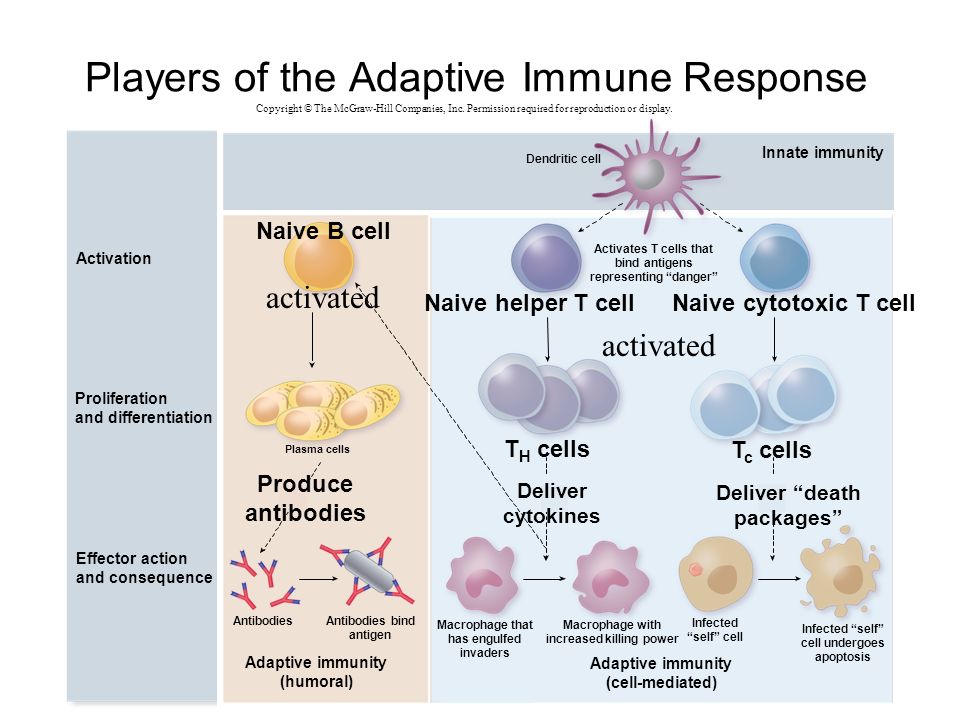
Is it possible to have a miscarriage without bleeding
Miscarriage without bleeding: Symptoms and diagnosis
Most of the time, bleeding is the first sign of a miscarriage. However, a miscarriage can occur without bleeding, or other symptoms may appear first.
Many women prefer the term pregnancy loss to miscarriage. Pregnancy loss is most common within the first weeks of pregnancy, and the risk steadily declines as the pregnancy progresses.
It is important to remember that pregnancy symptoms shift over time. These changes do not always signal a pregnancy loss.
Anyone who believes that they have lost a pregnancy, with or without bleeding, should seek medical attention.
Pregnancy losses do not always involve bleeding. In fact, a woman may not experience any symptoms and only learn of the loss only when a doctor cannot detect a heartbeat during a routine ultrasound.
Bleeding during pregnancy loss occurs when the uterus empties. In some cases, the fetus dies but the womb does not empty, and a woman will experience no bleeding.
Some doctors refer to this type of pregnancy loss as a missed miscarriage. The loss may go unnoticed for many weeks, and some women do not seek treatment.
According to the American Pregnancy Association, most losses occur within the first 13 weeks of pregnancy. While an estimated 10–25 percent of all recognized pregnancies end in a pregnancy loss, a loss in the second trimester is very rare.
Some women have no external symptoms of pregnancy loss. When the loss occurs early on, a woman may have few signs of pregnancy, which can make identifying the loss more difficult.
It is normal to experience changes in pregnancy signs over time, particularly in the transition from the first to the second trimester. These changes do not usually indicate the loss of the pregnancy.
Some warning signs of a pregnancy loss without bleeding include:
- a sudden decrease in pregnancy signs
- pregnancy tests that show a negative result
- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- back pain
If the pregnancy has advanced, fetal movement may noticeably slow or stop.
Most women seek treatment for a pregnancy loss when they experience bleeding. When there is no bleeding, a doctor may only diagnose a loss during a routine scan.
A doctor may also suspect a loss because of other indications, such as a drop in the levels of pregnancy hormones or an unusual decrease in other pregnancy signs.
Blood tests can determine the levels of hormones, which can help to assess the likelihood of a pregnancy loss. To conclusively diagnose a loss, a doctor must perform an ultrasound to check for a heartbeat.
The heartbeat does not develop until 6.5–7 weeks of gestation, so the absence of a heartbeat before this time does not indicate a loss.
To confirm a pregnancy loss, a doctor may choose to perform scans on multiple days.
To determine the reason for a loss, a doctor may also recommend genetic testing, further ultrasound scans, or blood testing.
The goal of treatment is to remove the fetus and tissue from the uterus and to prevent complications, such as a uterine infection. There is a variety of treatment options available, and a doctor or midwife will be able to advise on the best option.
There is a variety of treatment options available, and a doctor or midwife will be able to advise on the best option.
When pregnancy loss occurs without bleeding, it is often safe to wait for a few weeks before seeking treatment, because the uterus may empty on its own.
When this occurs, a woman can expect bleeding that involves passing the tissue. This usually lasts for less than a week, and cramping may accompany it.
If the uterus does not empty, or if a woman does not want to wait, the most common treatment options are:
- medication that encourages the release of the fetus
- a surgical procedure called dilation and curettage
A doctor may recommend pain medication to reduce associated cramping. Over-the-counter varieties are often effective. If they do not work, a doctor can prescribe something stronger.
In rare cases, pregnancy loss leads to a uterine infection, which requires treatment.
It is essential to consider mental health when choosing a course of treatment. Many women feel immense grief following a pregnancy loss. Guilt and anxiety are also common responses.
Many women feel immense grief following a pregnancy loss. Guilt and anxiety are also common responses.
Therapy and support groups can help. Some women might also benefit from using antianxiety or antidepressant medications.
Many women worry that they are responsible for the loss of their pregnancies. In most cases, this is untrue, and the loss is outside of a person’s control.
The most common cause of a pregnancy loss is a chromosomal abnormality that would have made it impossible for the baby to survive.
Less common causes include:
- infections
- illnesses
- physical injuries
- abnormalities in the uterus or other reproductive organs
- untreated medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney failure
- uterine polyps or adhesions
- endometriosis
The recovery time associated with a pregnancy loss depends on many factors, including how far along the pregnancy was.
For most women, the time to physically recover is relatively short. Women who undergo surgical removal of the fetus may experience no physical symptoms after any associated bleeding has stopped.
Women who undergo surgical removal of the fetus may experience no physical symptoms after any associated bleeding has stopped.
Those who experience complications, such as a uterine infection, can expect a longer recovery time.
However, the emotional effects of a pregnancy loss can last much longer. Some women grieve for a lifetime. Others feel better after conceiving another baby.
There is no standard timeline, no right way to grieve, and no right way to feel about a pregnancy loss.
Many women find that talking to loved ones, joining a support group, and meeting with a therapist who specializes in pregnancy loss helps.
A 2016 study found that women can safely try to become pregnant again during the cycle that follows a pregnancy loss. In fact, the researchers found that the odds of becoming pregnant may be slightly higher after a loss. Women who are ready to try again should not feel as though they have to wait.
Following a pregnancy loss, many women worry that they will be unable to become pregnant again. However, losses are common and the issues responsible often do not recur.
However, losses are common and the issues responsible often do not recur.
There is no right way to respond to the loss of a pregnancy. Many people need time to grieve, while others want to try again right away.
Likewise, losses can occur in many ways. Some involve no physical symptoms, while others are painful and require surgery.
Working with trusted healthcare providers can help a woman to deal with the physical and emotional effects of a pregnancy loss.
Miscarriage without bleeding: Symptoms and diagnosis
Most of the time, bleeding is the first sign of a miscarriage. However, a miscarriage can occur without bleeding, or other symptoms may appear first.
Many women prefer the term pregnancy loss to miscarriage. Pregnancy loss is most common within the first weeks of pregnancy, and the risk steadily declines as the pregnancy progresses.
It is important to remember that pregnancy symptoms shift over time. These changes do not always signal a pregnancy loss.
Anyone who believes that they have lost a pregnancy, with or without bleeding, should seek medical attention.
Pregnancy losses do not always involve bleeding. In fact, a woman may not experience any symptoms and only learn of the loss only when a doctor cannot detect a heartbeat during a routine ultrasound.
Bleeding during pregnancy loss occurs when the uterus empties. In some cases, the fetus dies but the womb does not empty, and a woman will experience no bleeding.
Some doctors refer to this type of pregnancy loss as a missed miscarriage. The loss may go unnoticed for many weeks, and some women do not seek treatment.
According to the American Pregnancy Association, most losses occur within the first 13 weeks of pregnancy. While an estimated 10–25 percent of all recognized pregnancies end in a pregnancy loss, a loss in the second trimester is very rare.
Some women have no external symptoms of pregnancy loss. When the loss occurs early on, a woman may have few signs of pregnancy, which can make identifying the loss more difficult.
It is normal to experience changes in pregnancy signs over time, particularly in the transition from the first to the second trimester. These changes do not usually indicate the loss of the pregnancy.
Some warning signs of a pregnancy loss without bleeding include:
- a sudden decrease in pregnancy signs
- pregnancy tests that show a negative result
- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- back pain
If the pregnancy has advanced, fetal movement may noticeably slow or stop.
Most women seek treatment for a pregnancy loss when they experience bleeding. When there is no bleeding, a doctor may only diagnose a loss during a routine scan.
A doctor may also suspect a loss because of other indications, such as a drop in the levels of pregnancy hormones or an unusual decrease in other pregnancy signs.
Blood tests can determine the levels of hormones, which can help to assess the likelihood of a pregnancy loss. To conclusively diagnose a loss, a doctor must perform an ultrasound to check for a heartbeat.
The heartbeat does not develop until 6.5–7 weeks of gestation, so the absence of a heartbeat before this time does not indicate a loss.
To confirm a pregnancy loss, a doctor may choose to perform scans on multiple days.
To determine the reason for a loss, a doctor may also recommend genetic testing, further ultrasound scans, or blood testing.
The goal of treatment is to remove the fetus and tissue from the uterus and to prevent complications, such as a uterine infection. There is a variety of treatment options available, and a doctor or midwife will be able to advise on the best option.
When pregnancy loss occurs without bleeding, it is often safe to wait for a few weeks before seeking treatment, because the uterus may empty on its own.
When this occurs, a woman can expect bleeding that involves passing the tissue. This usually lasts for less than a week, and cramping may accompany it.
If the uterus does not empty, or if a woman does not want to wait, the most common treatment options are:
- medication that encourages the release of the fetus
- a surgical procedure called dilation and curettage
A doctor may recommend pain medication to reduce associated cramping. Over-the-counter varieties are often effective. If they do not work, a doctor can prescribe something stronger.
Over-the-counter varieties are often effective. If they do not work, a doctor can prescribe something stronger.
In rare cases, pregnancy loss leads to a uterine infection, which requires treatment.
It is essential to consider mental health when choosing a course of treatment. Many women feel immense grief following a pregnancy loss. Guilt and anxiety are also common responses.
Therapy and support groups can help. Some women might also benefit from using antianxiety or antidepressant medications.
Many women worry that they are responsible for the loss of their pregnancies. In most cases, this is untrue, and the loss is outside of a person’s control.
The most common cause of a pregnancy loss is a chromosomal abnormality that would have made it impossible for the baby to survive.
Less common causes include:
- infections
- illnesses
- physical injuries
- abnormalities in the uterus or other reproductive organs
- untreated medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney failure
- uterine polyps or adhesions
- endometriosis
The recovery time associated with a pregnancy loss depends on many factors, including how far along the pregnancy was.
For most women, the time to physically recover is relatively short. Women who undergo surgical removal of the fetus may experience no physical symptoms after any associated bleeding has stopped.
Those who experience complications, such as a uterine infection, can expect a longer recovery time.
However, the emotional effects of a pregnancy loss can last much longer. Some women grieve for a lifetime. Others feel better after conceiving another baby.
There is no standard timeline, no right way to grieve, and no right way to feel about a pregnancy loss.
Many women find that talking to loved ones, joining a support group, and meeting with a therapist who specializes in pregnancy loss helps.
A 2016 study found that women can safely try to become pregnant again during the cycle that follows a pregnancy loss. In fact, the researchers found that the odds of becoming pregnant may be slightly higher after a loss. Women who are ready to try again should not feel as though they have to wait.
Following a pregnancy loss, many women worry that they will be unable to become pregnant again. However, losses are common and the issues responsible often do not recur.
There is no right way to respond to the loss of a pregnancy. Many people need time to grieve, while others want to try again right away.
Likewise, losses can occur in many ways. Some involve no physical symptoms, while others are painful and require surgery.
Working with trusted healthcare providers can help a woman to deal with the physical and emotional effects of a pregnancy loss.
Miscarriage, symptoms - Health Clinic 365 Yekaterinburg
Causes of miscarriage
Questions to the doctor about miscarriage
Diagnosis of miscarriage
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus.
Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus.
Miscarriage is quite common, but this fact does not make things any easier. It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Miscarriage symptoms .
Most miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage include:
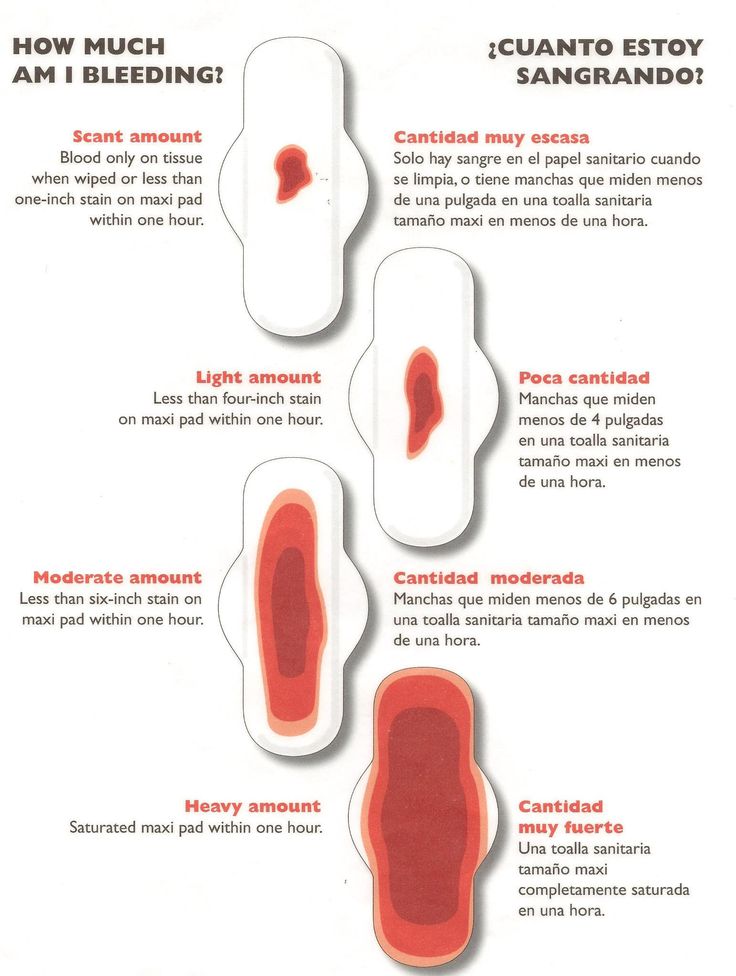
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting (although quite common in early pregnancy)
- Pain or cramps in the abdomen or lower back
- Fluid vaginal discharge or tissue fragments
It is important to consider the fact that in early pregnancy, spotting or vaginal bleeding is quite common. In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
Some women who have a miscarriage develop an infection in the uterus. This infection, also called septic miscarriage, can cause:
- Fever (feeling hot, chills)
- Body pains
- Thick, foul-smelling vaginal discharge
When to see a doctor.
Call your doctor if:
- Bleeding, even if only light spotting occurs
- Profuse, liquid vaginal discharge without pain or bleeding
- Isolation of tissue fragments from the vagina
You can put a piece of tissue to be isolated in a clean container and take it to your doctor for examination. It is unlikely that the study will give any accurate results, but if it is determined that the fragments of the excreted tissue are from the placenta, the doctor will be able to conclude that the symptoms that appear are not associated with the presence of a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy.
You can get more detailed information about miscarriage from the gynecologists of the Health 365 clinic in Yekaterinburg.
Prices
Gynecologist, initial appointment
2300 i
An obstetrician-gynecologist at the SM-Clinic Center for Reproductive Health spoke about the possibility of not noticing a miscarriage
Unfortunately, the loss of a child at an early stage of pregnancy is quite common. After the first miscarriage, a woman lives in constant fear and is afraid that the second attempt to become a mother will turn into a tragedy.
“A miscarriage is the spontaneous termination of a pregnancy before the fetus reaches a viable term. A fetus weighing up to 500 g is considered viable, which corresponds to a period of less than 22 weeks of pregnancy. Many women face this diagnosis. About 80 percent of miscarriages occur before 12 weeks of pregnancy.”
About 80 percent of miscarriages occur before 12 weeks of pregnancy.”
Causes of miscarriage
Approximately half of early miscarriages occur due to genetic pathologies in the development of the fetus, that is, from defects in the number and composition of chromosomes. It is in the first weeks that the formation of the baby's organs begins, which requires 23 normal chromosomes from each of the future parents. When at least one abnormal changes occur, there is a risk of losing a child.
At 8-11 weeks the rate of these miscarriages is 41-50%, at 16-19 weeks the rate of miscarriages due to chromosomal defects drops to 10-20%.
There are other causes of miscarriage. Among them:
- Congenital and acquired disorders of the anatomy of the genital organs If there are fibroids, polyps in the uterus, this can cause abnormal development of the embryo. The threat of miscarriage may be in women with an abnormal development of the uterus.
- Infectious causes Numerous studies have shown that the risk of miscarriage increases in the presence of sexually transmitted infections. Dangerous for a pregnant woman are measles, rubella, cytomegalovirus, as well as diseases that occur with an increase in body temperature. Intoxication of the body often leads to the loss of a child.
- Endocrine causes Problems with gestation occur with diabetes, thyroid diseases, disorders of the adrenal glands.
- Unfavorable ecology, exposure
- Blood clotting disorder (thrombosis, antiphospholipid syndrome) APS (antiphospholipid syndrome) is a disease in which the human body produces a lot of antibodies to phospholipids, the chemical structures that make up parts of cells. The body mistakenly perceives its own phospholipids as foreign and begins to defend itself against them: it produces antibodies to them that damage blood components.
- Lifestyle and bad habits Nicotine addiction, alcohol use, obesity.
 Blood clotting increases, microthrombi appear in small vessels that feed the fetal egg and placenta. Blood circulation in the fetal egg is disturbed. As a result, the pregnancy stops or the growth of the fetus slows down. Both of these lead to miscarriage. All this is due to the hormonal background that has changed during pregnancy.
Blood clotting increases, microthrombi appear in small vessels that feed the fetal egg and placenta. Blood circulation in the fetal egg is disturbed. As a result, the pregnancy stops or the growth of the fetus slows down. Both of these lead to miscarriage. All this is due to the hormonal background that has changed during pregnancy. Is it possible not to notice a miscarriage
Sometimes women mistake a miscarriage for normal menstruation. This occurs during the so-called biochemical pregnancy, when there is a violation of the implantation of the embryo at a very early stage and menstruation begins. But before the appearance of spotting, the test will show two strips.
The classic variant is when a miscarriage is manifested by bleeding against the background of a long delay in menstruation, which rarely stops on its own. Therefore, even if a woman does not follow the menstrual cycle, the signs of an interrupted pregnancy will be immediately noticed by the doctor during examination and ultrasound.
Alarm
The symptoms of a miscarriage can be completely different, and depending on them, as a rule, it is possible to predict the likelihood of maintaining and successfully continuing this pregnancy.
For the threat of miscarriage is characterized by pulling pains in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, scanty bloody discharge from the genital tract. Ultrasound signs: the tone of the uterus is increased, the cervix is not shortened and closed, the body of the uterus corresponds to the gestational age, the fetal heartbeat is recorded.
Started miscarriage - pain and discharge from the genital tract are more pronounced, the cervix is ajar.
Miscarriage in progress - cramping pains in the lower abdomen, copious bloody discharge from the genital tract. On examination, as a rule, the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age, the cervix is open, the elements of the fetal egg are in the cervix or in the vagina.
Incomplete miscarriage - the pregnancy was interrupted, but there are delayed elements of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity. This is manifested by ongoing bleeding due to the lack of a full contraction of the uterus.
Non-progressive pregnancy - the death of an embryo (up to 9 weeks) or a fetus up to 22 weeks of gestation in the absence of any signs of termination of pregnancy.
Important!
Severe abdominal pain and spotting at any stage of pregnancy is a reason for an urgent appeal to an obstetrician-gynecologist with a solution to the issue of hospitalization in a gynecological hospital.
Is it possible to avoid miscarriage
“Today, there are no methods for preventing miscarriages,” the doctor says. “Therefore, it is very important to comprehensively prepare for pregnancy before it occurs by visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist and following all the necessary recommendations for examination and taking the necessary drugs. ”
”
But if, nevertheless, the pregnancy could not be maintained, then the birth of a child can be planned again no earlier than 3-6 months after the miscarriage. This time is needed to figure out, together with the attending physician, what are the causes of miscarriage and whether it is possible to avoid them in the future.
By the way, a common misconception for both women and men is that only the woman is to blame for the loss of pregnancy, but this is far from being the case.
“A man is also responsible, which is why future dads are required to perform a study - a spermogram and be screened for genital infections, since with a pathology of spermatozoa, the likelihood of miscarriage due to genetic abnormalities increases many times,” emphasizes our expert.
There is always a chance
Most women whose first pregnancy ends in a miscarriage, when examined before pregnancy and the causes are eliminated, have a high chance of a successful next pregnancy (about 85 percent).