Morning sickness blighted ovum
Blighted Ovum (Anembryonic Pregnancy): Causes & Symptoms
Overview
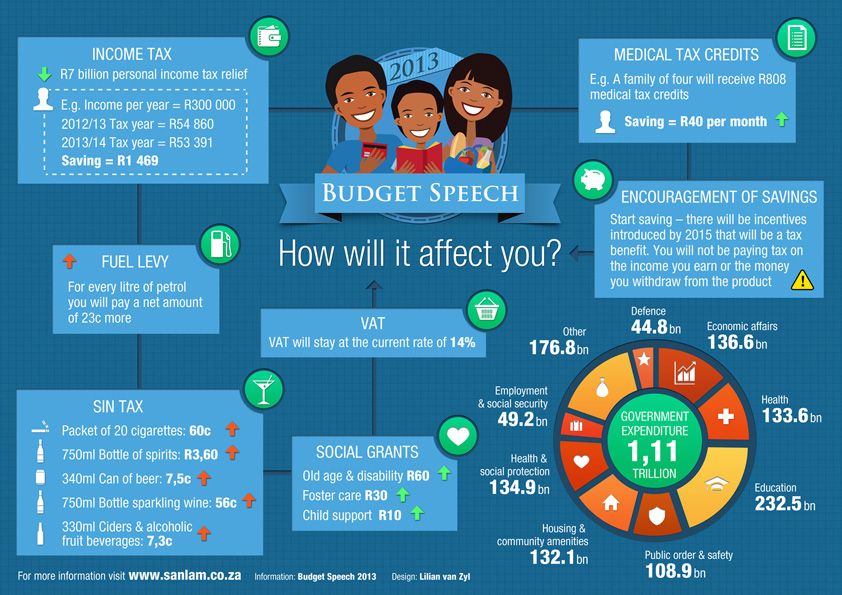
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.What is a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum (also called an anembryonic pregnancy) is a type of early miscarriage that occurs when a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but does not develop into an embryo. The embryo will stop growing, but the gestational sac (where the embryo would develop) continues to grow. The placenta and empty gestational sac will release pregnancy hormones — even without an embryo present. This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
When does a blighted ovum happen?
A blighted ovum causes an early miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. During fetal development, a fertilized egg turns into a blastocyte. At around four weeks of pregnancy, this blastocyte implants in the wall of the uterus and develops into an embryo. When you have a blighted ovum, the gestational sac that would hold the embryo continues to grow, even without an embryo present. The following can occur:
- A blighted ovum happens so early in pregnancy, that you never realize you are pregnant.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy only to discover a blighted ovum at your first ultrasound.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy but then experience a miscarriage.
How common is a blighted ovum pregnancy?
A blighted ovum is the number one cause of first trimester miscarriages.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum can occur so early in pregnancy that you never knew you were pregnant. In other cases, you may experience signs of pregnancy such as a missed menstrual period or a positive pregnancy test. You can have symptoms of early pregnancy, such as breast tenderness and morning sickness.
Other times your symptoms will resemble those of a miscarriage:
- Vaginal bleeding: Spotting (light bleeding), bleeding or passing light gray tissue or blood clots.
- Cramping: Mild to moderate cramping in your pelvic and abdominal region.
The only way to confirm a blighted ovum is through an ultrasound. It will show a gestational sac that is missing an embryo inside.
What causes a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum is usually caused by chromosomal or genetic problems during cell division. During conception, the egg will begin to divide shortly after being fertilized by sperm. Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
How does a blighted ovum miscarriage start?
A blighted ovum miscarriage will cause vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping. A miscarriage usually feels more intense than your regular menstrual period. You can take an over-the-counter medicine like acetaminophen to relieve cramping. Avoid lifting anything heavy or any strenuous exercise as it can increase your bleeding. You may experience spotting for several weeks after a miscarriage.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a blighted ovum diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will diagnose a blighted ovum using transvaginal ultrasound. This happens in the first trimester, usually between seven and nine weeks of pregnancy. An embryo should be visible at this time in pregnancy. With a blighted ovum, the gestational sac will be empty.
- You will lie back on an exam table and place your feet in stirrups like you do for a pelvic exam. Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus.
- A blighted ovum will appear as an empty sac — almost like a bubble.
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.
People are often unaware that they have a blighted ovum. This is because your placenta continues to give off hormones, making your body think you are pregnant. This is also why you can still have symptoms of pregnancy, including a positive pregnancy test.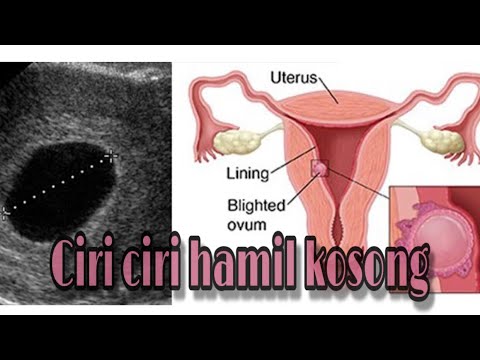
If you’ve already experienced bleeding or signs of a miscarriage, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound to look at the contents of your uterus to diagnose a blighted ovum.
Some healthcare providers will collect a series of blood samples that check the levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your body. HCG is known as the pregnancy hormone because it's only produced if you are pregnant. The level of hCG in your blood increases rapidly in early pregnancy and reaches its peak around weeks eight to ten. If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
Management and Treatment
How is a blighted ovum treated?
For some people, there may be no treatment needed, because your body passes the embryo through your vagina (a miscarriage). If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
- Dilation & Curettage (D&C): This is a surgical procedure to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will dilate, or open, the cervix and use medical tools and suction to remove the pregnancy tissues from your uterus. This is done under sedation or general anesthesia.
- Natural miscarriage: If it's safe, you may be able to watch and wait to see if your body eventually releases the pregnancy tissues. It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins.
- Medication-induced miscarriage: You may be given a medication called misoprostol to trigger your body to miscarry.
 This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled four to six weeks after a miscarriage or D&C. You may be given another ultrasound to confirm the uterus is empty. Your healthcare provider will check for signs of infection and make sure there were no complications.
What are the complications of a blighted ovum?
Complications of a blighted ovum are uncommon, but the possible complications could include:
- Excessive bleeding or hemorrhage.
- Infection.
- Scarring (from the D&C procedure).
- Tears in the uterus (from the D&C procedure).
How long does it take to recover from a blighted ovum?
Recovering from a blighted ovum miscarriage or D&C can last from one or two weeks to a month. Cramping generally lasts up to a week, but bleeding can last several weeks. Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
You can resume normal activities when you feel comfortable. Bleeding can increase with strenuous activity or exercise. Hormones may remain in your body and delay your menstrual cycle. Most people will get their period within four to six weeks after a blighted ovum.
It may take longer to recover emotionally from a blighted ovum miscarriage. You may have feelings of sadness, anger or confusion. It’s OK to take time to grieve. Ask your friends and family for support.
Prevention
Can a blighted ovum be prevented?
A blighted ovum can’t be prevented. Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Outlook / Prognosis
How soon after a blighted ovum can I get pregnant again?
Most healthcare providers recommend having one or two regular menstrual cycles before trying to conceive again after any type of miscarriage.
What are my chances of having another blighted ovum?
Your chances of having another blighted ovum are low. Most people go on to have healthy, full-term pregnancies. If you experience more than one blighted ovum, your healthcare provider may suggest testing to determine if there is an underlying cause.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- Excessive bleeding from your vagina.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Fever that does not go away.
- Symptoms that get worse over time.
- Severe pain that isn’t helped with pain medicine.
When should I go to the ER?
Go to the nearest ER If you experience heavy vaginal bleeding — more than two pads per hour for two consecutive hours — or have symptoms of anemia like dizziness, palpitations or paleness.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Losing a pregnancy is upsetting and confusing. Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
- Can I let my body miscarry or should I take medication to induce a miscarriage?
- What are the risks of miscarriage?
- Do I have to have a D&C?
- What are the risks of a D&C?
- How long can I expect to bleed or have cramping?
- Is there any indication this will happen again?
- When can I start trying to conceive?
- Do I need to come back for another ultrasound?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a blighted ovum considered a miscarriage?
Yes, a blighted ovum is a miscarriage. A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
How long can you carry a blighted ovum?
The amount of time you can carry a blighted ovum varies. Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Can a blighted ovum turn into a baby?
No, an empty gestational sac will not turn into an embryo. The formation of the embryo occurs within two weeks of conception. By the time the gestational sac is formed, the cells should have already formed the embryo. Your healthcare provider will be able to examine your gestational sac to confirm that no embryo has developed.
Do hCG levels rise with blighted ovum?
Yes, most of the time hCG levels will rise, giving you a positive pregnancy test and symptoms of pregnancy. This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
Is a blighted ovum more common with IVF?
A blighted ovum is not more common with IVF (In Vitro Fertilization). Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Losing a pregnancy is difficult. If you are struggling after a miscarriage, speak with your healthcare provider so they can recommend support groups or counselors. Finding support may help you get through this hard time. Most people who have had a blighted ovum will go on to have a healthy pregnancy.
Blighted Ovum Miscarriage - Meaning, Treatment, Causes
A blighted ovum is a miscarriage that occurs very early in pregnancy. The fertilized egg is unable to develop into an embryo after it has attached to the uterine wall. This type of miscarriage usually occurs within the very early stages of pregnancy (weeks 2-6), often before a woman even knows she's pregnant.
Still, losing your baby, even at an early stage of pregnancy, can be devastating for the parents, far more so than people appreciate who have not been through it.
Unfortunately, blighted ovum miscarriages are not rare. It is the leading cause of miscarriages. A blighted ovum is one of the more common forms of miscarriages and is invariably associated with a chromosomal abnormality.
Thankfully, as we discuss below, having an early miscarriage like this does not have any impact on having a healthy pregnancy in the future. This article addresses the causes of blighted ovum, treatment for it, and the long-term outlook for fertility after a miscarriage from an anembryonic pregnancy.
What Is a Blighted Ovum Miscarriage?
A blighted ovum occurs very early in the process of embryonic development. When sperm reaches an egg, the egg becomes fertilized and begins the rapid production of new cells within only a few hours. With a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg will grow from a clump of cells into an embryo by the 10th day of development.
The embryo will then implant itself into the wall of the uterus. This triggers the release of high levels of pregnancy hormones in the body and causes the placenta to start developing to support the fetus. The fetus will continue to grow over the next few weeks, and around the 6th week of pregnancy, it will finally be visible on an ultrasound.
When blighted ovum occurs, this initial process is not completed. Sometimes the fertilized egg is not able to develop into an embryo but still implants itself into the uterus. In other cases, the transition from fertilized egg to embryo was successful but the embryo stops developing a few days after attaching.
For a doctor to diagnose a blighted ovum, an ultrasound will be performed and the doctor will identify an empty gestational sac with no signs of an embryo. This empty sac can usually be confirmed by the 8th week of pregnancy when the embryo would normally be visible. How long you carry a blighted ovum depends on what stage the blighted ovum miscarries.
What Causes Blighted Ovum Miscarriage?
There are several causes of a blighted ovum. The common thread is any anembryonic pregnancy is a genetic error or a genetic mistake.
From research conducted on multiple women who experienced a blighted ovum, there is a consensus that the wide majority of blighted ovum miscarriages are due to abnormal chromosomes[2]. The fertilized egg or embryo might be missing chromosomes or developed too many. This disrupts the normal process of development. In rare cases, genetic mutations can also be a cause for a blighted ovum, specifically for embryos that stopped developing after attaching to the uterus.
A blighted ovum is similar to other miscarriages in the sense that there was some developmental abnormality that ultimately caused the pregnancy to fail. It can create feelings of loss and despair, but it's important to understand that there is no way to prevent it from happening and women should not blame themselves. For early miscarriages, there is often no way to know that something has gone wrong until your doctor identifies it. If you are a woman reading this, you have already heard this but you should hear it again: it is not your fault.
For early miscarriages, there is often no way to know that something has gone wrong until your doctor identifies it. If you are a woman reading this, you have already heard this but you should hear it again: it is not your fault.
How Common is Blighted Ovum Miscarriage?
Accurate occurrence rates for blighted ovum miscarriages are understandably difficult because many women choose not to share their miscarriage stories. However, miscarriages are actually very common, with around 10-20% of pregnancies ending in miscarriage[4]. In that statistic, early miscarriages are most prevalent with 80% of them occurring within the first 12 weeks. Additionally, many women have one or multiple miscarriages before they have a normal pregnancy.
The statistics for how common blighted ovum is can be hard to measure due to difficulties diagnosing the condition. Since it occurs so early, women may not even know they were pregnant and do not notice the miscarriage happening. From what is known, experts believe blighted ovum accounts for a third of miscarriages that occur before 8 weeks gestation[3].
From what is known, experts believe blighted ovum accounts for a third of miscarriages that occur before 8 weeks gestation[3].
Blighted Ovum Symptoms
Even though the embryo is not developing properly or has stopped altogether, a woman may experience early pregnancy symptoms since the body has recognized something attached to the uterus.
Until the embryo has been expelled from the body, hormones are still being produced and pregnancy tests can have positive results. A woman may have morning sickness, bloating, sore breasts, and other common symptoms that show up during the first weeks of pregnancy. However, some signs may indicate a woman has a blighted ovum or is experiencing a miscarriage:
- Abnormal heavy bleeding
- Severe abdominal cramping
- An ultrasound that shows an amniotic sac is but is missing an embryo
A blighted ovum is confirmed when a sonogram shows no fetal heart tone.
Treatment for Blighted Ovum
After you have been diagnosed with a blighted ovum, there are a few different treatments available depending on how your body reacts to the attached egg or embryo.
For some women, there may be no treatment at all, as the body recognizes that there is no development and naturally passes the embryo by expelling the contents of the uterus. In these cases, the miscarriage will be similar to a heavy period, which can feel completely normal for someone unaware they had a blighted ovum.
If the blighted ovum is diagnosed but the body continues to act pregnant and releases hormones, your doctor may wait a few days to see if the body adjusts and eventually passes the embryo. If the body continues to keep the embryo attached despite no development, medication or surgery can be used to clear the contents of the uterus. Medication like Cytotec can induce a miscarriage which causes temporary heavy bleeding. A brief surgical procedure can be also be given by dilating the cervix and manually emptying the uterus.
A brief surgical procedure can be also be given by dilating the cervix and manually emptying the uterus.
Can A Blighted Ovum Give a False Positive Pregnancy Test?
A blighted ovum may occur before a woman is aware she is pregnant. What often happens in these cases is the placenta will continue to develop after the miscarriage. This is called an anembryonic pregnancy in which the body does not adapt to the miscarriage and continues to prepare for the baby. This will often lead to a false positive pregnancy test.
Can I Get Pregnant Again After a Blighted Ovum?
Miscarriages can be scary and make you feel like something is wrong with your fertility, but in most cases, this is not reality. Miscarriages are a natural part of pregnancies and often have no bearing on how fertile you are. Having one anembryonic pregnancy is usually no cause for concern. Normal pregnancies after a blighted ovum are normal. Statistics show you will likely have a normal and healthy pregnancy in the future, even immediately after a blighted ovum.
In a study involving women with early miscarriages, around 80% were able to have a successful pregnancy within the next five years[1]. The reason for these success stories is that treatments used for blighted ovum also have no negative effects on future pregnancies, even for surgical procedures.
If you have experienced multiple blighted ova or are struggling with miscarriages, there may be a different underlying problem, such as a hormone imbalance or genetic mutation. Your doctor can run tests to identify possible causes for complications in development.
How Long Can You Carry a Blighted Ovum?
When deciding how long to carry a blighted ovum, you are trying to balance the ease and low risk of a natural miscarriage (Dilation and Curettage or D&C surgery, for example, has some risks) versus the risk of infection if you do not have a natural miscarriage. Some suggest you can wait between 9 to 11 weeks with an anembryonic pregnancy.
But you want to discuss with your doctor who will be able to best gauge the optimal path for you.
How Long Until I Can Try to Get Pregnant After a Blighted Ovum?
Doctors often suggest women wait three months before attempting to conceive after a blighted ovum while others say less. You should talk to your doctor.
Do the COVID-19 Vaccines Cause a Blighted Ovum?
Three studies have been published that showed women are not at higher risk for a miscarriage after taking a COVID-19 vaccine.
Sources and Additional Reading
Chaudhry, K., et al. (2021). Anembryonic Pregnancy. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
This article provided an overview of a blighted ovum. It detailed its risk factors, clinical presentation, treatment and management options, differential diagnosis, and prognosis. The researchers also reported on patient education and the enhancement of healthcare team outcomes.
Sanni, R. R., et al. (2020). Blighted Ovum: A Case Report. Women’s Health Open Journal.
This case study looked at a late 20-something woman who suffered a blighted ovum. The researchers recommended healthcare providers should know how to properly manage and treat a blighted ovum.
Andriani, F., & Mardhiyah, I. (2019, March 22). Blighted ovum detection using convolutional neural network. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2084(1), 020012.
This article looked at the use of the convolutional neural network method to timely detect a blighted ovum. The researchers reported that the algorithm implementation’s accuracy was less than 60 percent. However, they also reported that this was because of the lack of data and the difficulties of distinguishing between blighted ovum and non-blighted ovum data.
Aroke, D., et al. (2018). Blighted ovum and tubal pregnancy: a rare form of heterotopic pregnancy: case report. BMC Research Notes, 11(1), 1-4.
This case study looked at a 25-year-old woman who suffered both a blighted ovum and an ectopic pregnancy. She underwent surgery. Her pregnancy was ultimately uneventful. The researchers concluded that blighted ova and ectopic pregnancies could occur at the same time. They recommended timely diagnoses and prompt management that could yield a favorable prognosis.
Horner-Johnson, W., et al. (2017). Live birth, miscarriage, and abortion among US women with and without disabilities. Disability and health journal, 10(3), 382-386.
This study looked at the live birth, miscarriage, and abortion rates among American women with and without disabilities. The researchers found that women with disabilities were less likely to have live births compared to women without. However, they reported that these differences were insignificant when controlling for covariates. They also found that women with complex limitations were more likely to suffer miscarriages. The researchers concluded that disability status did not have a significant impact on pregnancy outcomes.
Smith, L.F., et al. (2009). Incidence of pregnancy after expectant, medical, or surgical management of spontaneous first trimester miscarriage: long term follow-up of miscarriage treatment (MIST) randomised controlled trial. BMJ, 339.
This study looked at whether three early miscarriage management methods impacted future pregnancy rates. The researchers found that the live birth rates across all three groups were similar. They concluded that miscarriage management methods did not impact subsequent pregnancy rates.
Lathi, R. B., et al. (2007). Cytogenetic testing of anembryonic pregnancies compared to embryonic missed abortions. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, 24(11), 521-524.
This study compared the abnormality rate detected by cytogenetic testing in first semester miscarriages involving a fetal pole or a blighted ovum. The researchers found that 65 percent of all miscarriages showed abnormalities. They also found that the rates were 58 percent in miscarriages involving a blighted ovum and 68 percent in miscarriages involving a fetal pole. The researchers concluded that cytogenetic testing would help determine abnormalities during pregnancy.
The researchers concluded that cytogenetic testing would help determine abnormalities during pregnancy.
Regan, L., & Rai, R. (2000). Epidemiology and the medical causes of miscarriage. Baillieres Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 14(5), 839-854.
This study summarized a miscarriage’s epidemiology and medical causes. It also discussed the genetic abnormalities that contribute to a miscarriage.
Why do you feel sick in the morning on an empty stomach
Nausea in the morning on an empty stomach is most common in pregnant women due to intoxication, but it is not uncommon for males or even children to have this problem
Do not worry too much if you have encountered such a problem once, it is likely that this is a banal poisoning. But, if nausea in the morning on an empty stomach does not go away, you should immediately consult a doctor. Some people are used to dealing with this problem with folk remedies and medicines and they really get better, but it is worth considering that most likely the disease or pathology itself continues to develop. And as a result, it will turn into a more serious form. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of morning sickness and prescribe the most effective treatment. nine0004
And as a result, it will turn into a more serious form. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of morning sickness and prescribe the most effective treatment. nine0004
Possible diseases
Most often, morning sickness on an empty stomach may indicate the presence of the following diseases: unpleasant symptoms. This is due to inflammatory processes in the duodenum 12. The patient can also be tormented by: burning, bloating during and after eating, heartburn. nine0013 Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) - also characterized by nausea in the morning, as well as after eating fatty or fried foods. This disease is easily confused with gastritis due to the similarity of symptoms, but with pancreatitis, the patient begins to have problems with stools and an unpleasant, bitter taste in the mouth.
 Accompanying symptoms are pain in the right hypochondrium and excessive gas formation. nine0014
Accompanying symptoms are pain in the right hypochondrium and excessive gas formation. nine0014 Other causes of nausea in the morning
After excluding the above diseases from the list of causes, the following causes can be considered:
- Pregnancy. Intoxication and nausea in the morning is often found in pregnant women, especially in the early stages. This is a normal reaction of the body to significant changes and hormonal changes. It is very important to completely exclude drugs for the treatment of the digestive tract during pregnancy. These funds can have an extremely negative impact on the health of the patient, the unborn child and the course of pregnancy. Therefore, you will have to endure this ailment and get by with folk remedies, but be sure to consult your doctor. nine0014
- Migraine. Morning sickness on an empty stomach may precede a severe headache. You will most likely still feel a lot of noise and increased sensitivity to smells.
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
 The problem of morning sickness can be accompanied by headache and dizziness. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk starting this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke.
The problem of morning sickness can be accompanied by headache and dizziness. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk starting this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke. - Cardiovascular disease - rarely, nausea on an empty stomach occurs with heart failure or developing myocardial infarction. If nausea is accompanied by pain, a feeling of heaviness and tightness behind the sternum, numbness or tingling in one half of the body, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible, as this may be an incipient myocardial infarction. nine0014
- Increased intracranial pressure - Nausea and regurgitation in infants can occur when pressure increases inside the ventricles of the brain.
What to do if you feel sick in the morning
It is important to understand that regular morning sickness is a signal of the presence of a pathology or disease and it is highly undesirable to self-medicate. Be sure to consult a doctor for an examination, but if you don’t have such an opportunity at the moment, there are several effective ways that will help reduce or temporarily get rid of this problem:
- Medicines.
 You need to be very careful and you must be sure that morning sickness is not the cause of pregnancy or an intestinal disease.
You need to be very careful and you must be sure that morning sickness is not the cause of pregnancy or an intestinal disease. - Ginger root, mint and lemon drinks. You can make infusions of these products for maximum effect, simply by adding them to a glass and boiling water, after 15 minutes you will have a very effective and safe (in the absence of allergies) remedy for morning sickness. YOU can also just add them to hot tea. nine0014
- Medicinal collection - if nausea relentlessly torments you in the morning, you can try a collection of mint, oak bark and celandine. To prepare the drink, take 1 tsp of mint leaves, dried oak bark and chopped celandine, pour 0.5 l of boiling water and boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. After the broth is cooled and filtered, take 1 tablespoon 3-5 times a day before meals.
- During pregnancy. There are some little tricks you can use. For example, do not get out of bed quickly, drink plenty of fluids. Eliminate fatty and heavy foods from your diet.
 Eat small meals several times a day. nine0014
Eat small meals several times a day. nine0014
You might be interested
Tired of nausea in the morning? Constantly sick after eating? We understand the reasons!
- Why do you feel sick in the morning?
- Causes of nausea after eating
- How to determine the exact cause of nausea?
- What to do if the gastroenterologist did not reveal violations? nine0013 Treatment
Nausea, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn are familiar to everyone. I overate on fatty delicacies at the festive table - unpleasant sensations will not be long in coming. I drank expired kefir or too much alcohol - nausea is right there. The reasons are simple and clear. In the first case, there were not enough enzymes to digest food, and the liver had to work at its limit. In the second, toxic substances entered the body, which caused poisoning. These symptoms are unpleasant, but they are temporary. And they usually go away after a few days or even hours. But what if you feel sick all the time? We need to figure out the reasons! nine0004
I overate on fatty delicacies at the festive table - unpleasant sensations will not be long in coming. I drank expired kefir or too much alcohol - nausea is right there. The reasons are simple and clear. In the first case, there were not enough enzymes to digest food, and the liver had to work at its limit. In the second, toxic substances entered the body, which caused poisoning. These symptoms are unpleasant, but they are temporary. And they usually go away after a few days or even hours. But what if you feel sick all the time? We need to figure out the reasons! nine0004
Why do you feel sick in the morning?
Waking up daily in the morning with a feeling of nausea, which causes you to refuse breakfast and take a long time to "come to yourself", may be associated with nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux (reflux of bile into the esophagus). By itself, it is not a pathology, since normally it occurs mainly after eating and does not cause discomfort. The body for its suppression includes compensatory antireflux mechanisms.
But if an unpleasant symptom is observed frequently and lasts for a long time, then we can talk about gastroesophageal reflux disease or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. MRI of the abdominal cavity will help to find out the exact cause and make a diagnosis. nine0004
Causes of nausea after eating
Nausea after breakfast or lunch can be caused by heavy meals (mainly fatty), overeating, psychogenic eating disorders (anorexia, bulimia).
But in most cases, the patient's unpleasant condition is associated with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, colitis, peptic ulcer, enteritis.
How to determine the exact cause of nausea?
The range of possible violations, as we see, is quite "rich". Nausea can be caused by the liver, gallbladder, biliary tract, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, duodenum, lower esophageal sphincter, and gastroesophageal junction. nine0004
Problems can cause inflammation, erosion, ulcers, cysts, tumors, gallstones. The cause may be stenosis (narrowing) of the output section of the stomach, fibrosis, cirrhosis and fatty degeneration of the liver (hepatosis). Often, patients are diagnosed with functional disorders.
The cause may be stenosis (narrowing) of the output section of the stomach, fibrosis, cirrhosis and fatty degeneration of the liver (hepatosis). Often, patients are diagnosed with functional disorders.
Abdominal MRI is recommended to determine the gastrointestinal cause of nausea and rule out a tumor causing dysphagia (food obstruction and stagnation).
A highly informative study allows the patient not to run around the doctors' offices, checking each organ separately. And immediately simulate a three-dimensional image of each organ, see its layered sections. And get an idea of the overall picture: the thickness and changes in the walls of the stomach, the state of the gallbladder, the size of the liver, pancreas, duodenum, esophagus, track their functions in real time. MRI provides better visualization of the gastrointestinal tract than CT, so this method is preferable in most cases. nine0004
Examination can be done without and with contrast. In the second case, the cost of abdominal MRI will be higher, but the study will provide more accurate information on tumor neoplasms.
What should I do if the gastroenterologist has not identified any abnormalities?
It also happens that after the examination, the gastroenterologist tells the patient that no pathologies have been detected on his part. However, such joyful news does not yet mean that the person who came with complaints is heroically healthy. nine0004
The etiopathogenesis of nausea may be associated with:
- vascular pathologies;
- hypertension;
- diseases of the inner ear;
- endocrine disorders;
- brain and CNS pathologies;
- head injuries and post-traumatic syndromes;
- viral, bacterial and parasitic infections (often not associated with the gastrointestinal tract, but affecting the lungs, ENT organs, CNS).
Treatment
Nausea is not a disease, but a symptom of some disorder or disease. Therefore, if it is not associated with toxic poisoning, then you need to look for and eliminate the cause, and not fight the effect.