How much does ccms pay per child in texas
Reimbursement Rates | Workforce Solutions for North Central Texas
Maximum Reimbursement Rates
The North Central Texas Workforce Development Board sets the maximum rate that will be reimbursed to a provider caring for a CCS child. These rates are set based on a market rate survey that considers the age of the child and the amount of time he/she receives care each day. Enhanced rates are paid to CCS Providers who attain certifications as Texas Rising Star (TRS) or Texas School Ready (TSR). Child Care Services is not allowed to reimburse a provider above their actual published rate, which is the rate non-TWC subsidy families pay.
LCCC = Licensed Child Care Center
LCCH = Licensed Child Care Home
RCCH = Registered Child Care Home
FT = Full Time
PT = Part Time
| Provider Type | Provider Rating | Inf-FT | Inf-PT | Tod-FT | Tod-PT | Pre-FT | Pre-PT | Sch-FT | Sch-PT | Inf-BT | Tod-BT | Pre-BT | Sch-BT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCCC | Reg | LCReg | 4LCReg | $44. |
$39.40 | $42.00 | $37.00 | $39.60 | $31.20 | $37.80 | $29.40 | $40.19 | $37.85 | $32.63 | $30.83 |
| LCCC | TRS2 | LC2 | 4LC2 | $47.04 | $41.37 | $44.10 | $38.85 | $41.58 | $32.76 | $39.69 | $30.87 | $42.20 | $39.75 | $34.27 | $32.38 |
| LCCC | TRS3 | LC3 | 4LC3 | $47.94 | $42.16 | $44.94 | $39.59 | $42.38 | $33. 39 39 |
$40.45 | $31.46 | $43.01 | $40.50 | $34.92 | $32.99 |
| LCCC | TRS4 | LC4 | 4LC4 | $52.40 | $46.80 | $46.40 | $41.00 | $43.18 | $34.02 | $41.21 | $32.05 | $47.62 | $41.92 | $35.58 | $33.61 |
| LCCC | TSR | LCTSR | 4LCTSR | $44.80 | $39.40 | $42.00 | $37.00 | $41.58 | $32.76 | $37.80 | $29.40 | $40.19 | $37.85 | $34. 27 27 |
$30.83 |
| LCCH | Reg | LHReg | 4LHReg | $39.80 | $36.60 | $37.60 | $34.80 | $36.60 | $32.00 | $35.00 | $29.80 | $37.07 | $35.28 | $32.79 | $30.69 |
| LCCH | TRS2 | Lh3 | 4Lh3 | $41.79 | $38.43 | $39.48 | $36.54 | $38.43 | $33.60 | $36.75 | $31.29 | $38.92 | $37.04 | $34.42 | $32.22 |
| LCCH | TRS3 | Lh4 | 4Lh4 | $42. 59 59 |
$39.17 | $40.24 | $37.24 | $39.17 | $34.24 | $37.45 | $31.89 | $39.67 | $37.75 | $35.08 | $32.84 |
| LCCH | TRS4 | Lh5 | 4Lh5 | $46.40 | $41.80 | $42.00 | $37.94 | $39.91 | $34.88 | $38.15 | $32.49 | $42.47 | $38.63 | $35.74 | $33.46 |
| LCCH | TSR | LHTSR | 4LHTSR | $39.80 | $36.60 | $37.60 | $34.80 | $38.43 | $33. 60 60 |
$35.00 | $29.80 | $37.07 | $35.28 | $34.42 | $30.69 |
| RCCH | Reg | RHReg | 4RHReg | $37.20 | $34.00 | $35.00 | $32.00 | $32.80 | $27.20 | $27.80 | $26.40 | $34.47 | $32.51 | $28.16 | $26.64 |
| RCCH | TRS2 | Rh3 | 4Rh3 | $39.06 | $35.70 | $36.75 | $33.60 | $34.44 | $28.56 | $29.19 | $27.72 | $36.19 | $34.14 | $29.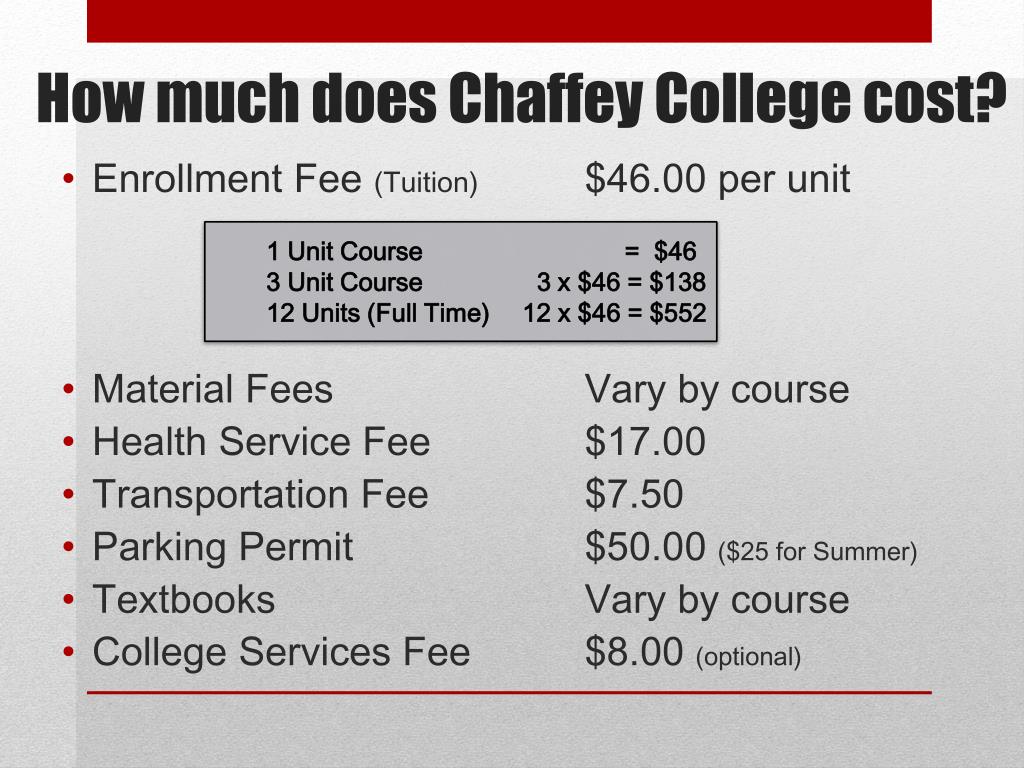 56 56 |
$27.97 |
| RCCH | TRS3 | Rh4 | 4Rh4 | $39.96 | $36.38 | $37.45 | $34.24 | $35.10 | $29.11 | $29.75 | $28.25 | $36.90 | $34.79 | $30.13 | $28.51 |
| RCCH | TRS4 | Rh5 | 4Rh5 | $44.40 | $38.80 | $40.00 | $34.88 | $35.76 | $29.66 | $30.60 | $28.78 | $39.62 | $35.75 | $30.70 | $29.09 |
| RCCH | TSR | RHTSR | 4RHTSR | $37. 20 20 |
$34.00 | $35.00 | $32.00 | $34.44 | $28.56 | $27.80 | $26.40 | $34.47 | $32.51 | $29.56 | $26.64 |
| Relative | Reg | Relative | 4Relative | $13.00 | $11.00 | $13.00 | $11.00 | $13.00 | $11.00 | $13.00 | $11.00 | $11.29 | $11.34 | $11.34 | $11.34 |
Reimbursement Schedule
FY23
Get Newsletter Updates
Sign up to be the first to hear about Workforce Solutions in your area
Subscribe
COST OF CHILD CARE IN TEXAS: A BREAKDOWN FOR 2022
By Paulina Richter – Last updated
Are Texas Child Care Costs as Bad as They Seem?
You’ve probably seen your local news talking about how the cost of child care in Texas is rising in 2022, and if you haven’t, you’ll be surprised to hear how child care is evolving. In fact, child care in Texas can be more expensive than a public college education. A study commissioned by MarketWatch discovered that the average cost of child care for a 4 year old reached $7000 annually.
In fact, child care in Texas can be more expensive than a public college education. A study commissioned by MarketWatch discovered that the average cost of child care for a 4 year old reached $7000 annually.
Whether you’re a new or existing parent, you’re probably anxious about how you’re going to afford quality childcare. The fear is that costs will continue to rise until they are simply unaffordable. Furthermore. The Economic Policy Institute found that one of the biggest overhead costs a family bears in Texas is childcare. In fact, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Service Standards revealed in a study that child care for infants is affordable for only 15.8 percent of Texas families.
It’s no surprise that parents across Texas are upset and concerned that they simply won’t be able to manage child care fees.
What Are Child Care Costs In Texas in 2022?
First, let’s look at the State overall. We’ll focus on the total average monthly cost per age group for daycare and child care. Texas Health And Human Services qualifies it as: “Child day care includes center-based and home-based operations that provide care for children 13 years or younger for less than 24 hours a day while parents or guardians are at work or school. This includes Child Care Centers, School-age Program, Before or After-School Programs, Licensed Child Care Homes, Registered Child Care Homes, and Listed Family Homes.”
Texas Health And Human Services qualifies it as: “Child day care includes center-based and home-based operations that provide care for children 13 years or younger for less than 24 hours a day while parents or guardians are at work or school. This includes Child Care Centers, School-age Program, Before or After-School Programs, Licensed Child Care Homes, Registered Child Care Homes, and Listed Family Homes.”
The cost of child care changes depending on the age group. For this guide, we’ll look at the averages for pre-school child care and after school childcare.
Average Pre School Childcare Costs In Texas
According to the Economic Policy Unit: “The average annual cost of infant care in Texas in 2022 is $9,324—that’s $777 per month. Child care for a 4-year-old costs $7,062—or $589 each month.”
Average After School Childcare Costs In Texas
According to the 2021 Cost Of Care Survey, the national average for after-school child care is $976 (based on 15 hours per week). The average in Texas is $184.65, making Texas significantly lower than the national average.
The average in Texas is $184.65, making Texas significantly lower than the national average.
How Do Child Care Costs Compare Across the Top 10 Cities in Texas in 2022?
Now that we’ve seen that childcare costs are below the US average, let’s drill down further and look if they’re different across Texas. According to Numbeo, The Cost of Living Index, child care costs per month range from:
- Houston Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $944.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $840.
- San Antonio Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $815.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $697.
- Dallas Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $1049.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $850.
- Austin Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $1020.

- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $960.
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $1020.
- Fort Worth Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4 years old), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $933.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $747.
- El Paso Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $523.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $652.
- Arlington Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $933.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $720.
- Corpus Christi Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $703.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $690.
- Plano Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $945.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week for 1 Child $840.
- Laredo Child Care
- Preschool (Aged 1-4), Full Day, Monthly for 1 Child: $470.
- After School (Aged 5-13) based on 15 hours per week) for 1 Child $750.
As you can see, there is a significant difference between:
- The highest monthly rate pre-school rate in Dallas, at $1049 and Laredo at $470
- The highest monthly after school rate in Austin at $960 and El Paso at $652
Why Does Child Care Cost So Much In Texas?
When calculating where your child care dollar goes, it’s important to check out how the total cost per month breaks down. For instance, childcare centers offer a range of extras, including:
- Special food requirements
- Extra activities, e.g. yoga or learning a second language for older kids
- Attractions and days out
- Facilities to accommodate special needs
When choosing childcare, it’s always best to check what’s optional and if you really need it. Getting the best deal by cutting out unnecessary extras is critical in choosing the right child care package. This is a great way to determine what’s a fair price for child care.
This is a great way to determine what’s a fair price for child care.
What Are The Other Issues Parents Face When Trying To Get Childcare?
The impact of rising child care costs on parents in Texas is really focused on 2 main issues:
- Lack of day care centers. Because of the pandemic, the closing of child care centers has sped up. The result, a massive shortfall in provision.
- Lower-income families simply can’t afford it.
According to the Economic Policy Institute: “Child care is out of reach for low-wage workers. A minimum wage worker in Texas would need to work full time for 32 weeks, or from January to August, just to pay for child care for one infant.”
What Qualifications Do Day Care Center Staff Need In Texas?
When looking at choosing a child care center, it’s a good idea to check out the provider’s qualifications. Because of the vulnerable nature of specific jobs, Texas State prescribes staff are over 18 years old and hold a high school diploma or an equivalent certification relevant to the position.
Do Family Child Care Centers Need To Be Licensed In The State Of Texas?
All child care centers that care for 1-3 children are required to be licensed with the State of Texas. They are required to follow several detailed and strict standards in order to be qualified. If you’re considering one, feel free to give each of them a thorough examination, but also feel secure in the standards set by the Texas Health and Human Services Commission. If the center cares for over 6 kids, then they have to be registered and meet other state requirements.
How Texas Child Care Costs Compare to Other States
A comparison of the 10 states with the highest child care, preschool, infant care, and day care annual costs in 2022:
- Massachusetts ($20,913)
- California ($16,945)
- Minnesota ($16,087)
- Connecticut ($15,591)
- New York ($15,394)
- Maryland ($15,335)
- Colorado ($15,325)
- Washington ($14,554)
- Virginia ($14,063)
- Illinois ($13,802)
Monthly allowance for a child of a serviceman who is doing military service on conscription
The applicant has the right to file a complaint against the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services (complaint), including in the pre-trial (out of court) procedure in the following cases:
- violation of the application registration deadline;
- violation of the term for the provision of public services; nine0005 requirement from the applicant for documents, information or actions not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them;
- refusal to accept documents, the submission of which is provided for by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services; nine0006
- requesting from the applicant, when providing a public service, a fee not provided for by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
- refusal of the authorized body, its officials to correct the misprints and errors made by them in the documents issued as a result of the provision of public services or violation of the deadline for such corrections;
- violation of the term or procedure for issuing documents based on the results of the provision of public services; nine0006
- suspension of the provision of public services, if the grounds for suspension are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts.

Subject of complaint
The subject of the complaint is a violation of the rights and legitimate interests of the applicant, unlawful decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services, violation of the provisions of the administrative regulations and other regulatory legal acts that establish requirements for the provision of public services. nine0003
Ways to make a complaint
A citizen has the right to file a complaint in writing on paper by mail or in person to any PFR Client Service, as well as in electronic form:
- on the official website pfr.gov.ru;
- portal vashkontrol.ru;
- portal do.gosuslugi.ru.
The reason for the appeal may be dissatisfaction with the quality of the provision of public services by the PFR, violation of the terms for the provision of services, violation of the terms for registering a request for a service, refusal to correct errors or typos, refusal to provide a public service, refusal to accept documents, demand for an additional fee. nine0003
nine0003
Procedure for filing and handling a complaint
The complaint must contain:
- name of the authorized body, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of its officials providing public services, and (or) their leaders, decisions and actions (inaction) of which are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant, information about the place of residence, as well as contact phone number (numbers), e-mail address (s) (if any) and postal address to which the answer should be sent to the applicant; nine0006
- information about the appealed decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head;
- arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head.
The applicant shall submit documents (if any) confirming his arguments or copies thereof.
When filing a complaint in electronic form, the documents specified in paragraph 106 of the administrative regulations may be submitted in the form of an electronic document signed with an electronic signature, the form of which is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. In this case, an identity document of the applicant is not required.
In the authorized body, officials authorized to consider complaints are determined, who ensure:
- receiving and handling complaints; nine0006
- sending complaints to the body authorized to consider them.
Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of an official of the authorized body are considered by the head of the authorized body or an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints. Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the head of the authorized body are considered by an official of the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation authorized to consider complaints.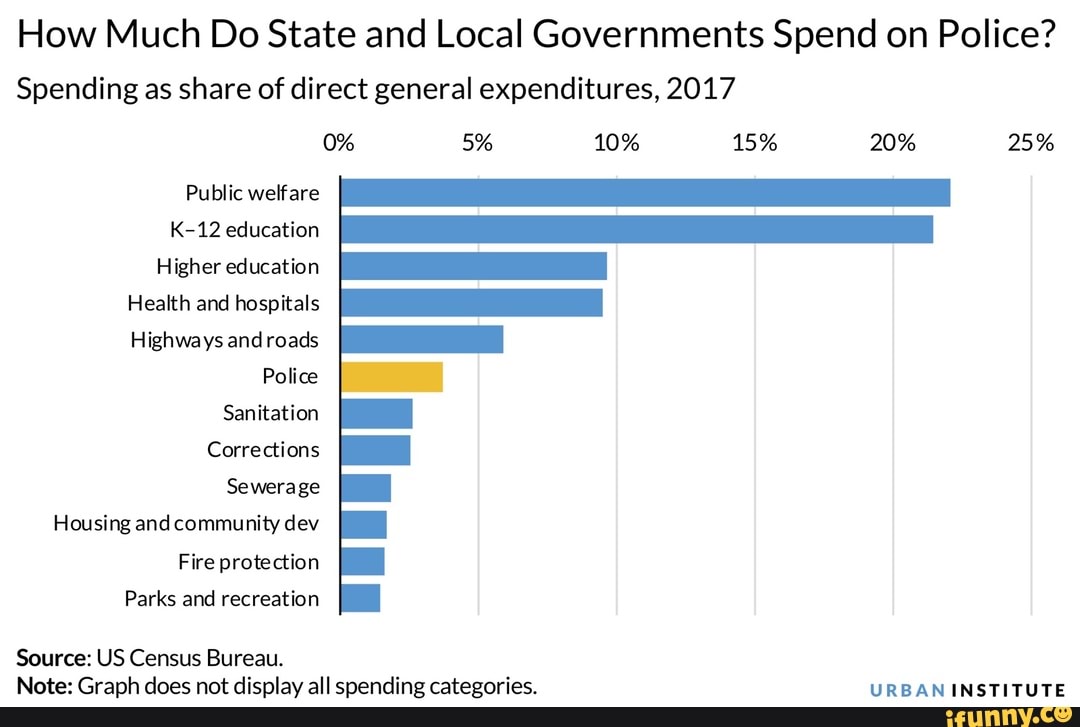 nine0003
nine0003
If the complaint is filed by the applicant with a body whose competence does not include making a decision on the complaint, within 3 working days from the date of its registration, the said body sends the complaint to the body authorized to consider it and informs the complainant in writing about the redirection of the complaint.
The authorized body ensures:
- equipment for receiving complaints;
- informing applicants about the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body by posting information on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single portal, service portal; nine0006
- advising applicants on the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body at a personal appointment, by phone, using the website of the authorized body;
- conclusion of agreements on interaction between the multifunctional center and the authorized body in terms of the implementation by the multifunctional center of receiving complaints and issuing the results of consideration of complaints to the applicant;
- formation and quarterly submission to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment of reports on complaints received and considered (including the number of satisfied and unsatisfied complaints).
 nine0006
nine0006
Deadlines for considering a complaint
A complaint received by the authorized body shall be subject to registration no later than the working day following the day of its receipt.
The complaint is subject to consideration within 15 working days from the date of its registration, and in the event of an appeal against the refusal of the authorized body to accept documents from the applicant or to correct misprints and errors, or in the event of an appeal against a violation of the established deadline for such corrections - within 5 working days from the date of its registration. nine0003
Result of consideration of the complaint
The result of the consideration of the complaint is the adoption of one of the following decisions:
- satisfy the complaint, including in the form of cancellation of the decision made by the authorized body, correction of typos and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services, return to the applicant of funds, the collection of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the subjects Russian Federation, municipal legal acts; nine0006
- refuse to satisfy the complaint.

When satisfying the complaint, the authorized body takes comprehensive measures to eliminate the identified violations, including the issuance of the result of the public service to the applicant no later than 5 working days from the date of the relevant decision, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A complaint may be denied in the following cases:
- availability of a court decision that has entered into legal force on a complaint about the same subject and on the same grounds;
- filing a complaint by a person whose powers have not been confirmed in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of a decision on a complaint made earlier in accordance with the requirements of the Rules for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations endowed with in accordance with federal laws, the powers to provide public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.
 1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0006
1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint. nine0006
A complaint may be left unanswered in the following cases:
- presence in the complaint of obscene or offensive expressions, threats to life, health and property of an official of the authorized body, as well as members of his family;
- the inability to read any part of the text of the complaint, the last name, first name, patronymic (if any) and (or) the postal address of the applicant indicated in the complaint.
In response to the results of the consideration of the complaint, the following shall be indicated: nine0003
- name of the public service provider that considered the complaint, position, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the official who made the decision on the complaint;
- number, date, place of the decision, including information about the official of the authorized body, the decision and (or) action (omission) of which is being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant;
- grounds for making a decision on the complaint; nine0006
- decision made on the complaint;
- if the complaint is found to be justified, the terms for eliminating the identified violations, including the term for providing the result of the public service;
- information on the procedure for appealing against the decision taken on the complaint.
In the event that, during or as a result of consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints shall send the available materials to the prosecutor's office. nine0003
The procedure for informing the applicant about the results of the consideration of the complaint
A reasoned response based on the results of the consideration of the complaint is signed by the official authorized to consider the complaint and sent to the applicant in writing or, at the request of the applicant, in the form of an electronic document signed by the electronic signature of the official authorized to consider the complaint, the type of which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, no later than the day following the day the decision is made on the results of the consideration of the complaint. nine0003
Procedure for appealing a decision on a complaint
The applicant has the right to appeal the decision taken on the complaint by sending it to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment.
If the applicant is not satisfied with the decision made during the consideration of the complaint or the absence of a decision on it, then he has the right to appeal the decision in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The applicant's right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint
The applicant has the right to receive comprehensive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint.
Ways to inform complainants about the procedure for filing and considering a complaint
Information on the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is posted on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single Portal, Services Portal, and can also be communicated to the applicant orally and (or) in writing. nine0003
List of regulatory legal acts regulating the procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) of the authorized body, as well as its officials
The procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeals against decisions and actions (inaction) of the body providing the public service, as well as its officials, is regulated by Federal Law No. 210-FZ of July 27, 2010 “On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services” and the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 16 .2012 No. 840 “On the procedure for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations vested in accordance with federal laws with powers to provision of public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of I am state and municipal services and their employees”. nine0003
210-FZ of July 27, 2010 “On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services” and the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 16 .2012 No. 840 “On the procedure for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations vested in accordance with federal laws with powers to provision of public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of I am state and municipal services and their employees”. nine0003
Motherhood in America
Among the promises made by Democratic candidates in this campaign, there is a full paid maternity leave.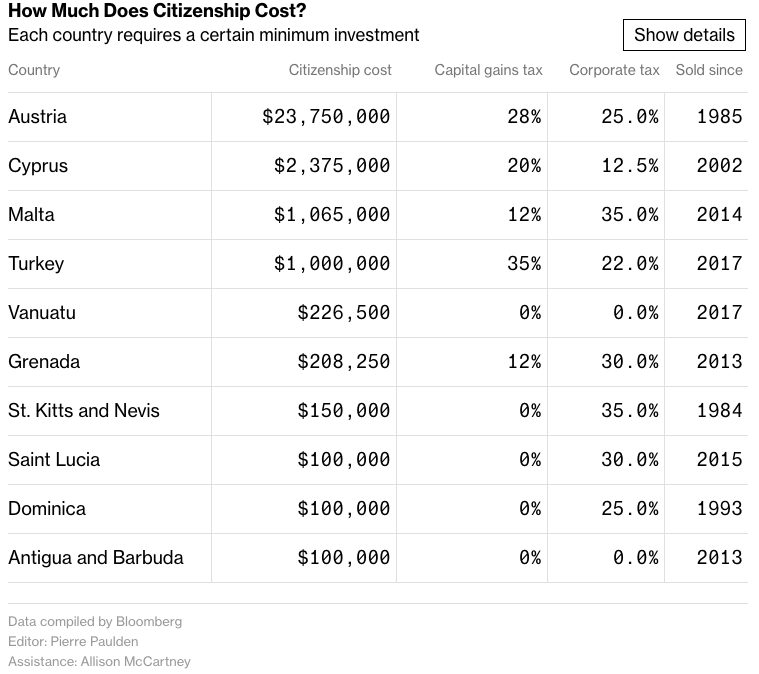 Hillary Clinton and Bernie Sanders advocate 12 weeks of paid family leave. Interestingly, Republican candidates avoid this topic. Some states have decided not to wait for the issue to be resolved at the federal level. New York recently legalized part-paid maternity leave, becoming the fourth state to guarantee paid leave for mothers. Why is the US the only developed country without paid maternity leave? Details - video report. nine0003
Hillary Clinton and Bernie Sanders advocate 12 weeks of paid family leave. Interestingly, Republican candidates avoid this topic. Some states have decided not to wait for the issue to be resolved at the federal level. New York recently legalized part-paid maternity leave, becoming the fourth state to guarantee paid leave for mothers. Why is the US the only developed country without paid maternity leave? Details - video report. nine0003
The mother of a ten-month-old boy named Sam says that she had to leave her job when her son was born.
“I could have kept my job, but all my earnings would have gone to pay for kindergarten, so there was no point,” says Laura. “If we had the opportunity to go on maternity leave for a year while maintaining our salary, it would be nice, because this is how it is done in many developed countries.”
In the US, this is not possible even in the most generous states such as California, New Jersey, Rhode Island, and New York, where women can take short, part-paid maternity leave. nine0003
nine0003
Women's Economic Policy labor law expert Sarah Glyin explains the situation:
“Only in these states, having a baby doesn't hit the family budget that hard. California pays 55 percent of wages for six weeks, New Jersey pays 67 percent of wages for six weeks, Rhode Island is only 4 weeks, and New York has been the most generous, and in the near future will fully pay new mothers 12 weeks of maternity and parental leave. There are no such programs at the federal level yet.” nine0003
Employers are required by US federal law to give mothers 12 weeks of unpaid maternity leave. Companies with less than 50 employees are excluded from this law - for them it is financially burdensome.
Many mothers return to work a few weeks after the birth of a child, 25 percent even two weeks later, unless, of course, they have come up with some ingenious way to pay the bills. For example, fundraising through social networks has recently become popular. nine0003
Experts blame the current situation on the outdated labor code of 1930, which legislators stubbornly refuse to revise.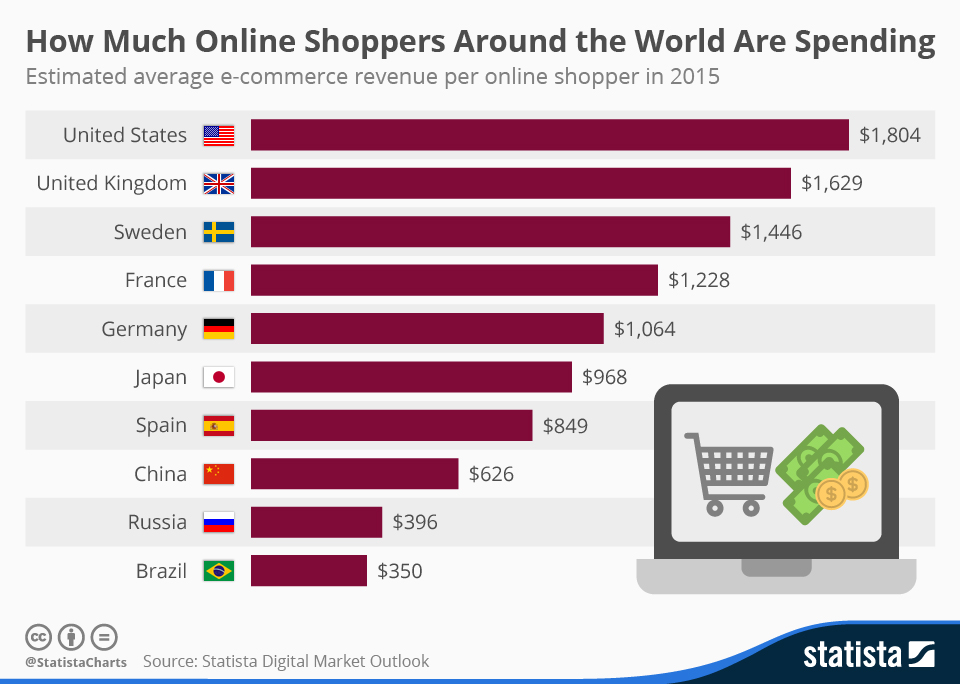 In the first half of the twentieth century, a working man could well provide for his family, while a woman raised children.
In the first half of the twentieth century, a working man could well provide for his family, while a woman raised children.
“Legislators will never understand that most women are working today,” says Glyn. – And among them there are many mothers, including mothers with newborn children. Laws adopted decades ago do not reflect the current realities of the economy.” nine0003
However, some American companies are adapting to the new requirements of employees and provide maternity leave not only for mothers, but also for fathers.
Joe is the father of a newborn boy. He is pleased to receive six weeks of paid leave for young parents:
“It is the choice of employers whether to pay maternity leave to employees or not. The best companies do it."
Companies such as Adobe, Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Google and YouTube work this way. When looking for promising employees, business takes into account the desire of an employee to have the opportunity of paid maternity leave.