Inside of a pregnant woman
Pregnancy Precautions: FAQs (for Parents)
Almost as soon as you see that little line on the home pregnancy test, the worry seems to set in. You start thinking about the two cups of coffee you had at work yesterday, the glass of wine you sipped at dinner last week, the tuna steak you devoured for lunch 2 weeks ago.
No doubt about it, pregnancy can be one of the most thrilling and most worrisome times in a woman's life. Of course, when you're pregnant, what you don't put into your body (or expose it to) can be almost as important as what you do.
But worrying out about every little thing you come into contact with can make for a long and stressful three trimesters. And fretting about things you did before you knew you were pregnant or before you found out they could be hazardous won't do you or your baby any good.
Questions abound regarding what women can and can't do during pregnancy. But the answers may not always come from the most reliable sources, so you might worry unnecessarily. Some warnings are worth listening to; others are popular but unproven rumors.
Knowing what could truly be harmful to your baby and what's not a real concern is the key to keeping your sanity during these 40 weeks.
The Top Pregnancy Hazards
You'll need to be particularly mindful of a handful of things during your pregnancy, some of which are more harmful than others. Your doctor (or other health care provider) will talk to you about what should be completely avoided, what should be greatly reduced, and what should be carefully considered during pregnancy.
Alcohol
Should I avoid it? Yes! Although it may seem harmless to have a glass of wine at dinner or a mug of beer out with friends, no one knows what's a "safe amount" of alcohol to drink during pregnancy. Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is caused by drinking a lot of alcohol during pregnancy. What that amount is versus a safe amount is really not known. Because of the uncertainty, it's always wise to be cautious and not drink any alcohol at all during pregnancy.
What are the risks to my baby? Alcohol is one of the most common causes of physical, behavioral, and intellectual disabilities. It can be even more harmful to a developing fetus than heroin, cocaine, or marijuana use.
Alcohol is easily passed along to the baby, whose body is less able to get rid of alcohol than the mother's. That means an unborn baby tends to develop a high concentration of alcohol, which stays in the baby's system for longer periods than it would in the mother's. And moderate alcohol intake, as well as periodic binge drinking, can possibly damage a baby's developing nervous system.
What can I do about it? If you had a drink or two before you even knew you were pregnant (as many women do), don't worry too much about it. But your best bet is to not drink any more alcohol for the rest of your pregnancy.
If you're an alcoholic or think you may have a drinking problem, talk to your doctor about it. He or she needs to know how much alcohol you've consumed and when during your pregnancy to get a better idea of how your unborn baby might be affected. Your doctor also can start you on a path to getting the help you need to stop drinking — for your sake and your baby's.
Your doctor also can start you on a path to getting the help you need to stop drinking — for your sake and your baby's.
P
Caffeine
Should I avoid and/or limit it? Yes. It's wise to cut down or stop caffeine intake. Studies show that caffeine consumption of more than 200–300 milligrams a day (about 2–3 cups of coffee, depending on the portion size, brewing method, and brand) might put a pregnancy at risk. Less than that amount is probably safe.
What are the risks to my baby? High caffeine consumption has been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage and, possibly, other pregnancy complications.
What can I do about it? If you're having a hard time cutting out coffee all at once, here's how you can start:
- Cut your consumption down to one or two cups a day.
- Gradually reduce the amount by combining decaffeinated coffee with regular coffee.
- Eventually cut out the regular coffee altogether.
And remember that caffeine is not only in coffee. Green and black tea, cola, and other soft drinks contain caffeine. Try switching to decaffeinated products (which may still have some caffeine, but in much smaller amounts) or caffeine-free alternatives.
If you're wondering about chocolate, which also has caffeine, the good news is that you can eat some in moderation. A cup of brewed coffee has 95–135 milligrams of caffeine, but the average chocolate bar has 5–30 milligrams. So, small amounts of chocolate are fine.
Certain Foods
Are there some I should avoid? Yes. Foods that are more likely to be contaminated with bacteria or heavy metals are ones to try to avoid or limit your exposure to. Those you should steer clear of during pregnancy include:
- soft, unpasteurized cheeses (often advertised as "fresh") such as feta, goat, Brie, Camembert, blue-veined cheeses, and Mexican queso fresco
- unpasteurized milk, juices, and apple cider
- raw eggs or foods containing raw eggs, including mousse, tiramisu, raw cookie dough, eggnog, homemade ice cream, and Caesar dressing
- raw or undercooked fish (sushi), shellfish, or meats
- paté and meat spreads
- processed meats like hot dogs and deli meats (these should be very well cooked before eating)
Also, although fish and shellfish can be an extremely healthy part of your pregnancy diet (they contain beneficial omega-3 fatty acids and are high in protein and low in saturated fat), you should avoid eating certain kinds due to high levels of mercury, which can damage the brain of a developing fetus.
Fish to avoid:
- shark
- swordfish
- king mackerel
- tilefish
- tuna steak (limited amounts of canned, preferably light, tuna is OK)
What are the risks to my baby? Although it's important to eat plenty of healthy foods during pregnancy, you also need to avoid foodborne illnesses, such as listeriosis, toxoplasmosis, and salmonella, which are caused by the bacteria that can be found in certain foods. These infections can be life-threatening to an unborn baby and may cause birth defects or miscarriage.
What can I do about it? Be sure to thoroughly wash all fruits and vegetables, which can carry bacteria or be coated with pesticide residue. And be mindful of what you're buying at the grocery store or when dining out.
When you choose seafood, eat a variety of fish and shellfish and limit the amount to about 12 ounces per week — that's about two meals. Common fish and shellfish that are low in mercury include: canned light tuna, catfish, pollock, salmon, and shrimp. But because albacore (or white) tuna has more mercury than canned light tuna, it's best to eat no more than 6 ounces (or one meal) of albacore tuna a week.
But because albacore (or white) tuna has more mercury than canned light tuna, it's best to eat no more than 6 ounces (or one meal) of albacore tuna a week.
You may have to skip a few foods during pregnancy that you normally enjoy. But just think how delicious they'll taste when you can have them again!
P
Changing the Litter Box
Should I avoid it? Yes. Pregnancy is the prime time to get out of cleaning kitty's litter box. But that doesn't mean that you have to keep away from Fluffy!
What are the risks to my baby? An infection called toxoplasmosis can be spread through soiled cat litter boxes and can cause serious problems in a fetus, including prematurity, poor growth, and severe eye and brain damage. A pregnant woman who becomes infected often has no symptoms but can still pass the infection on to her developing baby.
What can I do about it? Have someone else change the litter box, making sure to clean it thoroughly and regularly, then wash his or her hands well afterward.
OTC and Prescription Medicines
Should I avoid them? Some, yes; others, no. There are many medicines you should not use during pregnancy. Be sure to talk to your doctor about which prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) drugs you can and can't take, even if they seem like no big deal.
What are the risks to my baby? Even common OTC medicines that you can buy in stores without a prescription may be off-limits during pregnancy because of their potential effects on the baby. Certain prescription medicines may also harm the developing fetus. (The type of harm and extent of possible damage depends on the kind of medication.)
Also, although they may seem harmless, herbal remedies and supplements are not regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). That means that they don't have to follow any safety standards and thus could be harmful to your baby.
What can I do about it? To make sure you don't take anything that could put your baby at risk, talk to your doctor about:
- any medicines you're taking — prescription and OTC — and ask which are safe to take during pregnancy
- any concerns you have about natural remedies, supplements, and vitamins
Also, let all of your health care providers know that you're pregnant so that they'll keep that in mind when recommending or prescribing any medicines. If you were prescribed a medication before you became pregnant for an illness, disease, or condition that you still have, your doctor can help you weigh the potential benefits and risks of continuing your prescription.
If you were prescribed a medication before you became pregnant for an illness, disease, or condition that you still have, your doctor can help you weigh the potential benefits and risks of continuing your prescription.
If you become sick (for example, with a cold) or have symptoms that cause you discomfort or pain (like a headache or backache), talk to your doctor about medicines you can take and other ways to help you feel better without medication.
Also, if you are in your third trimester, talk to your health care professional if you are scheduled to have surgery or a medical procedure that would require the use of general anesthesia. The FDA has issued a warning about its possible effects on an unborn baby's brain development.
P
Recreational Drugs
Should I avoid them? Yes!
What are the risks to my baby? Pregnant women who use drugs may be placing their unborn babies at risk for:
- premature birth
- poor growth
- birth defects
- behavior and learning problems
And their babies could also be born addicted to those drugs.
What can I do about it? If you've used any drugs at any time during your pregnancy, it's important to tell your doctor. Even if you've quit, your unborn child could still be at risk for health problems. If you're still using drugs, talk to your doctor for help on how to quit. Health clinics such as Planned Parenthood also can recommend health care providers, at little or no cost, who can help you quit your habit and have a healthier pregnancy.
Smoking
Should I avoid it? Yes! You wouldn't light a cigarette, put it in your baby's mouth, and encourage your little one to puff away. As ridiculous as this sounds, pregnant women who continue to smoke are allowing their fetus to smoke too. The smoking mother passes nicotine, carbon monoxide, and many other chemicals to her growing baby.
Likewise, you should avoid people who are smoking, whether they're coworkers, friends, family members, or people in public places.
What are the risks to my baby? If a pregnant woman smokes, it could cause:
- miscarriage or stillbirth
- prematurity
- low birth weight
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
- asthma and other respiratory problems
And the risks to a fetus from regular exposure to secondhand smoke include low birth weight and slowed growth.
What can I do about it? If you smoke, having a baby may be the reason you need to quit. Talk to your doctor about options for kicking the habit.
If you spend time with people who smoke, ask them nicely to do it outside — and away from you if you're outside as well.
P
Artificial Sweeteners (Sugar Substitutes)
Should I avoid them? Some are OK, others are best to avoid.
Aspartame, sucralose, stevioside, and acesulfame-K have been found to be safe to use in moderation during pregnancy. However, you should avoid aspartame if you or your partner has a rare hereditary disease called phenylketonuria (PKU), in which the body can't break down the compound phenylalanine, which is found in aspartame. In that case, you should avoid aspartame altogether since your baby may also be born with the disease.
Experts are still unsure about whether saccharin, which is found in some foods and in the little pink packets, is safe to use during pregnancy — it can cross the placenta and could stay in the fetus' tissue. Also, a sweetener called cyclamate is banned in the United States because of concerns about a possible link to cancer.
Also, a sweetener called cyclamate is banned in the United States because of concerns about a possible link to cancer.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? Although some people say that the artificial sweetener aspartame is linked to birth defects and illnesses, government authorities and medical groups throughout the world have evaluated aspartame and approved it as safe for human consumption, including during pregnancy.
Research done during the 1970s suggested that saccharin caused bladder cancer in lab rats when given in large quantities. Since then, though, those studies have often been called into question. Also, a warning saying that it could cause cancer was removed from all saccharin-containing products' labels in 2000.
What can I do about it? With aspartame, sucralose, stevioside, and acesulfame-K, moderation is the key. It's OK to have an occasional diet soda or sugar-free food with these sweeteners here and there. But if you're really craving something sweet, it's probably better to have the real thing, as long as it's in moderation.
If you've already had something with saccharin in it during your pregnancy, don't obsess about it. It's highly unlikely that small amounts could harm your baby.
Still, it's wise to check product labels and try to avoid — or at least limit — anything with artificial sweeteners (especially saccharin), just to be safe. After all, this is one time in your life when you have a good reason to avoid diet foods! And the more naturally flavored whole foods you eat during pregnancy, the better.
Flying
Should I avoid it? No, not unless your due date is near or your doctor tells you that you or your baby has a medical condition that warrants keeping you near home. Women with certain health conditions — like high blood pressure (hypertension) or blood clots, a history of miscarriage, premature labor, ectopic pregnancy, or other prenatal complications — are encouraged not to fly.
Otherwise, most healthy pregnant women can fly up to 4 weeks before their due date. After that, it's best to stay close to home in case you deliver.
After that, it's best to stay close to home in case you deliver.
Note: it is recommended that pregnant women not fly to areas with high altitudes, regions with disease outbreaks, or where certain vaccines are recommended for travelers beforehand.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? For women with healthy pregnancies, there are no significant risks. However, women who have difficult pregnancies, especially involving their cardiovascular system, could be compromised by air flight and should discuss any flying plans with their doctor.
What can I do about it? Discuss any plans for lengthy or distant travel with your doctor during your last trimester, just in case. If he or she says it's OK, check with the airlines to find out what their policies are regarding flying during pregnancy. (Most airlines will allow pregnant women to fly up until week 37.)
To make sure your flight is as comfortable as possible:
- Move your lower legs regularly and/or get out of your seat (especially during long flights) to promote blood circulation and help prevent blood clots.

- Wear support stockings to further prevent clotting in your legs.
- Keep your seatbelt on when you're seated to keep the jostling of turbulence to a minimum.
Hair Dyes
Should I avoid them? No. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), because very little dye is absorbed through the skin, dying your hair is "most likely safe" during pregnancy, despite what doctors in years past may have advised. That's good news for many expectant women — coloring your hair can be a great little confidence boost when everything else going on with your body feels so out of your control.
While very few studies have closely looked at the many different kinds of hair treatments and their potential effects on a fetus, what is known shows that hair treatments are most likely safe.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? None that are currently known.
What can I do about it? If you're concerned but want to give yourself a little lift, try having your hair highlighted. This uses far fewer chemicals than dying your entire head of hair.
This uses far fewer chemicals than dying your entire head of hair.
p
High-Impact Exercise
Should I avoid it? Yes. For most pregnant women, low-impact exercise is a great way to feel better and help prepare the body for labor. Low-impact exercise increases your heart rate and intake of oxygen while helping you avoid sudden or jarring actions that can stress your joints, bones, and muscles. Unless your doctor tells you otherwise, stick to low-impact exercise.
How much is enough? The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes (that's 2 hours and 30 minutes) of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week for healthy women who are not already highly active or used to doing vigorous-intensity activity. If you were very active or did intense aerobic activities before getting pregnant you may be able to continue your exercise routine, as long as your doctor says it's safe for you and your baby.
It's wise to avoid some exercises and activities, such as:
- weight training and heavy lifting (after the first trimester)
- sit-ups (also after the first trimester)
- contact sports
- scuba diving
- bouncing
- jarring (anything that would cause a lot of up and down movement, such as horseback riding)
- leaping
- a sudden change of direction (such as downhill skiing)
- anything with an increased risk for falling, like gymnastics
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? High-impact exercise can cause increased pressure on the structures within the uterus that could lead to problems such as premature labor or bleeding.
What can I do about it? Some of the healthy ways pregnant women can stay fit include walking, swimming, water aerobics, yoga, and Pilates. But be sure to talk to your doctor before starting — or continuing — any exercise routine during pregnancy.
P
Household Chemicals
Should I avoid them? Some, yes; others, no. While chemicals like ammonia and chlorine may make you nauseated because of the smell, they're not toxic, says the March of Dimes. But others (such as some paints, paint thinners, oven cleaners, varnish removers, air fresheners, aerosols, carpet cleaners, etc.) might be.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? It depends on the product. Some household chemicals may have no effect, while others in high doses could be harmful.
What can I do about it? Here a few tips to help keep household chemicals use safe during your pregnancy:
- Talk to your doctor about any concerns you have with chemicals you use at home or at work.

- Look at product labels before using any product. If it's unsafe to use during pregnancy, the label should say that it's toxic. Find out not only if it's safe for you to use, but if it's safe for you to be around when being used by someone else. If the label doesn't specify, contact the manufacturer.
- Open windows and doors, and use rubber gloves and a mask when cleaning with or using any chemical.
- Wash your hands and arms, even if you wore gloves, after using any chemical.
- Opt for natural products like baking soda, borax, and vinegar for cleaning.
- Have someone else paint the baby's nursery, as much you'd probably like to do it yourself. And definitely don't help with the removal of paint if your home was built before 1978 as it may contain lead-based paint. Although many paints today are considered safer than those of the past, it's still a good idea to let someone else handle painting. You can always take over the decorating duties after the paint dries!
Bug Sprays (Insecticides, Pesticides, Repellents)
Should I avoid them? Yes. They're considered poisons, and pregnant women should stay away from them as much as possible.
They're considered poisons, and pregnant women should stay away from them as much as possible.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? Although the occasional household use of insecticides might not be dangerous, it's best to be careful. High levels of exposure may cause:
- miscarriage
- premature delivery
- birth defects
As for insect repellents (which may contain DEET, or diethyltoluamide), the risks aren't fully known. So, it's best to either not use them at all during pregnancy or to wear gloves to place a small amount on socks, shoes, and outer clothing instead of putting repellents directly on your skin.
What can I do about it? If you have a real problem with pesky bugs around your home, the March of Dimes suggests the following:
- Use safer methods of removal such as boric acid, which you should be able to find at your local hardware store.
- Make sure someone else applies the pesticides.

- When pesticides are sprayed outside, close all windows and turn off air-conditioning units and window fans to prevent the fumes from entering your home.
- Remove utensils, food, and dishes from areas where the chemicals will be used.
- Stay away from the treated area during the application and after for the amount of time specified on the product label.
- After pesticide use indoors, have someone else wash any treated area where food is prepared or served.
- Wear rubber gloves when gardening outside where pesticides have been used.
- Have your water supply tested regularly if you have well water and use pesticides, fertilizers, or weed killers.
P
Lead
Should I avoid it? Yes. However, exposure to high lead levels is rare for women in the United States.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? Exposure to high levels of lead can cause:
- miscarriage
- premature delivery
- low birth weight
- developmental delays
But even low levels of lead can cause subtle problems with behavior and learning in children.
What can I do about it? If your home was built before 1978, it could have lead-based paint. But it only becomes a problem if the paint is chipping, peeling, or being removed. Some homes also may have lead pipes or copper piping with lead solder that can allow lead to enter the tap water.
If you have an older home or think that you may have lead piping or soldering and are concerned about lead exposure, you can have a professional come out to test your water, the dust in your home, the soil outside, and/or the paint around your home for lead.
Make sure that anyone who removes any potentially lead-based paint from your home:
- is a professional trained in removing lead paint (getting rid of lead-based paint isn't a project for a do-it-yourselfer!)
- removes it when you're not there
- doesn't scrape, sand, or use a heat gun to remove the paint (these methods may send lead dust into the air)
- thoroughly cleans the area immediately afterward
To help reduce potential lead levels in your tap water, you can run the water for 30 seconds before using it and/or buy a water filter that specifically says on the packaging that it removes lead.
Overheating (Hot Tubs, Saunas, Electric Blankets, etc.)
Should I avoid or limit it? Yes. You should limit activities that would raise your core temperature above 102°F (38.9°C). They include:
- using saunas or hot tubs
- taking very hot, long baths and showers
- using electric blankets or heating pads
- getting a high fever
- becoming overheated when outside in hot weather or when exercising
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? If your body temperature goes above 102°F (38.9°C) for more than 10 minutes, the elevated heat can cause problems with the fetus. Overheating in the first trimester can lead to neural tube defects and miscarriage. Later in the pregnancy, it can lead to dehydration in the mother.
What can I do about it? Instead of hot tubs or saunas, take a dip in a cool pool. And it's probably a good idea to stick to warm or slightly hot baths and showers. If you have a fever during your pregnancy, talk to your doctor about ways to lower it. And follow your body's cues that you're getting overheated when exercising or enjoying the great outdoors in the warmer months.
If you have a fever during your pregnancy, talk to your doctor about ways to lower it. And follow your body's cues that you're getting overheated when exercising or enjoying the great outdoors in the warmer months.
But if you've already become overheated during your pregnancy, don't worry too much about it. Chances are, you removed yourself from the uncomfortable situation before any damage was done.
Self-Tanners, Sunless Tanners
Should I avoid them? Maybe. Although there's no proof that self-tanners are harmful to an unborn baby, there haven't been many studies done on their effects to a fetus.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? No risks specific to tanning have been documented.
What can I do about it? For a summer glow, skip the self-tanner and apply some bronzer to your face, neck, shoulders, and chest. And if you do decide to try a self-tanner, that's far safer than lying out in the sun and becoming potentially overheated. Overheating in the first trimester, as discussed above, can lead to significant problems for the baby; later in the pregnancy, it could lead to dehydration in the mother. Still, ask your doctor before applying any "tan in a bottle."
Overheating in the first trimester, as discussed above, can lead to significant problems for the baby; later in the pregnancy, it could lead to dehydration in the mother. Still, ask your doctor before applying any "tan in a bottle."
p
Sex
Should I avoid it? No. Most pregnant women having a "normal" pregnancy can continue having sex — it's perfectly safe for both mom and the baby, even up until the delivery. Of course, you'll probably need to adapt positions for your own comfort as your belly gets bigger.
Doctors may advise against sexual intercourse if they anticipate or find significant complications with a woman's pregnancy, including:
- a history or threat of miscarriage
- a history of pre-term labor (previously delivering a baby before 37 weeks) or signs indicating the risk of pre-term labor (such as premature uterine contractions)
- unexplained vaginal bleeding, discharge, or cramping
- leakage of amniotic fluid (the fluid that surrounds the baby)
- placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta (the blood-rich structure that nourishes the baby) is situated down so low that it covers the cervix (the opening of the uterus)
- incompetent cervix, a condition in which the cervix is weakened and dilates (opens) early, raising the risk for miscarriage or premature delivery
- multiple fetuses (having twins, triplets, etc.
 )
)
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? You should not have sex with a partner whose sexual history is unknown to you or who may have a sexually transmitted disease (STD), such as herpes, genital warts, chlamydia, or HIV. If you become infected, the disease may be passed to your baby, with potentially dangerous effects.
What can I do about it? Talk to your doctor about any discomfort you have during or after sex or any other concerns.
Tap Water, Drinking Water
Should I avoid it? Not necessarily. Before you go out and buy a 9-month supply of bottled water, tell your doctor where you live and whether you have public water or well water.
It's also important to note that just because water is bottled doesn't necessarily mean it's safer. Although bottled water (which is regulated by the FDA) may taste better or just different, tap water meets the same Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standards.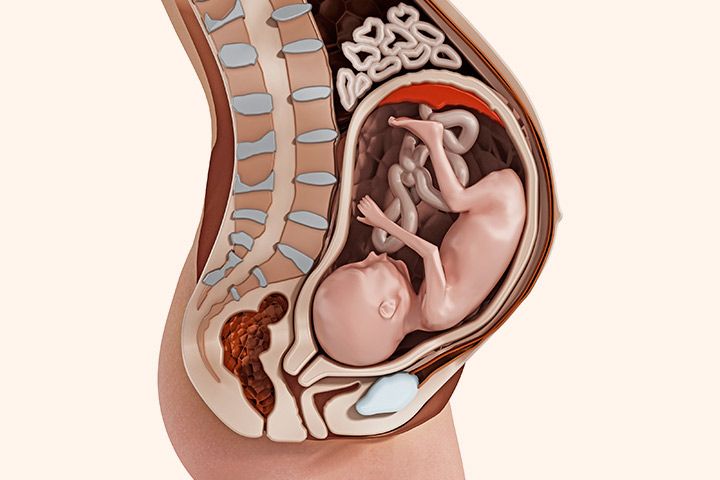
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? Different studies show different things, according to the March of Dimes. Some have found that the chlorine used to treat public water can turn into chloroform when it mixes with other materials in the water, which can increase the risk of miscarriage and poor fetal growth. But other studies have found no such links. Also of concern to some is the potential for the water to be contaminated by things like lead and pesticides. If you have well water, you should probably have it checked regularly, such as once a year, whether you're pregnant or not.
What can I do about it? If you're worried, contact your local water supplier to get a copy of the annual water quality report. If you're still concerned and/or have private well water, have your water tested by a state-certified laboratory. This can cost anywhere from $15 to hundreds of dollars, depending on the number of contaminants you want to have your water tested for.
To help ease your mind, you could also buy a water filtration system to help lower the levels of lead, some bacteria and viruses, and chemicals such as chlorine. Be sure to read the product's label, as some filters do more than others.
Countertop pitcher and faucet-mounted units are fairly inexpensive (some for under $50), whereas systems used to treat your entire home's water supply are much pricier (up to thousands of dollars). You can also have refillable water coolers delivered to your home, often through wholesale — or bulk items — stores.
p
Teeth Whiteners, Teeth Bleaching
Should I avoid them? Maybe. As with self-tanners, no good studies have been done on teeth whiteners that say for sure whether they're safe to use if you're expecting. And some makers of whitening products do caution against using them during pregnancy. Some dentists encourage waiting until after pregnancy to get your teeth whitened and others say that the procedures are safe. The concern is mostly about the chemicals used in teeth whitening products that could be swallowed and the potential effect on a fetus.
The concern is mostly about the chemicals used in teeth whitening products that could be swallowed and the potential effect on a fetus.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? There's currently no evidence that teeth whitening can harm a fetus.
What can I do about it? Talk to your doctor before using whitening products. If you'd rather wait until after your pregnancy to try to make your teeth pearly white, simply brush regularly with whitening toothpaste, which may give a little extra kick to your smile.
Vaccinations
Should I avoid them? Many, yes; others, no. It's best to wait until after your pregnancy for most vaccines, but a few are considered safe. Your doctor may say it's OK to get a vaccine if:
- there's a good chance that you could be exposed to a particular disease or infection and the benefits of vaccinating you outweigh the potential risks
- an infection would pose a risk to you or your baby
- the vaccine is unlikely to cause harm
The flu shot fits the criteria above and is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during any stage of pregnancy.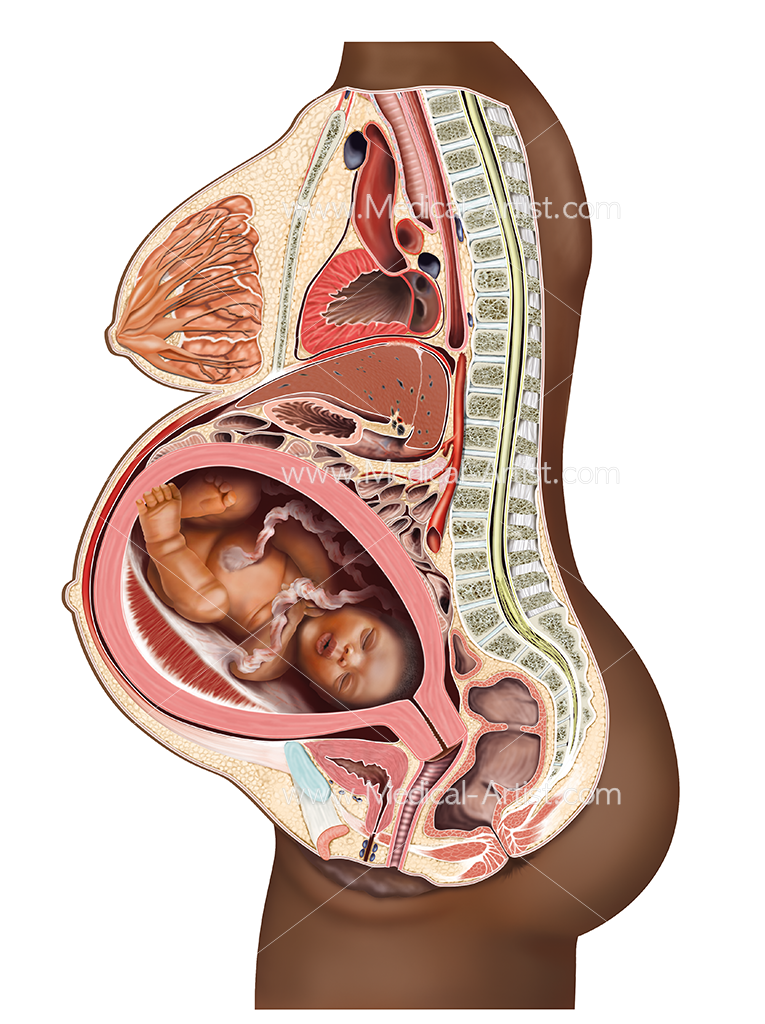 Pregnant women should only get the shot made with the inactivated virus. The flu vaccine previously also came in a nasal spray (or mist) form, but it contained live strains of the virus and was never safe for moms-to-be. Currently, the nasal spray is not recommended for anyone because the CDC found that it didn't prevent cases of the flu between 2013 and 2016.
Pregnant women should only get the shot made with the inactivated virus. The flu vaccine previously also came in a nasal spray (or mist) form, but it contained live strains of the virus and was never safe for moms-to-be. Currently, the nasal spray is not recommended for anyone because the CDC found that it didn't prevent cases of the flu between 2013 and 2016.
The flu vaccine can curb flu-related problems for expectant moms, who are at higher risk of complications from the illness. And, the vaccine is safe — studies show no harmful effects to a fetus. It also helps protect a mother and her baby from getting the flu (and other viruses) in the baby's first year of life.
The Tdap vaccine (against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis) is now recommended for all pregnant women in the second half of each pregnancy, regardless of whether or not they had the vaccine before, or when it was last given. This new recommendation was made in response to a rise in pertussis (whooping cough) infections, which can be fatal in newborns who have not yet had their routine vaccinations.
In addition to the flu shot and Tdap vaccine, other vaccines the CDC considers safe during pregnancy, but only if truly necessary, are:
- hepatitis B
- meningitis
- rabies
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? Live-virus vaccines — those containing a live organism — aren't recommended for pregnant women because of the risk that the actual infection or disease the vaccine is meant to prevent may be passed along to the unborn baby. However, this depends on the circumstances and whether the vaccine would ultimately be safer to receive than being exposed to the actual disease. For example, the chickenpox vaccine may be safer to your unborn baby than getting the infection. So, it's important to speak to your doctor if you believe that you may have been exposed to a disease.
For the most part, though, researchers don't know what the risks of some vaccines may be to a fetus. So, it's wise to just wait to be vaccinated unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
What can I do about it? Be sure to talk to your doctor before getting any vaccination during pregnancy. Also tell your doctor if you became pregnant within 4 weeks of having a vaccine. And if your workplace requires certain vaccines, be sure to let them know you're pregnant before agreeing to be immunized.
P
X-Rays
Should I avoid them? Yes and no. If your doctor thinks it's truly necessary — for your own well-being or your baby's — to get one during your pregnancy, then it's highly unlikely that low levels of X-ray radiation will be harmful. However, if you can safely wait to get an X-ray until after your baby is born, then that's probably the best way to go.
What are the risks, if any, to my baby? Health experts say that X-rays are most likely safe during pregnancy. Most diagnostic X-rays emit much less than 5 rads, which is the limit of what the FDA suggests a pregnant woman should be exposed to.
Different imaging studies use different amounts of radiation and the direction of the X-ray beam also affects the possible exposure to the fetus. Dental X-rays, for example, aren't cause for much concern because the X-ray area is far from the uterus.
What can I do about it? Researchers believe that a fetus is more at risk for damage by radiation because of the rapid rate with which its cells are dividing. Always make sure that your health care providers (including your dentist and the X-ray technician) know about your pregnancy before you get an X-ray. Also make sure that your stomach is covered with a lead apron.
If you're concerned and would rather not get an X-ray at all during pregnancy, your doctor may be able to use an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) test during the first trimester or an ultrasound anytime.
Keeping Things in Perspective
Although some things are unsafe during pregnancy, try not to spend too much time wondering and worrying.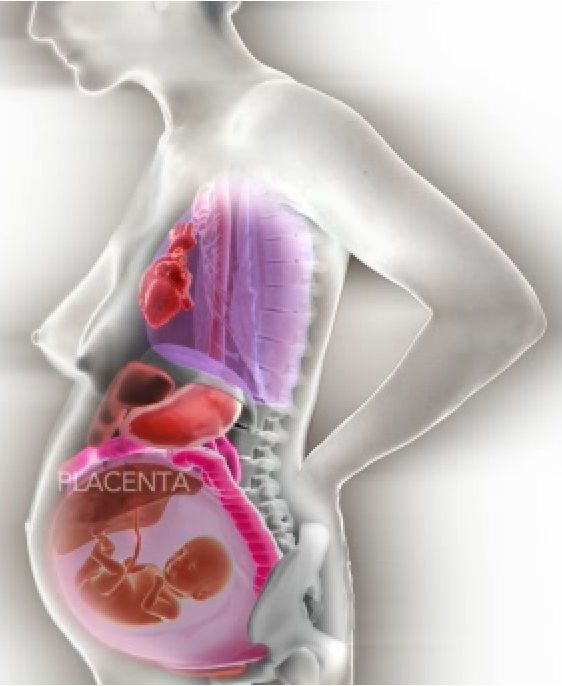 When in doubt, just use common sense — if it seems like a bad idea, doesn't need to be done right now, or might be risky, hold off at least until you've talked with your doctor about it. He or she can likely help ease your mind and may even say it's fine to do something you never expected to be able to do until after your special delivery.
When in doubt, just use common sense — if it seems like a bad idea, doesn't need to be done right now, or might be risky, hold off at least until you've talked with your doctor about it. He or she can likely help ease your mind and may even say it's fine to do something you never expected to be able to do until after your special delivery.
Above all, make sure to follow the most important healthy pregnancy habits — eat right; get plenty of rest; steer clear of drugs, alcohol, and tobacco — and you'll be well on your way to keeping both you and your baby healthy.
18 Weeks Pregnant | Pregnancy
You may feel your baby move for the first time around now. If you are feeling something now, it may feel like a gentle fluttering sensation.
What's happening in my body?
You might be starting to feel a bit clumsier as your belly gets bigger. Your breasts may have gone up a size, too, particularly if it's your first pregnancy. Your blood pressure is probably a bit lower than it was, so do not leap up from the sofa, or it could make you feel dizzy.
Your baby has been moving around for the past couple of months, but you might not have noticed. You may start feeling some movement now though – it feels like a bubbling or fluttering inside your belly.
You may also notice a line down your stomach, called the “linea nigra” (Latin for "black line"). This is normal skin pigmentation and nothing to worry about. It will probably vanish a few months after the birth.
Your anomaly scan
You'll be offered an anomaly scan at around 18 to 20 weeks. This is a scan that looks at your baby in detail to see if there is anything unusual about their development and appearance. It can pick up a range of conditions, but not all of them.
The scan will not hurt you or your baby, but it may feel a bit uncomfortable as the sonographer may have to apply a bit of pressure on your stomach to get the best possible view.
Read more about why scans are offered and what they involve on the NCT website.
Is it a boy or a girl?
The sonographer may be able to tell you at this scan, but not everyone wants to know, and it's not always the hospital policy to reveal the sex of the baby. If you do not want to know, tell them before you start of your scan appointment.
If you do not want to know, tell them before you start of your scan appointment.
Free prescriptions and dental care
Did you know that prescriptions are free during pregnancy? NHS dental treatment is also free. You just need a Maternity Exemption Certificate or card (MatEx).
Ask your midwife, GP or health visitor for the application form FW8. Your certificate will be valid for up to a year after your baby's due date or date of birth.
2nd trimester pregnancy symptoms (at 18 weeks)
Hopefully you are feeling more energetic and able to manage your pregnancy symptoms now. If you are struggling with day-to-day life, talk to your midwife or doctor, they are there to support you.
Your signs of pregnancy could include:
- stretch marks (read about stretch marks on week 17's page)
- tiredness and sleeping problems (week 19 has information about feeling tired)
- swollen and bleeding gums (week 13 has information about gum health during pregnancy)
- pains on the side of your belly, caused by your expanding womb (known as "round ligament pains")
- headaches
- nosebleeds
- bloating and constipation (read about bloating on week 16's page)
- indigestion and heartburn (week 25 talks about digestive problems)
- sore breasts
- leg cramps
- feeling hot
- dizziness
- swollen hands and feet
- urine infections
- vaginal infections (see week 15 for vaginal health)
- darkened skin on your face or brown patches – this is known as chloasma or the "mask of pregnancy"
- greasier, spotty skin
- thicker and shinier hair
You may also experience symptoms from earlier weeks, such as:
- morning sickness (read about dealing with morning sickness on week 6's page)
- weird pregnancy cravings (read about pregnancy cravings on week 5's page)
- a heightened sense of smell
- mood swings (week 8's page has information on mood swings)
- a white milky pregnancy discharge from your vagina and light spotting (seek medical advice for any bleeding)
Read Tommy's guide to common pregnancy symptoms.
What does my baby look like?
Your baby, or foetus, is around 14.2cm long from head to bottom, and weighs around 190g. That's approximately the size and weight of a sweet red pepper.
Your baby's hearing, feeling, swallowing and sucking reflexes are developing this week. They will also be doing a lot of wriggling around and moving their arms and legs.
Action stations
Many women will tell their employer after they've had their first pregnancy scan at around 12 weeks. Once you tell your employer, you have maternity rights and can attend antenatal appointments during paid work time. You can also ask for a risk assessment of your workplace to ensure that you're working in a safe environment.
It's a good time to tone up your pelvic floor muscles. Gentle exercises can help to prevent leakage when you laugh, sneeze or cough. Get the muscles going by pretending that you're having a wee and then stopping midflow. Visit Tommy's for more ideas about pelvic floor exercises.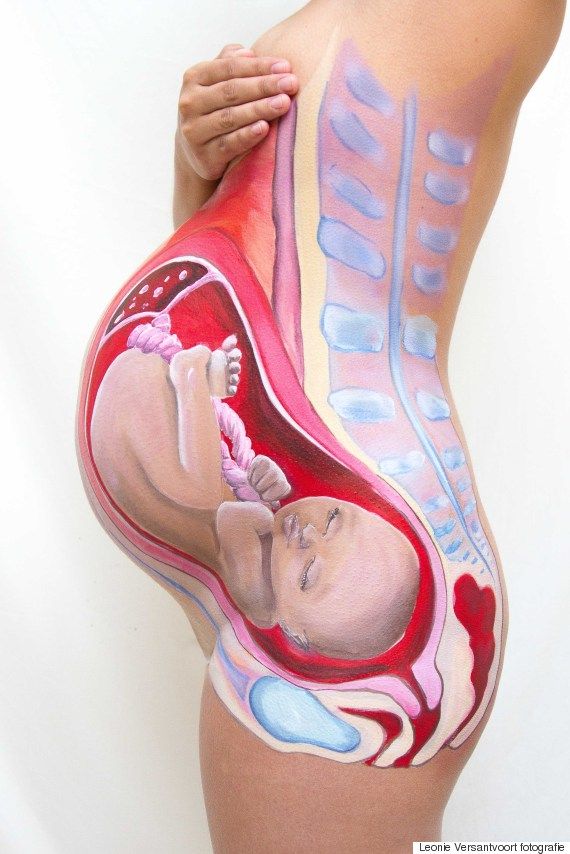
Ask your midwife or doctor about online antenatal classes – they may be able to recommend one. The charity Tommy's has lots of useful information on antenatal classes and preparing you for birth.
Even if you've had children before, they're still worth going to as you can meet other parents-to-be. The NCT offers online antenatal classes with small groups of people that live locally to you.
To keep bones and muscles healthy, we need vitamin D. From late March/early April to the end of September, most people make enough vitamin D from sunlight on their skin. However, between October and early March, you should consider taking a daily vitamin D supplement because we cannot make enough from sunlight.
Some people should take a vitamin D supplement all year round, find out if this applies to you on the NHS website. You just need 10 micrograms (it's the same for grown-ups and kids). Check if you're entitled to free vitamins.
It's recommended that you do 150 minutes of exercise a week while pregnant. You could start off with just 10 minutes of daily exercise - perhaps take a brisk walk outside. Check out Sport England's #StayInWorkOut online exercises (scroll to the pregnancy section). Listen to your body and do what feels right for you.
You could start off with just 10 minutes of daily exercise - perhaps take a brisk walk outside. Check out Sport England's #StayInWorkOut online exercises (scroll to the pregnancy section). Listen to your body and do what feels right for you.
There's no need to eat for 2. You don't need any extra calories until the third trimester, which starts in week 28. Try to eat healthily, with plenty of fresh fruit and veg, and avoid processed, fatty and salty foods. You may be able to get free milk, fruit and veg through the Healthy Start scheme.
You and your family should follow the government and NHS guidance on coronavirus (COVID-19):
To find out about about COVID-19 and pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding, have a look at advice on the:
Physiological changes in the body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy. nine0003
These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy. nine0003
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.
The mother's circulatory system during pregnancy has to pump more blood to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.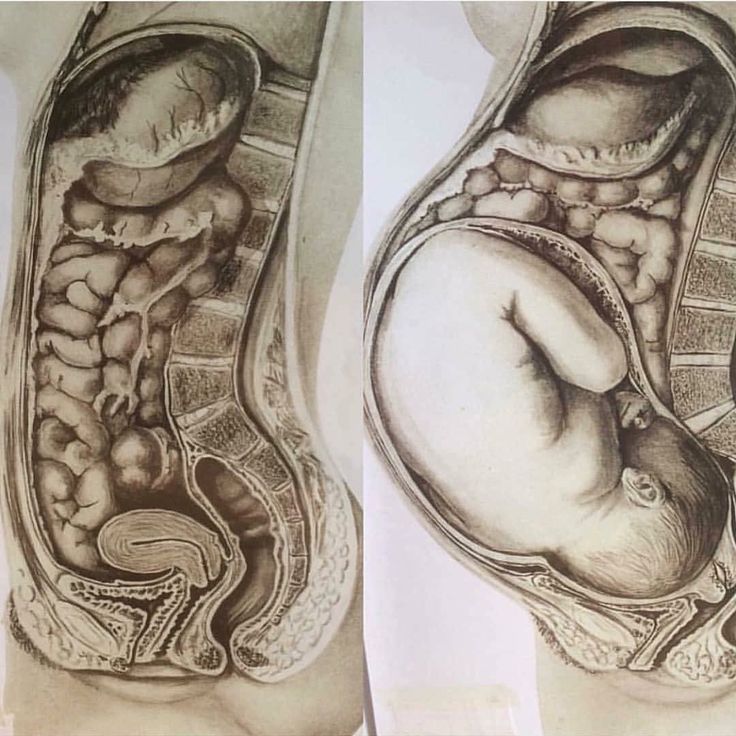 In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. nine0003
In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. nine0003
And changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), cravings for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur. nine0003
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. Walls vaginas will loosen and become more elastic. External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth. nine0003
In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth. nine0003
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released.
Changes in the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus. nine0003
This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus. nine0003
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women). nine0003
Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women). nine0003
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Changes in the cervix during pregnancy
Pregnancy is always pleasant, but sometimes not planned. And not all women have time to prepare for it, to be fully examined before its onset. And the detection of diseases of the cervix already during pregnancy can be an unpleasant discovery.
The cervix is the lower segment of the uterus in the form of a cylinder or cone. In the center is the cervical canal, one end of which opens into the uterine cavity, and the other into the vagina. On average, the length of the cervix is 3–4 cm, the diameter is about 2.5 cm, and the cervical canal is closed. The cervix has two parts: lower and upper. The lower part is called the vaginal, because it protrudes into the vaginal cavity, and the upper part is supravaginal, because it is located above the vagina. The cervix is connected to the vagina through the vaginal fornices. There is an anterior arch - short, posterior - deeper and two lateral ones. Inside the cervix passes the cervical canal, which opens into the uterine cavity with an internal pharynx, and is clogged with mucus from the side of the vagina. Mucus is normally impervious to infections and microbes, or to spermatozoa. But in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the mucus thins and becomes permeable to sperm. nine0003
On average, the length of the cervix is 3–4 cm, the diameter is about 2.5 cm, and the cervical canal is closed. The cervix has two parts: lower and upper. The lower part is called the vaginal, because it protrudes into the vaginal cavity, and the upper part is supravaginal, because it is located above the vagina. The cervix is connected to the vagina through the vaginal fornices. There is an anterior arch - short, posterior - deeper and two lateral ones. Inside the cervix passes the cervical canal, which opens into the uterine cavity with an internal pharynx, and is clogged with mucus from the side of the vagina. Mucus is normally impervious to infections and microbes, or to spermatozoa. But in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the mucus thins and becomes permeable to sperm. nine0003
Outside, the surface of the cervix has a pinkish tint, it is smooth and shiny, durable, and from the inside it is bright pink, velvety and loose.
The cervix during pregnancy is an important organ, both in anatomical and functional terms. It must be remembered that it promotes the process of fertilization, prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity and appendages, helps to "endure" the baby and participates in childbirth. That is why regular monitoring of the condition of the cervix during pregnancy is simply necessary. nine0003
It must be remembered that it promotes the process of fertilization, prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity and appendages, helps to "endure" the baby and participates in childbirth. That is why regular monitoring of the condition of the cervix during pregnancy is simply necessary. nine0003
During pregnancy, a number of physiological changes occur in this organ. For example, a short time after fertilization, its color changes: it becomes cyanotic. The reason for this is the extensive vascular network and its blood supply. Due to the action of estriol and progesterone, the tissue of the cervix becomes soft. During pregnancy, the cervical glands expand and become more branched.
Screening examination of the cervix during pregnancy includes: cytological examination, smears for flora and detection of infections. Cytological examination is often the first key step in the examination of the cervix, since it allows to detect very early pathological changes that occur at the cellular level, including in the absence of visible changes in the cervical epithelium. The examination is carried out to identify the pathology of the cervix and the selection of pregnant women who need a more in-depth examination and appropriate treatment in the postpartum period. When conducting a screening examination, in addition to a doctor's examination, a colposcopy may be recommended. As you know, the cervix is covered with two types of epithelium: squamous stratified from the side of the vagina and single-layer cylindrical from the side of the cervical canal. Epithelial cells are constantly desquamated and end up in the lumen of the cervical canal and in the vagina. Their structural characteristics make it possible, when examined under a microscope, to distinguish healthy cells from atypical ones, including cancerous ones. nine0003
The examination is carried out to identify the pathology of the cervix and the selection of pregnant women who need a more in-depth examination and appropriate treatment in the postpartum period. When conducting a screening examination, in addition to a doctor's examination, a colposcopy may be recommended. As you know, the cervix is covered with two types of epithelium: squamous stratified from the side of the vagina and single-layer cylindrical from the side of the cervical canal. Epithelial cells are constantly desquamated and end up in the lumen of the cervical canal and in the vagina. Their structural characteristics make it possible, when examined under a microscope, to distinguish healthy cells from atypical ones, including cancerous ones. nine0003
During pregnancy, in addition to physiological changes in the cervix, some borderline and pathological processes may occur.
Under the influence of hormonal changes that occur in a woman's body during the menstrual cycle, cyclic changes also occur in the cells of the epithelium of the cervical canal. During the period of ovulation, the secretion of mucus by the glands of the cervical canal increases, and its qualitative characteristics change. With injuries or inflammatory lesions, sometimes the glands of the cervix can become clogged, a secret accumulates in them and cysts form - Naboth follicles or Naboth gland cysts that have been asymptomatic for many years. Small cysts do not require any treatment. And pregnancy, as a rule, is not affected. Only large cysts that strongly deform the cervix and continue to grow may require opening and evacuation of the contents. However, this is very rare and usually requires monitoring during pregnancy.
During the period of ovulation, the secretion of mucus by the glands of the cervical canal increases, and its qualitative characteristics change. With injuries or inflammatory lesions, sometimes the glands of the cervix can become clogged, a secret accumulates in them and cysts form - Naboth follicles or Naboth gland cysts that have been asymptomatic for many years. Small cysts do not require any treatment. And pregnancy, as a rule, is not affected. Only large cysts that strongly deform the cervix and continue to grow may require opening and evacuation of the contents. However, this is very rare and usually requires monitoring during pregnancy.
Quite often, in pregnant women, during a mirror examination of the vaginal part, polyps cervix. The occurrence of polyps is most often associated with a chronic inflammatory process. As a result, a focal proliferation of the mucosa is formed, sometimes with the involvement of muscle tissue and the formation of a pedicle. They are mostly asymptomatic. Sometimes they are a source of blood discharge from the genital tract, more often of contact origin (after sexual intercourse or defecation). The size of the polyp is different - from millet grain rarely to the size of a walnut, their shape also varies. Polyps are single and multiple, their stalk is located either at the edge of the external pharynx, or goes deep into the cervical canal. Sometimes during pregnancy there is an increase in the size of the polyp, in some cases quite fast. Rarely, polyps first appear during pregnancy. The presence of a polyp is always a potential threat of miscarriage, primarily because it creates favorable conditions for ascending infection. Therefore, as a rule, more frequent monitoring of the cervix follows. The tendency to trauma, bleeding, the presence of signs of tissue necrosis and decay, as well as questionable secretions require special attention and control. Treatment of cervical polyps is only surgical and during pregnancy, in most cases, treatment is postponed until the postpartum period, since even large polyps do not interfere with childbirth.
They are mostly asymptomatic. Sometimes they are a source of blood discharge from the genital tract, more often of contact origin (after sexual intercourse or defecation). The size of the polyp is different - from millet grain rarely to the size of a walnut, their shape also varies. Polyps are single and multiple, their stalk is located either at the edge of the external pharynx, or goes deep into the cervical canal. Sometimes during pregnancy there is an increase in the size of the polyp, in some cases quite fast. Rarely, polyps first appear during pregnancy. The presence of a polyp is always a potential threat of miscarriage, primarily because it creates favorable conditions for ascending infection. Therefore, as a rule, more frequent monitoring of the cervix follows. The tendency to trauma, bleeding, the presence of signs of tissue necrosis and decay, as well as questionable secretions require special attention and control. Treatment of cervical polyps is only surgical and during pregnancy, in most cases, treatment is postponed until the postpartum period, since even large polyps do not interfere with childbirth. nine0003
nine0003
The most common pathology of the cervix in women is erosion . Erosion is a defect in the mucous membrane. True erosion is not very common. The most common pseudo-erosion (ectopia) is a pathological lesion of the cervical mucosa, in which the usual flat stratified epithelium of the outer part of the cervix is replaced by cylindrical cells from the cervical canal. Often this happens as a result of mechanical action: with frequent and rough sexual intercourse, desquamation of the stratified squamous epithelium occurs. Erosion is a multifactorial disease. The reasons may be: nine0003
- genital infections, vaginal dysbacteriosis and inflammatory diseases of the female genital area;
- is an early onset of sexual activity and a frequent change of sexual partners. The mucous membrane of the female genital organs finally matures by the age of 20-23. If an infection interferes with this delicate process, erosion is practically unavoidable;
- is a cervical injury.
 The main cause of such injuries is, of course, childbirth and abortion;
The main cause of such injuries is, of course, childbirth and abortion; - hormonal disorders; nine0096
- , cervical pathology may also occur with a decrease in the protective functions of immunity.
The presence of erosion does not affect pregnancy in any way, as well as pregnancy on erosion. Treatment during pregnancy consists in the use of general and local anti-inflammatory drugs for inflammatory diseases of the vagina and cervix. And in most cases, just dynamic observation is enough. Surgical treatment is not carried out throughout the entire pregnancy, since the excess of risks and benefits is significant, and after treatment during childbirth, there may be problems with opening the cervix. nine0003
Almost all women with various diseases of the cervix safely bear and happily give birth to beautiful babies!
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital of IDKClinic "Mother and Child" Entuziastov Samara
nine0002 All directionsSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children's)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomOther gynecological operationsTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic examinationsUltrasound examinations for adults 01.