How often can you give benadryl to a child
Benadryl Dosing | Framingham Pediatrics
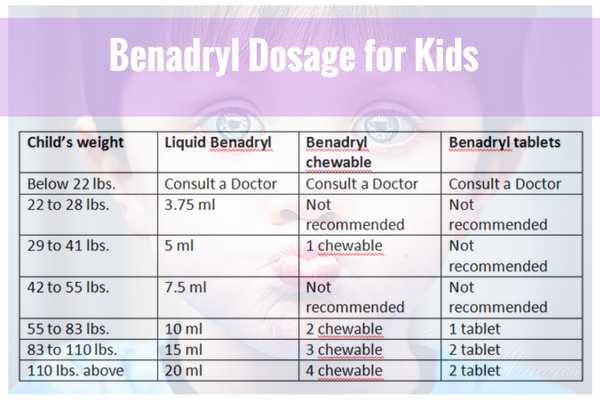
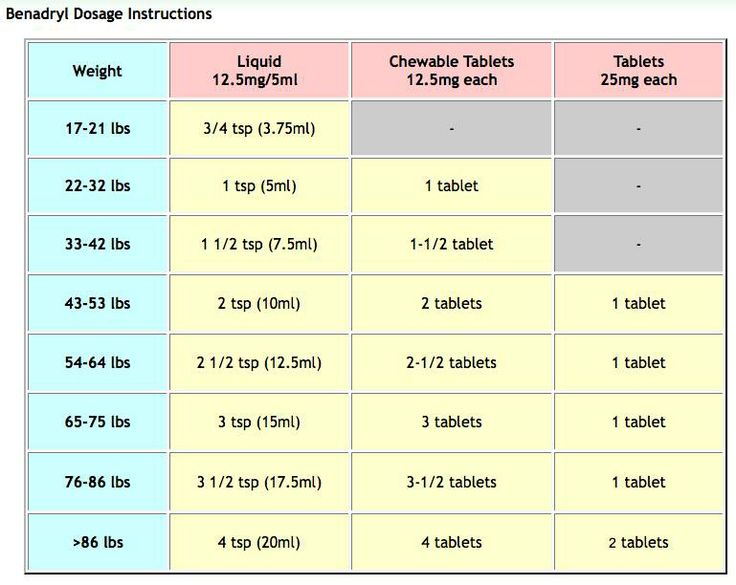
| Child's Weight | 20-24 | 25-37 | 38-49 | 50-99 | 100+ | lbs |
| Liquid 12.5 mg | ¾ | 1 | 1 ½ | 2 | - | tsp |
| Liquid 12.5 mg/5 milliliter (mL) | 4 | 5 | 7 ½ | 10 | - | mL |
| Chewable 12.5 mg | - | 1 | 1 ½ | 2 | 4 | tablets |
| Tablets 25 mg | - | ½ | ½ | 1 | 2 | tablets |
| Capsules 25 mg | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | caps |
Indications: Treatment of allergic reactions, nasal allergies, and hives.
- AGE LIMITS: Avoid Benadryl (diphenhydramine) under 2 years of age unless instructed by healthcare provider.
- DOSAGE: Determine by finding child's weight in the top row of the dosage table
- MEASURING the DOSAGE: Syringes and droppers are more accurate than teaspoons. If possible, use the syringe or dropper that comes with the medication. If you use a teaspoon, it should be a measuring spoon. Never use a kitchen spoon to measure medication dosing.
- 1 measured teaspoon equals 5ml
- 1/2 a teaspoon equals 2.5ml.
- FREQUENCY: May repeat every 6 hours as needed
- ADULT DOSAGE: 50 mg
- CHILDREN’S BENADRYL FASTMELTS: Each Fastmelt tablet contains the equivalent of 12.5 mg of Diphenhydramine HCL and dosed the same as chewable tablets
- RISK of SIDE EFFECTS: May cause drowsiness and occasionally excitation instead.
 DO NOT DRIVE OR OPERATE HEAVY MACHINERY AFTER TAKING BENADRYL.
DO NOT DRIVE OR OPERATE HEAVY MACHINERY AFTER TAKING BENADRYL.
Source: adapted from HealthyChildren.org.
The information contained on this website should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Benadryl Dosing | Contact Us
Diphenhydramine Dosing Table - HealthyChildren.org
Log in | Register
Safety & Prevention
Safety & Prevention
Diphenhydramine (also known as Benadryl®) is a medicine used to treat allergic reactions, hives and allergies that affect the nose (called nasal allergies).
It is an "over-the-counter" medicine, meaning that you can get it without a doctor's prescription. There are other medicines like diphenhydramine that might be safer for young children.
There are other medicines like diphenhydramine that might be safer for young children.
The table* below can help you figure out the right amount of diphenhydramine to give. Use your child's weight to decide on the right amount. You can find the weight in the top row of the chart.
*Table notes:
- Age of child: Do not give diphenhydramine to children less than 6 years of age unless your child's doctor tells you to. There are other medicines that are like diphenhydramine but will not make your child sleepy (like loratadine, cetirizine, fexofenadine) that can be bought without a prescription and are safer for young children.
- Measuring the dose for liquid medicines (should be in "mL" or metric units): It is easier to give the right amount of medicine when using a syringe than when using a kitchen teaspoon or tablespoon. Use the tool that comes with the medicine. If a tool does not come with the medicine, ask your pharmacist for one.
- How often to give the medicine (frequency): You can give diphenhydramine every 6 hours as needed.
- Adult dose: 50 mg
- Side effects: This medicine can make a child sleepy. Some children, however, may get more excited and active instead of getting sleepy. Because this medicine can make people sleepy, it is important to be careful when driving or using heavy machines after taking this medicine. This is especially important for teens who are driving.
More information
- How to Use Liquid Medicines for Children
- Using Over-the-Counter Medicines With Your Child
- AAP Allergy Tips
- Create an Allergy and Anaphylaxis Emergency Plan
- Last Updated
- 10/21/2021
- Source
- American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Quality Improvement and Patient Safety (Copyright © 2021)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Benadryl Dosages, Forms and Benefits | SingleCare - Product Information
Home >> Product Information >> Benadryl Dosage: How Much is Safe to Take?
Product information
Benadryl forms and strengths | Benadryl for adults | Benadryl for children | Dosage table of Benadryl | Dosage of Benadryl for Allergies | Dosage of Benadryl for motion sickness | Dosage of Benadryl for insomnia | Benadryl for pets | How to take Benadryl | FAQs
Benadryl is an over-the-counter medication that temporarily relieves allergy symptoms caused by a natural substance in the body called histamine. Diphenhydramine, the active ingredient in the branded drug Benadryl, is an antihistamine that blocks the activity of histamine and reduces symptoms such as runny nose, watery eyes, and itching.
Diphenhydramine also causes drowsiness and slows down the part of the brain that controls nausea.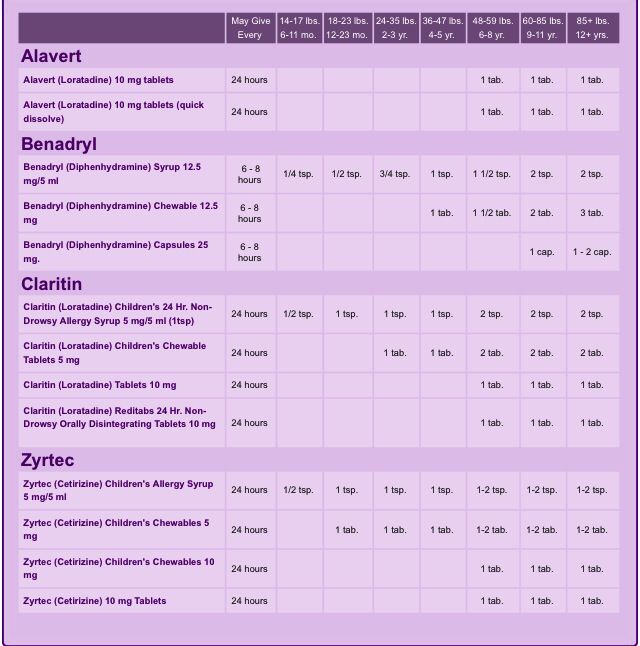 For these reasons, Benadryl may also be used to relieve occasional insomnia or prevent motion sickness.
For these reasons, Benadryl may also be used to relieve occasional insomnia or prevent motion sickness.
For patients over 12 years of age, the standard dosage of Benadryl Allergy is 25 to 50 mg (milligrams) - one to two tablets or capsules - every four to six hours. Children aged 6 to 11 years can be given Benadryl at a maximum dose of 25 mg (one tablet or capsule) every four to six hours. Benadryl can be taken with or without food.
RELATED: What is a Benadryl Allergy? | Benadryl Allergy Coupons
Benadryl Formulations and Strengths
Benadryl tablets and softgels contain 25mg of diphenhydramine hydrochloride and are usually taken by adults and children 6 years of age and older. Benadryl Allergy Plus, however, also contains 10 mg of phenylephrine hydrochloride, a nasal decongestant. Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion should not be given to children under 12 years of age unless directed by a doctor.
Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion should not be given to children under 12 years of age unless directed by a doctor.
- Benadryl Allergy Ultratab : 25 mg of diphenhydrammine on tablet
- Benadryl Lov-Geli from allergies without dyes : 25 mg of diphenhydramin for gel capsule Bendril Plus, 25 MG Fengidrazin
Benadryl Adult Dosage
The standard adult dose of Benadryl is one to two tablets or softgels (25-50mg) every four to six hours.
- Standard Adult Dose of Benadryl: One to two tablets/capsules (25-50mg) every four to six hours.
- Maximum adult dosage of Benadryl: Two tablets/capsules (50 mg) every four hours, maximum 12 tablets (300 mg) in 24 hours.
Benadryl dosage for children
Benadryl dosages may depend on the age or weight of the children. Children's allergy to Benadryl is more suitable for children aged 6 to 11 years. Contains half the dose of diphenhydramine (12. 5mg) as Benadryl Allergy, Children's Benadryl Allergy, sold in a child-friendly liquid and chewable tablet form.
5mg) as Benadryl Allergy, Children's Benadryl Allergy, sold in a child-friendly liquid and chewable tablet form.
- Children's dosage of Benadryl for children 2 to 5 years of age: Do not give unless directed by a physician.
- Benadryl dosage for children 6 to 11 years old: One to two chewable tablets or 5 to 10 ml every four to six hours, maximum 12 tablets or 60 ml in 24 hours.
- Pediatric dosage of Benadryl for children 12 years of age and older: Two to four chewable tablets or 10 to 20 ml every four to six hours, maximum 24 tablets or 120 ml in 24 hours.
RELATED: What is Children's Benadryl? | Benadryl coupons for children
Benadryl (adult drug) can be given to children between 6 and 11 years of age, but should not be given to children under 6 years of age. Although Benadryl Allergy can be used to relieve insomnia. in children 12 years of age and older, it should not be used as a sleeping pill in children under 12 years of age.
- Standard dose of Benadryl for children under 6 years: Do not give unless directed by a doctor.
- Standard dose of Benadryl for children 6 to 11 years old: One tablet/capsule (25 mg) every four to six hours.
- Maximum dosage of Benadryl for children aged 6 to 11 years: One tablet/capsule (25 mg) every four hours, maximum six tablets (150 mg) in 24 hours.
Children aged 6 to 11 should not be given Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion except under the direction of a pediatrician.
0128

Benadryl dosage for allergy symptoms
Benadryl relieves symptoms caused by allergies, hay fever, or the common cold, including runny nose, nasal congestion, sinus pressure, sneezing, rash, watery or itchy eyes, and itchy nose. It is also indicated for the relief of pruritus (pruritus) caused by the release of histamine due to an allergic reaction (contact dermatitis), urticaria (urticaria), or insect bites.
- Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and older): 25–50 mg every four to six hours.
- Pediatric patients (6-11 years): 25 mg every four to six hours.
- Patients with renal insufficiency:
- Creatinine clearance 10-30 ml/min: No adjustment.
- Dialysis: no adjustment and no additives.
- Other warnings: Talk to your doctor before taking Benadryl if you have any of the following:
- Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and older): 25 to 50 mg 30 minutes before travel and every six to eight hours while traveling.
- Pediatric patients (6-11 years old): 12.5 to 25 mg 30 minutes before travel and every six to eight hours during travel.
Benadryl Dosage for Insomnia
Benadryl may be used for the occasional relief of insomnia or travel-related insomnia in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older.
- Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and older): 25 to 50 mg 30 minutes before bedtime.
- Pediatric patients (6-11 years): Do not give unless directed by a physician.
Benadryl Dosage for Pets
Benadryl is not approved for use in pets, but veterinarians prescribe diphenhydramine in dogs, cats, and large animals to treat allergic reactions, nose allergies, itching, hives, motion sickness, and anxiety problems.
 Veterinarians also use diphenhydramine to treat certain types of cancer (mast cell tumors), shock, life-threatening allergic reactions, and other conditions.
Veterinarians also use diphenhydramine to treat certain types of cancer (mast cell tumors), shock, life-threatening allergic reactions, and other conditions.
The standard veterinary dosage is 2 to 4 mg diphenhydramine per kilogram of body weight (1 to 2 mg per pound) two or three times a day. However, check with your veterinarian before giving your pet Benadryl or any other over-the-counter medication.
RELATED: How to Treat Allergies in Cats and Dogs
How to Take Benadryl
For healthy adults and children 12 years of age and older, take one to two tablets or capsules by mouth every four to six hours or every doctor's instructions. Benadryl can be taken with or without food.
- Follow the instructions on the medicine label if you are taking this medicine without a prescription.
- If you are taking this medicine with a prescription, your doctor will tell you how much to use. Do not use more than indicated.

- Swallow the tablet or softgel whole. Do not crush, break or chew it.
Safety Tips
When taking or using Benadryl, you can consider the following safety and efficacy tips:
- Always check the expiration date. If the medicine has expired, dispose of it safely and buy a new box.
- Benadryl should be stored at room temperature (68°C -77F)
- Check all other medicines you or your child are taking to make sure they also do not contain diphenhydramine or phenylephrine. Both are commonly found in combination with cold, flu, or allergy medications. Pay special attention to topical itch medications that may contain diphenhydramine. These drugs, including topical diphenhydramine, should never be used with Benadryl.
- Do not take Benadryl with alcohol or sedatives.
- People who have glaucoma, breathing problems due to emphysema or chronic bronchitis, or difficulty urinating due to an enlarged prostate should talk to a doctor before taking Benadryl.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their physician before taking Benadryl.
- Although Benadryl is approved for use in children 6 years of age and older, Benadryl Allergy should not be used as a sleep aid in children under 12 years of age.
- For motion sickness, take Benadryl 30 minutes before travel or movement. If you are going on a long trip, take the following doses every six to eight hours.
- Record the time for each dose in a diary or schedule so that the next dose is not given too soon.
- Benadryl is a sedative, so do not operate machinery or drive if you feel tired, drowsy or lose concentration. Before taking diphenhydramine, it is recommended to remove obstacles and dangers in the house.
Benadryl Dosage FAQ
How long does Benadryl last?
When taken as directed, Benadryl Allergy usually starts working 30 minutes after ingestion and reaches peak levels in the body in about two hours. In general, food does not affect the absorption of Benadryl and does not reduce its effectiveness.
 However, regular use of Benadryl can lead to tolerance. Over time, the standard dose may gradually lose effectiveness.
However, regular use of Benadryl can lead to tolerance. Over time, the standard dose may gradually lose effectiveness. How long does Benadryl stay in your body?
At the recommended dosage, the effects of Benadryl should last between four and six hours, but this may vary. Generally, the amount of time Benadryl stays in the system increases with age.
Health care providers measure how long a drug stays in the body by its half-life, which is the time it takes for the body to eliminate half the amount of the drug in the body. The half-life of diphenhydramine in children is four to seven hours (average five hours). For adults, the elimination half-life is seven to 12 hours (mean nine hours). For the elderly, the elimination half-life is nine to 18 hours (mean: 13.5 hours).
What happens if I miss a dose of Benadryl?
No problem if you don't take a dose of Benadryl. Take the missed dose at any time. The dosing schedule will be reset, so wait at least four hours before taking your next dose.
 Do not take extra medicine to make up for a missed dose.
Do not take extra medicine to make up for a missed dose. How can I stop taking Benadryl?
You can safely use Benadryl regularly to treat allergic reactions, insomnia, or motion sickness. It should only be used occasionally as a sleep aid. Diphenhydramine - This is sometimes abused. Chronic use of Benadryl, especially to relieve anxiety or insomnia, can lead to addiction and withdrawal symptoms if Benadryl is stopped quickly. High doses of Benadryl can cause severe heart problems, seizures, coma and death. Before you stop taking Benadryl, talk to your doctor about lowering your Benadryl dose or using alternative medications or treatments to reduce anxiety or treat insomnia.
You should stop taking Benadryl and consult your doctor if you experience excessive nervousness, drowsiness, allergic reactions, or if symptoms do not improve after seven days.
What can be used instead of Benadryl Allergy?
Health care professionals generally do not recommend the use of first-generation antihistamines such as diphenhydramine, the active ingredient in Benadryl.
 Second-generation antihistamines are as effective as diphenhydramine but do not cause as much sedation or drowsiness. Instead of Benadryl Allergy, you can choose several second-generation OTC antihistamines such as Claritin (loratadine), Alavert (loratadine), Allegra (fexofenadine), Zyrtec (cetirizine), and Xyzal (levocetirizine).
Second-generation antihistamines are as effective as diphenhydramine but do not cause as much sedation or drowsiness. Instead of Benadryl Allergy, you can choose several second-generation OTC antihistamines such as Claritin (loratadine), Alavert (loratadine), Allegra (fexofenadine), Zyrtec (cetirizine), and Xyzal (levocetirizine). What is the maximum dosage of Benadryl?
The maximum dose is 50 mg (two tablets or softgels) every four hours to a maximum of 300mg (12 tablets or softgels) in any 24 hour period for adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older.
For children aged 6 to 11 years, the maximum dose is 25 mg (one tablet or softgel) every four hours, but not to exceed 150 mg (six tablets or capsules) in any 24 hour period.
What interacts with Benadryl?
Food does not affect the absorption or effectiveness of Benadryl.
Some over-the-counter and prescription drugs may interact with Benadryl, and some may reduce the effectiveness of Benadryl.
 Medicines that depress or slow down the central nervous system, such as tranquilizers, alcohol, or sedatives, may increase the side effects of Benadryl, such as drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, dry mouth, and blurred vision. Always check with your doctor before taking Benadryl Allergy with central nervous system depressants or other medicines.
Medicines that depress or slow down the central nervous system, such as tranquilizers, alcohol, or sedatives, may increase the side effects of Benadryl, such as drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, dry mouth, and blurred vision. Always check with your doctor before taking Benadryl Allergy with central nervous system depressants or other medicines. Benadryl Allergy Plus Congestion also contains phenylephrine, a stimulant. When taken with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), a family of medications that includes certain types of antidepressants, antibiotics, and drugs for Parkinson's disease, phenylephrine can cause dangerous and potentially life-threatening increases in blood pressure. Do not take Benadryl with an MAOI or within 14 days of stopping an MAOI inhibitor. Check with your doctor, pharmacist, or other health care provider if you think a medicine you are taking may be an MAO inhibitor.
- Diphenhydramine for Animals, VCA Hospitals
- Chronic Diphenhydramine Abuse and Withdrawal Syndrome, Neurology: Clinical Practice
- Antihistamine Doses, MSD Veterinary Manual
- Pharmacological Treatment of Motion Sickness Pharmacist
- FDA warns of serious problems with high doses of allergy drug diphenhydramine.
 , FDA
, FDA
Diphenhydramine (Systemic | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Adult Medication
ShareThis document, provided by Lexicomp ® , contains all the information you need to know about this medicine, including indications, directions for use, side effects, and when your healthcare provider should be contacted.
Trade names: USA
Aler-Dryl [OTC] [DSC]; Allergy Childrens [OTC]; Allergy Relief Childrens [OTC]; Allergy Relief [OTC]; Anti-Hist Allergy [OTC]; Aurodryl Allergy Childrens [OTC] [DSC]; Banophen [OTC]; Benadryl Allergy Childrens [OTC]; Benadryl Allergy Extra Str [OTC]; Benadryl Allergy Ultratabs [OTC]; Benadryl Allergy [OTC]; Complete Allergy Relief [OTC]; Di-Phen [DSC]; Diphen[DSC]; Diphen[OTC]; Diphenhist [OTC] [DSC]; Geri-Dryl [OTC]; GoodSense Sleep Aid [OTC]; M-Dryl [OTC]; Naramin [OTC]; Nighttime Sleep Aid [OTC]; Nytol Maximum Strength [OTC] [DSC]; Nytol [OTC] [DSC]; Ormir [OTC] [DSC]; PediaCare Children's Allergy [OTC]; Pharbedryl [OTC]; Siladryl Allergy [OTC]; Simply Sleep [OTC]; Sleep Tabs [OTC] Total Allergy Medicine [OTC]; Total Allergy [OTC]; Vanamine PD [OTC] [DSC]; ZzzQuil [OTC]
Brand names: Canada
Diphenist
What is this drug used for?
- Used to relieve cough.

- It is used to relieve the symptoms of allergies.
- It is used for motion sickness.
- It is used to treat symptoms such as Parkinson's disease caused by other health problems.
- It is used to treat sleep disorders.
What should I tell my doctor BEFORE taking this drug?
- If you have an allergy to this drug, any of its ingredients, other drugs, foods or substances. Tell your doctor about your allergies and how they have manifested.
- If the patient is a premature baby or newborn. Do not give this form of drug to a premature or newborn baby.
This list of drugs and conditions that may interfere with this drug is not exhaustive.
Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all medicines you take (both prescription and over-the-counter, natural medicines and vitamins) and any health problems you have. You need to make sure that this drug is safe for your conditions and in combination with other drugs you are already taking. Do not start or stop taking any drug or change the dosage without your doctor's advice.
Do not start or stop taking any drug or change the dosage without your doctor's advice.
What do I need to know or do while taking this drug?
All forms:
- Tell all your health care workers that you are taking this drug. These are doctors, nurses, pharmacists and dentists.
- Do not take the drug in higher doses than prescribed by your doctor. Taking more than the prescribed amount of the drug increases the risk of serious side effects.
- Do not take this drug for longer than the length of time your doctor has prescribed.
- Avoid driving and other activities that require increased attention until you see how this drug affects you.
- Do not use with other products containing diphenhydramine.
- Avoid drinking alcohol while taking this drug.
- Check with your doctor before using marijuana, other forms of cannabis, or prescription or over-the-counter drugs that can slow you down.
- If you are 60 years of age or older, take this drug with caution.
 You may experience more side effects.
You may experience more side effects. - If the patient is a child, use this drug with caution. Children may have a higher risk of some side effects.
- Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. The benefits and risks for you and your child will need to be discussed.
Drugs for the treatment of sleep disorders:
- This drug is not intended for use in children under 12 years of age. However, your doctor may decide that the benefits of this drug outweigh the risks. If your child has received this drug, ask your doctor about the benefits and risks. If you have any questions about how to give this drug to a child, talk with your doctor.
All other dosage forms:
- Different brands of this drug may be for use in children of different ages. Talk to your doctor before giving this drug to a child.
- Do not use for sleep disorders in children. Consult your doctor.
What side effects should I report to my doctor immediately?
WARNING. In rare cases, this drug can cause serious and sometimes deadly side effects in some patients. Call your doctor right away or get medical help if you have any of the following signs or symptoms that could be associated with serious side effects:
- Signs of an allergic reaction, such as rash, hives, itching, red and swollen skin with blisters or peeling, possibly accompanied by fever, wheezing or wheezing, tightness in the chest or throat, difficulty breathing, swallowing or speaking, unusual hoarseness, swelling in the mouth, face, lips, tongue or throat.
- Severe dizziness or fainting.
- Balance change.
- Decreased attention.
What are some other side effects of this drug?
Any medicine can have side effects. However, for many people, side effects are either minor or non-existent. Contact your doctor or seek medical attention if these or any other side effects bother you or do not go away:
- Feeling dizzy or sleepy.
- Thickening of the mucous membrane of the nose or throat.
- Nervous tension and agitation.
- Nausea or vomiting.
This list of possible side effects is not exhaustive. If you have any questions about side effects, please contact your doctor. Talk to your doctor about side effects.
You can report side effects to the National Health Board.
You can report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-332-1088. You can also report side effects at https://www.fda.gov/medwatch.
What is the best way to take this drug?
Use this drug as directed by your doctor. Read all the information provided to you. Strictly follow all instructions.
All oral preparations:
- Take with or without food. Take with food if medicine causes nausea.
Sleep disorders:
- Take this drug at bedtime.
Chewable and oral disintegrating tablets:
- Should be thoroughly chewed or allowed to dissolve in the mouth.

- If you have phenylketonuria, talk to your doctor. Some foods contain phenylalanine.
Chewables.
- Place the oral strip on your tongue and let it dissolve.
All liquid formulations:
- Liquid doses should be measured with caution. Use the dispenser that comes with the medicine. If the dispenser is not provided in the package, ask the pharmacist for a dosing agent for this drug.
- If you have phenylketonuria, talk to your doctor. Some foods contain phenylalanine.
Liquid (suspension):
- Shake well before use.
Injection:
- For intramuscular or intravenous injections.
- This drug can cause tissue damage when injected into the skin or into fatty tissue under the skin. Consult your doctor.
What should I do if I miss a dose of a drug?
Preparations for the treatment of sleep disorders:
- This drug should be taken as needed.
 Do not take the drug more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Do not take the drug more often than prescribed by your doctor.
All other oral preparations:
- If you take the drug regularly, take the missed dose as soon as you can.
- If it's time for your next dose, don't take the missed dose and then go back to your regular dosing schedule.
- Do not take 2 doses or an additional dose at the same time.
- In most cases, this drug is used as needed. Do not take the drug more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Injection:
- See your doctor for further instructions.
How do I store and/or discard this drug?
All oral preparations:
- Store at room temperature, protected from light. Store in a dry place. Do not store in the bathroom.
All liquid formulations:
- Don't freeze.
Liquid (suspension):
- Throw away any unused servings after 8 weeks.
Injection:
- If you need to store this drug at home, check with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist for storage conditions.
All forms:
- Keep all medicines in a safe place. Keep all medicines out of the reach of children and pets.
- Dispose of unused or expired drugs. Do not empty into a toilet or sewer unless instructed to do so. If you have any questions about disposing of medicines, ask your pharmacist. Drug disposal programs may be in place in your area.
General drug information
- If your health does not improve or even worsens, see your doctor.
- Do not give your medicine to anyone and do not take other people's medicines.
- Some medicines may come with other patient information leaflets. If you have questions about this drug, talk with your doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care professional.
- Some medicines may come with other patient information leaflets. Check with your pharmacist. If you have questions about this drug, talk with your doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care professional.
- If you think you have overdosed, call a poison control center or get medical help right away. Be prepared to tell or show what drug you took, how much, and when it happened.
Consumer Use of Information and Limitation of Liability
This summary information includes a summary of the diagnosis, treatment, and/or drug product. It is not intended to be a comprehensive source of data and should be used as a tool to help the user understand and/or evaluate potential diagnostic and treatment options. It does NOT include all information about conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or risks that may apply to a particular patient. It should not be considered medical advice or a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment provided by a physician based on a medical examination and assessment of the patient's specific and unique circumstances. Patients should consult with their physician for full information about their health, medical issues, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding the use of medications.