is very high and moisture loss is also significant.
However, parents need to know when and how much water should be given to newborns and how the type of feeding affects fluid requirements.
Water while breastfeeding
Newborns can drink water from four to five months. It is better to do this between feedings - if the baby feels thirsty, he drinks water with pleasure. How much water can you give a newborn? Here, as in adults, everything is individual. Usually, pediatricians advise giving a certain amount of liquid per day with a calculation of no more than 100 ml per kg of weight, but this also includes breast milk. So the water, in fact, remains 30-70 ml.
You can feed your newborn from a bottle with a nipple or even from a spoon – this will facilitate the introduction of complementary foods later, because the baby will already know how to use a spoon. But the most important rule is voluntariness: if the child is naughty and does not want to drink, you should not insist.
Water with formula or formula feeding
Formula feeding differs markedly from natural feeding - infant formula contains much more protein than mother's milk, so the baby needs additional fluids. Lack of water, especially when feeding too rich formula, can lead to constipation in children. The extra water will help empty the bowels and make your baby feel better.
Lack of water, especially when feeding too rich formula, can lead to constipation in children. The extra water will help empty the bowels and make your baby feel better.
With artificial or mixed feeding, water can be given earlier than with breastfeeding. Unlike formulas, which should be 36-37°C, the water can be slightly cooler: 26-30°C in the first one or two months of life, and at an older age - about 20°C.
All paediatricians agree that with the introduction of complementary foods, water becomes essential. Usually, babies who received only milk or formula before the introduction of complementary foods begin to drink solid food only after one to two months. And babies, accustomed to water, are not capricious and drink it with pleasure after each feeding.
When is water given to newborns?
Babies should be given water some time after meals and between feedings. Do not forget that the volume of the child's stomach is very small, which means that he simply cannot drink a large amount of water at once - a few teaspoons will suffice for a start.
In some situations, the need for fluid increases. Most often, overheating and very dry indoor air leads to a lack of moisture. Many parents are so afraid of colds in a child that they wrap him in clothes and do not observe the temperature regime in the children's room, which leads to a decrease in air humidity and dehydration of the baby's body. The optimal temperature for a nursery is 20 ° C, and humidity is 50–70%. Dry air leads to increased breathing, a decrease in the protective functions of the body, difficulty swallowing and colic. And in summer, in hot weather, overheating is added to all these problems, because of which the child sweats and loses precious moisture. It is easy to determine the first signs of dehydration: this is rare urination (normally - about 20 times a day), dryness of the mucous membranes, skin, tongue. In such a situation, water is simply necessary.
Many paediatricians recommend giving newborns water to drink even when they are sick - with fever or colic, which are easily recognized by tucked up legs, a tense tummy and restlessness of the child. A few sips of warm water can also help with hiccups.
A few sips of warm water can also help with hiccups.
What kind of water should I give my baby?
Boiled water and water from open sources
Many parents believe that children should drink boiled water, but this is a misconception. Boiling leads to the destruction of only part of the bacteria, in addition, such water contains in excess chloride compounds that are very harmful to young children. Water from open sources is also dangerous - it may contain a high content of nitrates and bacteria from the soil and other harmful impurities. And, of course, babies should not be given healing mineral or sparkling water.
In addition, water from ordinary filter jugs designed to purify water for adults is not suitable for infants.
Bottled water
Baby water is sold in pharmacies and supermarkets. As a rule, on the bottle it has a special marking and information that this product has been tested by the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. Water for a baby is different from the usual "adult" drinking water. In particular, other requirements for the content of minerals are imposed on it:
Water for a baby is different from the usual "adult" drinking water. In particular, other requirements for the content of minerals are imposed on it:
- total minerals less than 200–300 mg/l;
- calcium - less than 60 mg/l;
- potassium less than 5–20 mg/l;
- sodium less than 20 mg/l;
- magnesium - less than 10-35 mg/l.
Boiling such water is not required, but it can be stored only for a day from the moment of opening and always in the refrigerator. The best container for bottled baby water is a glass bottle or polycarbonate container (bottles made of this material are marked with the number seven on the bottom).
Specially filtered water
Regardless of the brand of bottled baby water and price, it is impossible to be completely sure of its quality. Alas, there are also unscrupulous manufacturers, in addition, product quality may suffer during improper transportation or poor storage conditions.
Many parents, striving to give their children the best from the first days of their lives, “prepare” children's water on their own. Purifying water with quality home filters allows them to be sure that the filtered water does not contain harmful chemicals and bacteria. Moreover, advanced filters enrich the water with the necessary microelements that a growing child's body needs so much. Using water purification systems, parents themselves control its quality - this gives them the opportunity not to doubt the result. Filtering water at home is somewhat similar to making fresh juice: in both cases, the consumer can follow the process and get a natural and fresh drink. Meanwhile, it is impossible to control the technological process in large-scale production, and it is not known exactly how useful such a product is.
Another benefit of using home filters is their cost-effectiveness. Water obtained by home filtration is ten times cheaper, although it is not inferior in quality to water from a supermarket, and often even surpasses it. It is suitable both for feeding the baby, and for preparing milk mixtures and cereals for him. For its natural taste and crystal purity, older children will also love it, for whom water filtered according to all the rules will also be very useful.
It is suitable both for feeding the baby, and for preparing milk mixtures and cereals for him. For its natural taste and crystal purity, older children will also love it, for whom water filtered according to all the rules will also be very useful.
Water should be included in a child's diet from birth. It is vital that it undergoes thorough mechanical and biological purification and has a balanced composition of useful substances. When using bottled water, it is useful to carefully read the information on the label. As with any other product, it is advisable to take a bottle with a fresh production date. When using filtered water, keep an eye on the expiration date of the filter, clean or replace the elements of the device in a timely manner.
Should I give my child bottled water?
Many young mothers are interested in the question - is it necessary to give water to a newborn baby? In this case, the doctor gives a variety of advice - some argue that breastfed babies do not need additional water, others assure the opposite. To get an answer to this question, it is necessary to understand in more detail how and when the baby should be watered, and what water can be used for this.
To get an answer to this question, it is necessary to understand in more detail how and when the baby should be watered, and what water can be used for this.
Mother's breast milk, which the child receives from the first days of life, is both food and drink for him - it is known that 90% of it consists of water. Thus, the breastfed baby receives all the amount of fluid he needs. Thanks to special enzymes, mother's milk has a beneficial effect on the digestion process. In addition, the female body is able to independently adapt to the needs of the baby, regulating the composition of breast milk. When the baby needs more liquid, he begins to breastfeed more, thus receiving more foremilk (it is less saturated), which not only quenches thirst well, but also restores electrolyte balance.
If we take into account all of the above, we can decide that the baby does not need ordinary water as a drink at all. But in fact, sometimes it is necessary. However, it is possible to give water to a child who is not yet three months old only on the recommendation of a pediatrician. Babies who are already 4 months old can drink water - this will not affect the breastfeeding process in any way. There are absolutely no contraindications to water if the baby drinks it with pleasure. On the contrary, you should be wary of a lack of fluids, which can cause much more harm to the child. We must not forget that newborns have a very fast metabolism, due to which the loss of moisture can be very significant.
Babies who are already 4 months old can drink water - this will not affect the breastfeeding process in any way. There are absolutely no contraindications to water if the baby drinks it with pleasure. On the contrary, you should be wary of a lack of fluids, which can cause much more harm to the child. We must not forget that newborns have a very fast metabolism, due to which the loss of moisture can be very significant.
Water for baby during breastfeeding
You can give your baby water from about 4-5 months. It is best to do this not during feeding, but between them. When the baby feels thirsty, he will gladly drink water from the bottle. As for the norm of fluid for a child, this is a very individual question. As a rule, pediatricians advise giving babies about 100 mg of liquid per 1 kg of body weight, while the liquid includes breast milk. Water in this case will be from 30 to 70 ml.
The baby can drink water from an ordinary bottle with a nipple, you can also use a spoon for this (it will help to accustom the child to complementary foods, which will be needed soon). However, the main rule to remember is that the baby must drink water voluntarily, in no case should he be forced to do so.
However, the main rule to remember is that the baby must drink water voluntarily, in no case should he be forced to do so.
Mixed or formula-fed baby water
Artificial feeding has significant differences from natural feeding. The fact is that infant formula contains much more protein than mother's milk. A formula-fed baby has a special need for extra fluids. If you constantly give him a rich nutrient mixture, this can cause constipation. The additional water received by the baby will improve his well-being and contribute to the normal emptying of the intestines.
If the child is on mixed or artificial feeding, then you can start giving water to him a little earlier - already from 1 or 2 months of life. In this case, the water temperature should be cooler than the temperature of the nutrient mixture. Pediatricians assure that babies who are on artificial or mixed feeding definitely need water.
When can newborns be given water?
You can give your baby a drink immediately after eating. You can also drink it in between feedings. It is important to remember that babies have a very small stomach in volume, and they will not physically be able to drink a lot of water. It is enough to give him 2-3 teaspoons of water. Gradually, this dose can be slightly increased.
You can also drink it in between feedings. It is important to remember that babies have a very small stomach in volume, and they will not physically be able to drink a lot of water. It is enough to give him 2-3 teaspoons of water. Gradually, this dose can be slightly increased.
There are situations in which the need for additional liquid for the baby increases dramatically - for example, when the child has been in a room that is too dry for a long time, or has become slightly overheated. Some parents are too afraid of catching a cold while bathing, and maintain a high temperature in his room - because of this, the humidity in the room decreases, and the baby's body is dehydrated. To prevent this from happening, the air temperature in the baby's room should be maintained at 20 degrees, and the humidity should be between 50 and 70%.
If the air in the room is too dry, the child begins to breathe rapidly, swallowing becomes difficult and colic begins. With overheating, which most often occurs in summer, the baby sweats more, as a result of which the body loses moisture. Signs of dehydration can be signs such as dry skin and mucous membranes, as well as infrequent urination. Pediatricians agree that during illness, newborns need to be given water - for example, with colic, or at elevated temperature. The water in this case should be warm.
Signs of dehydration can be signs such as dry skin and mucous membranes, as well as infrequent urination. Pediatricians agree that during illness, newborns need to be given water - for example, with colic, or at elevated temperature. The water in this case should be warm.
Water is necessary for the child in such cases:
- at high temperatures - you can give him a little drink from a spoon, and just moisten his lips with water;
- with diarrhea - you need to give the child a little drink, after which it is imperative to show it to the pediatrician;
- when there is fever without temperature - water can be given to the baby in a small amount;
- for constipation - the liquid will help to empty the intestines without discomfort for the child;
- with vomiting - water will prevent dehydration and cleanse the stomach;
- for hiccups - water will relieve spasm of the diaphragm, which happened from hypothermia, and also help to get rid of excess air in the stomach.

What kind of water should a baby drink?
Some parents are sure that only boiled water can be given to babies. Actually it is not. When water is boiled, not all bacteria die in it. And in the composition of such water there are chloride compounds that are extremely harmful to babies. Water obtained from open sources can be no less dangerous, as it contains bacteria from the soil and nitrates. In no case should children be given carbonated or mineral medicinal water with a complex chemical composition. Water purified by home filters is also not suitable for babies.
Where can you get water that will not harm the child? It is best to buy it in a pharmacy. Special water for babies is labeled on the bottle, it contains the optimal amount of minerals for the baby. Water from the pharmacy does not need to be boiled, but after opening it can be stored for no more than a day, and only in the refrigerator. It is best to immediately pour such water into a glass container with a tight-fitting lid.
What methods of purifying water for a baby can be used?
The most economical and easiest option to provide your baby with high-quality drinking water is to buy a special "children's" water filter. This can be a jug-type device - it is inexpensive, it is very easy to use such a filter, and the degree of water purification is very high - the device effectively removes chlorine, bacteria, pesticides and particles of mechanical impurities from ordinary tap water. For the manufacture of such filters, only high-quality safe plastic is used, which is approved by pediatricians. Water purified in this way can be used not only for feeding the baby, but also for preparing various decoctions and infant formulas.
Can I give my baby water during hiccups?
What is hiccups? This is an involuntary contraction of the muscles of the diaphragm and larynx. Babies are especially susceptible to hiccups, since their diaphragm muscles are characterized by increased excitability. Hypothermia, air entering the stomach, nervous overexcitation and accumulation of gases in the intestines often lead to hiccups.
Hypothermia, air entering the stomach, nervous overexcitation and accumulation of gases in the intestines often lead to hiccups.
As soon as a child has hiccups, you need to immediately eliminate its cause. If the baby is cold, it needs to be warmed up. In order for air to come out of the stomach, the baby should be held in a “column”. A few sips of warm water will also help to cope with hiccups.
It is necessary to give water to a child with hiccups, as this measure will quickly eliminate the cause of discomfort.
If you do everything right and give water to the baby only when he really needs it, then there will be no harm - on the contrary, the child will receive the necessary amount of fluid for the normal functioning of the body.
Information about higher organizations
Ministry of Health of the Russian FederationOfficial portal of the Mayor and the Government of MoscowDepartment of labor and social protection of the population of the city of Moscow: on Mondays from 15. 00 to 18.00Department of health of the city of MoscowDepartment of RosZdravNadzor for the city of Moscow and the Moscow region: Mon - Thu: 9:00 - 17:45, Fri: 9:00 - 16:30, Sat - Sun: days off Office of Rospotrebnadzor for the city of MoscowFKU Main Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise for the city of Moscow: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday from 8.30 to 17.30 .Directorate for coordinating the activities of medical organizations DZMMosvolunter. Responsible person for cooperation with volunteer organizations: Adylov Seyran Midatovich, tel. +7 499-250-01-75
00 to 18.00Department of health of the city of MoscowDepartment of RosZdravNadzor for the city of Moscow and the Moscow region: Mon - Thu: 9:00 - 17:45, Fri: 9:00 - 16:30, Sat - Sun: days off Office of Rospotrebnadzor for the city of MoscowFKU Main Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise for the city of Moscow: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday from 8.30 to 17.30 .Directorate for coordinating the activities of medical organizations DZMMosvolunter. Responsible person for cooperation with volunteer organizations: Adylov Seyran Midatovich, tel. +7 499-250-01-75
Information for the public
Assessment of the quality of servicesIndependent assessment of the quality of services provided by medical organizationsQuestionnaire for assessing the quality of services provided by medical organizations on an outpatient basisDrugsCrowdsourcing projects of the Government of MoscowAmbulance and Emergency Medical Service in the City of MoscowAssistance Center for Medical WorkersMoscow City Compulsory Medical Insurance FundInsurance companiesFederal budgetary healthcare institution " Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow "Official resource of the Healthy Russia program.