Measuring uterus during pregnancy
What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Measure It
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Is Fundal Height?
- What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
- How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
- What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
- What Can Impact Fundal Height?
- What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
Choosing to have a baby can be a magical experience. But there are also many unknowns that come with pregnancy. You’re doing everything you can to care for your body and your unborn child, but you may wonder how to know if your baby is growing well in your uterus (womb).
Measuring fundal height is one way to keep track of your baby’s development while you’re pregnant.
What Is Fundal Height?
It’s the distance from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus.
Measuring your fundal height is one test your doctor may do at your pregnancy check-ups. Other ways they may check on your baby’s health include checking your physical health, running labs on your body, listening to your baby’s heartbeat, checking how often your baby moves, and looking at your baby with an ultrasound.
Doctors combine all of these factors to give you the most accurate understanding of how well your baby is developing.
What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
Doctors use your fundal height measurement to test how well your baby is growing.
It’s one of many tests doctors use to measure your baby’s growth. Your fundal height is compared to your estimated pregnancy date to suggest whether your baby is growing on track.
If your fundal height isn’t what you expect it to be, it doesn’t automatically mean that there’s something wrong with your baby. But if your fundal height is on track, you may be able to rest a little easier knowing your baby is growing the way your doctors are expecting it to.
How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
Understand that even trained doctors can have a hard time measuring it accurately.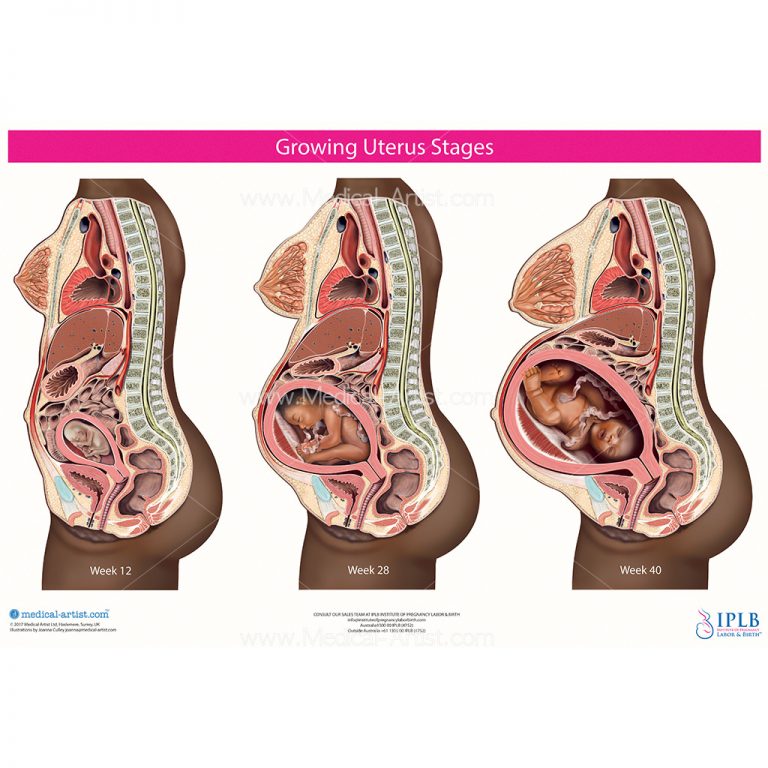 So, before you try measuring fundal height at home, have your doctor show you where your pubic bone is and how to locate the top of your uterus.
So, before you try measuring fundal height at home, have your doctor show you where your pubic bone is and how to locate the top of your uterus.
Once you know, here are the basic steps to follow.
- Empty your bladder first. Studies show that a full bladder can change fundal height measurements by several centimeters.
- Next, lay down on your back with your legs out in front of you. Using a tape measure that measures centimeters, place the zero marker at the top of the uterus.
- Move the tape measure vertically down your stomach and place the other end at the top of your pubic bone. This is your fundal height measurement.
What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
Starting at 24 weeks, your fundal height should be about the same number of centimeters as the number of weeks you’ve been pregnant.
Your fundal height may be off by up to 2 centimeters in either direction and still be considered normal.
So, for example, if you’re 30 weeks pregnant, a fundal height of 28 to 32 centimeters is considered to be a normal range.
What Can Impact Fundal Height?
There are a number of things that can affect it. Not all of these factors have to do with your baby. For example, your fundal height measurement may not be accurate if:
- You have a BMI of 30 or more.
- You have a history of uterine fibroids.
- Your bladder is full.
- You’re not lying on your back when you take the measurement.
There are other reasons your fundal height may be bigger or smaller than expected. If your fundal height is larger than expected, it may be because:
- You have too much amniotic fluid.
- You’re having more than one baby.
- Your baby is larger than expected.
If your fundal height is smaller than expected, it may be because:
- Your baby is smaller than expected.
- You don’t have enough amniotic fluid.
- Your baby’s growth is being restricted.
Your fundal height measurement may also be off if your pregnancy is further along, or less far along, than you thought. Your due date is an estimate based on the last day of your last period, so it can sometimes be inaccurate.
Your due date is an estimate based on the last day of your last period, so it can sometimes be inaccurate.
Doctors usually use the assumption that you have a standard 28-day period when making their due date predictions. Since periods and ovulation windows can vary, your doctor may have been off by a couple of weeks when first predicting your due date.
What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
If your fundal height isn’t measuring as expected, your doctor will need to do some follow-up tests to determine the root cause. These tests could include an ultrasound to get a better look at your baby or labs to test the health of your body.
An unusual fundal height measurement on its own is an indication that there’s something happening with your baby.
Once your doctor has figured out why your fundal height measurement is off, they can help you figure out what steps need to be taken next, if any, to help your baby grow at a healthy rate.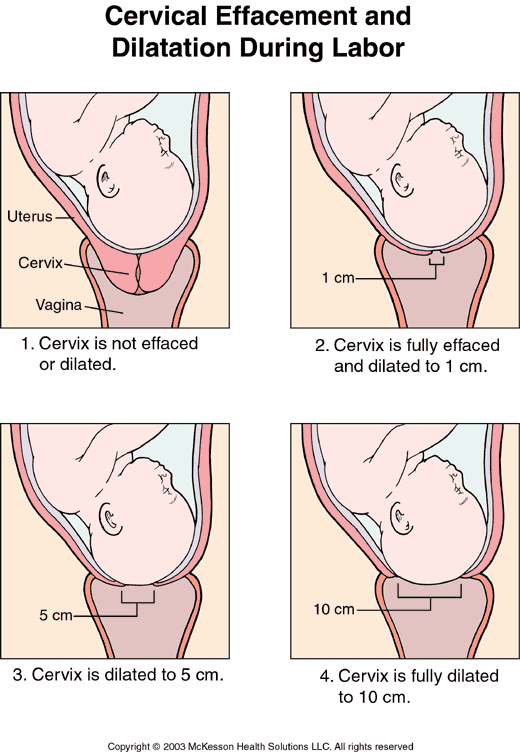
What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Measure It
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Is Fundal Height?
- What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
- How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
- What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
- What Can Impact Fundal Height?
- What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
Choosing to have a baby can be a magical experience. But there are also many unknowns that come with pregnancy. You’re doing everything you can to care for your body and your unborn child, but you may wonder how to know if your baby is growing well in your uterus (womb).
Measuring fundal height is one way to keep track of your baby’s development while you’re pregnant.
What Is Fundal Height?
It’s the distance from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus.
Measuring your fundal height is one test your doctor may do at your pregnancy check-ups.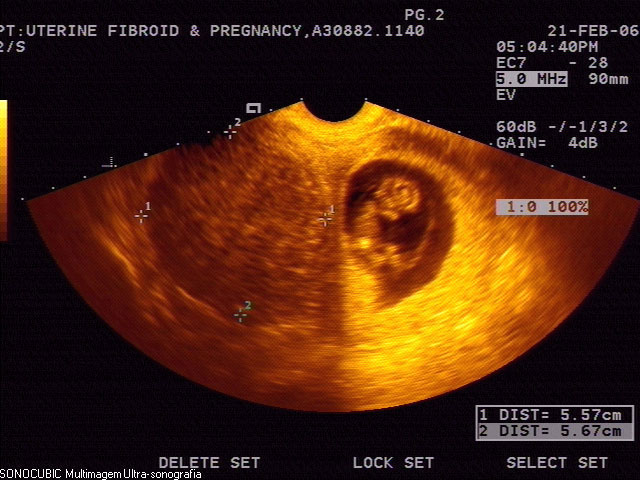 Other ways they may check on your baby’s health include checking your physical health, running labs on your body, listening to your baby’s heartbeat, checking how often your baby moves, and looking at your baby with an ultrasound.
Other ways they may check on your baby’s health include checking your physical health, running labs on your body, listening to your baby’s heartbeat, checking how often your baby moves, and looking at your baby with an ultrasound.
Doctors combine all of these factors to give you the most accurate understanding of how well your baby is developing.
What Does Fundal Height Tell You About Your Baby?
Doctors use your fundal height measurement to test how well your baby is growing.
It’s one of many tests doctors use to measure your baby’s growth. Your fundal height is compared to your estimated pregnancy date to suggest whether your baby is growing on track.
If your fundal height isn’t what you expect it to be, it doesn’t automatically mean that there’s something wrong with your baby. But if your fundal height is on track, you may be able to rest a little easier knowing your baby is growing the way your doctors are expecting it to.
How Do You Measure Fundal Height?
Understand that even trained doctors can have a hard time measuring it accurately.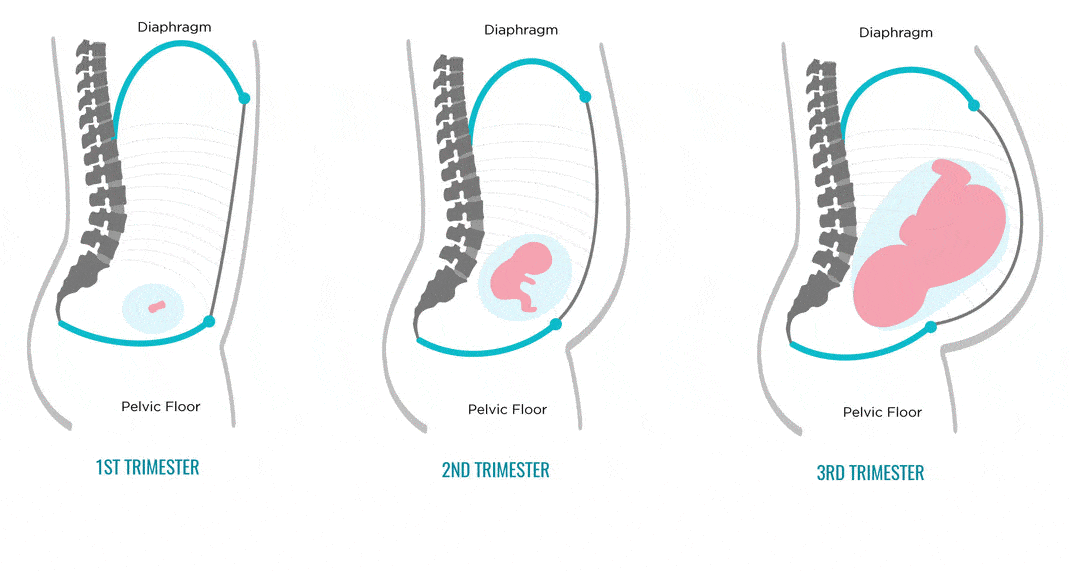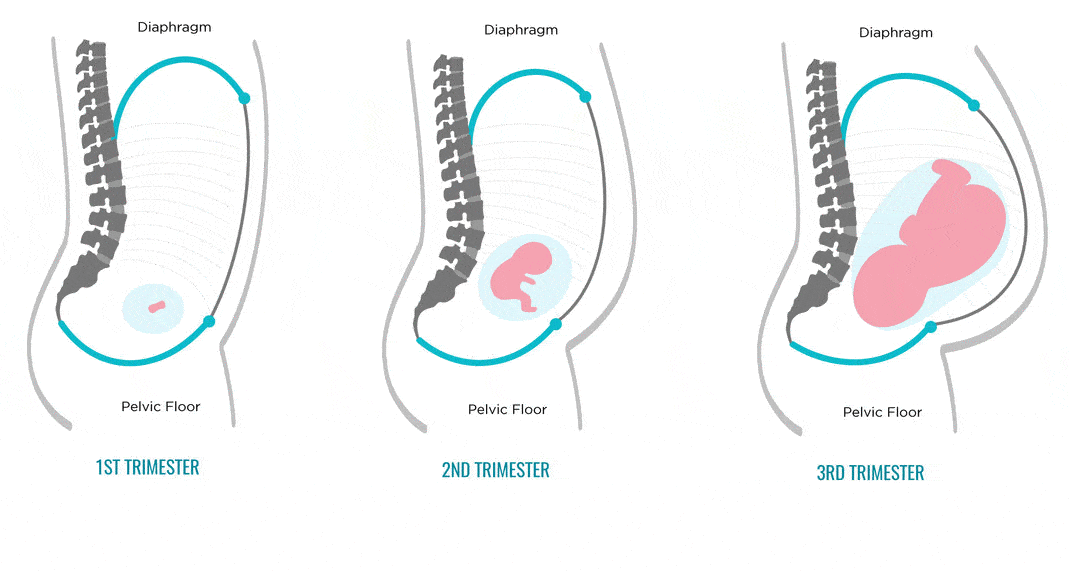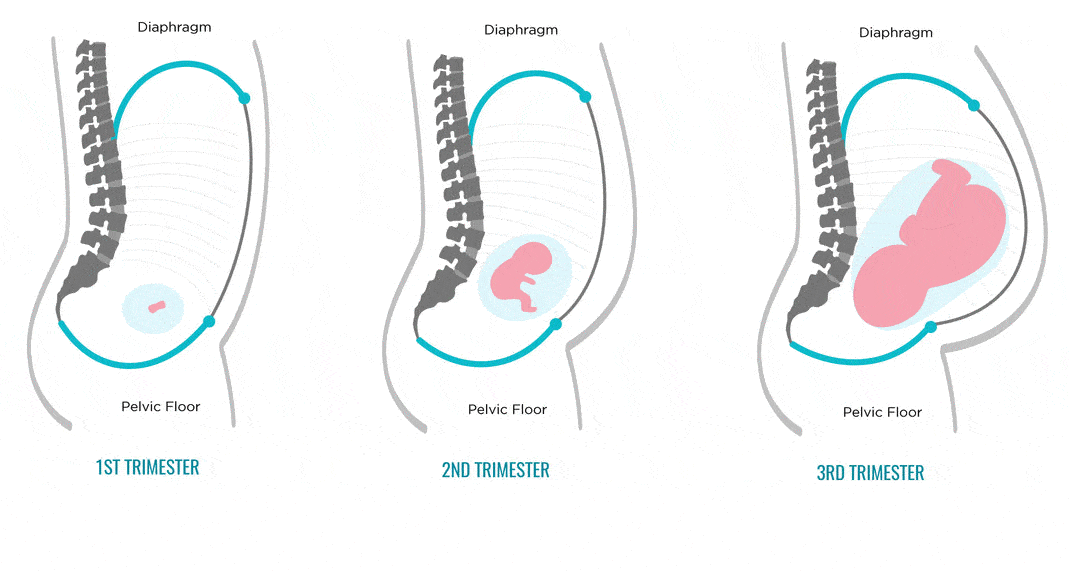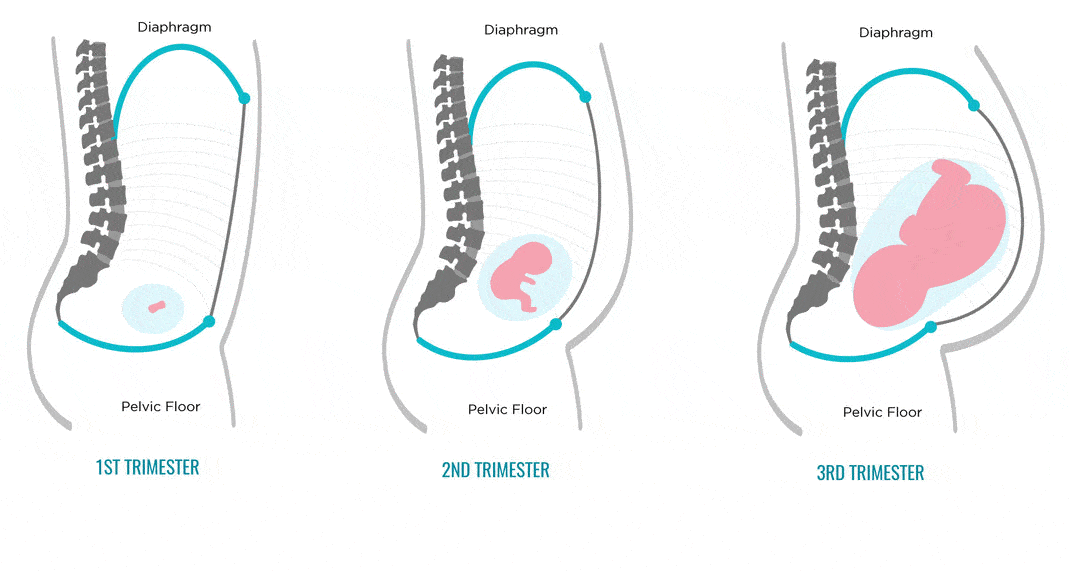 So, before you try measuring fundal height at home, have your doctor show you where your pubic bone is and how to locate the top of your uterus.
So, before you try measuring fundal height at home, have your doctor show you where your pubic bone is and how to locate the top of your uterus.
Once you know, here are the basic steps to follow.
- Empty your bladder first. Studies show that a full bladder can change fundal height measurements by several centimeters.
- Next, lay down on your back with your legs out in front of you. Using a tape measure that measures centimeters, place the zero marker at the top of the uterus.
- Move the tape measure vertically down your stomach and place the other end at the top of your pubic bone. This is your fundal height measurement.
What Should Your Fundal Height Be?
Starting at 24 weeks, your fundal height should be about the same number of centimeters as the number of weeks you’ve been pregnant.
Your fundal height may be off by up to 2 centimeters in either direction and still be considered normal.
So, for example, if you’re 30 weeks pregnant, a fundal height of 28 to 32 centimeters is considered to be a normal range.
What Can Impact Fundal Height?
There are a number of things that can affect it. Not all of these factors have to do with your baby. For example, your fundal height measurement may not be accurate if:
- You have a BMI of 30 or more.
- You have a history of uterine fibroids.
- Your bladder is full.
- You’re not lying on your back when you take the measurement.
There are other reasons your fundal height may be bigger or smaller than expected. If your fundal height is larger than expected, it may be because:
- You have too much amniotic fluid.
- You’re having more than one baby.
- Your baby is larger than expected.
If your fundal height is smaller than expected, it may be because:
- Your baby is smaller than expected.
- You don’t have enough amniotic fluid.
- Your baby’s growth is being restricted.
Your fundal height measurement may also be off if your pregnancy is further along, or less far along, than you thought.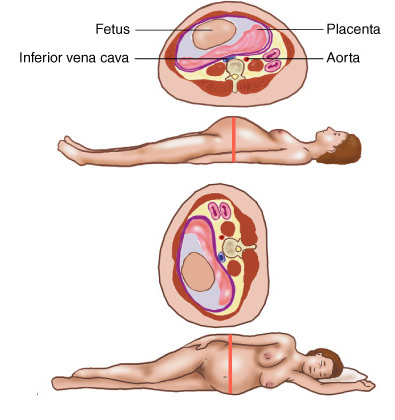 Your due date is an estimate based on the last day of your last period, so it can sometimes be inaccurate.
Your due date is an estimate based on the last day of your last period, so it can sometimes be inaccurate.
Doctors usually use the assumption that you have a standard 28-day period when making their due date predictions. Since periods and ovulation windows can vary, your doctor may have been off by a couple of weeks when first predicting your due date.
What Should You Do if You’re Concerned About Your Fundal Height?
If your fundal height isn’t measuring as expected, your doctor will need to do some follow-up tests to determine the root cause. These tests could include an ultrasound to get a better look at your baby or labs to test the health of your body.
An unusual fundal height measurement on its own is an indication that there’s something happening with your baby.
Once your doctor has figured out why your fundal height measurement is off, they can help you figure out what steps need to be taken next, if any, to help your baby grow at a healthy rate.
What is the length of the cervix indicates the likelihood of preterm birth - clinic "Dobrobut"
Publication date: 2020-06-30
Cervicometry during pregnancy - what it is
Cervicometry is a transvaginal ultrasound technique that measures the length of the cervix. When the cervix is too short, there is an increased risk of preterm labor. How cervicometry is done and in what cases the study is indicated will be discussed below. nine0003
Norms of the length of the cervix by week of pregnancy
Cervicometry during pregnancy - what is it? This is the most reliable way to measure the length of the closed part of the cervix. The transvaginal ultrasound technique is superior in accuracy to the transabdominal method for determining the length of the cervix. Cervicometry is performed for all pregnant women, but for women who have had a history of preterm birth, the results of the study are especially important. These patients are shown cervicometry every 15 days in the interval from 14 to 24 weeks of pregnancy. For other pregnant women, a single examination at 20-24 weeks is recommended. The procedure is absolutely safe for the mother and fetus and is practically no different from a standard ultrasound examination. nine0003
For other pregnant women, a single examination at 20-24 weeks is recommended. The procedure is absolutely safe for the mother and fetus and is practically no different from a standard ultrasound examination. nine0003
Norms of the length of the cervix by week of pregnancy:
- 16-20 weeks: 40-45 mm;
- 25-28 weeks: 35-40 mm;
- 32-36 weeks: 30-35 mm.
If the cervix is 30 mm or more, the likelihood of preterm birth does not exceed the general population. What length of the cervix indicates a high risk of preterm birth? If a shortened cervix (less than 15 mm) is detected, urgent hospitalization and a set of measures to prevent preterm birth (cervical cerclage, progesterone administration) are indicated. If, according to the results of cervicometry, the length of the cervix is less than 25 mm, then the patient is given a conclusion “ECHO-signs of CCI” with a recommendation to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist. nine0003
Cervicometry: preparation and technique
Empty the bladder before the examination. Cervicometry is performed in the lithotomy position (the woman lies on her back with bent knees). The doctor gently inserts the ultrasound probe into the vagina towards the anterior fornix. In this case, a sagittal view of the organ is obtained. The mucosa of the endocervix serves as a reference point for determining the position of the internal os. The doctor measures the closed part of the cervix, starting from the external os and up to the V-shaped notch of the internal os. This concludes the study and the patient is given a conclusion. nine0003
Cervicometry is performed in the lithotomy position (the woman lies on her back with bent knees). The doctor gently inserts the ultrasound probe into the vagina towards the anterior fornix. In this case, a sagittal view of the organ is obtained. The mucosa of the endocervix serves as a reference point for determining the position of the internal os. The doctor measures the closed part of the cervix, starting from the external os and up to the V-shaped notch of the internal os. This concludes the study and the patient is given a conclusion. nine0003
Transvaginal cervicometry detects a number of important clinical conditions that range from preterm labor to polyhydramnios (polyhydramnios). Detection of a short cervix by transvaginal ultrasound at 18–24 weeks of gestation is the most important predictor of spontaneous preterm birth. If the length of the cervix at 14–24 weeks of gestation is less than 15 mm, then with a probability of 50%, preterm birth may occur at a gestational age of up to 33 weeks. In women with a previous unfavorable anamnesis, a pattern can be traced: the shorter the cervix, the more likely recurrent preterm birth, and with a length of less than 10 mm, the probability increases to 90%. That is why it is so important during pregnancy to be observed by a gynecologist and timely conduct transvaginal cervicometry.
In women with a previous unfavorable anamnesis, a pattern can be traced: the shorter the cervix, the more likely recurrent preterm birth, and with a length of less than 10 mm, the probability increases to 90%. That is why it is so important during pregnancy to be observed by a gynecologist and timely conduct transvaginal cervicometry.
The price of ultrasound cervicometry can be found on our website https://www.dobrobut.com
Related services:
Gynecological Check-up
Colposcopy
Do you want to get an online explanation from the doctor of the Dobrobut MS?
Download our Google Play and App Store app
nine0003
Our doctors
See all doctors 715
Our certificates
Certificate no. QIZ 804 468 C1
Certificate no. QIZ 804 469 C1
QIZ 804 469 C1
Certificate No. QIZ 804 470 C1
Certificate no. QIZ 804 471 C1
View all certificates
Request a call back
nine0002 Enter your phone numberOther articles
Pediatric colonoscopy: what parents need to know about this examination
Colonoscopy for a child: important information for parents. How to prepare for a colonoscopy of a small child. Where to do a study in Kyiv, cost and reviews
What is parkinsonism, its signs and methods of treatment
How is parkinsonism different from parkinson's disease. Symptoms and signs, treatment of parkinsonism. Possible complications and preventive measures. nine0003
Basic principles for the treatment of torticollis in infants
Muscular torticollis: clinical manifestations, treatment and preventive measures. Orthopedic pillow for torticollis: how to choose the right one. What young parents need to know about this pathology.
Orthopedic pillow for torticollis: how to choose the right one. What young parents need to know about this pathology.
Prices for intervertebral disc replacement - information for patients
What patients need to know about lumbar disc replacement. The cost of the prosthesis of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc. Disability after surgery - truth and myths
View all articles
Request a call back
Enter your phone number
Cervicometry (ultrasound of the cervix) - Reproductive medicine, gynecology, pregnancy monitoring, urology
Cervicometry is an ultrasound examination of the cervix, which allows you to determine in advance the risk of spontaneous abortion or other pathologies of gestation and timely prevent the problem.
Procedure summary
Ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy is done at different times. As a rule, the procedure is prescribed for a period of 12-22 weeks. But if a woman already had problems with bearing or a multiple pregnancy, then cervicometry is prescribed until the 15th week, and at the 20th week of gestation it is recommended to undergo a second examination.
As a rule, the procedure is prescribed for a period of 12-22 weeks. But if a woman already had problems with bearing or a multiple pregnancy, then cervicometry is prescribed until the 15th week, and at the 20th week of gestation it is recommended to undergo a second examination.
Cervicometry is performed using a special transfuser, which is inserted into the woman's birth canal. This allows you to comprehensively assess the condition of the neck of the organ, measure its length and inspect the inner surface of the cervical canal. nine0003
Ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy is safe not only for the woman, but also for the unborn child. The channel is measured both externally and internally. More objective data is obtained by measuring the channel from the inside.
Who should be examined
Cervicometry is recommended for women during gestation if:
- a multiple pregnancy is diagnosed;
- before conception, an operation was performed on the reproductive organs; nine0020
- was previously diagnosed with isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- the cervix is shortened.
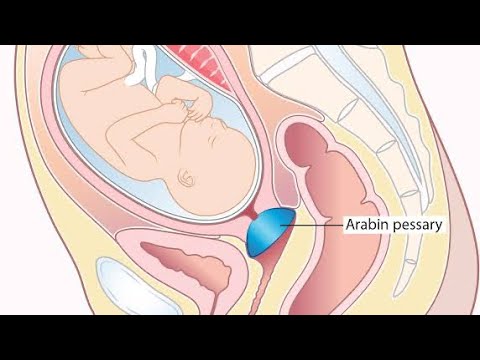
When analyzing the results, the doctor compares the results obtained with the reference and gives a conclusion about the risk of miscarriage.
Pre-laboratory preparation
Preparation for ultrasound does not differ from similar examinations of other organs of the reproductive system, except for one point - for examination, the woman's bladder must be emptied of the contents, since the full bladder does not allow visualization of the cervix. It is also desirable that the intestines be empty and not gassed, for which it is allowed to take Espumizan or Almagel the day before. nine0003
Reference values and interpretation of indicators
Ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy shows changes in canal length at different gestational ages:
| Gestational timing (weeks) | Length of cervical canal (mm) |
| 16-20 | 40-45 |
| 24 | ~37 |
| 25-28 | 35-40 |
| 32-36 | 30-35 |
If the length is less than the reference values, then the risk of miscarriage is very high.