How early in pregnancy can braxton hicks start
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
If you feel tightening or cramping in your abdomen during your pregnancy, you may be having Braxton Hicks contractions. This is normal and not a sign that you’re ready to give birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions are sometimes called ‘false’ or ‘practice’ contractions.
What are Braxton Hicks contractions?
Braxton Hicks contractions are a tightening in your abdomen that comes and goes. They are contractions of your uterus in preparation for giving birth. They tone the muscles in your uterus and may also help prepare the cervix for birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions don’t cause labour and aren’t a sign that labour is beginning.
If you’re not sure whether what you’re experiencing is Braxton Hicks contractions or actual labour, contact your doctor or midwife. They will be able to tell by doing a vaginal examination — if there are no signs that your cervix is changing, it is not labour.
What do they feel like?
Braxton Hicks contractions feel like muscles tightening across your belly, and if you put your hands on your belly when the contractions happen, you can probably feel your uterus becoming hard.
The contractions come irregularly and usually last for about 30 seconds. While they can be uncomfortable, they usually aren’t painful.
If the pain or discomfort of your contractions eases off, they’re probably Braxton Hicks contractions.
When do you get them?
Braxton Hicks contractions occur from early in your pregnancy but you may not feel them until the second trimester. If this is your first pregnancy, you might start to feel them from about 16 weeks. In later pregnancies, you may feel Braxton Hicks contractions more often, or earlier. Some women won’t feel them at all.
Some women won’t feel them at all.
In late pregnancy, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions more often — perhaps as much as every 10 to 20 minutes. This is a sign that you are preparing for labour — known as prelabour.
How are Braxton Hicks contractions different from labour pain?
There are some differences between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labour contractions that will help your doctor or midwife decide whether you are in labour:
Braxton Hicks contractions:
- don’t result in your cervix thinning and opening
- usually last for about 30 seconds
- can be uncomfortable, but usually aren’t painful
- come and go at irregular times
- usually occur no more than once or twice an hour (until late in the pregnancy), a few times a day
- usually stop if you change position or activity or go for a walk
- usually go if you have a warm bath or shower
Real labour contractions:
- result in your cervix thinning and opening
- last 30 to 70 seconds
- become very regular
- get closer together
- last longer as time goes by
- get stronger or come more often when you walk
- get stronger over time
Should I call my doctor or midwife?
If you are less than 37 weeks pregnant, contractions can be a sign of premature labour. Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
- you feel pain, pressure or discomfort in your pelvis, abdomen or lower back
- the contractions become stronger, closer together and more regular
- there is fluid leaking or gushing from your vagina
If you are full-term, you may choose to wait until a bit later in your labour, depending on what you have arranged with your doctor or midwife. If your waters break, or your contractions are strong and 5 minutes apart, it’s time to go to the hospital.
As any stage of pregnancy, you should contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you:
- you have persistent pain in your abdomen
- you have vaginal bleeding
- you notice your baby’s movements have slowed or stopped
- you feel very unwell
If you are in doubt, don’t hesitate to call your doctor or midwife for advice.
How can I ease the discomfort?
Braxton Hicks contractions are normal and don’t need treatment. But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
- lying down
- taking a walk
- relaxing in a warm bath
- having a massage
It may help to practise your breathing exercises during your Braxton Hicks contractions.
Sources:
Raising Children Network (23 weeks pregnant), RANZCOG (Labour and birth), Elsevier Patient Education (Braxton Hicks Contractions)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: October 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Giving birth - stages of labour
- Health professionals involved in your pregnancy
- Signs of premature labour
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move position.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Giving birth - contractions
Contractions are when the muscles in your uterus tighten and then relax. They occur throughout the later stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What happens to your body in childbirth
During childbirth, your body's hormones, ligaments and muscles, as well as the shape of your pelvis, all work together to bring your baby safely into the world.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - uterus
The uterus is your growing baby’s home during pregnancy. Learn how the uterus works, nurtures your baby and how it changes while you are pregnant.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Preterm labour - MyDr.com.au
Going into labour before your 37th week of pregnancy is called preterm labour, or premature labour. Find out what it means for you and your baby.
Read more on myDr website
38 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
38 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
26 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
26 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Giving birth - early signs of labour
You can know the early signs of labour, even if you cannot predict when your labour will begin. Find out also what to do if something appears to be wrong.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth
From conception to giving birth, a woman's body goes through many physical changes. Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Braxton Hicks Contractions - StatPearls
Deborah A. Raines; Danielle B. Cooper.
Author Information
Last Update: August 8, 2022.
Continuing Education Activity
Braxton-Hicks contractions, also known as prodromal or false labor pains, are contractions of the uterus that typically are not felt until the second or third trimester of the pregnancy. Braxton-Hicks contractions are the body's way of preparing for true labor, but they do not indicate that labor has begun. Because many pregnant patients have not been educated about Braxton-Hicks contractions, they often seek care and undergo unnecessary evaluation for these contractions. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of patients with Braxton-Hicks contractions and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in educating the patient about the condition.
Braxton-Hicks contractions are the body's way of preparing for true labor, but they do not indicate that labor has begun. Because many pregnant patients have not been educated about Braxton-Hicks contractions, they often seek care and undergo unnecessary evaluation for these contractions. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of patients with Braxton-Hicks contractions and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in educating the patient about the condition.
Objectives:
Describe the etiology of Braxton-Hicks contractions.
Review the presentation of a patient with Braxton-Hicks contractions.
Explain how to evaluate a patient with Braxton-Hicks contractions.
Employ strategies to improve interprofessional communication, which will improve outcomes in patients with Braxton-Hicks contractions.
Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
Introduction
Braxton Hicks contractions are sporadic contractions and relaxation of the uterine muscle.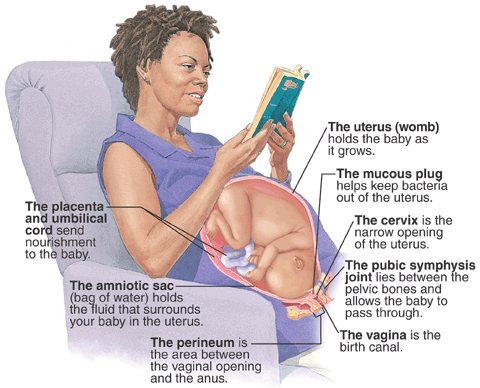 Sometimes, they are referred to as prodromal or “false labor" pains. It is believed they start around 6 weeks gestation but usually are not felt until the second or third trimester of the pregnancy. Braxton Hicks contractions are the body's way of preparing for true labor, but they do not indicate that labor has begun or is going to start.
Sometimes, they are referred to as prodromal or “false labor" pains. It is believed they start around 6 weeks gestation but usually are not felt until the second or third trimester of the pregnancy. Braxton Hicks contractions are the body's way of preparing for true labor, but they do not indicate that labor has begun or is going to start.
Braxton Hicks contractions are a normal part of pregnancy. They may be uncomfortable, but they are not painful. Women describe Braxton Hicks contractions as feeling like mild menstrual cramps or a tightening in a specific area of the abdomen that comes and goes.[1][2][3]
Braxton Hicks contractions can be differentiated from the contractions of true labor. Braxton Hicks contractions are irregular in duration and intensity, occur infrequently, are unpredictable and non-rhythmic, and are more uncomfortable than painful. Unlike true labor contractions, Braxton Hicks contractions do not increase in frequency, duration, or intensity. Also, they lessen and then disappear, only to reappear at some time in the future. Braxton Hicks contractions tend to increase in frequency and intensity near the end of the pregnancy. Women often mistake Braxton Hicks contractions for true labor. However, unlike true labor contractions, Braxton Hicks contractions do not cause dilatation of the cervix and do not culminate in birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions tend to increase in frequency and intensity near the end of the pregnancy. Women often mistake Braxton Hicks contractions for true labor. However, unlike true labor contractions, Braxton Hicks contractions do not cause dilatation of the cervix and do not culminate in birth.
Etiology
Braxton Hicks contractions are caused when the muscle fibers in the uterus tighten and relax. The exact etiology of Braxton Hicks contractions is unknown. However, there are known circumstances that trigger Braxton Hicks contractions including when the woman is very active, when the bladder is full, following sexual activity, and when the woman is dehydrated. A commonality among all these triggers is the potential for stress to the fetus, and the need for increased blood flow to the placenta to provide fetal oxygenation.[4][5][6]
Epidemiology
Braxton Hicks contractions are present in all pregnancies. However, each woman's experience is different. Most women become aware of Braxton Hicks contractions in the third trimester, and some women are aware of them as early as the second trimester. Sometimes Braxton Hick contractions occurring near the end of the third trimester of pregnancy are mistaken as the onset of true labor. It is not unusual, especially in a first pregnancy, for a woman to think she is in labor only to be told it is Braxton Hicks contractions and not true labor.
Sometimes Braxton Hick contractions occurring near the end of the third trimester of pregnancy are mistaken as the onset of true labor. It is not unusual, especially in a first pregnancy, for a woman to think she is in labor only to be told it is Braxton Hicks contractions and not true labor.
Pathophysiology
Braxton Hicks contractions are thought to play a role in toning the uterine muscle in preparation for the birth process. Sometimes Braxton Hicks contractions are referred to as "practice for labor." Braxton Hicks contractions do not result in dilation of the cervix but may have a role in cervical softening.
The intermittent contraction of the uterine muscle may also play a role in promoting blood flow to the placenta. Oxygen-rich blood fills the intervillous spaces of the uterus where the pressure is relatively low. The presence of Braxton Hicks contractions causes the blood to flow up to the chorionic plate on the fetal side of the placenta. From there the oxygen-rich blood enters the fetal circulation.
History and Physical
When assessing a woman for the presence of Braxton Hicks contractions, there are some key questions to ask. Her response to these questions will assist the healthcare provider to differentiate Braxton Hicks contractions and true labor contractions.[7][8][9]
How often are the contractions? Braxton Hicks contractions are irregular and do not get closer together over time. True labor contractions come at regular intervals, and as time goes on, they get closer together and stronger.
How long are the contractions? Braxton Hicks contractions are unpredictable. They may last less than 30 seconds or up to 2 minutes. True labor contractions last between 30 to less than 90 seconds and become longer over time.
How strong are the contractions? Braxton Hicks contractions are usually weak and either stay the same or become weaker and then disappear. True labor contractions get stronger over time.
Where are the contractions felt? Braxton Hicks contractions are often only felt in the front of the abdomen or one specific area.
 True labor contractions start in the midback and wrap around the abdomen towards the midline.
True labor contractions start in the midback and wrap around the abdomen towards the midline.Do the contractions change with movement? Braxton Hicks contractions may stop with a change in activity level or as the woman changes position. If she can sleep through the contraction, it is a Braxton Hicks contraction. True labor contractions continue and may even become stronger with movement or position change.
During the physical assessment, the provider may palpate an area of tightening or a "spasm" of the uterine muscle, but the presence of a uterine contraction in the uterine fundus is not palpable. The woman will be assessed for the presence of uterine bleeding or rupture of the amniotic membrane. An examination of the cervix reveals no change in effacement or dilatation as a result of the Braxton Hicks contractions.
Evaluation
There are no laboratory or radiographic tests to diagnose Braxton Hicks contractions. Evaluation of the presence of Braxton Hicks contractions is based on an assessment of the pregnant woman's abdomen, specifically palpating the contractions.
Treatment / Management
By the midpoint of pregnancy, the woman and provider should discuss what the woman may experience during the remainder of the pregnancy. Braxton Hicks contractions are one of the normal events a woman may experience. Teaching her about Braxton Hicks contractions will help her to be informed and to decrease her anxiety if they occur.[10][11][12]
There is no medical treatment for Braxton Hicks contractions. However, taking action to change the situation that triggered the Braxton Hicks contractions is warranted. Some actions to ease Braxton Hicks contractions include:
Changing position or activity level: if the woman has been very active, lie down; if the woman has been sitting for an extended time, go for a walk.
Relaxing: take a warm bath, get a massage, read a book, listen to music, or take a nap.
Drinking water to rehydrate.
If these actions do not lessen the Braxton Hicks contractions or if the contractions continue and are becoming more frequent or more intense, the patient's healthcare provider should be contacted.
Also, if any of the following are present the healthcare provider should be contacted immediately:
Vaginal bleeding
Leaking of fluid from the vagina
Strong contractions every 5-minutes for an hour
Contractions that the woman is unable to "walk through"
A noticeable change in fetal movement, or if there are less than ten movements every 2 hours.
Differential Diagnosis
Amenorrhea
Ascites
Full bladder
Hematometra
Nausea
Ovarian cysts
Pseudocyesis
Uterine fibroids
Vomiting
Pearls and Other Issues
In addition to Braxton Hicks contractions, there are other causes of abdominal pain during pregnancy. Some normal reasons for abdominal pain during pregnancy, in addition to Braxton Hicks contractions and true labor contractions, include:
Round ligament pain or a sharp, jabbing feeling felt in the lower abdomen or groin area on one or both sides.

Higher levels of progesterone can cause excess gas during pregnancy.
Constipation may be a source of abdominal pain.
Circumstances in which abdominal pain is a sign of a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention include:
Ectopic pregnancy.
Placental abruption. A key symptom of placental abruption is intense and constant pain that causes the uterus to become hard for an extended period without relief.
Urinary tract infection symptoms include pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen as well as burning with urination.
Preeclampsia is a condition of pregnancy occurring after 20-weeks gestation and characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Upper abdominal pain, usually under the ribs on the right side, can be present in preeclampsia.
If a woman is unsure if she is experiencing Braxton Hicks contractions or another condition, a discussion with a healthcare provider is needed. The healthcare provider may recommend a visit to the office setting or labor and delivery for an examination by a healthcare professional to determine the cause of the abdominal pain.
The healthcare provider may recommend a visit to the office setting or labor and delivery for an examination by a healthcare professional to determine the cause of the abdominal pain.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Braxton hicks contractions are fairly common and it is important for the emergency department physician labor & delivery nurse and nurse practitioner to be aware that this is not true labor. If there is any doubt, the obstetrician should be consulted. However, at the same time, the onus is on the healthcare workers to rule out true labor. Other organic disorders like appendicitis, urinary tract infection or cholecystitis must also be ruled out. With the right education, patients with braxton hicks contraction will not needlessly rush to the ED every time they sense a contraction.
Review Questions
Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
Comment on this article.
References
- 1.
Hanghøj S.
 When it hurts I think: Now the baby dies. Risk perceptions of physical activity during pregnancy. Women Birth. 2013 Sep;26(3):190-4. [PubMed: 23711581]
When it hurts I think: Now the baby dies. Risk perceptions of physical activity during pregnancy. Women Birth. 2013 Sep;26(3):190-4. [PubMed: 23711581]- 2.
MacKinnon K, McIntyre M. From Braxton Hicks to preterm labour: the constitution of risk in pregnancy. Can J Nurs Res. 2006 Jun;38(2):56-72. [PubMed: 16871850]
- 3.
Dunn PM. John Braxton Hicks (1823-97) and painless uterine contractions. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999 Sep;81(2):F157-8. [PMC free article: PMC1720982] [PubMed: 10448189]
- 4.
Lockwood CJ. The diagnosis of preterm labor and the prediction of preterm delivery. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Dec;38(4):675-87. [PubMed: 8616965]
- 5.
Arduini D, Rizzo G, Rinaldo D, Capponi A, Fittipaldi G, Giannini F, Romanini C. Effects of Braxton-Hicks contractions on fetal heart rate variations in normal and growth-retarded fetuses. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1994;38(3):177-82. [PubMed: 8001871]
- 6.

Kofinas AD, Simon NV, Clay D, King K. Functional asymmetry of the human myometrium documented by color and pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasonographic evaluation of uterine arcuate arteries during Braxton Hicks contractions. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Jan;168(1 Pt 1):184-8. [PubMed: 8420324]
- 7.
Lockwood CJ, Dudenhausen JW. New approaches to the prediction of preterm delivery. J Perinat Med. 1993;21(6):441-52. [PubMed: 8006770]
- 8.
Rhoads GG, McNellis DC, Kessel SS. Home monitoring of uterine contractility. Summary of a workshop sponsored by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the Bureau of Maternal and Child Health and Resources Development, Bethesda, Maryland, March 29 and 30, 1989. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jul;165(1):2-6. [PubMed: 1677235]
- 9.
Oosterhof H, Dijkstra K, Aarnoudse JG. Fetal Doppler velocimetry in the internal carotid and umbilical artery during Braxton Hicks' contractions.
 Early Hum Dev. 1992 Aug;30(1):33-40. [PubMed: 1396288]
Early Hum Dev. 1992 Aug;30(1):33-40. [PubMed: 1396288]- 10.
Oosterhof H, Dijkstra K, Aarnoudse JG. Uteroplacental Doppler velocimetry during Braxton Hicks' contractions. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1992;34(3):155-8. [PubMed: 1427416]
- 11.
Bower S, Campbell S, Vyas S, McGirr C. Braxton-Hicks contractions can alter uteroplacental perfusion. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jan 01;1(1):46-9. [PubMed: 12797102]
- 12.
Hill WC, Lambertz EL. Let's get rid of the term "Braxton Hicks contractions". Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Apr;75(4):709-10. [PubMed: 2314790]
Third trimester - Motherhood in Khabarovsk
Third trimester, 25-28 week
Changes in a woman's body: 24-28 weeks
By this time you may be having Braxton-Hicks contractions (false contractions). You may suffer from constipation, sometimes a small amount of colostrum may come out of the nipples. By the 24th week, the apex of the uterus will reach a point above the level of the navel. You may be more worried about heartburn, because as the uterus grows, it will put pressure on the stomach and other internal organs. The pressure of the uterus and on the bladder will increase, so there will be a need for more frequent urination. nine0003
You may suffer from constipation, sometimes a small amount of colostrum may come out of the nipples. By the 24th week, the apex of the uterus will reach a point above the level of the navel. You may be more worried about heartburn, because as the uterus grows, it will put pressure on the stomach and other internal organs. The pressure of the uterus and on the bladder will increase, so there will be a need for more frequent urination. nine0003
How the body changes, 29week
How your body changes at 28 weeks pregnant
The uterus begins to change shape. She has a pronounced lower section with thin walls and an upper section with thick ones. This change helps the baby get into a comfortable position for childbirth and prepares the cervix for dilation during contractions. At this time, you probably often have an upset stomach. nine0003
She has a pronounced lower section with thin walls and an upper section with thick ones. This change helps the baby get into a comfortable position for childbirth and prepares the cervix for dilation during contractions. At this time, you probably often have an upset stomach. nine0003
Your tummy is already round, plump and most likely protrudes forward quite high - at the level of the navel.
Third trimester, 7 month
How do you feel at 7 months pregnant?
The internal organs are displaced upwards and, together with the uterus, compress the diaphragm, thereby inhibiting the free movements of the lungs. Shortness of breath appears, which increases with physical exertion, in the hypochondrium due to the pressure of the uterus, pain occurs. Get plenty of rest, while exercising and walking, keep a moderate pace, eat more often and in small portions. In case of discomfort and pain, to reduce pressure on the diaphragm, sit "in Turkish", straightening your back. Usually, such sensations continue until the fetal head descends deeper into the pelvic cavity, which happens a few weeks before the first pregnancy, and immediately before the birth in the subsequent ones. nine0003
Shortness of breath appears, which increases with physical exertion, in the hypochondrium due to the pressure of the uterus, pain occurs. Get plenty of rest, while exercising and walking, keep a moderate pace, eat more often and in small portions. In case of discomfort and pain, to reduce pressure on the diaphragm, sit "in Turkish", straightening your back. Usually, such sensations continue until the fetal head descends deeper into the pelvic cavity, which happens a few weeks before the first pregnancy, and immediately before the birth in the subsequent ones. nine0003
If you feel that the contractions are becoming painful and regular, you should immediately consult a doctor, because this may be the beginning of preterm labor. With the help of special equipment, the doctor will be able to determine whether they are a threat to maintaining the pregnancy.
The dark line crossing the abdomen from top to bottom becomes more noticeable, stretch marks may appear. In the breast, the formation of colostrum, the precursor of milk, increases.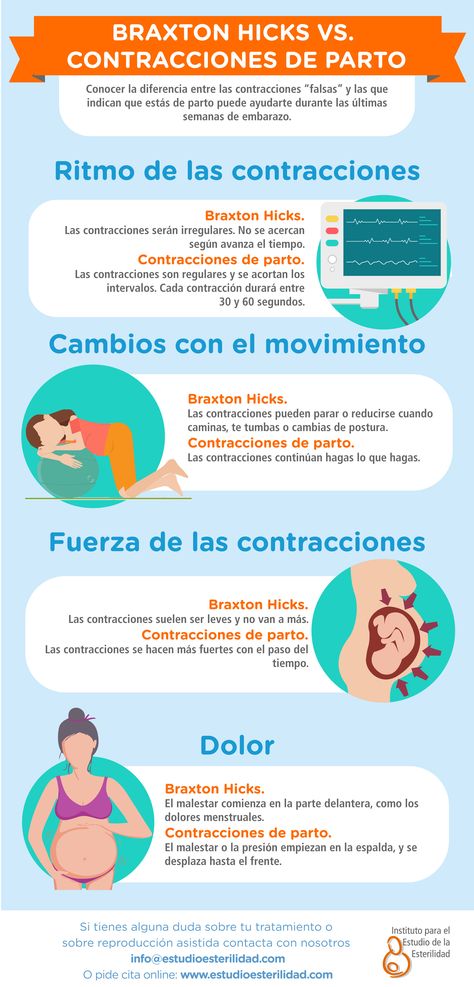 It is a sticky, watery liquid that will be the first food of a newly born baby. Use bra pads or a clean cloth if there is any discharge from your breasts. nine0003
It is a sticky, watery liquid that will be the first food of a newly born baby. Use bra pads or a clean cloth if there is any discharge from your breasts. nine0003
Third trimester, 7 month
7th month of pregnancy: weight and back pain
In the last three months you will gain approximately 300-500 grams per week. By the end of the seventh month, the total weight gain will reach 7-11 kg. We can say that now you have become quite clumsy. In late pregnancy, back pain is almost inevitable. Their cause is an increased level of the hormone relaxin, which relaxes all the ligaments and muscles, preparing them for childbirth. The action of relaxin is diverse. By loosening the muscles and ligaments of the pelvis, it changes the way a pregnant woman walks, making you waddle like a duck. Relaxing the muscular wall of the veins, relaxin leads to an increase in their varicose veins, the muscular sphincter of the esophagus - to the appearance of heartburn, and the muscles of the bladder - to the appearance of urinary incontinence. In order not to hurt your back, it is important to monitor your posture. Some happy women may not experience any discomfort, but this does not mean that their body is not preparing for the birth of a child. It all depends on various factors, including heredity and the level of physical fitness.
By the end of the seventh month, the total weight gain will reach 7-11 kg. We can say that now you have become quite clumsy. In late pregnancy, back pain is almost inevitable. Their cause is an increased level of the hormone relaxin, which relaxes all the ligaments and muscles, preparing them for childbirth. The action of relaxin is diverse. By loosening the muscles and ligaments of the pelvis, it changes the way a pregnant woman walks, making you waddle like a duck. Relaxing the muscular wall of the veins, relaxin leads to an increase in their varicose veins, the muscular sphincter of the esophagus - to the appearance of heartburn, and the muscles of the bladder - to the appearance of urinary incontinence. In order not to hurt your back, it is important to monitor your posture. Some happy women may not experience any discomfort, but this does not mean that their body is not preparing for the birth of a child. It all depends on various factors, including heredity and the level of physical fitness. nine0003
nine0003
Third trimester, 27-30 week
Third trimester: what to eat
If you are still working and have little time, it will be convenient to stock up on light snacks. Just do not eat fatty and sweet. Here are some tasty and healthy ideas:
- keep portion jars of canned fruits in their own juice on your desktop;
- for lunch, you can try to bring hummus and chopped fresh vegetables from home; nine0003
- indulge in nut mixes and dried fruits, including dried cherries, papaya, tangerines and other treats. They are rich in iron and fiber;
They are rich in iron and fiber;
- make yourself all kinds of vegetable salads;
- bring a handful of muesli and a carton of milk;
- occasionally treat yourself to a piece of a good fruit pie (if it has little dough and a lot of dried fruit filling, rich in fiber and iron).
How the body changes, 30 week
How your body changes at 29 weeks pregnant
All ligaments have softened under the influence of pregnancy hormones. This is done so that the pelvic bones move apart and release the baby out. Sometimes the softening is too drastic and the bones move apart too abruptly. Perhaps you sometimes have pain in the pelvis; if so, try to get plenty of rest and don't worry - everything is in order. nine0003
This is done so that the pelvic bones move apart and release the baby out. Sometimes the softening is too drastic and the bones move apart too abruptly. Perhaps you sometimes have pain in the pelvis; if so, try to get plenty of rest and don't worry - everything is in order. nine0003
It may be difficult for you to bend over, but you may find that your joints have become more mobile and now you can do things that you could not do before, such as sitting in a Turkish position or even in a lotus position. Perhaps your feet have become a little wider - due to swelling and the fact that they now have to carry a lot of weight - and you need roomy shoes without heels and without laces.
How the body changes, 31 week
How your body changes at 30 weeks pregnant
You already feel like a real hippo and you can't even imagine that in the next 10 weeks you will become even more. The bottom of the uterus is about 10 centimeters above the navel, and sometimes you feel fullness in your stomach - simply because the baby has stuffed all your insides. nine0003
The bottom of the uterus is about 10 centimeters above the navel, and sometimes you feel fullness in your stomach - simply because the baby has stuffed all your insides. nine0003
You may have Braxton Hicks contractions at this time.
If you had a low placenta early in your pregnancy, you will have an extra ultrasound to make sure it has moved up. The placenta moves up and "pulls away" from the cervix due to the ongoing reshaping of the uterus that began around week 28.
How the body changes, 32 week
How your body changes at 31 weeks pregnant
The uterus has already occupied almost the entire abdominal cavity and stands about 11 centimeters above the navel.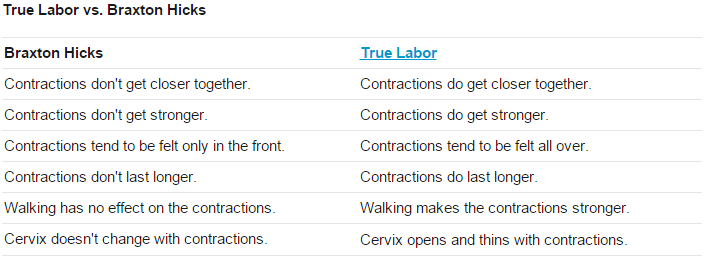
Around this time, you begin to realize that you will soon have a real baby. You will find the delight of choosing a name and the happiness of hugging a tiny warm little body.
nine0002 How the body changes, 33 weekHow your body changes at 32 weeks pregnant
The blue veins are already clearly visible on the chest. In addition, your bust is now huge, there are dark spots around the areola, and colostrum is probably leaking. For the past few weeks, a good supportive bra is a must for air, especially if your breasts have grown a lot.
In addition, your bust is now huge, there are dark spots around the areola, and colostrum is probably leaking. For the past few weeks, a good supportive bra is a must for air, especially if your breasts have grown a lot.
The uterus stands about 12 cm above the navel. Some women have round ligament pain at this time. The tummy grows, and the skin is greatly stretched. nine0003
How the body changes, 34 week
How your body changes at 33 weeks pregnant
The fundus of the uterus is probably already 13 cm above the navel, and the abdomen is already quite large and dense. It is difficult to bend over, and it is not possible to find a comfortable position for a long time.
It is difficult to bend over, and it is not possible to find a comfortable position for a long time.
If you feel very clumsy at this time, this is not unusual: the shape of the body has changed so much that your sense of balance will inevitably deceive you. If the baby lies head down, you will sometimes become sensitive to the right hypochondrium. Perhaps the baby's bottom is pressed against your liver and pushes it slightly to the side, which is why this area becomes sensitive. When the child changes position, the feeling goes away. If it is persistent, tell your doctor about it, because pain in the hypochondrium on one side is sometimes a sign of preeclampsia. nine0003
How the body changes, 35 week
How your body changes at 34 weeks pregnant
Most primiparas by 36 weeks find that their belly has drooped. But many babies sink much earlier, and some expectant mothers feel the touch of the baby's head on the pelvic floor muscles.
But many babies sink much earlier, and some expectant mothers feel the touch of the baby's head on the pelvic floor muscles.
Your tummy is very large and it is difficult for you to have a big meal. Eat little and often. nine0003
How the body changes, 36 week
How your body changes at 35 weeks pregnant
During your pregnancy, your insides had to undergo a major remodeling. A baby needs so much space that your intestines, stomach, bladder, and even lungs are either pushed out of the way or squashed down. No wonder you are out of breath. It is simply amazing how cleverly our body adapts to everything - after all, even such serious changes remind of themselves only with heartburn. Hold on - the finish line is near. nine0003
A baby needs so much space that your intestines, stomach, bladder, and even lungs are either pushed out of the way or squashed down. No wonder you are out of breath. It is simply amazing how cleverly our body adapts to everything - after all, even such serious changes remind of themselves only with heartburn. Hold on - the finish line is near. nine0003
How the body changes, 37 week
How your body changes at 36 weeks pregnant
Well, take a deep breath. .. Did it work? Congratulations, your baby has started letting go! This means that he stuck his head into the upper opening of the pelvis, preparing for childbirth. And this, in turn, means that the lungs are now more spacious and you can start breathing again. In addition, the stomach is now not so crowded, so you can finally eat well. nine0003
.. Did it work? Congratulations, your baby has started letting go! This means that he stuck his head into the upper opening of the pelvis, preparing for childbirth. And this, in turn, means that the lungs are now more spacious and you can start breathing again. In addition, the stomach is now not so crowded, so you can finally eat well. nine0003
Now is the time to think about what you will need for childbirth and prepare your bag for the hospital.
Third trimester, 25-37 week
Arrangement of a nursery: necessary purchases
In the third trimester of pregnancy, future parents begin to think about those things that will be needed first of all for arranging a nursery. We offer an approximate list of necessary things that will help you not to get lost in the store:
We offer an approximate list of necessary things that will help you not to get lost in the store:
- baby crib or cradle;
- a pair of bedding sets; nine0003
- chest of drawers or wardrobe;
- main light regulator or night lamp;
- changing table;
- a set of soft bumpers in the crib;
- bags for used diapers;
- a heater for a children's room for the cold season.
Third trimester, 27-38 week
Third trimester of pregnancy: your uterus
Your uterus has already "reached" the diaphragm, approaching its highest position, its fundus is now about 12 cm above the navel. In the following weeks, your baby will likely assume the head-down position if he hasn't already, and will remain in that position until birth. As the baby's head enters deeper into the pelvic cavity, you will notice that the stomach also releases. nine0003
In the following weeks, your baby will likely assume the head-down position if he hasn't already, and will remain in that position until birth. As the baby's head enters deeper into the pelvic cavity, you will notice that the stomach also releases. nine0003
Braxton Hicks contractions for how long - 25 recommendations on Babyblog.ru
For fifteen years now we have been living not just in the new century, but in the new millennium. For twenty years we have been using computers and the Internet everywhere. It would seem that with the progress of technology, people have enormous opportunities for the exchange of progressive information, knowledge and best practices. But the real picture is almost the opposite: false, untruthful information, often presented under the “sauce” of intimidation and deceit, is spread and accepted by people faster and easier than truthful and useful information. nine0003
The worst thing that is now observed in medicine is the filing of many conditions, including quite normal ones, and some diagnoses as something terrible and dangerous, threatening a person’s life, requiring aggressive and extensive treatment immediately. Obstetrics is no exception. On the contrary, in recent years this branch of medicine has grown in a number of countries into a kind of machine of deliberate harm to a pregnant woman and her unborn child.
Obstetrics is no exception. On the contrary, in recent years this branch of medicine has grown in a number of countries into a kind of machine of deliberate harm to a pregnant woman and her unborn child.
The concept of "commercial diagnosis", introduced by me ten years ago, is no longer denied by many people and is even used by them in everyday life, conversations and discussions of the situation in the healthcare system. Both doctors and people of other specialties began to talk and write about obstetric aggression. Nevertheless, the number of fictitious diagnoses that do not exist in most countries of the world is striking not only by their backwardness, but also by the lack of a logical analysis of the situation, signs, and examination results when they are made (more precisely, invented). nine0003
INCOMPATIBILITY OF SPOUSES
Typically, such a diagnosis sounds when:
- unsuccessful planning of pregnancy and infertility;
- loss of pregnancy, even the first or one;
- spontaneous habitual miscarriages;
- in exceptionally "striking cases" in the presence of one child or several healthy children.
If we talk about some kind of “spousal incompatibility”, then we can only talk about psychological incompatibility or sexual temperaments, but there is no other “incompatibility”. nine0003
Allergic reaction to semen is extremely rare in humans, but the diagnosis would be allergy, not incompatibility.
If a married couple cannot conceive, it may be infertility, which requires proper diagnosis. There are different types of infertility or infertility factors, which means that there will be a different approach to the examination of a married couple and treatment.
Very fashionable commercial HLA (human leukocyte antigen) testing in the world of progressive medicine is used in organ and tissue transplantation, to diagnose a number of autoimmune diseases, confirm paternity and monitor the effectiveness of the treatment of a number of diseases, but has nothing to do with conceiving children, carrying a pregnancy , and even more so with the "incompatibility of the spouses. " "Genetic incompatibility of partners" is another invention for imposing an expensive examination and treatment. nine0003
" "Genetic incompatibility of partners" is another invention for imposing an expensive examination and treatment. nine0003
If one of the partners has affected genes, that is, there are changes in the form of mutations, then such changes may be associated with problems in conceiving and bearing offspring, but this is not incompatibility. This may be a specific diagnosis (disease, syndrome) on the part of one or both partners. And the recommendations of some doctors to carry out IVF in such cases using the same sexual material, or to find a sexual partner outside of marital relations in order to conceive a child, do not always sound professional. nine0003
TOXICOSIS
The concept of "toxicosis" appeared in Soviet obstetrics in the early 1990s, when everyone in the world of progressive medicine had already completely abandoned this concept. Toxicosis means “a state of poisoning” (toxins are poison), and the logical conclusion is that this is pregnancy poisoning, that is, the embryo / fetus poisons the body, and therefore the life of the expectant mother. But doesn’t a mother poison her unborn child with poor-quality food, water, medication, smoking, and even drinking alcohol? nine0003
But doesn’t a mother poison her unborn child with poor-quality food, water, medication, smoking, and even drinking alcohol? nine0003
In the West, they quickly realized the absurdity of such a “diagnosis” and tried to switch to the concept of “preeclampsia”, that is, a condition associated with gestation (pregnancy). However, this definition was also abandoned very quickly, because the more science and medicine developed, the faster the exchange of advanced information and experience, the faster doctors began to understand that many “strange” phenomena during pregnancy are not diseases, but variants of the norm. and vice versa - all complications of pregnancy have specific specific names, which should appear as diagnoses. nine0003
In post-Soviet medicine, a completely normal phenomenon - nausea and vomiting at the beginning of pregnancy - is still called early toxicosis (in the rest of the world these are just unpleasant symptoms of this condition), and edema, which for the vast majority of women are normal, hypertension in pregnant women, preeclampsia, eclampsia and about ten other complications of pregnancy, which are independent diagnoses, and not a comprehensive mythical toxicosis. nine0153 Remember: there is no such diagnosis - toxicosis!
nine0153 Remember: there is no such diagnosis - toxicosis!
UTERINE TONE / HYPERTONE
For the first time, normal uterine contractions from the beginning of pregnancy to the end of childbirth were described by the English physician John Braxton Hicks in 1872. Mistakenly, such contractions are called "training bouts", which is not true. In the publication of this doctor, it was about normal uterine contractions throughout pregnancy, and not before childbirth.
The uterus is a muscular organ, therefore, just like any muscle, it has its own mode of contractions, which depends on many factors and can be observed both outside of pregnancy and during pregnancy. nine0153 The diagnosis "tonus" or "hypertonicity" was invented by post-Soviet ultrasound doctors and the rest of the world does not exist in obstetrics, therefore it does not require treatment, and even more so inpatient, with the use of a large number of drugs that have also not been used in modern obstetrics for a long time ("Papaverine" , "No-shpa", "Viburkol", vitamin E, magnesia, etc. )
)
THREAT OF LOSS OF PREGNANCY
I have already raised the topic of "threat of abortion" more than once, especially since it is consonant with the topic of "preservation of pregnancy". In reality, the threat to a pregnant woman comes more from the medical staff than really from someone else or something (nature), because it is people who intimidate, put pressure on the psyche with negative scenarios, escalate the situation, harm with unsafe treatment. nine0003
The only diagnosis in obstetrics that has a word root consonant with “threat” is “threatened abortion”. This diagnosis is made according to strict criteria, and not because of “tone / hypertonicity of the uterus”, it does not require treatment, because there is no cure.
All other types of threats are fictitious diagnoses. In obstetrics, it is customary to talk about risk factors and determine the group or degree of risk for the development of one or another pregnancy complication (low risk, high risk). Against the background of the presence of various risk factors, pregnancy can proceed quite normally and end safely. nine0003
nine0003
RH AND GROUP CONFLICT
In modern obstetrics there is no such concept or diagnosis as "Rh conflict" or "group conflict". Worst of all, such a “diagnosis” intimidates a married couple to such an extent that she refuses to conceive children: since it is absolutely impossible to get pregnant, then we are not trying. The presence of different blood types, as well as different Rh factors, is a normal phenomenon in human life and is not considered any conflict.
In modern obstetrics, there are more than 50 blood markers (antigens) for which antibodies (immunoglobulins) can be produced, and this condition is called alloimmunization, or sensitization. nine0003
During pregnancy, antibodies can be produced in the mother's body against fetal antigens, cross the placenta and destroy the fetal red blood cells, leading to anemia and fetal hemolytic disease. If hemolytic disease of the fetus occurs, then it will end either with the death of the fetus, or the birth of a child with hemolytic disease of the newborn. Unfortunately, many doctors do not understand the types of jaundice, do not know the current norm of bilirubin levels, so the diagnosis of "hemolytic disease of the newborn" in most cases turns out to be false, which means that aggressive treatment of such children is absolutely inappropriate. nine0003
Unfortunately, many doctors do not understand the types of jaundice, do not know the current norm of bilirubin levels, so the diagnosis of "hemolytic disease of the newborn" in most cases turns out to be false, which means that aggressive treatment of such children is absolutely inappropriate. nine0003
If we talk about really rare "blood conflicts", then they arise not between a man and a woman, but between a mother and a fetus. Therefore, the enthusiasm of some doctors for the search for antibodies in the blood of a man is so surprising. Also depressing is the fact of searching for antibodies in the mother's blood after childbirth in order to make a diagnosis of "hemolytic disease of the newborn." And the use of such a dangerous procedure as plasmapheresis, supposedly to “cleanse the blood” of antibodies, is shocking. This procedure has passed into the category of commercial ones, because it is expensive and brings considerable income to those who carry it out. nine0003
For the prevention of Rh sensitization in the mother, vaccination with immunoglobulins (D-antibodies) has long been used, which is carried out in the absence of a woman's own antibodies during pregnancy, after childbirth, abortion, and a number of procedures. This prophylaxis does not protect the current pregnancy, but it does prevent hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn in subsequent pregnancies. However, it is ineffective in preventing sensitization for all other blood markers.
This prophylaxis does not protect the current pregnancy, but it does prevent hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn in subsequent pregnancies. However, it is ineffective in preventing sensitization for all other blood markers.
HEREDITARY (GENETIC) THROMBOPHILIA
In post-Soviet obstetrics, over the past decade, there have been an extremely large number of positions of geneticists who do not understand prenatal genetic screenings and genetics in general, and hematologists (they are fashionably called hemostesiologists, hemastesologists), who do not understand blood and know absolutely nothing about normal changes in the composition of the blood, especially the blood coagulation system in pregnant women.
During pregnancy, blood viscosity increases despite an increase in blood (plasma) volume and a decrease in the concentration of many substances. Therefore, from the very first weeks, pregnancy is accompanied by a hypercoagulable state. It can persist for several weeks, not only after childbirth, but also after abortions and missed pregnancies. This is not a pathological condition, but normal physiological changes. nine0003
This is not a pathological condition, but normal physiological changes. nine0003
D-dimer, according to the level of which heparin is prescribed to all pregnant women in a row, is a derivative of fibrinogen. Both of these indicators increase from the first weeks of pregnancy, which is absolutely normal.
Commercially profitable genetic testing leads to the diagnosis of "thrombophilia" being overused, although several dozen diseases are known to be associated with disorders of the blood clotting process. There are several types of hereditary thrombophilia that have a clear name, and not just "genetic thrombophilia". There are also acquired thrombophilias, which often turn out to be not a separate diagnosis, but a laboratory and clinical symptom of other diseases. nine0003
The presence of genes and their combinations does not mean that a person has thrombophilia (and many other diseases). This may indicate a hereditary predisposition, but without clinical and laboratory confirmation, and even more so outside the state of pregnancy, such diagnoses are not made and blood thinning drugs are not prescribed.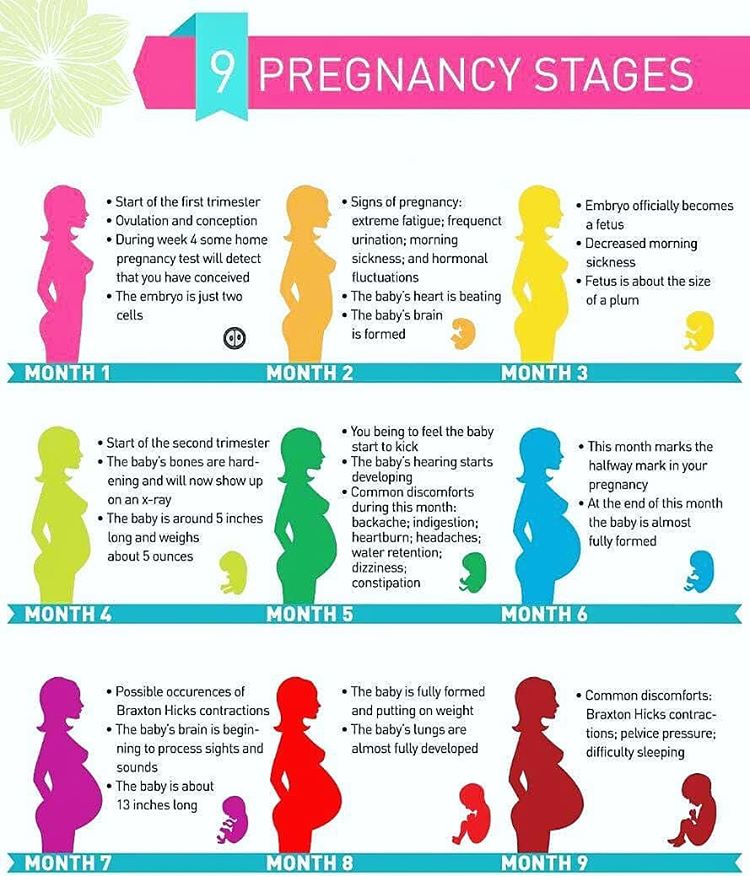
Bed rest in hospitals, where pregnant women are kept for weeks and even months, is recognized as the most dangerous factor in the formation of blood clots. It is also surprising that before pregnancy, many women had no idea about their "genetic disease", they took hormonal contraceptives that are incompatible with thrombophilia, and then after giving birth they continue to take them, forgetting about the terrible diagnosis. However, doctors quickly forget about him too. nine0003
OLD PLACENTA
The diagnosis of "old placenta", which often sounds in conjunction with the diagnosis of "uteroplacental insufficiency", was born by the same ultrasound specialists.
The placenta is a dynamic organ that undergoes regular changes as pregnancy progresses. Therefore, we can safely say that not only the placenta is aging, but also the fetus itself. The woman also gets older by 9 months!
Placenta insufficiency can be spoken of only when it does not fulfill its function. Just as there is heart or liver failure, placental failure can also exist. But its presence can only be determined by the state of the fetus. If the fetus develops normally and does not lag behind in growth (for this, growth charts must be kept and the exact gestational age must be known), then what kind of placental insufficiency can we talk about? nine0153 But what is depressing in all these stories with placentas is that a woman is offered different schemes for "rejuvenation" of the placenta, which necessarily include two fuflomycins - "Kurantil" and "Actovegin". Remember: the placenta cannot be rejuvenated!
Just as there is heart or liver failure, placental failure can also exist. But its presence can only be determined by the state of the fetus. If the fetus develops normally and does not lag behind in growth (for this, growth charts must be kept and the exact gestational age must be known), then what kind of placental insufficiency can we talk about? nine0153 But what is depressing in all these stories with placentas is that a woman is offered different schemes for "rejuvenation" of the placenta, which necessarily include two fuflomycins - "Kurantil" and "Actovegin". Remember: the placenta cannot be rejuvenated!
In addition, the diagnosis "placentitis" suddenly became fashionable, which was indeed used in veterinary medicine for a very long time, but never in obstetrics! Turning pregnant women into female animals?
oligohydramnios/polyhydramnios tendencies
When I hear or read about the diagnosis of oligohydramnios/polyhydramnios tendency, I want to respond with a great sense of humor: “You know, we all have a lot of tendencies. For example, there is a real tendency with age to get senile dementia. You can buy a lottery ticket - there will be a tendency to enrich. We sit in a car, drive along a highway - we tend to get into a traffic accident and even die. That's right, life tends to end. This means that pregnancy tends to end in term birth and the birth of a healthy baby. nine0003
For example, there is a real tendency with age to get senile dementia. You can buy a lottery ticket - there will be a tendency to enrich. We sit in a car, drive along a highway - we tend to get into a traffic accident and even die. That's right, life tends to end. This means that pregnancy tends to end in term birth and the birth of a healthy baby. nine0003
The extremely common diagnosis of "trends" is often the product of ultrasound specialists who somehow do not use the logical thinking of obstetrician-gynecologists to ask a simple question: what kind of nonsense is this?
The state of amniotic fluid is only in the form of a norm, polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios, but there are no trends. These conditions are determined by measuring one pocket (column) of amniotic fluid in centimeters, but most often by the sum of four (namely four, not two or three) pockets, that is, by determining the amniotic index of amniotic fluid (AIF). After 20 weeks, the normal AIH ranges from 8 to 24 cm, of course, adjusted for the condition of the fetus and other ultrasound findings. nine0003
nine0003
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios are practically not treated, therefore, volumetric regimens of antibiotics and fuflomycins, the same "Kurantil", "Actovegin", "Khofitol", "Viferon", "Tivorin" and other similar drugs, and with the obligatory presence of a pregnant woman in a hospital , is a manifestation of medical illiteracy.
fetal asphyxia
Most often, the diagnosis of fetal asphyxia appears in the conclusions of pathologists after pregnancy loss, as well as in stillbirth. Surprisingly, it is specialists who do not see the difference between hypoxia and asphyxia, who are just obliged to find out the cause of abortion and fetal death. nine0003
The baby is not breathing inside the uterus. His lungs don't work. Everything he receives from his mother in the form of nutrients and oxygen comes through the umbilical cord. The concept of hypoxia implies a violation of blood flow in the vessels of the fetus (impaired hemodynamics) due to the presence of usually two parallel conditions - anemia (anemia) and acidosis (increased acidity) due to oxygen starvation of tissues.