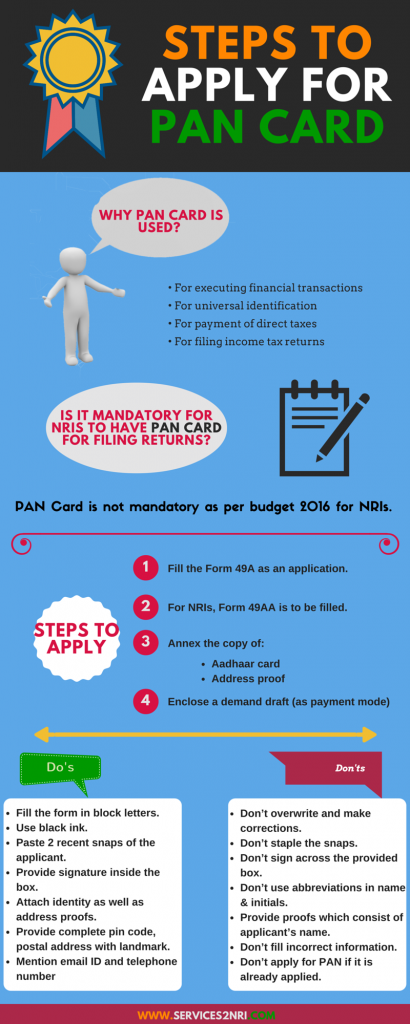
How to make a 1 month old poop
Your Baby's Not Pooping but Passing Gas? What You Should Know
Congratulations! You have a new little person in the house!
If you’re a newbie parent you might be feeling like you’re changing your baby’s diaper every hour. If you have other little ones, you already know that a diaper can tell a lot about a baby’s well-being, but that babies — like adults — can sometimes have common plumbing issues.
If your baby is not pooping but passing gas, don’t worry. Your baby is still getting the hang of this thing called digestion. This is a normal part of being a baby.
There are several reasons why your baby might not be pooping. This can be uncomfortable for them (and you) but in most cases it’s not a reason to worry. Here’s what to know and what to do about your baby’s gassiness and lack of poop.
In contrast to the early newborn days when it seems every diaper change is a poop, your baby will naturally poop less as they get to be a few weeks to several months old.
There is a range of healthy when it comes to how often a baby should poop. As long as your baby is feeding normally and gaining weight (1 to 2 pounds a month), don’t worry about the number of poops.
Some babies 2 months or older poop once a day or more often. Other babies poop once every few days or even once a week. Even if your baby is pooping less frequently, their poop should be soft and easy to pass when they do go.
Breastfeeding, formula, and solids
Pooping frequency depends in part on what your baby is eating.
If your baby is only being breastfed or chestfed they may not poop every day. This is because their body can use up almost all the components of breast milk for nutrition and there is very little left that needs to be eliminated. After the first 3 to 6 weeks or so, they can go even a whole week without a poop.
If your baby is formula-fed they should poop at least once every couple of days. But some babies poop every day, while some poop more often, up to several times a day. This is all within the typical range.
This is all within the typical range.
Because the look of your baby’s poop can vary, it can sometimes be hard to tell when a baby has diarrhea. Signs that there could be a problem include pooping more than once per feeding, or poop that is getting more watery over time. If you notice any of these signs, talk with your baby’s pediatrician or doctor.
Once your baby starts eating solid food, it’s a whole new game! You’ll soon learn which foods might give your baby gassiness without pooping and which their digestive system seems to poop out almost too quickly.
Color and texture
Pooping the rainbow is pretty normal for a baby. Different textures and smells are also completely normal.
In fact, your baby’s poop may move between several shades of brown, yellow, and green, depending in part on what they’re eating.
Chalky, red, or black poop might mean that there is a health issue. If you notice these changes, talk with your baby’s pediatrician immediately. You should tell your doctor or pediatrician if you notice blood in the poop, or if your baby looks sick.
You should tell your doctor or pediatrician if you notice blood in the poop, or if your baby looks sick.
Straining to poop
Don’t worry if your baby appears to be straining to poop. Straining while pooping is typical for young babies. This is because they are still learning how coordinate the muscles needed to poop.
Babies also spend a lot of time lying down, so gravity isn’t on their side to help pass poops!
But if your baby’s poops become hard or dry, talk with your pediatrician.
If your baby is formula-fed, poops less than once a day, and appears to be straining, this is another reason to talk with a doctor. It could be a sign of constipation.
A baby can sometimes get a little stopped up or constipated. In fact, up to 30% of children get constipated pretty regularly. This can make your baby pass gas (fart), even though they are not pooping. When they do go, the stool is hard.
On the other hand, your baby might get gassy in between poops, without constipation.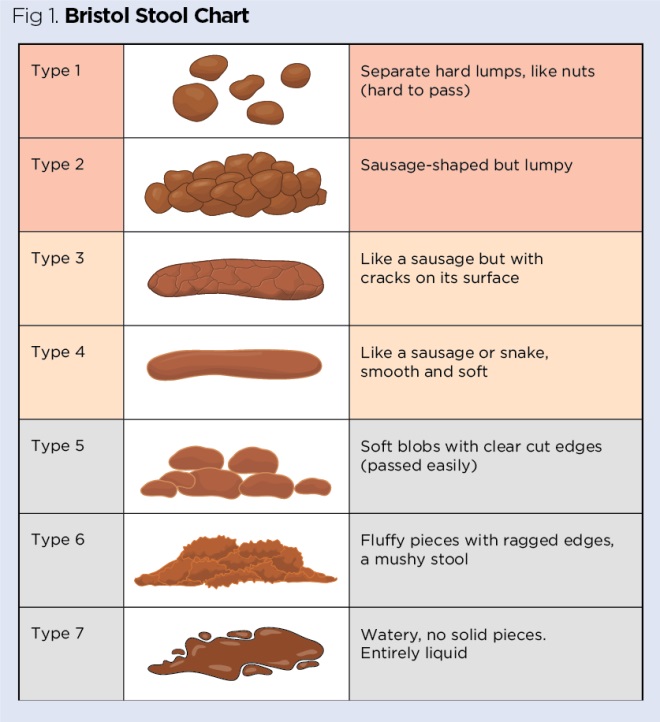 There are several common reasons why this might occasionally happen. Babies sometimes swallow air, which can lead to gas.
There are several common reasons why this might occasionally happen. Babies sometimes swallow air, which can lead to gas.
Some babies are just naturally gassy, just like they’re naturally cute. Sometimes a baby with stinky gas is just a baby with stinky gas. But if your baby seems to be having gas pains, bring it up with your pediatrician.
Breastfed babies
The good news is that babies who breastfeed or chestfeed are less likely to get constipated, because breast milk is generally easier to digest than formula.
If you’re nursing your baby, changes in your milk might have something to do with your baby’s poop frequency. Around 6 weeks after birth, your breast milk has little or no trace left of a yellowish substance called colostrum. Colostrum contains extra protein, antibodies, and other nutrients.
This liquid is one part of your breast milk that helps to give your newborn baby’s immune system a boost against germs. Colostrum may also work like a laxative, helping your baby poop in the first few weeks of life.
This may be one reason newborns poop several times a day. When there’s less colostrum — or none — your baby may have fewer poops.
Formula-fed babies
If your baby is feeding on formula, they might get gassy if they swallow air with feeding or if you change the kind of formula you use. A baby’s new digestive system can be finicky like that.
Some amount of gas is normal for all babies, and some babies just naturally pass more gas. If your baby is gassy, it doesn’t necessarily mean there is an issue or that you need to change anything to “fix” it.
If your baby is happily gassy and not showing symptoms of constipation or other issues, it’s fine to just let them be. But if your baby seems to be in pain due to gas, discuss it with your pediatrician.
Solids
When your baby starts trying solid foods, they might get gassy without pooping all over again. Introducing solid foods and new foods to your baby can cause little digestive hiccups.
It’s best to introduce new foods one at a time. This can help you pinpoint sensitivities or foods that cause gassiness or pooping issues for your little one.
This can help you pinpoint sensitivities or foods that cause gassiness or pooping issues for your little one.
If your baby is gassy but not pooping, check for other signs and symptoms of constipation:
- excessive crying or irritability
- decreased appetite
- severe straining or turning red without pooping
- small hard poops (when they do poop)
- dry poop (when they do poop)
In most cases, your baby’s gassiness and constipation will resolve on its own as their digestive system figures things out. Sometimes, you might need to give it a little nudge.
Call the doctor
If your newborn baby (under the age of 6 weeks) is not pooping at all or very rarely pooping, see your doctor immediately. In rare cases, not pooping can be a sign of an underlying health issue. Check for other symptoms like:
- vomiting
- refusing feeds
- excess crying
- stomach bloating
- arching their back like they are in pain
- fever
- blood in the stool
Any time you notice blood in your baby’s stool, it’s important to talk with your doctor right away.
Babies who are older than 6 weeks will occasionally be constipated. Call your doctor if your baby has not had a poop for longer than a week or if they get constipated with hard stools more than once or twice.
Home treatments
Ask your doctor if you should try home remedies for your little one, like:
- liquids: If your baby is over 6 months old (age is important here!), you can give them a few ounces of water. For babies at least 1 month old, you can talk with your doctor about giving them a small amount apple or pear juice — 1 ounce for each month of age, up to 4 months. These juices have a natural sugar called sorbitol that is also a laxative. Drinking this might help soften your baby’s poop. Babies who are eating solid food can have prune juice.
- food: If your baby is eating solids, give them fiber-rich foods to help pass the poop. Try puréed prunes, sweet potatoes, or fruits. Fiber-rich foods might make your baby gassy, but they often help with the poop!
- exercise: Your baby might just need to get moving to help them poop! Moving your baby’s legs as in a bicycle motion may help rev their digestion engine.
 You can also try holding your baby up so they are “walking” in your lap.
You can also try holding your baby up so they are “walking” in your lap. - massage and a warm bath: Try massaging your baby’s stomach and body. This can help relax them and get their digestion moving. You can also try a warm bath to help them relax.
- medications: If none of the changes in feeding, diet, or exercise help with the constipation, your doctor might recommend trying an infant glycerin suppository. These have to be put into your baby’s rectum, but they may be relieved and sleep peacefully when they can have a good poop! But be sure to talk with your baby’s doctor first if you are considering this option.
If your baby is gassy but not pooping, don’t worry. These common symptoms are normal in babies as they learn how to feed and digest food. Your baby might be constipated.
Call your baby’s pediatrician immediately if your newborn baby (under 6 weeks old) is not pooping at all. Also call if your baby (of any age) has constipation for longer than 5 to 7 days or if they also have other symptoms.
Constipation in babies - causes, signs and treatments
Constipation in babies - causes, signs and treatments | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
What is constipation?
Constipation is when your baby’s poo is hard and dry, making it difficult for them to poo. Sometimes, doing a hard poo can be painful. It’s common for babies to have constipation when they are changing from formula or breast milk to solid foods.
What is normal?
All babies are unique, and this includes how often they poo. There is a very wide range of ‘normal’. Some babies poo after every feed. Others will only poo once every few days. When it comes to how often they poo, once in 7 days, or 7 times in one day are both fine, so long as your baby is happy and well. But while the number of poos is not critical, if your baby seems to have pain when trying to poo or has a very hard, dry poo, you can speak with their doctor or child health nurse for advice.
But while the number of poos is not critical, if your baby seems to have pain when trying to poo or has a very hard, dry poo, you can speak with their doctor or child health nurse for advice.
Why is my baby constipated?
One of the main causes of constipation in babies is a change in diet. A change in diet may include:
- changing from being formula-fed
- changing from being breastfed
- exposure to new foods and flavours
- not drinking enough liquids (breastmilk, formula or water)
It is more common for bottle (infant formula) fed babies to have constipation than breast-fed babies.
If your baby has started eating solid food, a lack of fibre in their diet may also potentially cause of constipation. Some babies simply have a natural tendency towards constipation, even when they have a good diet and drink enough fluids. This doesn’t mean they are unhealthy or unwell.
Baby poo guide
Learn more about your baby's poo.
In extreme cases, rare illnesses can cause constipation such as:
- problems with nerve endings in the bowel
- problems relating to the spinal cord
- thyroid deficiency
- other metabolic disorders
All babies are checked for these conditions, so this is usually not something you need to be concerned about. But if you are worried about your baby or are notice that pooing is painful for them, seek medical advice.
How to recognise the signs of constipation
The main signs of constipation are hard, dry poos. The following are other signs of constipation:
- Your baby may show signs of straining when trying to pass a poo.
- Your baby may be unsettled, may seem fussy or irritated.
- Your baby may be eating less or feeding less well than usual.
- A tear or crack might appear in the skin around the anus, which may at times bleed.
In some cases, if your child is constipated, they may look bloated or their stomach may appear larger than usual. It can be possible to feel their poo (hard, solid lumps) while pressing softly on their stomach.
It can be possible to feel their poo (hard, solid lumps) while pressing softly on their stomach.
How to treat constipation at home
Try these tips to help babies who have difficulty passing poos:
- If your baby has infant formula, always measure the water first before adding the formula powder — this helps ensure that the ratio of water-to-formula is correct.
- If your baby is old enough to drink water, offer extra drinks (boiled and cooled first).
- Gently rub their stomach to help stimulate the bowel — your baby might also feel better with gentle massage to help manage the pain of constipation.
- A warm bath can help calm and settle your baby and relieve discomfort.
If your baby is older than 6 months, add some extra fruit and vegetables to their diet to boost their fibre intake.
If your child is older than 9 months, adding stewed prunes or apricots to their meal may help. They can have up to 3 tablespoons, 3 times a week. Cereal that has bran may also help mild constipation. Older babies can try prune juice diluted with water (half prune juice and half water). Start slowly, with 10 millilitres. Increase as needed until they can do a soft poo.
Cereal that has bran may also help mild constipation. Older babies can try prune juice diluted with water (half prune juice and half water). Start slowly, with 10 millilitres. Increase as needed until they can do a soft poo.
Does my child need to see a doctor?
Constipation is common. Often it will pass without intervention, or with the help of the strategies listed above. If you are worried that your baby has constipation, is uncomfortable or is in pain, their doctor can assess them and recommend baby-safe strategies. There are medical treatments for constipation that your doctor may consider, based on your baby’s circumstances.
If your baby was previously treated for constipation but still struggles to poo, it is important to go back to your doctor for a review. There are several treatments they can try.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne (Kids Health Information 2020 - Constipation), Queensland Health (Constipation in children), Perth Children’s Hospital (Constipation in children)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Poos and wees
- Your child's health
- Baby poo guide
Need more information?
Constipation in babies and children | Raising Children Network
Children with constipation have hard poo that’s difficult to push out. A high-fibre diet and regular toileting usually helps. Some children need laxatives.
Some children need laxatives.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Colic in infants - MyDr.com.au
Colic is a pattern of unexplained, excessive crying in an otherwise healthy and well-fed baby and happens to 1 in 5 Australian babies.
Read more on myDr website
All about baby poo
Babies poo! Some poo after every feed, while others can go for days without a dirty nappy. But what you do find in the nappy can say something your baby's health - learn more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Common myths about babies
Find out about some of the common myths you may hear or read about young babies.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Constipation and children - Better Health Channel
A healthy diet, plenty of fluids, exercise and regular toilet habits can help relieve constipation in children
Read more on Better Health Channel website
When can babies drink water?
You may wonder when it is safe to start giving your baby water. Whether you are breastfeeding or formula feeding, learn how and at what age to get started.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Poos and wees
Babies have very delicate skin and need changing soon after they wet themselves or passed a stool (poo) to prevent nappy rash and stop them from smelling.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breast feeding your baby - MyDr.com.au
Breast milk has long been known as the ideal food for babies and infants. Major health organisations recommend that women breast feed their babies exclusively until they are 6 months old, and continue breast feeding, along with solids, until they are 12 months old or more. Breast milk has many benefits.
Read more on myDr website
What's in the nappy? - video
It may not sound like fun, but checking your baby's poos and wees will help monitor their health and wellbeing.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breastfeeding... Is it for me? | Sydney Children's Hospitals Network
Before your baby is born, you should decide whether you wish to breastfeed your baby or not
Read more on Sydney Children's Hospitals Network website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
norm, how many times a day, color
So many experiences are connected with how a newborn baby "walks big". Mom is worried about the frequency of the stool, its color, consistency. So how do you determine if the crumbs are all right with digestion? Perhaps he needs help?
Many mothers know that it is very important to monitor the baby's stool, and during the examination, the pediatrician is always interested in how the baby walks in a big way. This information is one of the most important points in diagnosing the health of the crumbs. Unfortunately, quite often mothers mistakenly interpret the completely natural and safe states of the baby. And because of these mistakes, they can start unnecessary treatment and worry about the baby for no good reason. So let's figure out how a baby's chair should look like and when to worry and when not.
And because of these mistakes, they can start unnecessary treatment and worry about the baby for no good reason. So let's figure out how a baby's chair should look like and when to worry and when not.
Immediately after childbirth
When the baby is in the mother's tummy, he receives all the necessary substances and trace elements through the umbilical cord. The digestive system of the crumbs does not work, but his stomach is not empty. The baby sucks his fingers, opens his mouth and thus swallows a small amount of amniotic fluid. When the baby is born, this substance will be in his intestines and will gradually come out as the baby is attached to the chest and his digestive system begins to work.
So, the first stool of the baby is meconium: dark, plasticine-like feces. So the baby recovers the first day or two. Sometimes it gives him discomfort: the baby worries, cries, pushes, before he manages to go big. However, this is not always the case - many children recover easily, only slightly pushing.
If everything is in order with the baby, he was put to the breast in time and fed on demand, then his stool gradually changes. On the third or fifth day, the baby has the so-called "transitional stool", partly consisting of meconium, which is still in the gastrointestinal tract, partly from digested colostrum and milk. As a rule, streaks appear first in the meconium mass, then the feces gradually turn yellow. By the end of the first week, the baby's stool usually acquires the features of a normal infant: yellow, rather liquid.
When should you worry? If the baby did not go down in a big way in the first two days, it is necessary to consult a doctor. There are children with individual characteristics who will continue to do this less often than most babies. However, the cause of the stool retention should be determined by the doctor. If the crumbs have some kind of problem with intestinal patency, help will be needed immediately, but you should not diagnose your baby without a doctor.
We are at home
On the third or fifth day, the mother receives milk, and the baby has a fairly stable stool by the end of the first week. The literature sometimes says that the stool of newborns is "creamy", and this confuses mothers, who begin to suspect that something is not right with the crumbs. In reality, the stool of a healthy baby is liquid and not always homogeneous. The normal color of feces is yellow and its shades. You may notice lumps, a little mucus - it's not scary. Do not be afraid if the baby's feces have a greenish tint for up to three months due to the immaturity of the liver enzyme systems and the characteristics of bilirubin metabolism, such a condition has the right to be and also does not require treatment.
Many mothers sometimes worry that the baby's stool "suddenly" becomes watery and the baby walks in a big way with abundant gas, a sharp sound. Doctors in this case often suspect lactase deficiency. In reality, things usually go like this. In the period from 3 weeks to a month and a half, the baby has frequent growth spurts, so at certain moments the baby literally “hangs on the chest” to help the mother produce more milk. Within a day or a few, the baby needs to breastfeed more often and longer than before, and the mother begins to suspect that there is not enough milk. As a result, she often begins to shift the baby from one breast to another, and the baby receives mostly "forward" milk, which comes at the beginning of feeding from each breast. This milk is rich in carbohydrates and proteins, the baby is actively growing from it, however, the stool is liquid and gassy because of this milk (sometimes the “result” looks frothy if the baby is held over a pot or basin when he needs to clear out, and the mother can observe the consistency chair). In this situation, there is no need to panic - just the baby does not need to be constantly shifted from one breast to another, fearing that he is starving. Give the baby the opportunity to get "hind" milk, rich in fats, which will not cause flatulence and stay longer in the intestines.
In the period from 3 weeks to a month and a half, the baby has frequent growth spurts, so at certain moments the baby literally “hangs on the chest” to help the mother produce more milk. Within a day or a few, the baby needs to breastfeed more often and longer than before, and the mother begins to suspect that there is not enough milk. As a result, she often begins to shift the baby from one breast to another, and the baby receives mostly "forward" milk, which comes at the beginning of feeding from each breast. This milk is rich in carbohydrates and proteins, the baby is actively growing from it, however, the stool is liquid and gassy because of this milk (sometimes the “result” looks frothy if the baby is held over a pot or basin when he needs to clear out, and the mother can observe the consistency chair). In this situation, there is no need to panic - just the baby does not need to be constantly shifted from one breast to another, fearing that he is starving. Give the baby the opportunity to get "hind" milk, rich in fats, which will not cause flatulence and stay longer in the intestines.
In this situation (when the baby suddenly begins to clearly suck more milk), the mother may feel insecure and start drinking lactic teas. From this, more carbohydrates again begin to flow into her milk and the baby's stool becomes more liquid and with gases.
Similar problems due to "front" milk occur in the case of improper attachment to the breast, as a result of which the baby swallows the air and interrupts feeding itself, or simply cannot get "hind" milk. The best way out in this situation is to consult with a breastfeeding specialist to correct the application technique and stop panicking that the baby "does not have enough milk."
In short, don't worry if your baby has problems with this type of stool. Of course, the flora of his intestines is unstable, it is just beginning to be established - it takes at least three to four months. Your task is simply to feed the baby on demand and correctly and not to rush to treat him for imaginary diseases.
Delayed stool
Mothers worry not only about the appearance of the stool, but also because of its periodicity. How often should the baby "do things"? Normally, the baby walks in a big way several times a day, usually after feeding. However, in some children, the norm may be a chair and once a day, and even once every few days. Typically, these children have an anatomically weak anterior abdominal wall and intestinal motility. Such a periodicity of the stool can be considered the norm, if the baby still walks more regularly, the stool is of normal consistency and, in general, the baby is cheerful and cheerful and does not suffer from colic. It's not worth worrying. However, if the baby is allergic, then you need to do everything possible so that he goes to the toilet at least once a day. Atopic dermatitis is much more severe if the baby does not empty the intestines often enough - consult a doctor about this.
How often should the baby "do things"? Normally, the baby walks in a big way several times a day, usually after feeding. However, in some children, the norm may be a chair and once a day, and even once every few days. Typically, these children have an anatomically weak anterior abdominal wall and intestinal motility. Such a periodicity of the stool can be considered the norm, if the baby still walks more regularly, the stool is of normal consistency and, in general, the baby is cheerful and cheerful and does not suffer from colic. It's not worth worrying. However, if the baby is allergic, then you need to do everything possible so that he goes to the toilet at least once a day. Atopic dermatitis is much more severe if the baby does not empty the intestines often enough - consult a doctor about this.
Babies also have physiological delays in stool at the age of one and a half to five months. Here it is important to monitor the condition of the baby. If he experiences discomfort, you should consult a doctor. Children can hold back their stools for psychological reasons, just as adults sometimes cannot go to the toilet if they are nervous. Do not panic because of a one-time problem, but if the problem persists or recurs, consult your doctor.
Children can hold back their stools for psychological reasons, just as adults sometimes cannot go to the toilet if they are nervous. Do not panic because of a one-time problem, but if the problem persists or recurs, consult your doctor.
However, in babies there are not just "delays" of the stool, but also real constipation. Constipation is called not only when the baby does not go to the toilet at all, but also feces "peas", overdried, when a bowel movement is difficult. What could be the reason?
Regular constipation is usually caused by improper feeding of the crumbs. However, this condition can also occur if the mother does everything right, but she has her own health problems, for example, with the thyroid gland. Medications can also be the cause of constipation. For example, intestinal weakness is provoked by all kinds of sedative mixtures and drugs, which are often prescribed to children by neurologists at an early age. Even cough medicines or tooth gels can cause constipation. In any case, the doctor should deal with this. You should not give your baby medicines and laxatives on your own, or act on it mechanically with an enema or gas tube. It is better to discuss with the doctor the issues of feeding, drug treatment and the lifestyle of the baby - so you can understand the problem.
In any case, the doctor should deal with this. You should not give your baby medicines and laxatives on your own, or act on it mechanically with an enema or gas tube. It is better to discuss with the doctor the issues of feeding, drug treatment and the lifestyle of the baby - so you can understand the problem.
Weaning time
Of course, when you start to introduce complementary foods, the baby's stool pattern changes. First of all, you need to remember that the task of the first complementary foods (at 5, 6 months) is not to feed, but to help adapt to new tastes, to new food. Give the baby complementary foods in the amount of "lick" and only gradually move on to doses "with a marigold" or "half a teaspoon". Recall that you need to introduce one product into the diet of crumbs so that you can understand how and what the baby reacts to. Quite often, as soon as we give the baby “with a fingernail” some food, it is not digested - we find the product in the feces almost in its original form. Within one or two days, this is normal, the baby’s body has not figured out the new component in the stomach, but if this continues on the third day, the product must be removed from the diet, since it is obvious that the baby is not yet ready to accept it. You need to take a break for a week or two, without offering the baby anything but the breast, then try again with another product.
Within one or two days, this is normal, the baby’s body has not figured out the new component in the stomach, but if this continues on the third day, the product must be removed from the diet, since it is obvious that the baby is not yet ready to accept it. You need to take a break for a week or two, without offering the baby anything but the breast, then try again with another product.
The baby's body can also react more violently, for example, with loose stools and abdominal pain, and sometimes with allergies. In this case, you also need to cancel the product and keep the baby breastfed so that the gastrointestinal tract calms down.
When you introduce protein to your baby, he may react with constipation. To avoid this, you need to remember simple rules. Proteins require more liquid, so if this is your baby's first food (for example, cottage cheese), give him more breast milk. If you started introducing proteins when the baby is already drinking liquid, provide him with a drink. Do not worry about the fact that the introduction of new products has to be postponed - nothing terrible will happen to the baby. And be especially calm about the opinion that at 6-7 months the child needs to be given meat products so that he grows well. Not all children are able to absorb such a protein; for many, even a homogenized meat product at this age will lead to constipation and overload the kidneys. Let the baby eat breast milk for a longer time and receive vegetables and fruits as complementary foods - this way you will avoid many problems with the stool.
Do not worry about the fact that the introduction of new products has to be postponed - nothing terrible will happen to the baby. And be especially calm about the opinion that at 6-7 months the child needs to be given meat products so that he grows well. Not all children are able to absorb such a protein; for many, even a homogenized meat product at this age will lead to constipation and overload the kidneys. Let the baby eat breast milk for a longer time and receive vegetables and fruits as complementary foods - this way you will avoid many problems with the stool.
In general, mothers' concern about baby's stool is quite justified: after all, this is an important diagnostic symptom that allows you to understand a lot about the baby's condition. However, it must be remembered that not all situations require intervention, and most problems can be solved simply by correcting feeding mistakes. Do not rush to treat the baby and resort to medication, start with a diet.
Text: Anna Babina
Consultant: Olga Ivanovna Tkach, pediatrician, Center for Traditional Obstetrics
What is constipation in a newborn
The contents of a baby diaper is one of the key topics that young mothers discuss. They pay attention to the frequency of the stool, its consistency, color and smell. One of the most common problems they complain about to doctors or to each other is constipation in babies. We figure out what the baby’s chair depends on and how many days he may not go to the toilet for the most part.
They pay attention to the frequency of the stool, its consistency, color and smell. One of the most common problems they complain about to doctors or to each other is constipation in babies. We figure out what the baby’s chair depends on and how many days he may not go to the toilet for the most part.
Normal neonatal stool
During fetal development, nutrients are supplied to the baby through the umbilical cord. Through it, the metabolic products of the fetus are also excreted. The digestive system of a newborn begins to work only after childbirth, so it is logical that the baby does not poop in utero. But this does not mean that nothing gets into it.
During this period, the child actively swallows amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid). Its excretion from the body begins after the birth of the child and the start of breastfeeding. For the first time, a newborn goes to the toilet on the second day after birth. This stool is not like a baby's usual feces. Over time, he will return to normal.
How does the baby's stool change in the first months of life?
| Age | Child's chair |
| 1–3 days after birth | The chair is dense, pasty. Usually dark, sometimes greenish in color. The passage of meconium can cause discomfort to the baby. |
| 3–5 days after birth | The chair gradually brightens, becomes mushy. Usually does not cause any inconvenience to the child. But some problems may arise due to the fact that the digestive tract of the baby "learns" to work and is colonized by bacteria. |
| 2 weeks after birth | The work of the gastrointestinal tract is normalized. If the mother feeds the baby with breast milk, the stool is creamy, yellow. On artificial feeding it can be thicker. Not always homogeneous, there may be inclusions. |
| 1 month after birth | A month old baby can poop from one to several times a day. The chair is normalized and is both pasty and quite hard. Some children may also have stool retention. But if the separation of feces does not cause discomfort and anxiety in the baby, they should not bother the mother either. |
| 2 months after birth | The work of the intestine continues to improve. Two-month-old baby no longer goes to the toilet after every feed. The number of bowel movements is reduced to 1-2 per day. The stool is still not hard, more like slurry. It can be homogeneous and interspersed. |
Constipation is not considered that the baby cannot go to the toilet for a certain time. The main criteria at this age are not stool retention, but unpleasant sensations during defecation (the child cries before pooping), a large amount of stool and its hard consistency.
Because of what the child does not walk on large
Constipation is a reduction in the number of bowel movements relative to their normal number for this age. In addition, such a disorder of the stool is accompanied by the discharge of a large amount of dense stool. Thus, constipation is not just a decrease in the number of bowel movements, but also a change in the stool itself.
Other signs of constipation in a baby include the following:
- change in stool odor;
- a large amount of gases;
- anxiety of the baby during washing;
- restless sleep in a baby with frequent awakenings;
- intense crying that cannot be stopped.
Even if the baby goes to the toilet every day, but at the same time his feces become plentiful and dry, this indicates constipation in the child. At the same time, the absence of a bowel movement for several days, which does not cause any inconvenience to the baby, and normal mushy stools, even after a break, are not considered grounds for making such a diagnosis.
Causes of impaired defecation can be both normal and pathological. The most common causes of constipation in babies are:
- congenital malformations of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disruption of the digestive glands;
- violation of the normal colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by flora;
- the predominance of the mixture over breast milk;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- unsuitable mixture for the baby;
- allergic reactions;
- Iron-deficiency anemia.
Most often, the problem lies in improperly selected nutrition or dysbacteriosis in babies. The fact is that the child's intestines are sterile, and until the flora returns to normal, constipation can develop even in a one-month-old baby. Usually this condition does not require medical intervention, but the baby needs some help anyway.
Constipation is not just a delay in stool, but also a change in its consistency. It can be difficult for a young mother to understand when the lack of bowel movements is normal, and when the child needs help. Our doctors at a remote consultation will help you understand when a child needs help, advise on how to organize a baby’s diet and choose the right formula for him.
It can be difficult for a young mother to understand when the lack of bowel movements is normal, and when the child needs help. Our doctors at a remote consultation will help you understand when a child needs help, advise on how to organize a baby’s diet and choose the right formula for him.
When constipation of the baby requires medical attention
Most often, problems with defecation in infants occur due to improper feeding or due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract. However, in some cases, the absence of a chair requires medical intervention. It is especially dangerous if the newborn cannot go to the toilet and his meconium has not passed 2 days after birth.
This may indicate congenital problems with the gastrointestinal tract, which require additional diagnosis and examination by a neonatologist. In addition, other symptoms may indicate them. The main ones are:
- blood streaks or black blotches appear in the feces;
- close relatives have diagnosed diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the child burps frequently and profusely;
- he has vomiting with bile impurities;
- the child gains little or no weight;
- his stomach is very distended;
- the child's stool is like a ribbon;
- he refuses breast or bottle;
- the child cries a lot, and the parents cannot calm him down;
- his temperature rises;
- there are traces of calomania on the diaper, but the feces themselves do not go away.

If such symptoms are observed in the maternity hospital, it is necessary to report them to the neonatologist on duty. If they are found after discharge from the hospital, you need to call a pediatrician or report these symptoms during a patronage bypass. In cases where the child begins to vomit profusely and the temperature rises sharply, you need to call an ambulance.
Important! The minimum weight gain for children in the first three months of life is 150 grams per week or 600 grams per month. In the first month, the increase is calculated from the minimum weight, and not from birth weight.
How to treat stool problems in an infant
To help the baby cope with constipation, you need to understand what caused its development. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a survey of the mother and a physical examination - the doctor palpates the abdomen, examines the anus and performs a rectal examination. To determine the cause, an examination is also carried out - general tests of urine, blood and feces, ultrasound and others if necessary.
If pathologies are detected, a small patient is sent for treatment to a gastroenterologist, who will prescribe the appropriate treatment for the child. In other cases, it is recommended to change the lifestyle of both the nursing mother and the baby:
- A nursing mother is recommended a light diet without fried and fatty foods, with plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits. It is also worth reducing the amount of sugar in the diet, as it can cause fermentation in the digestive tract.
- Try to keep breastfeeding or mixed feeding as long as possible. Breast milk helps the digestive tract to ripen and form the correct flora.
- When transferring to artificial feeding, make sure that the mixture does not contain palm oil. It impairs the digestive processes and can cause constipation.
- If these measures do not help, the child may be prescribed pro- and prebiotics, which help to normalize the intestinal flora, after which the digestive processes also normalize.
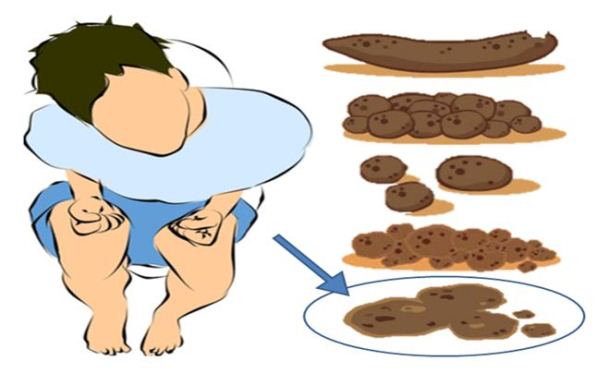
- As prescribed by the doctor, the baby may be prescribed laxatives, glycerin suppositories, microenemas and gas tubes. However, you should not get carried away with these drugs, since their constant use can lead to hypotension.
Massage of the abdomen can also help the newborn - stroke the baby's tummy in a circular motion in a clockwise direction and gently press the legs to the stomach. This will improve peristalsis and help the stool pass. A warm bath can also help the baby - it will relax the muscles and make it easier to pass the stool.
If we are not talking about pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, normalizing the nutrition of mother and child helps to fight constipation. Our doctors will help you choose the best diet, tell you when your child needs supplementary feeding, and determine when he needs medication.
FAQ
How do you know if a baby is constipated?
+
Normally, a child’s stool may be absent for several days, if the baby himself is calm at the same time, and the feces after that are soft and pass without problems.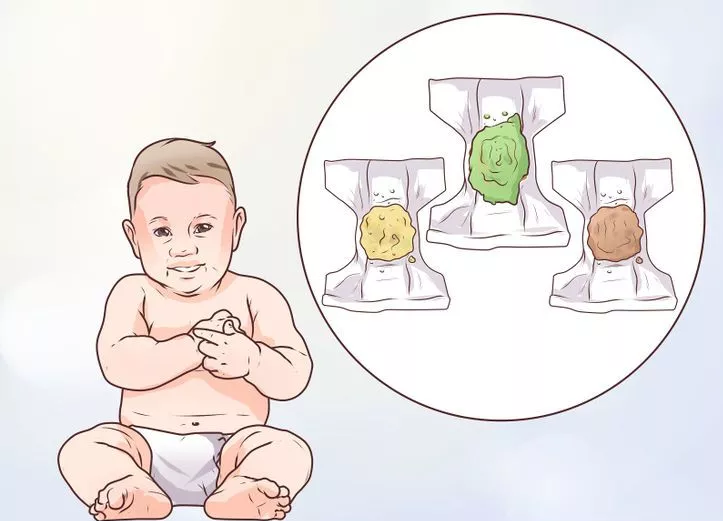 A sign of constipation is the presence of a hard plentiful stool and difficulty with the bowel movement itself.
A sign of constipation is the presence of a hard plentiful stool and difficulty with the bowel movement itself.
Why is there a delay in stool in infants?
+
Stool retention can develop due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract of the child, pathologies in the development of the intestines or digestive glands, dysbacteriosis, dehydration, an improperly selected mixture, or flaws in the diet of a nursing mother.
Can a newborn baby be given a laxative for constipation?
+
Do not give a newborn baby any medication without first consulting a doctor. Your doctor will assess the severity of your constipation and suggest ways to treat it with or without a laxative.
What to do if the baby has constipation? Should I force my baby to poop?
+
If the child is not bothered by anything, and the feces after the pass pass without problems, then there is no need to interfere in these processes. If the baby is clearly having difficulty with bowel movements, consult a doctor to find methods that facilitate this process.
If the baby is clearly having difficulty with bowel movements, consult a doctor to find methods that facilitate this process.
Can planting help with constipation?
+
Theoretically, an upright posture can help a child cope with constipation. However, these methods are rather auxiliary and will not lead to a stable result. It is more effective to adjust the diet and make sure that the child does not have dehydration.
Expert opinion
The absence of a chair in a child does not always mean that the baby has developed constipation. It is indicated by hard plentiful stools, restlessness and a swollen belly of the baby. The cause of a violation of the stool can be both pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, and flaws in the diet of the mother or baby. To determine when constipation requires treatment, the doctors of our service will help. They are available at any time of the day without queues and long waiting times.
 Due to the immaturity of the enzymatic system, it is greenish in color.
Due to the immaturity of the enzymatic system, it is greenish in color. -Step-1.jpg/aid1554278-v4-728px-Safely-Lose-Weight-(for-Teen-Girls)-Step-1.jpg)