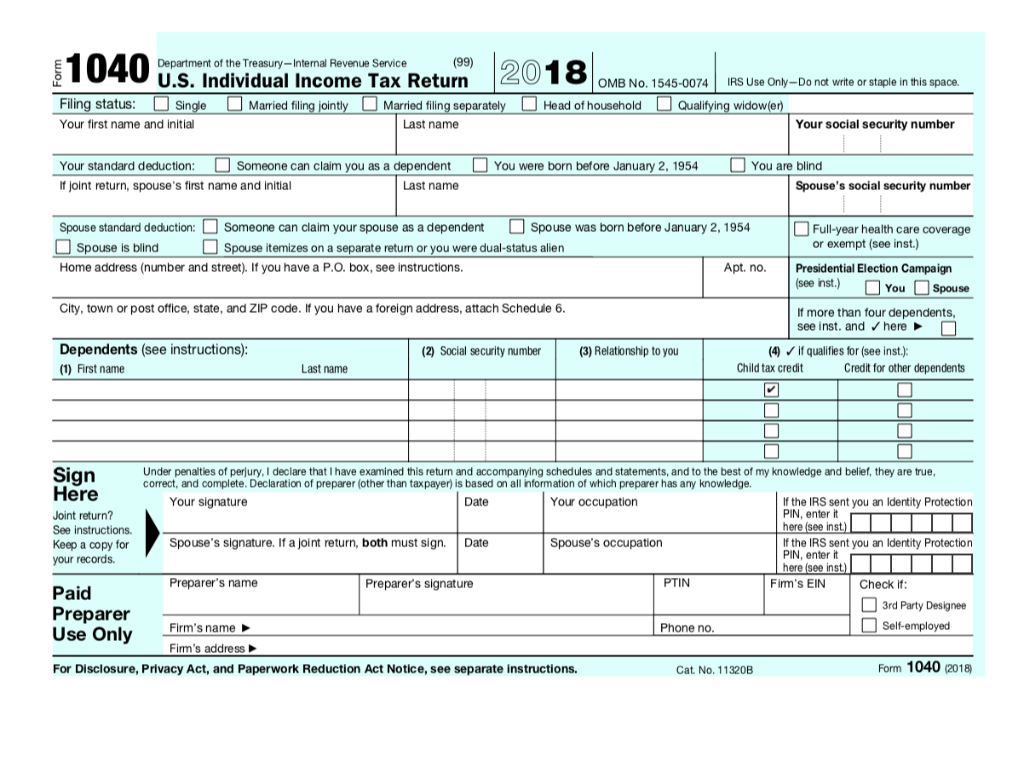
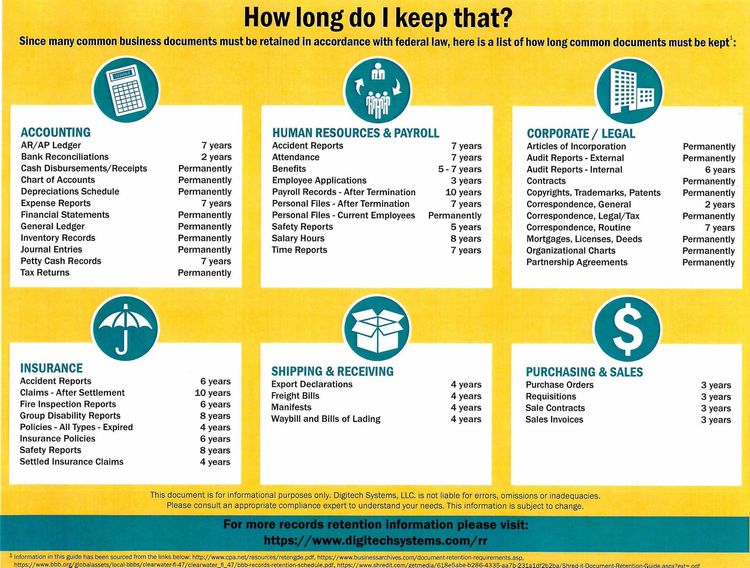
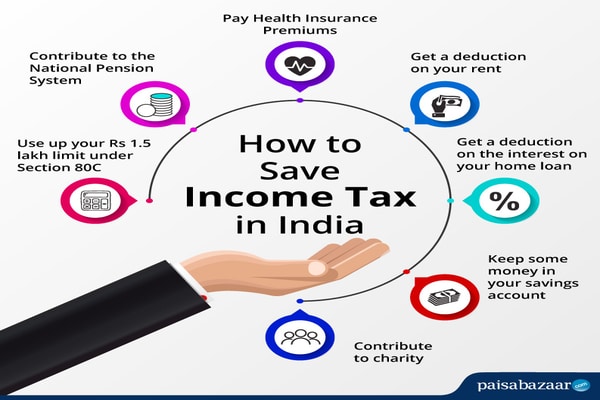
How to keep child support from taking tax refund
Stop Child Support from Taking the Tax Refund in 2022 + FAQs
- Last updated: April 2022
Lana Dolyna, EA, CTC
Senior Tax Advisor
If you’re behind on child support, the government will attempt to collect the payments in whatever way possible. This will include garnishing our wages and seizing your tax refunds.
There are several ways to stop the state and federal governments from taking your tax refunds including contacting your local Department of Child Support and Enforcement (DCSE) agency to file an appeal, setting up a payment plan for your delinquent payments, and requesting a hearing.
Ways to protect your tax refund
Contact your local DCSE agency
The division of Child Support and Enforcement is responsible for collecting child support but will hear appeals/good cause reasons for being arrears. Reasons for good cause changes to child support includes losing a job, the other parent getting a significant raise, or disability of the paying parent.
Set up a payment plan
Payment plans allow you to catch up on your late payments over time, but you will be charged interest. However, if a payment plan is in effect (and you are current on the payments) then your refund will not be seized.
Request a hearing
If you have an outstanding request for a hearing, DCSE may not seize your tax refund. The hearing will give you a chance to present your case for being delinquent on your payments and your plan for getting caught up. They may also take into consideration your reasons why you need your tax refund.
Pay the delinquent amount due
If you get caught up on your child support payments, the government will not take your refund. To make sure that they do not take your refund, you’ll want to make sure that you are caught up well in advance of your expected refund processing date.
Can child support take the advanced child tax credits?
Under the American Rescue Plan in 2021, advanced child tax credit payments were issued during the second half of 2021. This bill stated that the payments were not subject to seizure by the government for delinquent child support.
This bill stated that the payments were not subject to seizure by the government for delinquent child support.
It is unknown whether the IRS will restart the advanced child tax credit payments in the future and whether they would be subject to seizure.
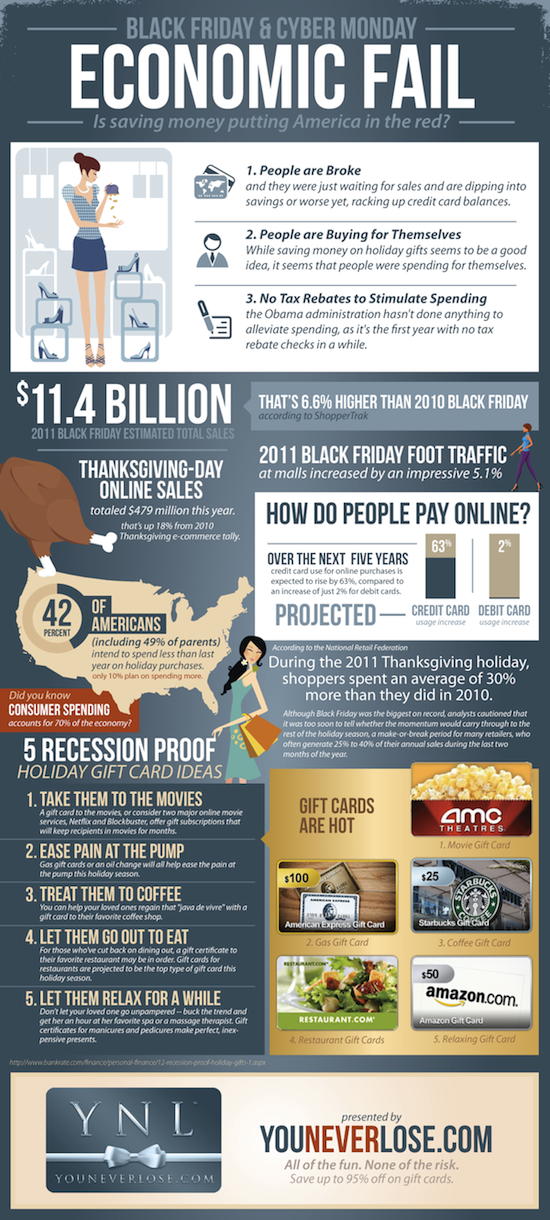
How can child support take my tax refund for child support?
The federal tax refund offset program started in 1981 and gives the IRS and state tax authorities the right to seize your refunds to pay delinquent child support. If the IRS intends to seize your refund, you will receive a notice in advance that you are on the list of refunds to be seized. If the amount you owe is less than your expected refund, the IRS may only withhold part of your refund.
If the IRS has an outdated address on file, you may not receive timely notice of their intent to seize your refund. Even if you do not receive the notice, the IRS still has the right to take it.
Can child support take my state tax refund?
Just like the IRS can pass your tax refunds on to the DCSE to pay delinquent child support payments, states can also seize your state tax refund to pay child support. The rules vary for each state, so you should check with your state agency.
The rules vary for each state, so you should check with your state agency.
Most states sent out notices prior to seizing a tax refunds for delinquent payments although the policy varies by state.
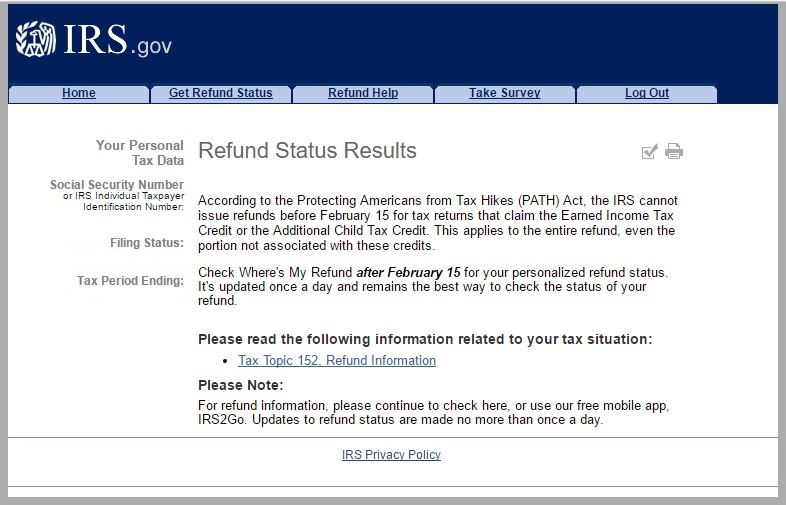
Does child support ever let you have your tax refund if you have delinquent child support?
The IRS stopped seizing tax refunds during 2020 and 2021 due to the COVID pandemic. This is the first time since 1981 that they have stopped seizing refunds for delinquent child support payments. It is unknown if they will continue to provide a waiver in future years.
During this period, many states also stopped seizing tax refunds to pay arrears child support, although each state differed in the amount of time they pause their policy of capturing refunds.
Are child support payments tax deductible?
Paying or receiving child support payments is not a taxable event. The child support payments are not deductible for the person paying the child support. They are not income for the person receiving the child support.
This differs from alimony payments which are deductible for agreements entered into prior to January 1, 2019. Divorce and separation agreements should differentiate between child support payments and alimony.
What other ways does delinquent child support affect my finances?
There are several ways that having delinquent child support may affect your finances. If you willfully refuse to submit payments, you may be held in contempt and be jailed which lowers your earning power.
If you are gainfully employed, DCSE may garnish your wages which means that they take a certain percentage or fixed dollar amount from each of your paychecks. Delinquent child support payments may be reported to the credit agencies and lower your credit score which lowers your ability to obtain a loan.
Questions about the child support services taking your tax money? We have the answers.
Does child support affect who can claim a dependent?
Claiming a child on your tax return is unrelated to the amount of child support you pay or receive.
Can I change my child support amount?
You can change your child support amount by petitioning the court to update your support agreement. You also negotiate with the child’s other parent to file a change motion.
How does the IRS know I owe child support?
Each state’s child support agency reports delinquent accounts to the IRS. The IRS compiles a list of delinquent accounts and sends out notices to anyone whose refund is at risk of being seized.
What if I pay child support but the other parent doesn’t acknowledge it?
To avoid this situation, all child support payments should be paid through DCSE so that there is an official record of the payment.
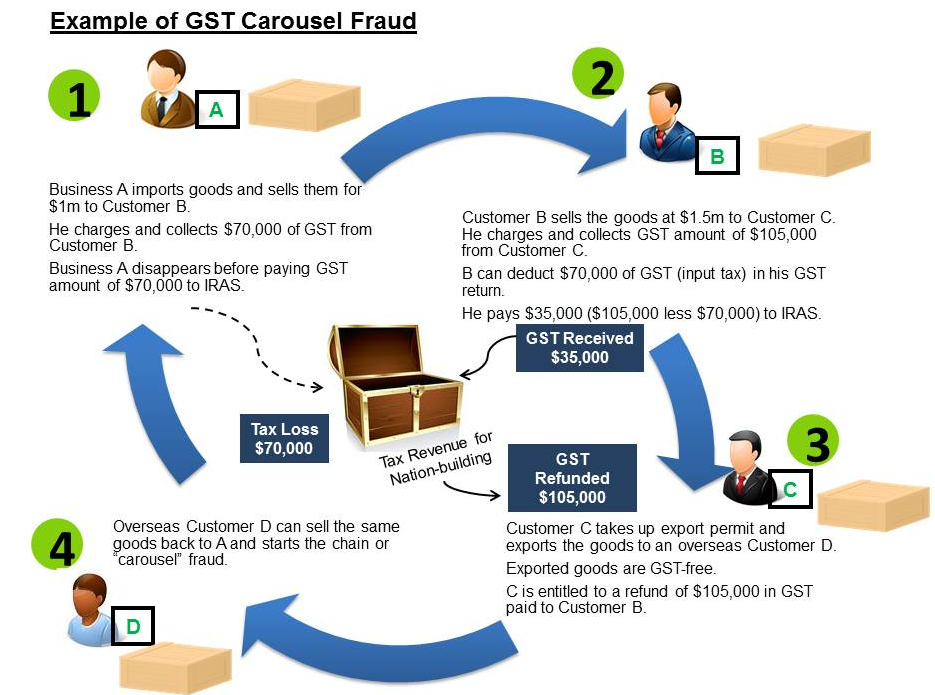
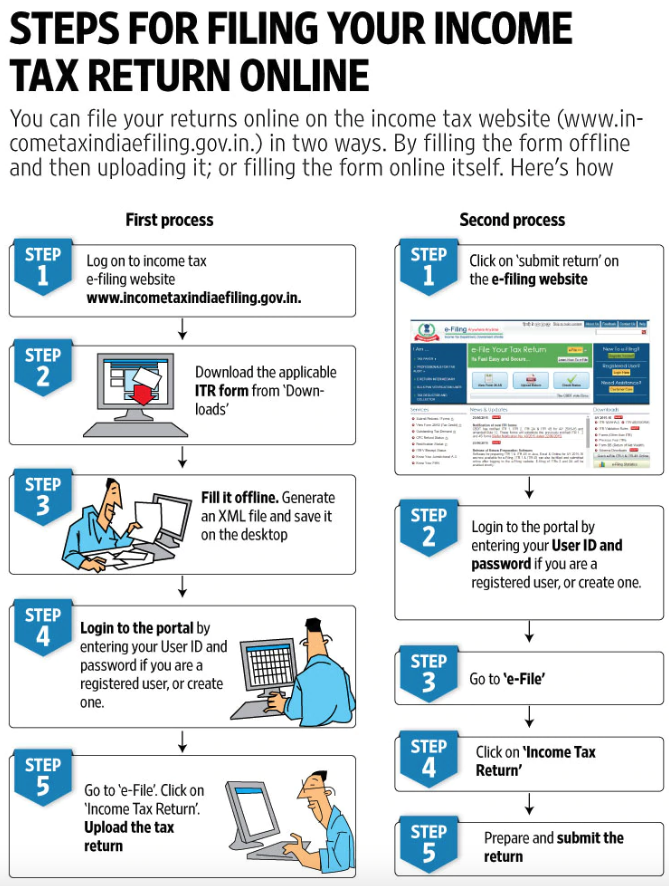
Can the IRS Take My Tax Refund for Child Support Arrears?
If you owe child support, the IRS might take your tax refund and coronavirus stimulus check.
Updated By Lina Guillen, Attorney
The Treasury Offset Program
Under the federal Treasury Offset Program, state child support enforcement agencies share information with the Treasury Department regarding parents that are behind on child support. With this information, the agency can intercept (take) federal tax returns and other payments to offset overdue child support.
With this information, the agency can intercept (take) federal tax returns and other payments to offset overdue child support.
If your state child support enforcement office has reported your overdue child support to the Treasury Department, the IRS will take your tax refund to cover the arrears (often called a tax refund seizure). The IRS will then give the money to the appropriate child support agency.
This same rule applies to coronavirus stimulus payments.
The Coronavirus Relief Act, Stimulus Checks, and Overdue Child Support
In March, Congress passed the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (the CARES act), which is a $2 trillion stimulus package to provide financial relief to businesses and individuals dealing with the COVID-19 economic fallout.
Under this package, American households will receive stimulus checks based on annual income: up to $1,200 per person, $2,400 for couples, and $500 per child under 17. You can see how much you'll receive using Nolo's online stimulus calculator.
However, if you're on the Treasury Offset list for unpaid child support, your stimulus check will be reduced by the amount you owe. It's unclear if you'll receive a notice in advance—to find out if your name is on the Treasury Offset list, call the toll-free IRS number at 1-800-304-3107.
Other past due debts to the government, like back taxes or overdue student loans will not trigger an automatic offset.
What to Do If You Receive Notice of an IRS Tax Refund Seizure
The Financial Management Service division of Treasury Department will send you a notice of a proposed tax refund seizure before it happens. Take this opportunity to address the proposed tax refund offset to decide on a course of action—you might be able to minimize the effect of the seizure on your finances.
The best way to avoid receiving a notice of an IRS Tax Refund Seizure is to pay child support on time. If you've lost your job or or are having trouble making your payments on time, you must take action. Contact your local child support agency for help or go back to court to see if you can modify child support based on your current income.
Contact your local child support agency for help or go back to court to see if you can modify child support based on your current income.
Ignoring your child support obligation or failing to make payments on time can subject you to contempt of court proceeding, fines, and other sanctions, like a tax refund seizure.
If you receive an IRS notice of tax refund seizure to cover child support arrears, here are some options:
If married, file an "Injured Spouse Allocation" form. If you're married to someone who owes child support—and you're not responsible for the debt—you can file an "Injured Spouse Allocation" form with the IRS. If you submit this properly, the IRS may allow you to keep your portion of the tax refund.
The IRS typically calculates this amount based on how much money your employer withheld from your wages for taxes the previous year. File this form with your return or immediately after receiving a notice of seizure.
File Chapter 13 bankruptcy. The bankruptcy code does not allow you to erase your child support arrears but it does allow you to restructure that arrearage and pay it down over a three to five year period. The bankruptcy court considers child support arrears a priority debt that gets paid before any other debt. (Learn more about paying child support in a Chapter 13 bankruptcy.)
The bankruptcy code does not allow you to erase your child support arrears but it does allow you to restructure that arrearage and pay it down over a three to five year period. The bankruptcy court considers child support arrears a priority debt that gets paid before any other debt. (Learn more about paying child support in a Chapter 13 bankruptcy.)
What to Do If You Are Owed Child Support
If you want the IRS to seize the refund of the person who owes you child support, it will do so automatically if the state child support enforcement office collects payments from your child's other parent.
However, if the child support enforcement office doesn't collect child support funds on your child's behalf, then you need to petition the court to request it be collected this way. That way, if your child's other parent falls behind on payments, the child support enforcement office will automatically report it to the Treasury Office to begin the process of intercepting tax refunds.
Talk to a Lawyer
Need a lawyer? Start here.
Alimony and other deductions | Accounting service "Interactive accounting"
Search in this category
Display in 2 columns
-
March 15, 2022
Amount of alimony from the average salary of a mobilized practitioner
Is it possible to pay alimony for a clerk's note from the average salary of a mobilized practitioner?...
-
June 2, 2020
Not enough salary to pay child support - how to be
During quarantine, many employees are on unpaid leave, some enterprises have declared downtime and employees are paid two-thirds of the salary (rate).
 Therefore, now a very topical issue is the deduction of alimony, established in a fixed amount of money or in an amount not less than the minimum guaranteed amount ...
Therefore, now a very topical issue is the deduction of alimony, established in a fixed amount of money or in an amount not less than the minimum guaranteed amount ... -
June 15, 2017
Whether to impose personal income tax and military tax indexation of alimony in a fixed amount of money?
Alimony, determined by the court in a fixed amount of money, is subject to indexation. Is this indexation considered an object of personal income tax and military tax? What is the position of the SFS specialists on this issue?...
-
March 16, 2017
The child is 18 years old: what is the basis for the termination of the collection of alimony
What is the basis (evidence) for not withholding child support from the employee upon reaching the age of majority of the child? .
 ..
.. -
December 7, 2016
The procedure for indexation of insurance payments and alimony in a fixed amount
As early as December 2016, enterprises and individual entrepreneurs will have to independently calculate the appropriate amount of alimony indexation in a fixed amount. How to determine the indexing factor? What problems can arise when collecting indexation amounts?...
-
October 28, 2016
How the amount of alimony is determined in the last month of their withholding
An enterprise, on the basis of a writ of execution, withholds child support from the salary of its employee.
 On November 10, 2016, the child will turn 18 years old. How to correctly calculate the amount of alimony for this month: for a full month or for a part of it, based on the working days of March or calendar days?...
On November 10, 2016, the child will turn 18 years old. How to correctly calculate the amount of alimony for this month: for a full month or for a part of it, based on the working days of March or calendar days?... -
October 28, 2016
Whether to withhold alimony from compensation for annual leave upon dismissal
Quite often there is a situation when an employee has unused annual leave days accumulated over several years. And if an employee quits, then compensation for unused annual leave is paid upon dismissal, respectively, the amount will be significant. However, should alimony be withheld from the entire amount of this compensation? ...
-
October 27, 2016
Indexation of alimony in a fixed amount - implementation is impossible?
As you know, in order for the norm to work, it is necessary to provide a mechanism for its implementation.
 Today, however, not only is there no such mechanism, but the situation has become more complicated. Therefore, we will analyze what is happening today and what issues need to be resolved in the near future ......
Today, however, not only is there no such mechanism, but the situation has become more complicated. Therefore, we will analyze what is happening today and what issues need to be resolved in the near future ...... -
October 26, 2016
Whether to withhold child support from sick leave
The enterprise withholds alimony from the employee's income according to the executive letter. Do I need to withhold child support from sick leave accrued in favor of this employee? ...
-
October 26, 2016
Is it necessary to withhold maintenance for an adult child who studies in absentia
An employee of the enterprise, from whose earnings, according to the decision of the state executor, alimony was withheld in favor of an adult child, the other day he provided a certificate from the university stating that his son was transferred to part-time education.
 Should the business continue to withhold child support? ... nine0003
Should the business continue to withhold child support? ... nine0003 -
October 26, 2016
If the employee received two writ of execution, and the amount of alimony on them exceeds 70%
How to get out of the situation when the company received two writ of execution, which oblige to withhold alimony, which in total amount to more than 70% allowed for collection? ...
-
October 25, 2016
Alimony from private entrepreneurs: the procedure for withholding and paying
According to the norms of the current legislation, both an employee and a private entrepreneur can be a payer of alimony.
 However, when collecting alimony from an individual entrepreneur, certain difficulties may arise in terms of determining the exact amount of his income from which these alimony are withheld ......
However, when collecting alimony from an individual entrepreneur, certain difficulties may arise in terms of determining the exact amount of his income from which these alimony are withheld ...... -
October 24, 2016
Child support: features of deduction, payment and recording
The article describes the procedure for withholding child support, ways to withhold them, terms of payment, amount, income from which deduction is carried out, features of their reflection in accounting and tax accounting ...
-
June 17, 2016
Maintenance indexation: what an accountant needs to know
The Commented Law amended the Law on Indexation and the Law on Enforcement Proceedings, according to which the amount of alimony, determined by the court in a fixed amount of money, is subject to indexation .
 ..
.. -
October 26, 2015
How to withhold alimony from the average earnings of mobilized
The enterprise calculates the average earnings of a mobilized worker. Prior to mobilization, alimony in the amount of 25% was forcibly withheld from the employee's salary. Should alimony be withheld from the average earnings of a mobilized employee and from the amount returned to him after the recalculation of personal income tax and military tax? ...
-
October 2, 2015
Loan repayment by deduction from salary
An enterprise has provided an employee with a cash loan in accordance with an agreement that does not provide for the accrual of interest.
 Can an enterprise deduct (withhold) the repayable loan amount from the employee's salary for the first half of the month?...
Can an enterprise deduct (withhold) the repayable loan amount from the employee's salary for the first half of the month?... -
September 28, 2015
How to transfer alimony if there are no details of the claimant's account in the executive documents
The company received a copy of the writ of execution on the withholding of alimony from the salary of an employee, in which only the full name is indicated. and the claimant's address. Can an enterprise withhold and transfer alimony to the creditor's card account? If yes, how to get details?...
-
July 3, 2013
Updated the list of cash payments to military personnel from whom alimony is not withheld
(commentary to the order of the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine dated May 15, 2013 No.
 316, hereinafter - Order No. 316, entered into force on July 2, 2013) This order approved the List of additional types of monetary security and other payments made in cash that are not subject to accounting when deducting alimony from the military personnel of the Armed Forces of Ukraine (hereinafter - List No. 316). E...
316, hereinafter - Order No. 316, entered into force on July 2, 2013) This order approved the List of additional types of monetary security and other payments made in cash that are not subject to accounting when deducting alimony from the military personnel of the Armed Forces of Ukraine (hereinafter - List No. 316). E...
Who and how can withhold money from your salary - Russian taxes
If you work officially, the employer withholds part of your salary and transfers it to the tax office.
Tatyana Skakunova
- The normative basis of deductions
- Mandatory deductions
- The sequence of retention
- deductions at the initiative of the employer
- Dethyzers
-
- Income from which no deductions are made
- How to apply different types of deductions together
Article published in Tinkoff Magazine with comments by Tatyana Skakunova, Deputy Head of Audit and Resident Consulting GSL Law & Consulting
In addition to tax payments, there are other situations when an employee receives less than what is required by an employment contract.
 I'll tell you who and how can take part of the salary legally.
I'll tell you who and how can take part of the salary legally. The basic rules for deductions from wages are set out in the labor code. Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation lists cases in which an employer can keep part of an employee's salary. Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation specifies the maximum amount of deductions: you cannot take all the income - something must remain for life. nine0003
The procedure for withholding personal income tax - personal income tax - is prescribed in chapter 23 of the tax code, and money from the earnings of a convicted person - in article 44 of the penal code.
Sometimes bailiffs take part of the debtor's salary. Articles 98 and 99 of the federal law "On Enforcement Proceedings" describe how this happens.
In some cases, the employer is required to withhold money from the salary - this does not depend on his will or the desire of the employee. nine0003
Personal income tax. People who are officially employed pay 13% of personal income tax from their labor income.
 Those who work "underhand" do not pay taxes and are at great risk.
Those who work "underhand" do not pay taxes and are at great risk. Employees do not take the money to the tax office themselves - it is done for them by the employer, who acts as a tax agent. He considers personal income tax, deducts it from his salary and transfers it to the tax office. And employees receive the amount already minus tax.
Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Personal income tax is a priority payment: first, the state takes its part, and the rest of the deductions are calculated from the salary, minus the tax.
Part 1 Art. 99 of the law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
Withholding loans under a writ of execution. For example, a person took a loan from a bank and did not repay it. The bank went to court, won the case and received a writ of execution.
A writ of execution is a document that gives the right to enforce the collection of a debt. There are other executive documents, such as a court order and a notary's executive inscription.
 nine0003
nine0003 This does not only work with banks: the same thing happens if the debtor does not return the money to the microfinance organization or to the neighbor on receipt. Both the bank, the MFI, and the neighbor are the debtor's creditors. As soon as the creditor receives a writ of execution, he turns into a claimant.
Art. 49 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
The creditor can take the writ of execution to bailiffs - they will initiate enforcement proceedings and try to collect the debt. There are several ways to do this, one of the most effective is to send the debtor's employer a wage foreclosure order. nine0003
The order specifies the total amount owed and the percentage of income to be withheld. The task of the employer is to fulfill what the bailiff wrote.
If the debt does not exceed 100,000 R, the recoverer has the right to present a writ of execution to the employer directly - without the help of bailiffs.
Art. 9 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
The employer begins deductions from the day he received the writ of execution.
 On the day of the salary, the debtor will be paid the amount already minus the money that is intended for the claimant. nine0003
On the day of the salary, the debtor will be paid the amount already minus the money that is intended for the claimant. nine0003 Art. 98 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
The employer sends the withheld money within three days according to the details from the resolution. As a rule, the money first goes to the bailiff service, and the bailiffs themselves transfer it to the claimant or distribute it among several claimants. If the creditor submitted the sheet directly to the employer, he will receive money immediately from him.
The deductions continue until the debt is repaid or the employee quits. If the employee left the organization, then the employer returns the writ of execution to the person from whom he received it - the recoverer or bailiffs. nine0003
Maintenance withholding by agreement. For example, ex-spouses agreed on the amount of alimony and made a written agreement. This agreement must be certified by a notary - then it will have the power of a writ of execution.
Art. 100 RF IC
If the alimony payer violates the agreement, the recipient has the right to recover the money forcibly. To do this, he needs to submit an agreement to the bailiffs or the employer of the alimony payer.
The employer withholds child support in the amount specified in the agreement, but not more than 70% of the salary. Let's say that the father of the child under the agreement undertakes to pay child support - 25,000 R per month. But this is the entire salary that he receives in his hands, minus personal income tax. If you take this money, then he will have nothing left - it’s impossible. Therefore, the employer will keep only 17,500 R - this is exactly 70% of the salary. And the remaining 7500 R is a debt that the father of the child will pay from other income. Art. 110 SK RF
Withholding alimony under a writ of execution. It is not always possible to agree on the payment of alimony amicably - then the court is involved in the dispute.
As a general rule, the recipient of alimony will first apply to the Justice of the Peace for a writ.
 This is a simplified procedure: there are no meetings and debates of the parties. The judge simply checks the documents and issues an order within five days if everything is done correctly. A court order is equal in strength to a writ of execution: it can also be submitted to bailiffs or directly to the employer. nine0003
This is a simplified procedure: there are no meetings and debates of the parties. The judge simply checks the documents and issues an order within five days if everything is done correctly. A court order is equal in strength to a writ of execution: it can also be submitted to bailiffs or directly to the employer. nine0003 Art. 122 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation
Some cases cannot be considered in writ proceedings, for example, when paternity must be established or if the payment of alimony affects the interests of other children. And it also happens that the debtor cancels the court order - this is not difficult. In such cases, the alimony recipient files a full-fledged claim, participates in court hearings and, if he wins, takes the writ of execution.
Art. 129 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation
Both the court order and the writ of execution indicate the amount of alimony in the form of a share of income - ½, ⅓, ¼ - or a fixed amount, for example, 20,000 R per month.
 nine0003
nine0003 Sometimes there are several creditors for one debtor. For example, a person owes three banks, the rent of the management company and alimony to his ex-wife. This forms a queue of claimants.
Withholding based on two writ of execution. Not all debts are equal: some are considered more important than others and are closed earlier. The bailiffs distribute the money among the claimants, taking into account the priority.
Art. 111 of the law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
Debts of the first stage: alimony, compensation for damage from a crime and various types of harm - moral, health, in connection with the death of a breadwinner. nine0003
Second line: obligations to employees. For example, the debtor - an individual entrepreneur - did not pay salaries to employees.
Third priority: debts to the state - taxes, contributions, fines.
And at the very end are the rest of the creditors.
The following principle works here: until the debts of one queue are closed, the money does not fall one step lower.
 For example, the debtor does not pay taxes to the state and the management company's communal apartment. The bailiffs are trying to collect both debts. His salary will go to taxes - this is a higher priority debt. And until this debt is closed, the management company will not receive a penny as part of the enforcement proceedings. This is how the sequence works. nine0003
For example, the debtor does not pay taxes to the state and the management company's communal apartment. The bailiffs are trying to collect both debts. His salary will go to taxes - this is a higher priority debt. And until this debt is closed, the management company will not receive a penny as part of the enforcement proceedings. This is how the sequence works. nine0003 Withholding amounts on several writ of execution of one queue. Debts within the same queue are also not equivalent: the bailiffs transfer the money recovered in proportion to the size of the debt. For example, the defaulter owes the bank 500,000 R, and the MFO - 100,000 R. His salary is 50,000 R. The total debt is 600,000 R. The debt to the bank is 83.33% of the total amount, and to MFIs - 16.67%. It is in these proportions that the collectors will divide the debtor's money. First, the employer withholds personal income tax from the debtor's salary: 50,000 R × 13% = 6,500 R. Remaining: 50,000 R − 6,500 R = 43,500 R.
 Another 50% is withheld from the balance in favor of creditors: 43,500 R x 50% = 21,750 R. The bank will receive: 21,750 R x 83.33% = 18,124 R. The MFI will get less: 21,750 R x 16.67% = 3,626 R.
Another 50% is withheld from the balance in favor of creditors: 43,500 R x 50% = 21,750 R. The bank will receive: 21,750 R x 83.33% = 18,124 R. The MFI will get less: 21,750 R x 16.67% = 3,626 R. Whether retroactive deductions are possible. The employer starts deductions from the day when he received the documents - retroactively is impossible.
Here, the creditor sent a writ of execution to the debtor by mail. But for some reason, the documents arrived very late: the sheet was dated January, and now it's already July. Then the debtor was lucky: he received a full salary for five months, and could be content with only half.
I'll tell you in what cases the employer has the right to keep part of the employee's salary. nine0003
Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
For the return of erroneously paid amounts - when, as a result of a counting error, the employee was transferred more than it should have been.
Rostrud believes that a counting error is a miscalculation when performing arithmetic operations.
 For example, a company has an hourly wage. The accountant incorrectly multiplied the cost of an hour by the time worked, and as a result, the employee was overpaid. In addition, the courts refer to counting errors as inaccuracies due to program failures. nine0003
For example, a company has an hourly wage. The accountant incorrectly multiplied the cost of an hour by the time worked, and as a result, the employee was overpaid. In addition, the courts refer to counting errors as inaccuracies due to program failures. nine0003 Letter of Rostrud No. 1286-6-1
To withhold erroneous transfers from wages, you must obtain the written consent of the employee. If there is no consent, the employer will have to go to court and prove that a counting error has occurred. The employee left the company of his own free will. When he was fired, his salary was calculated incorrectly and he was given extra money. As it turned out later, the error happened due to a failure in the 1C program. The ex-employee was sent a letter with a request to return the overpayment, which he ignored. Then the company went to court and proved that the reason for the overpayment was a counting error. The court confirmed that the former employee must return the money. nine0003
To pay off an advance given under various circumstances.
 An employer can give an employee money for future service expenses. For example, an employee is sent on a business trip and a certain amount is allocated in advance to the account - you need to report for it.
An employer can give an employee money for future service expenses. For example, an employee is sent on a business trip and a certain amount is allocated in advance to the account - you need to report for it. Within three days after returning from a business trip, the employee must draw up an advance report and attach documents to it that confirm his expenses - checks from the hotel, printouts of electronic tickets for the train or plane. nine0003
clause 26 of the regulation on the specifics of sending on business trips
The employer has the right to decide to withhold an advance payment from the salary for which the employee has not reported. But only if two conditions are met:
- The employee gave written consent to the retention.
- A month has not yet passed since the day when it was necessary to submit an advance report or return the money.
If the employee does not agree with the deduction or the term has already expired, then the accountable amounts are collected in court.
 nine0003
nine0003 Upon dismissal for unworked vacation days. An employer can provide employees with paid leave in advance.
Art. 122 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Let's say an employee has worked in a company for six months, for which 14 days of vacation are due. But he wants to rest longer, so he asks to let him go for 24 days. The employer agrees: provides and pays the employee an additional 10 days in advance.
If an employee does not work for a full year and leaves, there will be an overpayment for vacation pay. The employer has the right to withhold the overpayment from the calculation upon dismissal - and the consent of the employee is not required. nine0003
For damages. The employer has the right to recover from the employee compensation for the damage caused.
But this is a difficult procedure. First, the employer collects a commission and organizes an audit to calculate the amount of damage and find out who is to blame. An explanatory note is requested from the employee, and if he does not want to write it, the commission draws up an act of refusal.
Art. 247 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Based on the results of the audit, the employer establishes the exact amount of damage at market prices. For example, an employee broke a machine in a factory because he violated the operating instructions. Then you need to calculate the cost of repairing the equipment, and if it is no longer possible to restore it, then take the cost of a similar machine as damage. nine0003
Art. 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The employer has the right to decide to withhold compensation for damage from the salary, even if the employee does not agree with this. But only if two conditions are met:
- The amount of damage does not exceed the average monthly salary of the employee.
- A month has not yet passed since the date of determining the amount of damage.
st. 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
When the damage is more than the average monthly earnings, deduction is allowed only with the written consent of the employee or in court.
 nine0003
nine0003 The Labor Code provides that an employee can reach an agreement with the employer and pay damages in installments. And with the consent of the employer, the employee has the right to repair what he has broken, or to transfer to the company equivalent property for replacement.
Penalty deductions for non-compliance with the plan or misconduct. If an employee messed up or did not fulfill the plan, then it is impossible to withhold money from his salary. An employee receives a salary simply for coming to work and working there - it doesn’t matter if it’s bad or good. nine0003
For disciplinary offenses, such as being late or absenteeism, the labor code provides for special penalties: reprimand, reprimand and dismissal. But you can not reduce the salary part of the salary for this.
Art. 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
In many companies, employees receive not only a salary, but also a bonus. This is a variable part of the salary, which is paid for the achievement of certain results and compliance with the work schedule.

The bonus rules are usually prescribed in the internal documents of the employer - regulations and regulations - or in the employment contract or its annexes. The employer can indicate for what he will encourage, and for what he will deprive him of bonuses. In fact, the deprivation of the bonus is the deduction of money from the variable part of the salary. nine0003
For example, an organization has a regulation on bonuses. This document states that the employee will receive a bonus if he fulfills the sales plan - closes at least 10 deals per month - and does not receive disciplinary action. Then, if the employee does not cope with the plan or is late for work, he will be left without a bonus, but he will still receive a salary.
Types of deductions Term Personal income tax from salary On the day of salary. The withheld amounts are transferred to the tax office no later than the next day after payment Personal income tax from vacation and sickness benefits On the day of payment.  The withheld money is transferred to the tax office no later than the last day of the month of payment
The withheld money is transferred to the tax office no later than the last day of the month of payment According to executive documents On the day of salary. Withheld amounts are sent to the creditor or bailiffs within three days from the date of payment Unearned vacation pay On the day of dismissal Accountable amounts Month from the last day when the employee was supposed to submit an advance report Money, which are transferred due to counting errors month from the day, when the employee received an erroneous payment Damage to Month from the day when the employer established the amount of damage 4 8 Non-performance of the norm from the day the labor dispute commission or the court made a decision Sometimes employees themselves ask to deduct money from their salary. For example, a forgetful employee has to pay monthly mortgage payments.
 In order not to delay payment, he writes a statement to the employer, where he asks to transfer part of the salary to pay off the mortgage loan. nine0003
In order not to delay payment, he writes a statement to the employer, where he asks to transfer part of the salary to pay off the mortgage loan. nine0003 The employer is not obliged to comply with such instructions of the employee - he can agree or refuse. If he agrees, he must take into account: the legality of voluntary deductions is a complicated issue. It is possible that the labor inspectorate will not like such transfers, and the desire to meet the employee halfway will turn into litigation for the company.
The Ministry of Labor believes that this cannot be done: the Labor Code contains all the grounds for withholding and there is nothing there about statements from the employee. But Rostrud confirmed that the employer has the right to withhold money when the employee himself asked. nine0003
Yes, and the court said that this is possible: the employee has the right to dispose of his salary. If he wants the employer to transfer part of the money not to him, but somewhere else, then why not.
 And the norms of the labor code apply only to mandatory deductions and do not apply to voluntary ones.
And the norms of the labor code apply only to mandatory deductions and do not apply to voluntary ones. Different deductions have their own limitations.
In favor of the employer. An employer cannot take more than 20% of an employee's salary.
Here is an employee who received vacation pay "in advance" - for those days that he did not work. After the vacation, he wrote a letter of resignation - this is how an overpayment for vacation pay of 10,000 R was formed. Calculation upon dismissal already minus tax - 30,000 R. The employer has the right to withhold only 30,000 R × 20% = 6000 R from this money. The remaining 4000 R. the employee can pay voluntarily, and if he refuses, the employer will have to forgive him the debt. This money is considered an overpayment of wages, but there is no counting error, so it will not work to recover vacation pay in court. Another example. The employee did not report for an advance payment in the amount of 30,000 R and did not return this money.
 He agreed to deductions from the salary, which is 50,000 R per month in hand. The employer will take 20% from the salary - this is exactly 10,000 R. But the matter will not end there: deductions will continue from subsequent salaries. It will take three months to return the entire accountable amount.p. 5 review of judicial practice in civil cases of the Armed Forces for the third quarter of 2013
He agreed to deductions from the salary, which is 50,000 R per month in hand. The employer will take 20% from the salary - this is exactly 10,000 R. But the matter will not end there: deductions will continue from subsequent salaries. It will take three months to return the entire accountable amount.p. 5 review of judicial practice in civil cases of the Armed Forces for the third quarter of 2013 personal income tax. The personal income tax rate is 13%. For non-residents, it is higher - 30%.
p. 1, 3 art. 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
According to executive documents, they can take up to 50% of the salary. Even if the employee received several writ of execution, the employer is still obliged to keep at least half of his salary.
There are exceptions to this rule. In some cases, they withhold up to 70% - if this is a debt for alimony for minor children or for compensation:
- damage to health;
- crime damages;
- damage due to the death of the breadwinner.

Under a maintenance agreement. The employer must withhold as much as specified in the agreement, but not more than 70% of the salary.
At the initiative of the employee. The size of voluntary deductions is not limited: the employee can give at least the entire salary to where he decides.
Withholding Amount limit in favor of the employer to 20% NDFL 13%, 30% oscillators. Up to 70%, if it is alimony arrears, compensation for damages from a crime, harm due to the death of a breadwinner and harm to health Under an agreement on alimony Up to 70% At the initiative of the employee Unlimited Not all payments from your employer are subject to withholding. For example, debt under executive documents cannot be withheld:
- With financial assistance at the birth of a child, marriage or death of relatives.

- Travel expenses reimbursement.
- Compensation for the cost of vouchers to Russian sanatoriums.
- Reimbursement for moving to another city.
p. 8, 15 h. 1 art. 101 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
Even tax is not withheld from the entire salary if the employee has children. The more children, the less personal income tax: the first and second child reduce the tax base by 1400 R, each subsequent child by 3000 R. This is how the tax deduction for children works - we told in detail how to save with it.
paras. 4 p. 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for example, an employee received 50,000 R per month, but only 43,500 R in his hands, because 13% of the salary - 6,500 R - the employer withheld and transferred to the tax. When the employee had a child, not the entire salary began to be taxed , and part: 50,000 R - 1400 R = 48,600 R. The employer began to withhold: 48,600 R × 13% = 6318 R. Then the second child was born, and the taxable base decreased by another 1400 R.
 The budget began to receive even less: (48 600 R - 1400 R) x 13% = 6136 R. In addition, personal income tax does not have to be paid on certain types of payments from the employer:
The budget began to receive even less: (48 600 R - 1400 R) x 13% = 6136 R. In addition, personal income tax does not have to be paid on certain types of payments from the employer: - From reimbursement of expenses for transport and rental housing on business trips, if there are supporting documents - checks and receipts.
- Daily allowance on business trips - no more than 700 R when traveling in Russia and up to 2500 R when traveling abroad.
- Material assistance for the birth of children - no more than 50,000 R per child, paid within a year from the date of birth.
- Financial assistance in case of death of relatives.
- Financial assistance in the amount of not more than 4000 R per year - for any purpose. nine0014
st. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Deductions are easy to calculate if there are not many of them. Everything is more difficult when a horde of applicants line up for a salary: the tax office is waiting for personal income tax, the former spouse is waiting for alimony, banks are paying off loans, and the employer wants to return the accountable amounts.

Then for the employer the algorithm is as follows:
- Withhold personal income tax from the entire amount.
- Withhold debts on writ of execution from what is left.
- Agree with the employee on the voluntary contribution of money - otherwise it will not come to the return of accountable amounts. nine0014
I'll show you how it works using three examples:
Example 1. An employer collects 20% of an employee's salary every month for damages. But suddenly a writ of execution comes, according to which half of the salary now needs to be transferred to the bailiffs.
By law, after all deductions, the employee must have at least half of the salary. This means that those 20% that the employer used to get will now go to the bailiffs, and from them to the exactor.
Then the employer can sue the employee, get a writ of execution and join the queue of recoverers. Or arrange for the employee to voluntarily pay money for damages. There is a third option - forget and forgive.

Example 2. An employee took a loan from a microfinance organization and did not return it - now he gives half of the income to the recoverer on the writ of execution. The ex-wife of the debtor brings the employer an agreement on the payment of alimony, according to which 70% of the salary is due to her. nine0003
Alimony is first priority debt and loans fourth priority. First, the employer must withhold child support, and then everything else. H, after the alimony, the debtor will have only 30% of the salary - the MFI is not entitled to claim this part. It turns out that the creditor will not get anything from the salary.
Some debtors even make fictitious child support agreements to protect money from debt collectors. However, creditors may challenge such agreements.
Example 3. The employee has a debt - according to the executive document, the bailiffs take half of the earnings. He brings the boss a statement in which he asks to transfer the entire salary to a friend's bank card.
 nine0003
nine0003 This is not possible: deduction under a writ of execution is mandatory, but not at the initiative of the employee. The employee is not entitled to dispose of the part of the salary that is intended for the claimant. If the employer fulfills such an order, it will violate the law. For this, administrative and even criminal liability is provided.
It all depends on the reason for the retention: in each case, the documents are drawn up differently.
Sample application for payroll deduction. Suppose an employee wants the employer not to pay him a salary, but to dispose of this money in some other way. Then he must write an application addressed to the head in a free form. The main thing is to indicate the amount of deductions and account details where to transfer money. nine0003
It will not be possible to agree verbally. There is no way without a written statement - it is necessary for the employer to prove the legality of the deductions. The application will come in handy when the labor inspectorate comes up with the question: “Why are you transferring the salary to no one knows where, and not to the employee’s card?” Or if the employee suddenly decides that he did not ask for the money to be withheld and demands it back.

The application is written in free form: make sure that the amount of deductions and details for transfers are indicated. The employer must accept the application, but it is not obliged to satisfy it. nine0003
Hold consent form. Here are the types of deductions that are impossible without the consent of the employee:
- Return of accountable amounts.
- Compensation for damages if it is more than the average monthly salary of the employee.
- Refund of money paid out due to an accounting error.
First, the employee gives consent in writing, and only after that the employer can issue an order and take part of his salary.
Consent to retention is written in any form, but the date and signature of the employee must be included. nine0003
Sample hold order. The order is needed to withhold money at the initiative of the employer or employee. But to withhold personal income tax or debt under an executive document, an order is not required.
The employee must read the order against signature.
Sample provision for withholding unreturned accountable funds from wages. All rules for deducting accountable amounts are spelled out in the labor code, so no additional provision is required. But some employers are cunning and come up with documents to circumvent legal restrictions. nine0003
For example, by law, imprest amounts are allowed to be deducted from wages only with the written consent of the employee. Yes, and the amount of deduction is limited: no more than 20% of each salary.
The boss does not want to ask employees for permission and withhold the debt in installments of six months. Therefore, he invents a new provision, where he writes something like: “If the employee did not submit the advance report for the last month by the 5th day of the current month, then the employer has the right to withhold the accountable amounts in full from the employee’s salary. The employee's consent is not required.
 nine0003
nine0003 This is illegal: the labor code is more important than any internal regulations of the employer. The document is not valid if it worsens the position of employees in comparison with the requirements of the labor code.
Art. 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
You can complain about the illegal actions of the employer to the labor inspectorate and the prosecutor's office, and the deductions themselves can be challenged in court.
Art. 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Accounting entries differ depending on the basis for deducting money from the employee's salary. nine0003
Debit 70 credit 68, sub-account "Personal income tax settlements" - personal income tax withheld from the amounts accrued to employees. Withholding loans or alimony on a writ of execution.
Debit 70 credit 76, sub-account "Settlements under executive documents"
- money under the executive document was withheld from the employee's salary.

Debit 70 credit 76 - alimony was withheld from the employee's salary.
Withholding of accountable amounts.
Debit 94 credit 71 - accountable money not returned on time is reflected. nine0003
Debit 70 credit 94 - unreturned accountable amount withheld from salary.
REVERSE Debit 20 (26, 44) credit 70 - the amount of vacation pay for unworked vacation days has been reversed.
Debit 70 credit 51 (50) - amounts paid upon dismissal minus unearned vacation pay.
The tax base for personal income tax withholding for unworked vacation days is reduced by the amount of overpayment for vacation pay.
For example, vacation pay is overcharged - 19,000 R. Personal income tax from them: 19000 R × 13% \u003d 2470 R. Upon dismissal, the employee was charged 130,000 R. Personal income tax must be withheld: (130,000 R − 19,000 R) × 13% = 14,430 R.
Withholding personal income tax is reflected in the general order:
Debit 70 credit 68, sub-account "Calculations for personal income tax.
 "
" Debit 70 credit 73 - the cost of damage was deducted from the employee's salary by order of the manager.
Debit 70 credit 76 - payments were withheld from the salary at the initiative of the employee.
- The employer is obliged to withhold personal income tax and debt under executive documents from the salary. The employee's consent is not required. nine0014
- The employer has the right to withhold damages from the employee. His consent is not needed if the amount of damage does not exceed the average monthly earnings.
- An employer may withhold accountable amounts and overpayments due to an accounting error, but only with the employee's written consent.
- Unearned vacation pay can be withheld upon dismissal of an employee, even if he objects.
- The amount of deductions at the initiative of the employer is limited: no more than 20% of the employee's salary. nine0014
- According to executive documents, up to 50% of the salary is generally withheld, and for some types of debts, such as alimony, up to 70%.