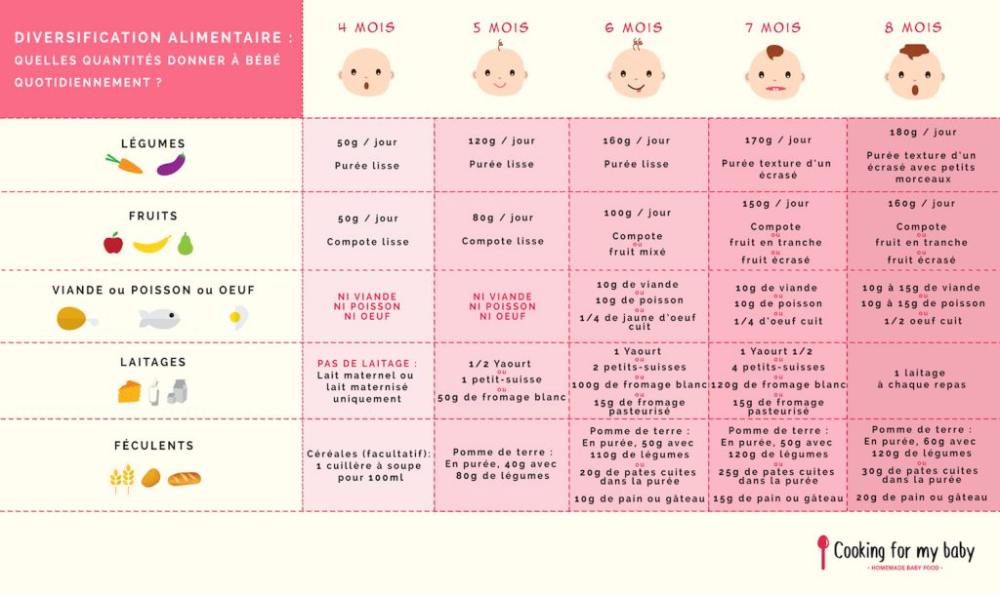
How much solid food should my 6 month old eat
Feeding your baby: 6–12 months
At 6 months of age, breastmilk continues to be a vital source of nutrition; but it’s not enough by itself. You need to now introduce your baby to solid food, in addition to breastmilk, to keep up with her growing needs.
Be sure you give your baby her first foods after she has breastfed, or between nursing sessions, so that your baby continues to breastfeed as much as possible.
When you start to feed your baby solid food, take extra care that she doesn’t become sick. As she crawls about and explores, germs can spread from her hands to her mouth. Protect your baby from getting sick by washing your and her hands with soap before preparing food and before every feeding.
Your baby's first foods
When your baby is 6 months old, she is just learning to chew. Her first foods need to be soft so they’re very easy to swallow, such as porridge or well mashed fruits and vegetables. Did you know that when porridge is too watery, it doesn't have as many nutrients? To make it more nutritious, cook it until it’s thick enough not to run off the spoon.
Feed your baby when you see her give signs that she's hungry – such as putting her hands to her mouth. After washing hands, start by giving your baby just two to three spoonfuls of soft food, twice a day. At this age, her stomach is small so she can only eat small amounts at each meal.
The taste of a new food may surprise your baby. Give her time to get used to these new foods and flavours. Be patient and don’t force your baby to eat. Watch for signs that she is full and stop feeding her then.
As your baby grows, her stomach also grows and she can eat more food with each meal.
Feeding your baby: 6–8 months old
From 6–8 months old, feed your baby half a cup of soft food two to three times a day. Your baby can eat anything except honey, which she shouldn't eat until she is a year old. You can start to add a healthy snack, like mashed fruit, between meals. As your baby gets increasing amounts of solid foods, she should continue to get the same amount of breastmilk.
Feeding your baby: 9–11 months old
From 9–11 months old, your baby can take half a cup of food three to four times a day, plus a healthy snack. Now you can start to chop up soft food into small pieces instead of mashing it. Your baby may even start to eat food herself with her fingers. Continue to breastfeed whenever your baby is hungry.
Each meal needs to be both easy for your baby to eat and packed with nutrition. Make every bite count.
Foods need to be rich in energy and nutrients. In addition to grains and potatoes, be sure your baby has vegetables and fruits, legumes and seeds, a little energy-rich oil or fat, and – especially – animal foods (dairy, eggs, meat, fish and poultry) every day. Eating a variety of foods every day gives your baby the best chance of getting all the nutrients he needs.
If your baby refuses a new food or spits it out, don’t force it. Try again a few days later. You can also try mixing it with another food that your baby likes or squeezing a little breastmilk on top.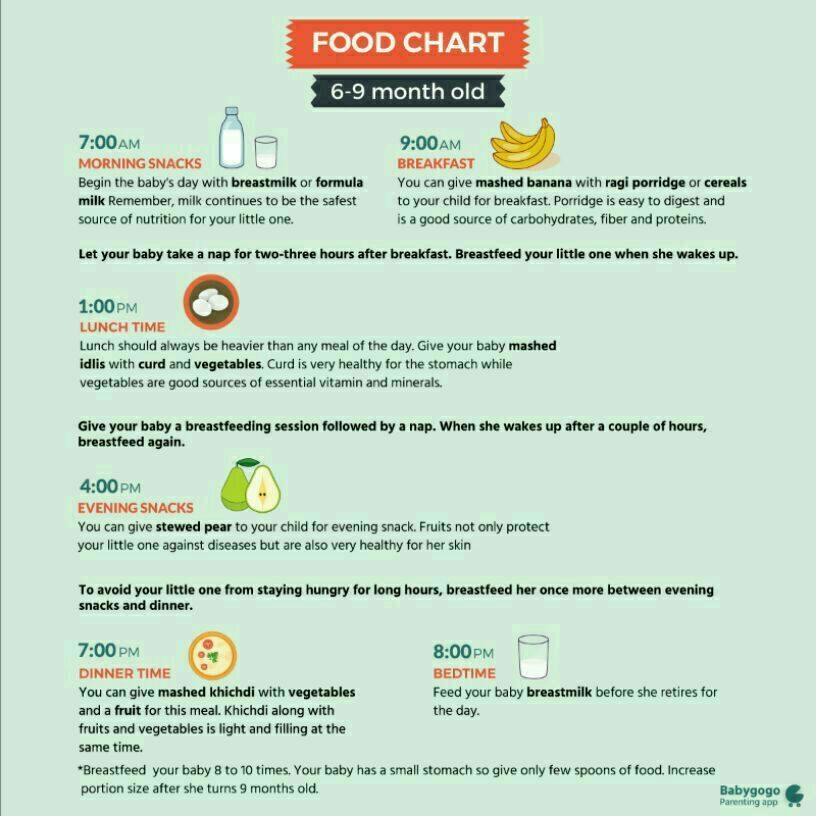
Feeding non-breastfed babies
If you're not breastfeeding your baby, she’ll need to eat more often. She'll also need to rely on other foods, including milk products, to get all the nutrition her body needs.
- Start to give your baby solid foods at 6 months of age, just as a breastfed baby would need. Begin with two to three spoonfuls of soft and mashed food four times a day, which will give her the nutrients she needs without breastmilk.
- From 6–8 months old, she’ll need half a cup of soft food four times a day, plus a healthy snack.
- From 9–11 months old, she’ll need half a cup of food four to five times a day, plus two healthy snacks.
How much should my baby eat? A guide to baby food portions
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Wondering how much to feed your baby? This can be hard to figure out, especially when you're starting solids and most of your baby's food ends up on your little one or the floor.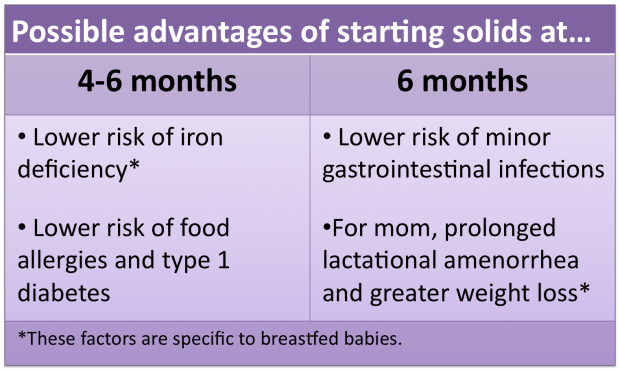 It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby eat?
Do you worry that your baby is eating too little or too much? Your baby will self-regulate her food intake based on what their body needs, so let their appetite be your guide.
It's helpful to have a reference point, however. Here are photos of how much solid food a baby typically eats in a day. You can also ask your baby's doctor for feeding advice.
This visual guide shows:
- Portions for infants who are new to solids (typically 4 to 6 months)
- Two sample meals for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
- Three sample meals and two snacks for an older baby (8 to 12 months) from a menu developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Your little one may eat less or more than what's shown here. Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Photo credit: iStock.com / UntitledImages
Watch for signs your baby is full
Lots of factors – including activity level, growth spurts or plateaus, illness, and teething – will affect your baby's appetite, which can vary daily.
End feeding when they signal that they're done. Signs of being full include:
- Turning their head away
- Refusing to open their mouth for another bite after they've swallowed (resist the urge to encourage your baby to have one last spoonful)
- Leaning back in their chair
- Playing with the spoon or food rather than eating
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 4- to 6-month-old should eat
When your baby is developmentally ready for solids, typically around 4 to 6 months, talk to their doctor about introducing solid foods.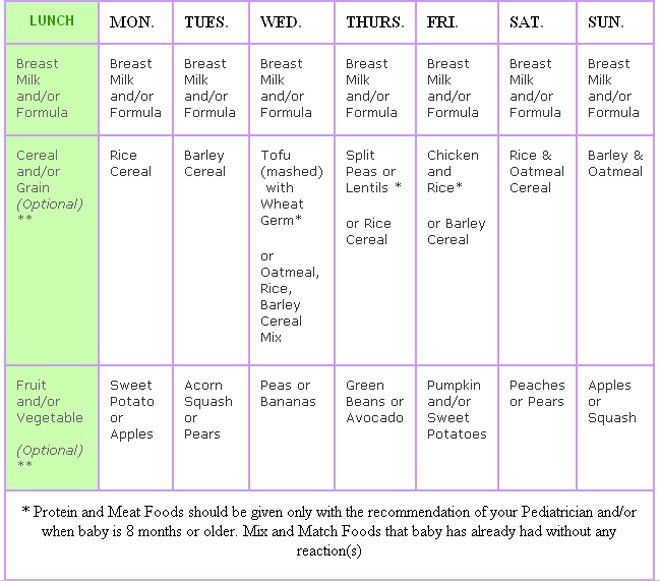 The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
- Start with a very small amount, 1 to 2 teaspoons, of a single-ingredient puree.
- Gradually increase to 1 to 2 tablespoons of food once a day.
- Follow your baby's fullness cues.
Popular first foods include pureed mango, banana, chicken, turkey, beef, peas, sweet potatoes, and infant cereal. It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 6- to 8-month-old should eat
As your little one gets more comfortable with solids, you can increase the frequency of meals and variety of food.
- Transition from one to two meals a day, typically by 8 months.
- Over time, add a second food to each meal.
 The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods.
The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods. - Once you've worked up to two meals with two foods each, aim for a balance of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains in their daily diet.
- Whenever you introduce a new food, start with a very small amount, a teaspoon or two, to allow your baby to get used to its flavor and texture.
- Start with a soupy consistency. Gradually add more texture as their eating skills improve.
Expect their intake of breast milk or formula to go down. They'll start drinking less of it as they eat more solid foods. Provide healthy options at mealtimes, and let them choose how much to eat.
Note: The jars in all photos are standard 4-ounce baby food jars.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
Cereal and fruit make an easy combination for a morning meal.
Grain: Iron-fortified, whole-grain infant cereal is a popular first grain. At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
Fruit: Babies love the natural sweetness of fruits like pears, apples, berries, prunes, and stone fruits. Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of fruit puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) of mashed or minced fruit.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
If you serve a grain and fruit in the morning, consider offering a protein-rich food and vegetable later in the day. Your child may eat more or less than the amounts shown.
Protein: A baby might transition from eating 1 to 2 tablespoons of meat puree at 6 months to 2 to 4 tablespoons at 8 months, for example. Other good protein sources include cheese, unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt, tofu, beans, and lentils.
Vegetables: Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of vegetable puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup). Try classic favorites like carrots, spinach, or butternut squash, as well as less traditional first foods such as parsnips, beets, or asparagus.
As your child's eating skills improve, gradually add more texture by dicing or mincing foods.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much an 8- to 12-month-old should eat
By 8 months or so, your baby is likely getting the hang of eating and needs to eat more calories to support their growing body. But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
During this period:
- Continue to give your baby breast milk or formula.
- Add morning and afternoon snacks. (Some babies this age are happy with breast milk or formula as their snack, while others gravitate toward solid foods.
 ) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
- Continue to aim for a mix of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Introduce coarser and chunkier textures, for example, by dicing or mincing food instead of pureeing it, and graduate to soft finger foods as your baby's eating skills improve.
- Avoid foods with added sugars. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars."
- Provide healthy options, and let your baby choose how much to eat.
To visualize daily portions for an 8- to 12-month-old, check out the following photos of a typical day's menu for a baby this age, developed by the AAP.
Your child may eat more or less than these amounts. If you're concerned about how much your baby is eating, talk to their doctor for advice.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a breakfast consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) whole-grain infant cereal mixed with formula or breast milk
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Morning snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a morning snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Note: This is an example of a morning snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Lunch for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a lunch consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt or cottage cheese, or minced meat
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced or mashed yellow or orange vegetable
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Afternoon snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features an afternoon snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit or unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 whole-grain teething biscuit or cracker
Note: This is an example of an afternoon snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months.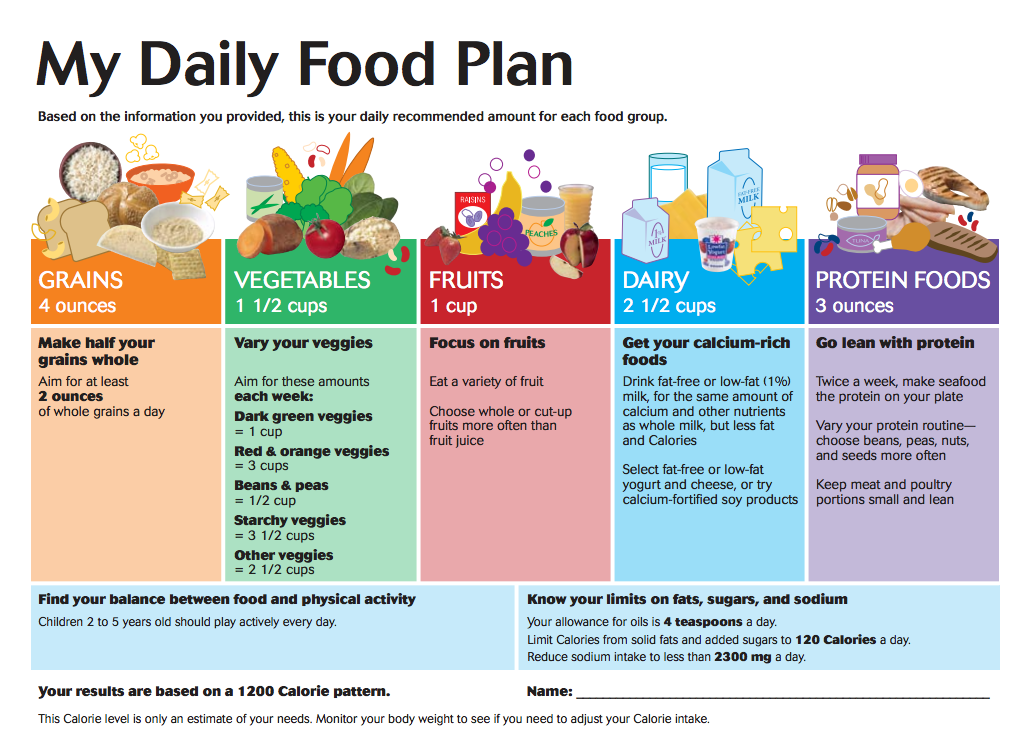 Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a dinner consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) minced or ground poultry or meat, or diced tofu
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2) cup diced, cooked green vegetable
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) noodles, pasta, rice, or potato
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby drink once they start eating solids?
Breast milk or formula will fully meet your child's hydration needs until they're about 6 months old. They may start drinking less as solid foods become a bigger part of their diet. Here are typical daily amounts by age – your baby's intake may be different, however.
6 to 8 months: 24 to 32 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
8 to 12 months: 24 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
Water: You can offer your baby water once they start eating solids, but let them self-regulate how much they drink. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving babies who are 6 to 12 months old 4 to 6 ounces of water a day, but what your baby decides to drink may vary. They may drink more on a hot day, for example.
Avoid juice: Juice isn't recommended for babies younger than 12 months.
Photo credit: iStock.com / SDI Productions
Your baby has the final say
Keep in mind that these portions are an estimate. The truth is, every baby is different, and there's no set amount of food that's appropriate for every baby at every stage.
If you're worried about whether your baby is eating enough – or too much – the best advice is to look for and respond to signs that your baby is full.
Your baby's doctor will chart their weight gain at regular intervals. If the doctor sees a consistent growth curve and doesn't have other concerns, your baby is most likely eating the right amount of food.
Hungry for more?
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
The 10 best foods for babies
The worst foods for babies
Using spices and seasoning in baby food
Elizabeth Dougherty
Elizabeth Dougherty is a veteran parenting writer and editor who's been contributing to BabyCenter since 2015. She's an intrepid traveler, devoted yogi, and longtime resident of Silicon Valley, where she lives with her husband and son.
Advertisement | page continues below
How much food should a child eat? What is a serving or serving size for a child? - Encyclopedia Baby food
Levchuk Victoria©
Moms often ask these questions, don't they? Most pediatricians will say, "Feed your baby as much as he can eat."
When a baby is introduced to complementary foods, make sure he is still getting the right amount of formula and/or mother's milk. Solid foods at an early stage are meant to be practiced. Complementary foods are not intended to provide complete nutrition to the baby like formula and/or breast milk.
Solid foods at an early stage are meant to be practiced. Complementary foods are not intended to provide complete nutrition to the baby like formula and/or breast milk.
Contents:
How much solid food a child should eat depends on many different things.
It should not be forgotten that the child is a human being and, like all of us, he has his own appetite. This affects how much complementary foods he will eat. As with adults, some babies eat more than others due to their individual appetite. Below are some of the main points that are important to remember when feeding your baby.
- A baby who was introduced to solid foods at four months of age is likely to eat more solid foods than a baby who first tried food at six months of age.
- A child who eats soft cut foods eats less than a child who is fed pureed foods.
- A child who is sick or teething may eat less than a few days ago, and then suddenly develops an atypical appetite.
- A child who is busy studying a carpet or a new book may not be interested in food at the moment.

- Naturally, growth retardation in infants also affects appetite. It can be brutal for weeks or days, and then all of a sudden, the child refuses to eat. Children who experience frequent growth spurts will tend to reduce their food intake during growth retardation.
How does a mother know if a child is eating enough adult food?
All pediatricians will say: "A child will never go hungry!" A huge number of healthy children will eat the right amount of food that they need. Parents need to fight the urge to offer "just one more bite" when a child shows they're done. After all, you don’t want to accidentally disrupt the child’s developing ability to self-regulate their feeding by continuing to try to feed or feed the child. It is important for parents to pay attention to the baby's signals, as the baby's feeding patterns will change daily and can be affected by the activities around him. By offering a good balanced diet, you can ensure that your child is eating the right amount of nutrients.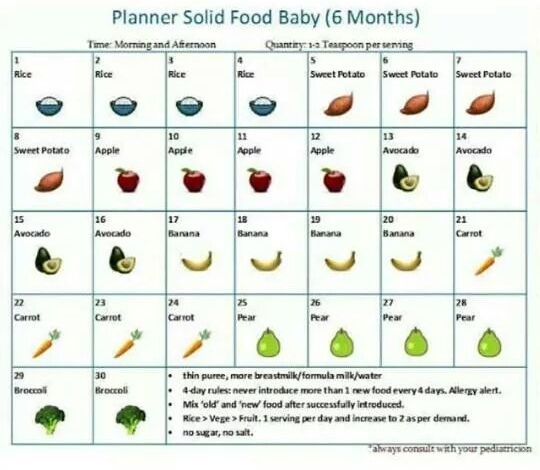
Feeding example
Babies should be able to sit up on their own and spoon feed before introducing complementary foods.
Why can't a mother introduce complementary foods to a child under 4 months of age? Introducing solid foods too early means that the baby receives less breast milk during infancy, and this reduces the chance of receiving the optimal benefits of protection against infection.
What to feed the baby:
Formula milk or mother's milk every 1-3 hours, formula milk 500-1200 grams per day seems hungry after the main breastfeeding, the baby is ready for the introduction of complementary foods! The child should be able to hold his head well, close his mouth with a spoon, and move food towards the back of his mouth. You can read all the signs of readiness for weaning here.
How to feed a child:
Dairy mixture or mother's milk
1-3 tablespoons of food for 1 or 2 dishes
-
6-8 months:
Dairy mixture and / or maternal milk still the main food at this age. Babies in this period are just starting solid foods, so the diet tried at 4-6 months of age will also apply. Some children can eat up to 230 grams of solid food 2-3 times a day.
Babies in this period are just starting solid foods, so the diet tried at 4-6 months of age will also apply. Some children can eat up to 230 grams of solid food 2-3 times a day.
What to feed the baby:
Formula milk or mother's milk
Complementary foods 2-3 times a day.
-
8-10 months:
Many babies will eat 3 meals a day at this stage; including cereals, fruits, vegetarian dishes, breads and meats, maybe eggs.
It is important for parents to pay attention to the baby's signals, as the baby's feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the activities around him. The child will eat only the right amount of food for himself.
How to feed a child:
Dairy mixture or maternal milk
Power feeding 3 times a day
-
10-12 months:
Many children will eat 3 times a day at this stage; including cereals, fruits, vegetarian dishes, bread, meat, fish, eggs.
It is important for parents to pay attention to the baby's signals, as the baby's feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the activities around him. The child will eat only the right amount of food for himself.
How to feed a child:
Dairy mixture or maternal milk
PRODUCT 3 times a day plus 2 additional snacks
Signs that the child wants to eat:
- leans behind a spoon
- Open Rot
- Grabs food and tries to put it in the mouth
Signs that the baby is full
- Closing the mouth when a spoon approaches it
- Spitting out food while feeding
- Turning the head to the side when the spoon approaches
A healthy, well-fed baby should wet diapers regularly and also have bowel movements once or twice a day.
When visiting a doctor, it is necessary to make sure that the child is healthy in order to properly monitor the child's height and weight according to the schedule.
If there is any doubt about feeding the baby, the pediatrician should be consulted about the foods and amounts of solid food. The doctor should be able to help arrange feedings as well as help allay concerns.
It is important to remember to consult with your pediatrician regarding the introduction of complementary foods for your baby and to specifically discuss any foods that may pose an allergy risk to your baby.
There are no two identical children who will eat the same foods. And the amount of food for each child individually!
To calculate your daily milk intake, you can use the following:
All of the baby's signals during feeding tell him that the baby is eating the right amount of food for him.
There is no exact rule or guideline for how much a child should eat during the day. Simply because every child is different. Babies will eat and drink as much formula or mother's milk as they need.
For example, one 7-month-old baby eats 2 whole jars of baby food in one day while another 7-month-old baby barely manages to eat one. Also, one child can eat every 2 hours in his 7 months, and the other every 3-4 hours. Again, each child has different nutritional and milk needs and these needs are tailored to the individual.
4 to 6 months
Breast milk is the best food for your baby.
It is very important that the baby consumes breast milk for as long as possible.
The right age to start complementary foods
It is recommended to start introducing complementary foods into the baby's diet no earlier than 4 months, but no later than 6 months*. At this age, the baby is in the active phase of development and reacts with curiosity to everything new! Some babies at 4 to 5 months of age can no longer satisfy their appetite with breast milk alone and need complementary foods for healthy growth. Other children have enough breast milk, and they are ready for the introduction of complementary foods only after 6 months. The decision to start complementary foods should always be made according to your baby's development. Do you feel like your baby is not getting enough breast milk? Does your baby hold his head on his own, show interest in new foods or a spoon? Then it's time to start feeding. If in doubt, consult your pediatrician.
The decision to start complementary foods should always be made according to your baby's development. Do you feel like your baby is not getting enough breast milk? Does your baby hold his head on his own, show interest in new foods or a spoon? Then it's time to start feeding. If in doubt, consult your pediatrician.
If your baby spits out the first spoonfuls of puree, be patient. After all, he must first learn to swallow it. Start with a few scoops and give your child time to get used to the new form of feeding.
*Recommendation of the Nutrition Committee of the European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN)
Why is complementary foods important for the baby?
After 4-6 months of life, mother's milk or milk formula alone is not enough to supply the child's body with all the nutrients and necessary energy. In addition, the transition to solid food trains the muscles of the mouth. And finally, with the introduction of complementary foods, the child will get acquainted with the variety of taste directions, which is also important for his development.
When to start complementary foods?
Gradually replace one breastfeed with complementary foods. First for lunch, then for dinner and finally for lunch. The mouse eats breakfast with the usual dairy food.
Starting complementary foods with HiPP products is easy. The first spoonfuls will be vegetable or fruit purees HiPP:
First step: lunch
We recommend that you start complementary foods at lunchtime with HiPP vegetable puree (for example, "Zucchini. My first puree", "Cauliflower. My first puree" or "Broccoli .My first puree"). Then, for satiety, feed your baby as always: breast or bottle. The amount of vegetable puree can be increased daily by 1 spoon. Be patient if your baby does not immediately love vegetables. Try repeating the vegetable puree in the following days. Next week, you can expand your diet with other varieties of HiPP vegetables (for example, "Carrots. My first puree" or "Potatoes. My first puree").
If your baby tolerates vegetables well, in the third week you can introduce cereal porridge into the diet, and as a dessert, offer a few spoons of fruit puree enriched with vitamin C.