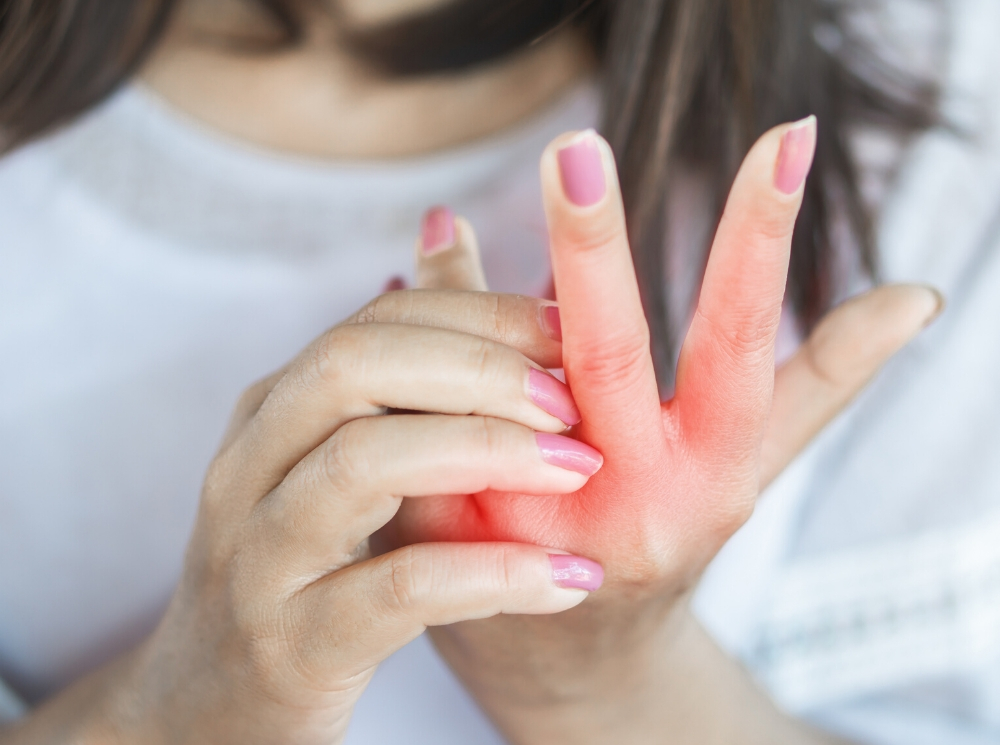
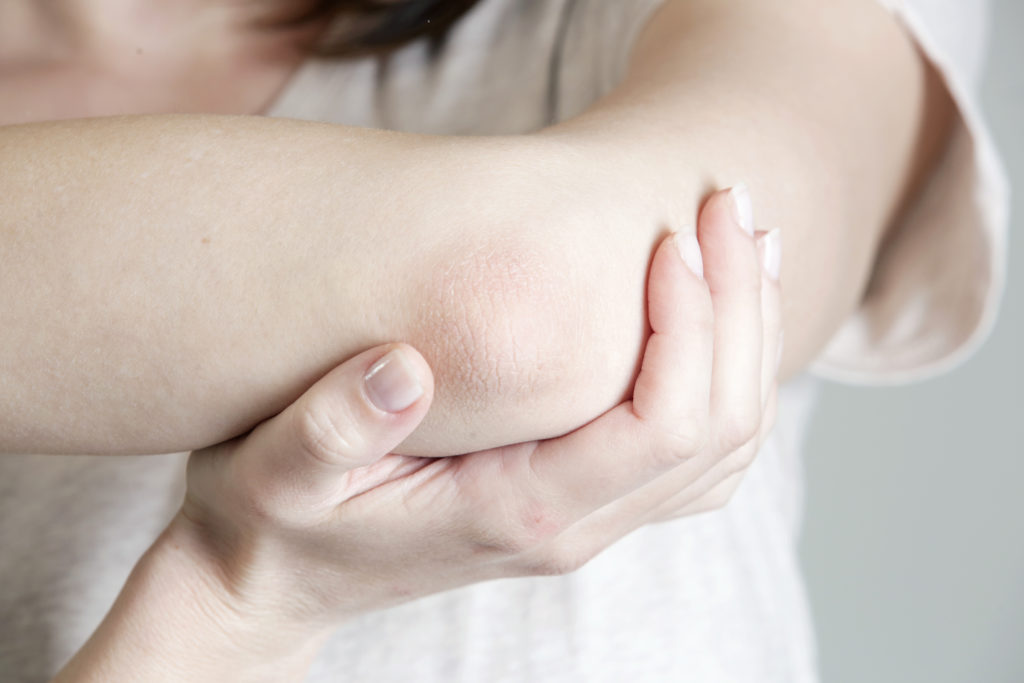
Itchy spots on hand
Pompholyx - NHS
Pompholyx (also called dyshidrotic eczema) is a type of eczema that affects the hands or feet. It's usually a long-term condition, but treatment can help control the symptoms.
Check if you have pompholyx
Pompholyx causes itchy blisters on the hands or feet that come and go. The symptoms usually last 2 to 3 weeks at a time.
The first symptom is often a burning or prickling feeling in the affected area.
Fluid-filled blisters then appear on the skin. These are usually very itchy and may leak fluid.Credit:
Vilaiphab Khanyavong
https://www.shutterstock.com/image-photo/dyshidrotic-eczema-allergic-skin-condition-symptom-2041694828
Credit:
DR. P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/600559/view
It can also affect the toes and soles of the feet.Credit:
ISM/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/1159184/view
If you're not sure it's pompholyx
Other conditions can cause sore, itchy patches or blisters on the hands and feet, including hand, foot and mouth disease, psoriasis or athlete's foot.
Do not try to diagnose yourself – see a GP if you're worried.
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
- you think you have pompholyx
- you have pompholyx and the blisters are very painful, leak yellow or green pus or are covered in a yellow-brown crust – these are signs of an infection
- you have any other changes to your skin you're worried about
Treatments for pompholyx
Pompholyx is usually a long-term condition that comes and goes over time.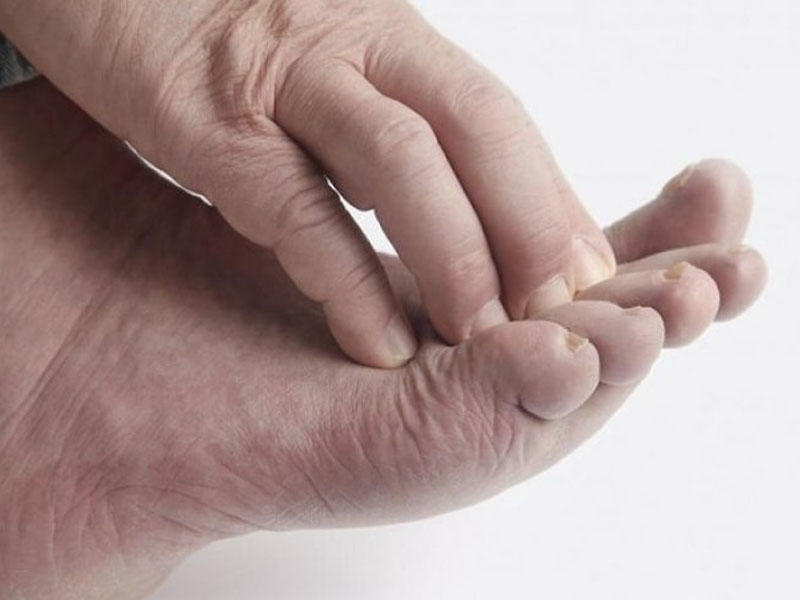 Treatment can help control the symptoms.
Treatment can help control the symptoms.
The main treatments for pompholyx are:
- moisturisers (emollients) – used every day to stop the skin becoming dry
- steroid creams and ointments (topical steroids) – used for a few weeks at a time to reduce irritation and soreness
If the blisters leak fluid, a GP may suggest soaking your skin in potassium permanganate solution. This helps dry the blisters and reduces the risk of them getting infected.
If the blisters become infected, a GP may prescribe antibiotics.
Treatments from a specialist
If your symptoms are severe or treatment is not helping, a GP may refer you to a skin specialist (dermatologist).
A dermatologist may recommend other treatments, such as:
- steroid tablets
- treatment with ultraviolet (UV) light
- other medicines, such as alitretinoin
Things you can do to ease symptoms of pompholyx
If you have pompholyx, your skin may get irritated easily. There are some things you can try to see if they help.
There are some things you can try to see if they help.
Do
-
wash your hands with warm (not hot or cold) water and use a moisturiser (emollient) soap substitute instead of regular soap
-
wear protective gloves (ideally with a cotton lining) when using chemicals like shampoos, cleansers and detergents
-
wear socks, tights or stockings made from cotton or silk, rather than nylon
-
wear shoes made from leather, rather than plastic or rubber
-
avoid anything you think causes your symptoms, such as cleansers or detergents
A pharmacist can help with pompholyx
If your skin gets very itchy and it affects your sleep, ask a pharmacist about antihistamines that make you drowsy (sedating antihistamines).
If you take these before going to bed, they can help you get to sleep.
What causes pompholyx
It's not clear exactly what causes pompholyx.
Certain things are thought to cause symptoms in some people, including:
- contact with strong chemicals like soaps, cleansers and detergents
- an allergy or sensitivity to certain metals, such as nickel or cobalt
- getting your hands wet regularly – for example, if you’re a hairdresser
- stress
- heat and sweat
Information:
If you notice something causes your symptoms, avoiding it as much as possible may help keep your symptoms under control.
Page last reviewed: 02 March 2022
Next review due: 02 March 2025
8 Common Causes and Treatment Options
Palm rash
A rash is a symptom that can cause your skin to itch, burn, or develop bumps. While not often an indicator of a more serious condition, a rash can be a sign of an infection or exposure to an irritant.
You can develop a rash all over the body, including the palms of your hands. Throughout the day, your hand comes in contact with people, the environment, and other irritants that can cause a reaction. Understanding the cause of your rash and symptoms can help your doctor diagnose your condition.
There are a number of conditions that may cause you to develop a rash on your palm. Some of the most common include:
- an allergic reaction
- dry skin
- contact dermatitis
- psoriasis
- hand, foot, and mouth disease
- dyshidrotic eczema
- impetigo
- ringworm
1.
 Allergic reaction
Allergic reactionFood allergies or medications can trigger an allergic reaction that may present as a rash. It may cause your hands or skin to itch, blister, or even develop hives.
Other common symptoms that may accompany your palm rash include:
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- itchy mouth
- swelling
- difficulty breathing
- difficulty swallowing
- anaphylactic shock
A severe allergic reaction and anaphylactic shock are considered a medical emergency. You should seek immediate medical attention if you have any of the more serious symptoms.
2. Dry skin
In the colder months, the weather can cause your skin to dry out. This can directly apply to your palms, causing your hands to itch and flake.
Eczema and some medications may also cause your skin to dry out and develop a rash. Scratching your palms may worsen your symptoms.
3. Ringworm
This fungal infection is a common but treatable condition. Ringworm is a skin infection that manifests as a ring-shaped rash on various parts of your body. On the palms, however, it won’t develop its characteristic ring-shaped pattern.
On the palms, however, it won’t develop its characteristic ring-shaped pattern.
In addition to a palm rash, you may experience:
- dry skin
- deep cracks
- thickened skin
- inflammation
4. Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a form of eczema that causes a rash when your skin or hands touch an irritant. Sometimes, skin rashes can happen immediately. In most cases, though, a skin or palm rash takes time to develop.
Contact dermatitis commonly occurs after touching:
- poison ivy
- poison oak
- nickel
- makeup
- latex gloves
- jewelry
You may also develop a palm rash from touching cleaning supplies, bleach, and some soaps. If you develop a palm rash that doesn’t improve or is accompanied by burning, seek immediate medical attention.
5. Psoriasis
This skin condition is a disease that can cause inflammation on various parts of your body, including your palms. Psoriasis can be inherited, but it may be triggered from injury to the skin, other skin conditions, or infection.
Other than inflammation on your palm, you may also experience:
- redness
- dry, scaly skin
- plaques, or thickened skin in affected areas
- painful cracks in your skin
6. Hand, foot, and mouth disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a highly contagious condition seen frequently among children. It’s a viral infection that can cause you to develop sores and a rash in your mouth and on your hands and feet.
Other symptoms you may experience with this infection include:
- fever
- sore throat
- blisters on your tongue
- red rash on your palm or soles
- appetite loss
This condition is likely to heal within a few days with only mild signs of symptoms. If your symptoms worsen or don’t improve, schedule an appointment with your doctor.
7. Dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema is a specific type of eczema that causes small, itchy blisters to develop on your palms. They typically appear in clusters and may be painful. The blisters will dry and peel within three weeks.
The blisters will dry and peel within three weeks.
If you’re diagnosed with this condition, you may also develop blisters on your fingers and the soles of your feet. Dyshidrotic eczema is most common among women, though it can occur in men. To date, there’s no cure for this condition.
8. Impetigo
Another common skin infection among children is impetigo. This condition causes you to develop blisters on your face, neck, and hands. Children are more likely to develop this infection if they already experience other skin conditions such as eczema or contact dermatitis from poison ivy.
Impetigo is contagious and can spread from person-to-person contact, or coming in contact with things an infected person has touched. Impetigo also causes itching and can be spread to other parts of the body from scratching.
Treating your palm rash depends on the underlying cause. Some rashes can heal on their own and require no treatment. In other cases, treatment could be as simple as using lotion to moisturize your dry skin.
If you’re experiencing an allergic reaction, allergy medicine or an antihistamine can reduce symptoms and eliminate your palm rash. If your rash is the result of dermatitis, eczema, or psoriasis, your doctor may prescribe a topical cream to suppress your immune response. For cases of eczema and psoriasis, avoid potential triggers and keep your hands moisturized to prevent dry skin.
For bacterial and viral infections, your doctor may prescribe you with a topical or oral antibiotic. If your symptoms don’t improve or worsen after treatment, seek immediate medical attention.
A palm rash is often a minor symptom that can be treated within a few days. However, some cases of palm rash are an indication of a more serious skin condition or infection.
If you begin to experience additional symptoms with your palm rash, or if your symptoms worsen, schedule a visit with your doctor or a dermatologist. They can help you diagnosis the condition and find the right treatment for you.
You can book an appointment with a dermatologist in your area using our Healthline FindCare tool.
Plaques on the skin - causes, what diseases it occurs in, diagnosis and treatment
- INVITRO
- Library
- Symptoms
Fungus
Allergy
Psoriasis
Keratoma
Mycosis
Nevus
Melanoma
16552 November 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment.
 In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.Plaques on the skin: the causes of occurrence, in what diseases they occur, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
Definition
A plaque is a pathological element with clear edges that rises above the skin surface or merges with it, more than 5 mm in size.In dermatology, many types of plaques are distinguished - about 70 diseases occur with the formation of these elements, which makes the plaque one of the most common rashes.
Plaque varieties
The shape of the plaques are round, oval and irregular in shape. Over time, the shape, surface and appearance of this element may change.
Over time, the shape, surface and appearance of this element may change. Due to the occurrence of plaques, they can be both a manifestation of skin diseases and a symptom of diseases of internal organs and systems (autoimmune reactions, liver diseases, oncological processes, allergic reactions).
Plaques are dry, smooth, red, brown, gray-white, etc.
Possible causes of plaques
Dry plaques on the skin in adults may be a manifestation of the following diseases: plaques with severe itching.
- Allergic reactions are characterized by the appearance on the skin of smooth dry plaques, pink spots, blisters, which are very itchy and cause severe discomfort. They can develop both when the skin comes into contact with the allergen, and when it gets on the mucous membranes (for example, with urticaria, hay fever, food and contact allergies).
- Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious skin disease in which scaly dry plaques form on the elbows, knees, scalp, prone to fusion and accompanied by mild itching.

- Dry plaques form on the skin if it is exposed to stress for a long time with the loss of its protective functions.
- Diseases of the digestive tract, accompanied by malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of vitamins and trace elements in the small intestine), chronic diseases of the liver and other organs, in which substances that are not normally present in the dermis accumulate, also lead to the appearance of dry plaques.
- Solar keratoma is a precancerous condition, which is characterized by the presence of many light grayish plaques on the skin.
- Drug toxidermia is an allergic reaction accompanied by the appearance of elements in the form of plaques on the skin. In severe cases, Lyell's syndrome or Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, may develop.
- Dühring's dermatitis (herpetiform) is a chronic skin disease with no established etiology, which is characterized by recurrent appearance of a rash of various morphologies on the skin, accompanied by severe skin itching and burning.
- Mycosis fungoides is a primary T-cell lymphoma of the skin, a malignant lymphoid lesion, primarily of the skin. Itchy red plaques appear on the skin, resembling eczema. In the initial stages, they respond well to treatment with hormonal ointments, but the disease itself requires more complex therapy.
- In children, the appearance of red spots and plaques on the skin is most often associated with an allergic reaction to food.
- Becker's nevus is an anomaly in the development of the dermis, when dark plaques with an uneven surface appear on the skin, on which hair can begin to grow over time.

- Pigmentary nevus - "birthmark", may rise above the skin, has a brown or dark color.
- Melanoma is the most malignant skin tumor characterized by rapid metastasis. It develops mainly from nevi and moles. If the nature of the surface, the boundaries of the mole change, its size increases, bleeding occurs, you should immediately contact a dermatologist or oncologist to exclude the development of melanoma.
- Basal cell skin cancer is more often localized on the head, face, neck, does not metastasize, is characterized by slow growth.
- Senile keratoma occurs in elderly people, most likely due to a lack of vitamins, an abundance of animal fats consumed, skin sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation due to a violation of its protective functions. Typical localization - face, neck, open areas of the body.
- Seborrheic keratoma is a yellowish plaque on the skin that eventually transforms into a dark brown growth that tends to flake off, itch severely, crack, bleed, and can serve as an entryway for infection.
- change in the shape of the plaque - the edges have become uneven;
- change in the surface of the plaque - cracks, ulcerations appeared;
- change in the size of the plaque - it began to grow rapidly above the surface of the skin or actively spread through it;
- discoloration of the plaque - in cases of malignancy, an uneven color of the formation is usually observed with areas of darker and lighter shades;
- the appearance of bleeding - both contact and spontaneous;
- enlargement of regional (nearby) lymph nodes.
- Clinical guidelines.
 Dermatitis herpetiformis // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016.
Dermatitis herpetiformis // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016. - Clinical guidelines. Urticaria in children // Union of Pediatricians of Russia; Russian Association of Allergists and Clinical Immunologists. 2018.
- Clinical guidelines. Toxidermia // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016.
- Clinical guidelines. Familial hypercholesterolemia // National Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis. 2018.
-
Cholesterol plaques
1677 November 18th
-
Hepatic colic
1184 09 November
-
Laryngeal edema
406 07 November
The appearance of red plaques on the skin indicates their good blood supply. Possible causes of this condition may be the following nosologies:
Brown plaques occur when melanin is deposited in the affected area of the dermis, which causes a brown (dark) color. Possible causes may be the following diseases:
Which doctors to contact
With the formation of plaques on the skin, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist to determine the causes of the appearance of this element of the rash.
Plaque diagnostics and examinations
For the diagnosis of fungal skin lesions, scraping from the affected area is used for subsequent microscopic examination.
The development of an allergic reaction requires seeking medical help to identify the allergen, prescribing antihistamines, and sometimes hormonal drugs. In clinical cases of allergy, along with skin tests, analyzes are performed using various sets of common allergens and triggers: a panel for respiratory allergens, for food allergens, and for a combination of both.
Respiratory Panel
Synonyms: Comprehensive Respiratory Allergen Test Panel; Respiratory allergens panel, Allergen respiratory profile, Allergy testing. Brief description of the study "Panel respira...
Brief description of the study "Panel respira...
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB
Add to cart
Food Panel, IgE
Food Allergen Panel: hazelnut, peanut, Walnut, almond, cow's milk, egg white, egg ...
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB
Add to cart
Food and Respiratory Panel
Panel different allergens: A mixture of grass allergens: fragrant spikelet; perennial rye; timothy; rye cultivated; Woolly buckthorn (GP3) IgE . ..
..
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB
Add to cart
In psoriasis, seeing a dermatologist and rheumatologist can help reduce the symptoms of the disease if appropriate therapy is prescribed. For the diagnosis, it is usually sufficient to examine, determine, the skin manifestations of psoriasis are so characteristic, but if necessary, a differential diagnosis is carried out, including a clinical blood test, feces for the presence of worm eggs and protozoa, and a histological examination of the skin.
Clinical blood test: general analysis, leukoformula, ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes)
Synonyms: Complete blood count, UAC. Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study CBC: general...
Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study CBC: general...
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
RUB 810
Add to cart
Fecal test for helminth eggs
Synonyms: Feces on worm eggs; Analysis of feces for eggs of worms. Ova and Parasite Exam; O&P; Stool O&P test. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for eggs of helminths&ra...
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 570
Add to cart
Fecal analysis for protozoa (PRO stool)
Synonyms: Analysis of faeces for protozoa. Parasite Exam, feces; Parasitic Examination, fecal. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for protozoa" Fecal analysis for ...
Parasite Exam, feces; Parasitic Examination, fecal. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for protozoa" Fecal analysis for ...
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
RUB 570
Add to cart
Histological examination of biopsy material and material obtained during surgical interventions (endoscopic material; tissues of the female reproductive system; skin, soft tissues; hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue; bone and cartilage tissue)
Taking biomaterial is paid separately. According to the requirements of clause 17 of the Rules for conducting pathological and anatomical studies, approved. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia. ..
..
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
2 880 RUB
Add to cart
Diseases of the stomach and intestines can also lead to plaque formation on the skin. To identify the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, it is enough to refer to therapist or gastroenterologist, conduct a number of endoscopic examinations (gastroscopy, and, if necessary, colonoscopy), ultrasound of the abdominal organs, perform some screening blood tests for diseases of the liver, intestines, stomach.
Gastroscopy
Examination of the mucosa of the upper gastrointestinal tract with the possibility of biopsy or endoscopic removal of small pathological ...
RUB 4,440 Sign up
Colonoscopy
Endoscopic examination of the colon to look for abnormalities, perform biopsies, and remove small polyps and tumors.
RUB 5,740 Sign up
Comprehensive ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen)
Scanning of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity to assess its functional state and the presence of pathology.
RUB 2,890 Sign up
Liver function tests: screening
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 1,935
Add to cart
Diagnosis of celiac disease: intolerance to cereal proteins (gluten)
Up to 8 business days
Available with house call
7 520 RUB
Add to cart
Gastropanel
Up to 9 working days
Available with house call
RUB 4,760
Add to cart
To clarify the diagnosis of keratoma, a skin biopsy is performed and epithelium scraping is performed, followed by microscopic and histochemical examination.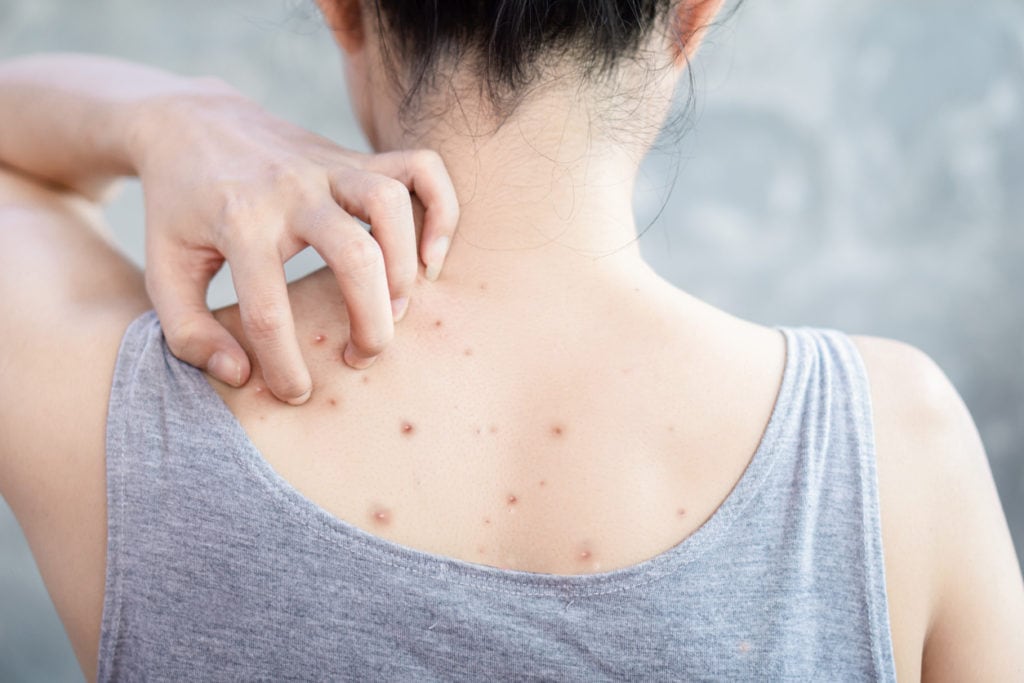
Histological examination of biopsy material and material obtained during surgical interventions (endoscopic material; tissues of the female reproductive system; skin, soft tissues; hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue; bone and cartilage tissue)
Taking biomaterial is paid separately. According to the requirements of clause 17 of the Rules for conducting pathological and anatomical studies, approved. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia...
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
2 880 RUB
Add to cart
Examination of scrapings and impressions of tumors and tumor-like formations
Material for research. Imprints and scrapings are obtained from pathological lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (except for the cervix and cervical canal). Relative to test...
Imprints and scrapings are obtained from pathological lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (except for the cervix and cervical canal). Relative to test...
Up to 2 working days
Available with house call
RUB 1,030
Add to cart
If atypical cells are detected in scrapings or biopsies, immediately contact oncologist.
If xanthoma appears on the skin, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist, take blood tests for lipid profile and blood glucose levels, and screen for diabetes.
Lipid profile screening
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
1 355 RUB
Add to cart
Glucose (in the blood) (Glucose)
Research material Serum or blood plasma. If it is not possible to centrifuge the sample 30 minutes after collection for serum/plasma separation...
If it is not possible to centrifuge the sample 30 minutes after collection for serum/plasma separation...
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
335 RUB
Add to cart
Diabetes management: advanced
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
RUB 5 820
Add to cart
What should I do if plaque appears on the skin?
Any newly appeared neoplasms should be shown to a dermatologist.![]() Their cosmetic removal without prior consultation with a specialist is fraught with serious consequences.
Their cosmetic removal without prior consultation with a specialist is fraught with serious consequences.
In addition, there are symptoms that require immediate medical attention:
Plaque treatment
When plaques of an allergic nature appear on the skin, antihistamines are prescribed, in cases of a severe course of the disease, glucocorticosteroids. In addition, it is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
In addition, it is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
Mycotic plaques require antifungal drugs, both local (ointments, creams) and systemic (tablets). Taking these drugs is associated with a high risk of side effects, and therefore it is possible only after consulting a doctor, accurate verification of the diagnosis and confirmation of the etiology of the disease.
Treatment of psoriasis is multi-stage and complex, it involves constant monitoring by a rheumatologist, taking cytostatics and other drugs, using ointments and shampoos to improve skin condition, using antihistamines to reduce itching, including physiotherapy and a hypoallergenic diet in the treatment regimen.
When confirming the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, properly selected therapy can stop the appearance of new plaques on the skin, as well as prevent the development of complications of the underlying disease.
Sources:
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
Recommendations
Show more
Fungus
Cystitis
Urethritis
Trauma
Prostatitis
Tumor
Pain in the urethra
Pain in the urethra: causes, diseases in which it develops, methods of diagnosis and treatment.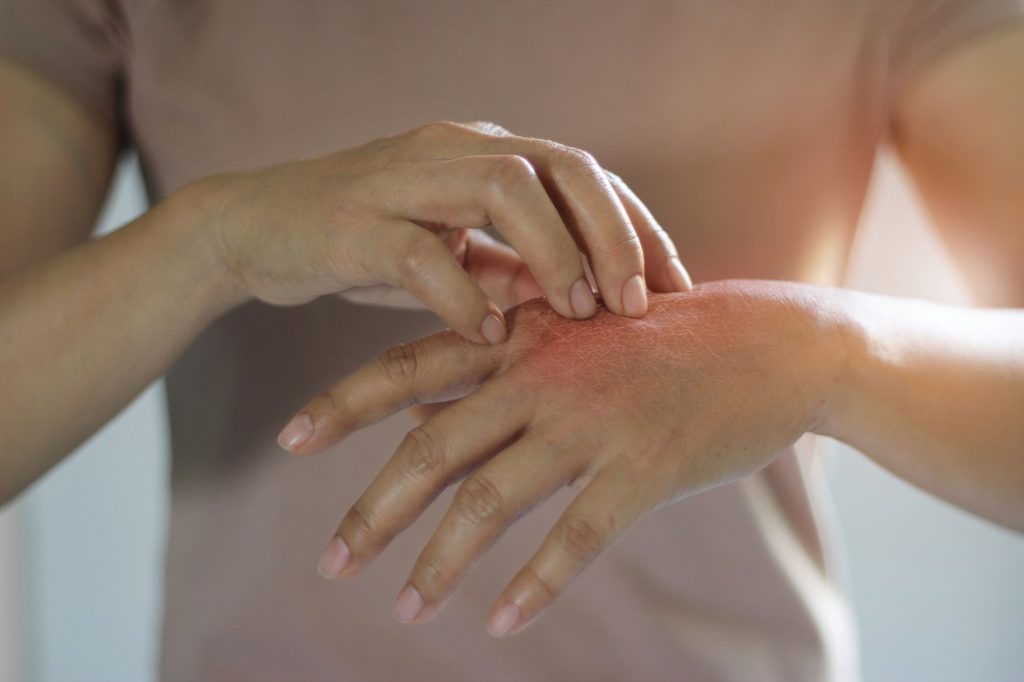
More
Fungus
Diarrhea
Allergy
Diabetes mellitus
Hemorrhoids
Intertrigo
Intertrigo: causes of occurrence, in what diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
More
Allergy
Fungus
Otitis
Sulfur plug
Mastoiditis
Tympanic membrane rupture
Otomycosis
Discharge from the ear, or otorrhoea
Discharge from the ear: causes, conditions, diagnosis and treatment.
More
Menopause
Climax
Pregnancy
Burn
Frostbite
Fungus
Mycosis
Psoriasis
Lichen planus
Brittle nails
Brittle nails cause significant discomfort. Traumatization and inflammation of the base of the nail plate is the first cause of fragility. Fragility and layering of the nail plate can be a symptom of a number of pathological conditions.
Traumatization and inflammation of the base of the nail plate is the first cause of fragility. Fragility and layering of the nail plate can be a symptom of a number of pathological conditions.
More
Diphtheria
Diabetes mellitus
Laryngitis
Tonsillitis
Fungus
Gastroesophageal reflux
Caries
Bad breath
Halitosis is a medical term used to describe bad breath.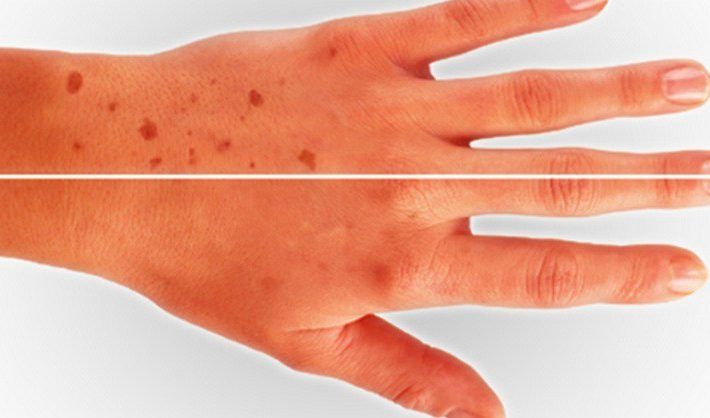 Bad breath can cause social and psychological problems. People suffering from halitosis experience difficulties in starting a family, finding employment and daily communication with other people.
Bad breath can cause social and psychological problems. People suffering from halitosis experience difficulties in starting a family, finding employment and daily communication with other people.
More
Nothing found
Try editing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from the list
Medical office not found
Try changing your query or select medical office from the list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
No results found
Try changing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
Acute urticaria - allergic skin reaction
Urticaria manifests itself as raised, well-circumscribed areas of erythema (redness) and swelling of the skin, which is very itchy.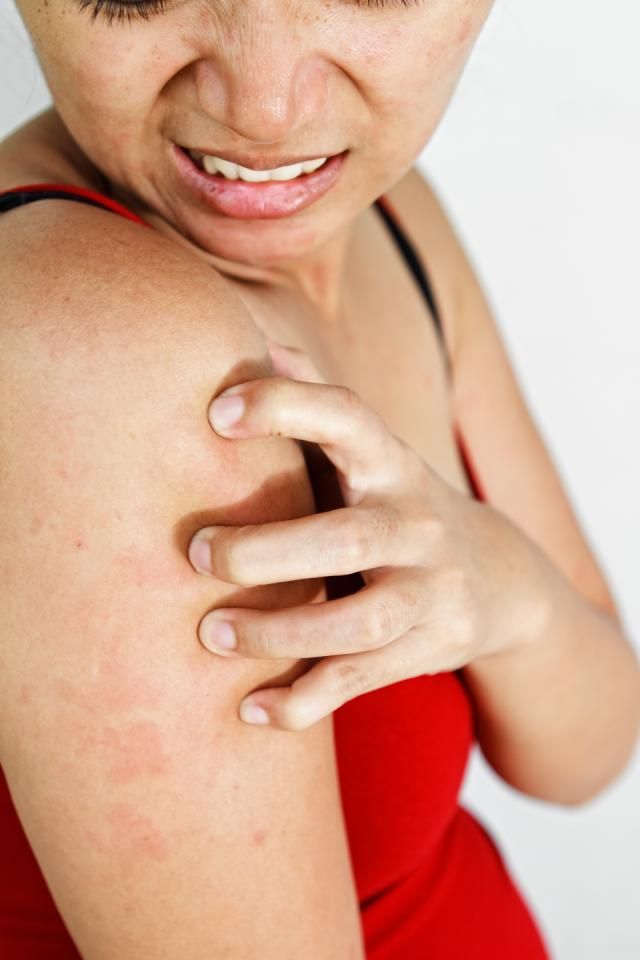 The intensity of itching can vary from mild to severe. Red spots on the skin can take any shape: be linear, round or oval, arched
The intensity of itching can vary from mild to severe. Red spots on the skin can take any shape: be linear, round or oval, arched
Urticaria can appear anywhere on the body, and the itchy patches may change shape, migrate, disappear, and reappear within short periods of time. However, to recognize this condition is quite simple - urticaria has one characteristic symptom: the center of the spots turns pale when pressed . At the same time, this does not mean that urticaria cannot be confused with any other of the many dermatological diseases that are similar in symptoms. So, it happens that only an experienced doctor can make a diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis of urticaria:
allergic contact dermatitis atopic dermatitis (eczema) erythema multiforme scabies Henoch-Schonlein disease (a form of allergic vasculitis) mastocytosis lichen pink.
Symptoms of urticaria may last from a few minutes to several months or even years (then we are talking about chronic urticaria). Usually spots with clear edges appear on the skin unexpectedly and disappear just as suddenly. If these symptoms last less than six weeks, urticaria is classified as acute.
Usually spots with clear edges appear on the skin unexpectedly and disappear just as suddenly. If these symptoms last less than six weeks, urticaria is classified as acute.
Acute generalized urticaria
Acute generalized urticaria stands out separately, which is distinguished by a larger area of spots on the body. In some cases, itchy patches or rashes can cover the entire body. Another specific point: the cause of acute generalized urticaria often cannot be established. According to some sources, the cause of this condition is not determined in more than 60% of cases.
Known/common triggers for acute generalized urticaria
Infections (eg, upper respiratory infections, pharyngitis, gastrointestinal infections, genitourinary tract infections, respiratory infections, fungal infections such as dermatophytosis, malaria, amoebiasis, hepatitis, mononucleosis, HIV, parasitic infections such as ascariasis, or trichinosis. Foods (most commonly shellfish, fish, eggs, cheese, chocolate, nuts, berries, tomatoes) Drugs: penicillins, sulfonamides, salicylates, NSAIDs, codeine, antihistamines Environmental factors (eg, pollen, chemicals, dust, mold ), as well as exposure to cold or heat Exposure to latex Emotional stress Physical overexertion
How acute urticaria develops
Upon contact with a trigger (irritant), the body reacts by releasing large amounts of the inflammatory mediator histamine, as well as a number of other pro-inflammatory molecules (cytokines).