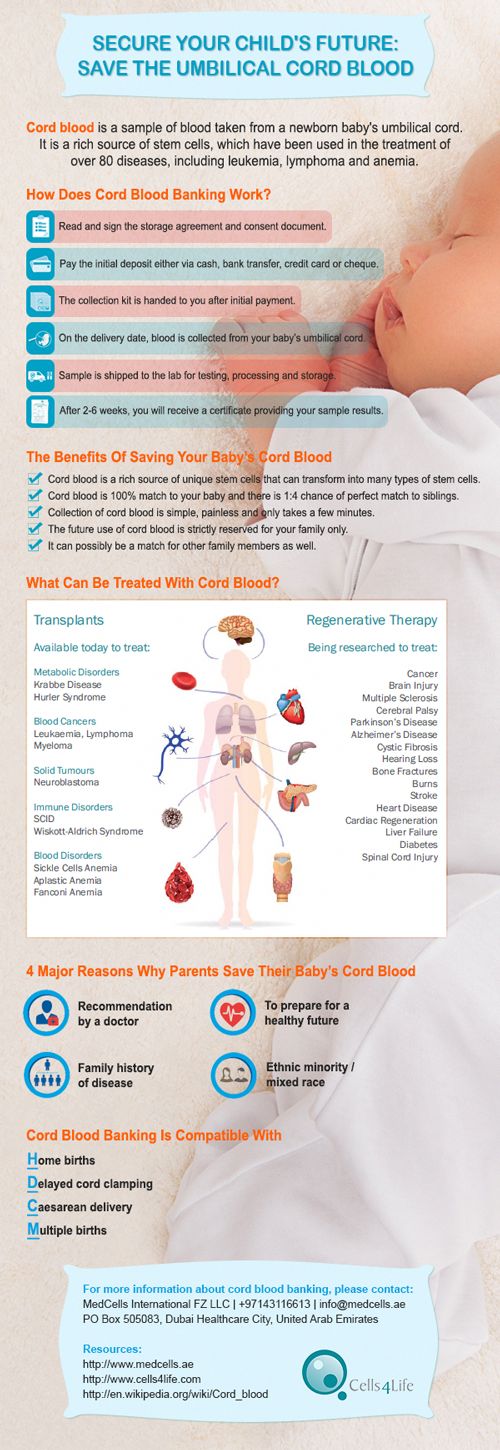
How do i know my child is teething
Baby teething symptoms - NHS
When it comes to teething, all babies are different. But your baby will probably get their first tooth some time during their first year.
Find out how to spot when your baby is teething and what order your baby's teeth are likely to appear in.
When do babies start teething?Some babies are born with their first teeth. Others start teething before they are 4 months old, and some after 12 months. But most babies start teething at around 6 months.
Teething symptomsBaby teeth sometimes emerge with no pain or discomfort at all.
At other times, you may notice:
- their gum is sore and red where the tooth is coming through
- they have a mild temperature of less than 38C
- they have 1 flushed cheek
- they have a rash on their face
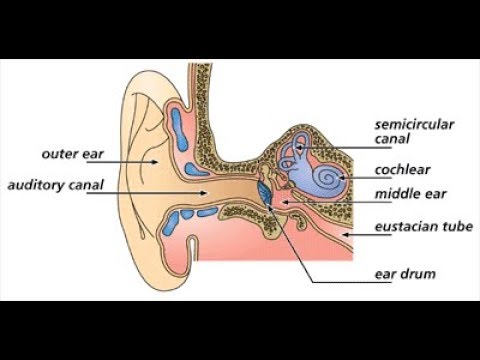
- they're rubbing their ear
- they're dribbling more than usual
- they're gnawing and chewing on things a lot
- they're more fretful than usual
- they're not sleeping very well
Read tips on how to help your teething baby.
Some people think that teething causes other symptoms, such as diarrhoea, but there's no evidence to support this.
You know your baby best. Get medical advice if they have any symptoms that are causing you concern. You can call NHS 111 or contact a GP.
Read more about spotting the signs of serious illness in babies and toddlers.
What order do baby teeth appear in?Here's a rough guide to how babies' teeth usually emerge:
- bottom incisors (bottom front teeth) – these are usually the first to come through, usually at around 5 to 7 months
- top incisors (top front teeth) – these tend to come through at about 6 to 8 months
- top lateral incisors (either side of the top front teeth) – these come through at around 9 to 11 months
- bottom lateral incisors (either side of the bottom front teeth) – these come through at around 10 to 12 months
- first molars (back teeth) – these come through at around 12 to 16 months
- canines (between the lateral incisors and the first molars) – these come through at around 16 to 20 months
- second molars – these come through at around 20 to 30 months
Most children will have all of their milk teeth by the time they are between 2 and 3 years old.
Page last reviewed: 9 August 2022
Next review due: 9 August 2025
Teething
Is this your child's symptom?
- The normal process of new teeth working their way through the gums
- Questions about teething
- Baby teeth come in between 6 and 24 months of age
- Caution: At least one tooth should be seen before using this care guide
Proven Symptoms of Teething
Teething has been researched in-depth. Kids who are teething are little different from kids who are not teething. Here are the main symptoms that have been proven:
- Drooling. Increased spit and drooling.
- Rash. Face rash from drooling. The drool contains little bits of food that are irritating to the skin.
- Chewing. Increased need to chew on things.
- Gum Pain.
 Gum pain is mild and not always present. May be due to mouth germs getting into the new break in the gum. Most often, your baby just acts a little more fussy. There's not enough discomfort to cause crying. It also doesn't hurt enough to cause sleep problems.
Gum pain is mild and not always present. May be due to mouth germs getting into the new break in the gum. Most often, your baby just acts a little more fussy. There's not enough discomfort to cause crying. It also doesn't hurt enough to cause sleep problems.
False Symptoms of Teething
- Teething does not cause fever, diarrhea, diaper rash or runny nose.
- It does not cause a lot of crying.
- It does not cause your baby to be more prone to getting sick.
- Caution about Fevers. Blaming teething for fevers can lead to a delay in seeking care for infections. Examples are ear and urinary tract infections. Another example is meningitis.
- There are 2 reasons why infections start between 6 and 12 months of age. One is the loss of antibodies transferred to baby from the mother at birth. The other is the developmental milestone of chewing on everything.
- Caution about Crying. Blaming teething for crying can lead to a delay of care for other illnesses.
 Examples are ear infections or other causes of pain.
Examples are ear infections or other causes of pain.
When to Call for Teething
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Your child looks or acts very sick
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- You think your child needs to be seen
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Normal teething
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
- Virtual Urgent Care
Care Advice for Teething
- What You Should Know About Teething:
- Teething is a natural process.

- It's harmless and it may cause a little gum pain.
- The main symptoms of teething are drooling and rubbing the gums.
- It does not cause fever or crying. If these are present, look for another cause.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Teething is a natural process.
- Gum Massage:
- Find the irritated or swollen gum.
- Rub it with your clean finger for 2 minutes.
- Do this as often as needed.
- Putting pressure on the sore gum can decrease pain.
- Age over 12 months. You can use a piece of ice wrapped in a wet cloth to rub the gum.
- Teething Rings (Teethers):
- Babies rub their own sore gums by chewing on smooth, hard objects.
- Offer a teething ring, pacifier or wet washcloth that has been chilled. Chill these items in the fridge. Do not use items frozen in the freezer.
- Age over 12 months. A piece of chilled banana may help.
- Do not use hard foods that could cause choking.
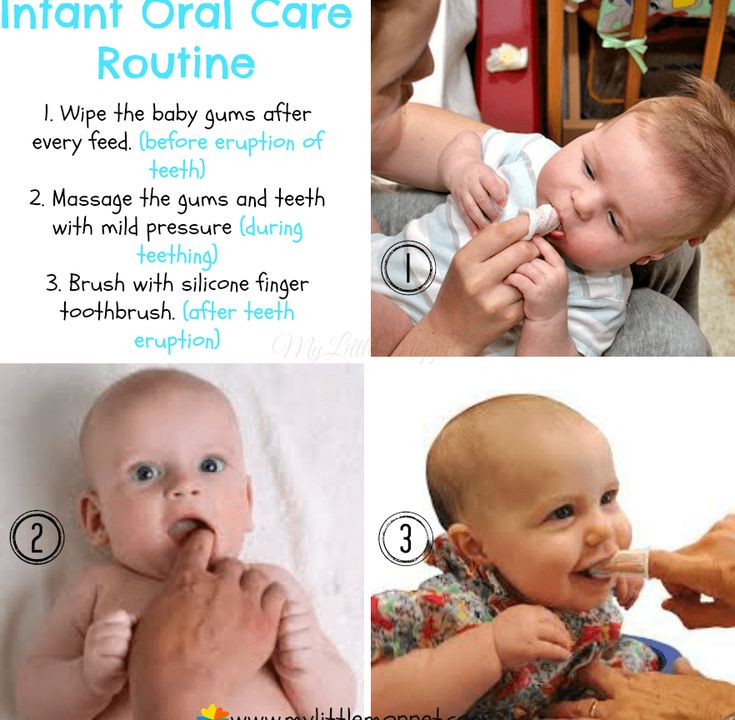 An example is a raw carrot.
An example is a raw carrot. - Do not use ice or popsicles that could cause frostbite of the gums.
- Avoid "teething necklaces." They are not approved by the FDA and are not helpful. They also have harmful risks including choking and death.
- Cup Feeding:
- If your baby refuses nipple feedings, try a cup.
- A spoon or syringe can also be used for a short time as needed.
- Pain Medicine:
- Pain medicines usually are not needed for the mild discomfort of teething.
- Fussiness often gets better with gum massage. If not, you can give an acetaminophen product (such as Tylenol). If age over 6 months, another choice is an ibuprofen product (such as Advil). Just do this for one or two days. (Reason: Frequent use can cause liver or kidney damage).
- Teething Gels: Do Not Use
- You can get special teething gels without a prescription.
- Most have benzocaine in them.
 They are not approved by the FDA at any age.
They are not approved by the FDA at any age. - Reason: Benzocaine can cause choking, bluish skin and allergic reactions. It can be very harmful if used during the first 2 years of life.
- Also, teething gels only give brief pain relief.
- Gum massage works much better.
- What to Expect:
- Most often, teething does not cause any symptoms.
- If your child is having some discomfort, it should pass in 2 or 3 days.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Crying occurs
- Fever occurs
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 02/22/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023.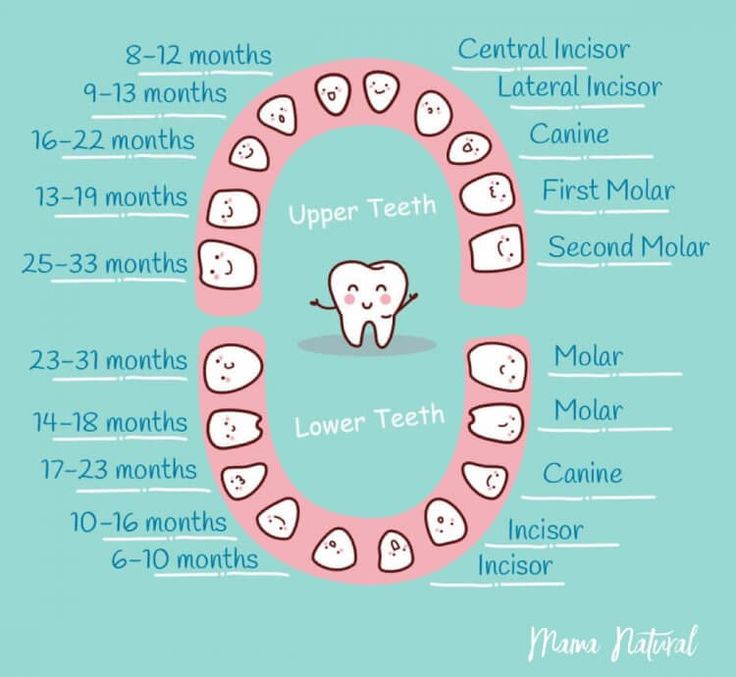 Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
How to understand that a child is teething
Teething symptoms can be very unpleasant. Often young parents do not understand what is happening with the child. Many of the symptoms are very common, and there are safe ways to relieve your baby's condition.
Salivation
Profuse salivation during teething is absolutely normal. Wipe your baby's face regularly with a tissue to avoid skin irritation and rashes. Wear clothes that are easy to wash, as your baby's saliva will regularly get on them.
Irritability
During the period when a sharp tooth breaks through the child's gums, one should not expect a good mood from him. Do not be surprised that the baby is naughty, cries more than usual, gets angry for nothing or for unknown reasons. Experts believe that irritability at this time is completely natural.
Eagerness to chew on hard objects
To reduce gum pain, the child may start chewing on toys and other hard objects. Keep everything that has sharp edges or small parts away from the child. To prevent your baby from putting unhygienic things in his mouth, give him special tooth rings, chilled vegetables, a damp cloth, or special cookies intended for children who are teething. At this time, the child may put his own fingers in his mouth more often, so pay extra attention to their cleanliness.
Keep everything that has sharp edges or small parts away from the child. To prevent your baby from putting unhygienic things in his mouth, give him special tooth rings, chilled vegetables, a damp cloth, or special cookies intended for children who are teething. At this time, the child may put his own fingers in his mouth more often, so pay extra attention to their cleanliness.
Decreased appetite and taste changes
Don't worry if your baby is eating less than usual. Breastfeeding or bottle feeding during teething can cause your baby too much discomfort and even pain. However, the baby should not go without food all day, and if he misses several feedings in a row, you should consult a pediatrician. In addition, the baby may refuse his favorite food, which at this time causes pain to the gums. If he has already switched to solid food, try feeding him, for example, yogurt that does not need to be chewed.
Anxiety and changing sleep patterns
Your baby may become restless. It is also possible that he will sleep at unusual times or not as well as before, begin to fall asleep worse and wake up more often. You can talk to your doctor about pain medications that are safe for children to help your child sleep better.
It is also possible that he will sleep at unusual times or not as well as before, begin to fall asleep worse and wake up more often. You can talk to your doctor about pain medications that are safe for children to help your child sleep better.
Fever
Experts say that although teething may be accompanied by a slight rise in temperature, fever is not a typical symptom. If your child has a high temperature, you should contact your pediatrician, as it may be a sign of some kind of disease.
Not a symptom of teething and diarrhoea. During this period, children have loose stools, but diarrhea indicates a disease, possibly of a viral nature. During teething, the child's body is under severe stress and becomes more vulnerable to viruses.
A child's oral health needs to be cared for from birth. Wipe your baby's gums with a damp gauze or tissue paper, and after the first tooth erupts, start using a soft-bristled toothbrush and a special toothpaste designed for babies.
Visit the Colgate website for more information about teething.
Teething in a child: timing, care, ways to relieve pain
Children will definitely appreciate the parental contribution to maintaining dental health when they grow up. In order to help the baby from the very beginning, it is necessary to know the structural features, the stages of formation and the correct order of teething.
Teeth development before eruption
Your baby's teeth should be taken care of long before they eruption. It is useful for expectant mothers to know that the rudiments of milk teeth are formed already at the 7-8th week of intrauterine development, and permanent ones at the end of 4 months. Not just teething timing, but even level enamel mineralization both milk and molars depends on how the pregnancy proceeds. Therefore, it is so critical that a woman receives all the vitamins, microelements and is as healthy as possible.
But not only food is important. The results of the research showed that in the presence of industrial harmful substances in the environment of the expectant mother during pregnancy and numerous stressful situations, the formation of all dental tissues is disrupted in the child and the timing of the appearance of milk teeth is shifted. Among children born to women with high blood pressure, late eruption of temporary teeth was noted in 56.7%. Approximately one third of the examined children born to mothers with heart defects revealed late eruption of temporary teeth, as well as deviations in the pairing and sequence of their eruption. The duration of pregnancy also plays a role. There is a pronounced dependence of the timing of the eruption of the first teeth on the degree of prematurity: the earlier the baby was born, the later the first teeth erupt [1, 2] .
Why baby teeth are needed
Nature has conceived the correct order and timing of teething in children.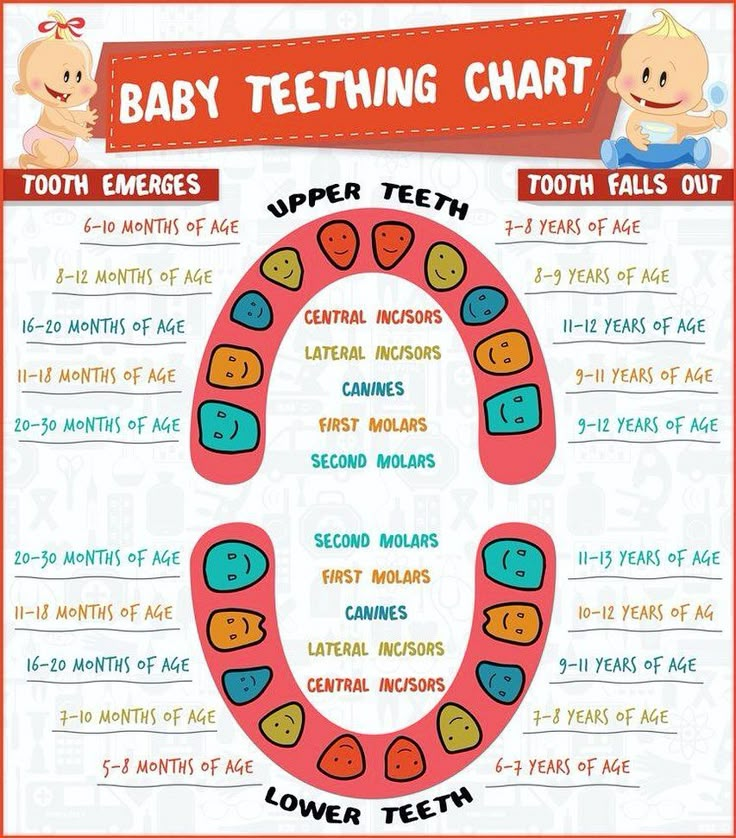 Evolutionarily, this is due to the need to form the bite and jaw bones for chewing and speech. Over the years, the bones grow, and the milk teeth, which at the beginning of their appearance fit snugly against each other, diverge by the age of 6-7, forming wide, natural interdental spaces for this period - tremas and diastemas.
Evolutionarily, this is due to the need to form the bite and jaw bones for chewing and speech. Over the years, the bones grow, and the milk teeth, which at the beginning of their appearance fit snugly against each other, diverge by the age of 6-7, forming wide, natural interdental spaces for this period - tremas and diastemas.
There are only 20 teeth in the milk bite. This is due to the fact that they must be correctly placed in the small children's jaw of the first years of a baby's life, and excludes crowding of teeth that provokes dental diseases. The last of the milk teeth are replaced at the age of 10-12 years. However, they are very important for the physiological formation of the jawbones and permanent occlusion.
Proper growth and health of milk teeth help:
-
rebuild the body from lactophoric to a mixed type of nutrition;
-
reserve space for the normal positioning of future molars;
-
form a mixed bite.

There is an erroneous opinion that milk teeth in case of infection with caries can not be treated, but immediately removed. But modern dentists are against such tactics. Early removal is fraught with displacement of neighboring milk teeth and the appearance of problems already with an adult bite. Therefore, it is so important to maintain the presence and health of all milk teeth until the moment when permanent teeth erupt on their own [3] .
The structure of milk teeth
Temporary teeth have thinner enamel, and their internal pulp cavity is larger compared to permanent ones. All this makes the tooth lighter, which helps with the eruption of permanent teeth, but at the same time accelerates the development of caries and pulpitis. However, there are bonuses: by the time the molars begin to erupt, which will remain with the child until the end of life, the roots of milk teeth even dissolve to ensure their rapid and relatively painless loss.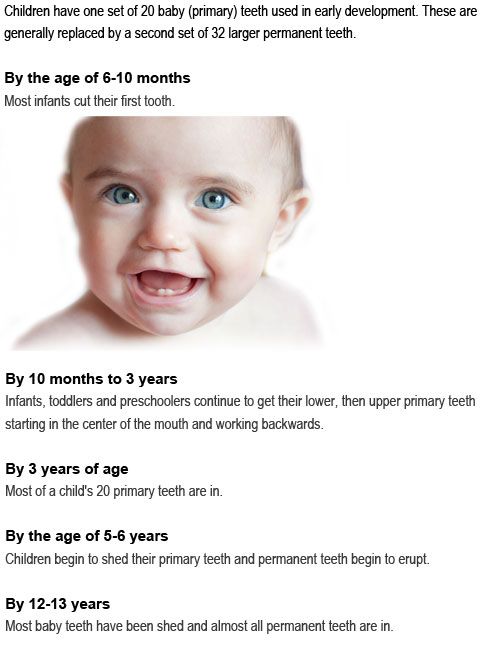
Terms of eruption of milk teeth
Teething is a genetically programmed event that occurs at a certain period. Physiological teething is characterized by three main features: certain timing, pairing and sequence of teething. Galaktionova M. Yu.
Baby teething rates vary by ethnicity. But as studies show, in general, the world is experiencing a reduction in the time from birth to the moment when the first tooth appears. This is due, according to most researchers, to the global acceleration of human development [1] . How and when milk teeth erupt is one of the indicators of a child's physical development.
Causes of violation of the order and timing of teething in children can be:
-
heredity;
-
climatic conditions;
-
nature of feeding;
-
certain diseases, such as rickets.
Standards for eruption of milk teeth according to the American Dental Association are presented in the table.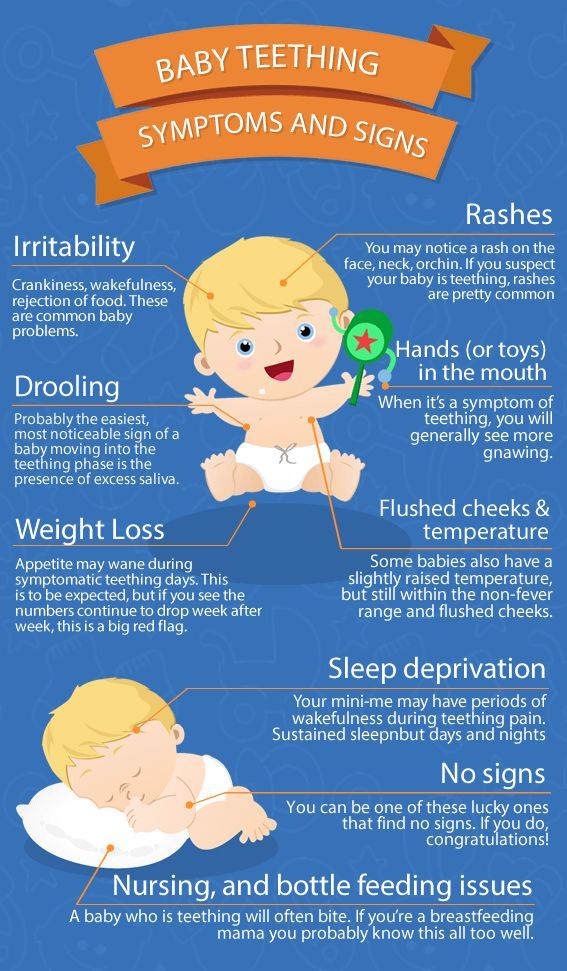
| Baby teeth | Upper jaw eruption / month | Lower jaw eruption / month |
| Center cutter | 8-12 | 6-10 |
| Lateral cutter | 9-13 | 10-16 |
| Fang | 16-22 | 17-23 |
| First molar | 13-19 | 14-18 |
| Second molar | 25-33 | 23-31 |
The specified periods are average indicators, varying depending on individual and family characteristics [4,5] . But the sequence of appearance of teeth is essential, and it is better to track and record it. From a physiological point of view, the correct order of eruption of milk teeth in children is important for bite formation .
But the sequence of appearance of teeth is essential, and it is better to track and record it. From a physiological point of view, the correct order of eruption of milk teeth in children is important for bite formation .
Teething aid
The appearance of milk teeth is not an easy process not only for the children themselves, but also for their parents. The most common teething symptoms:
-
swelling and redness of the gums;
-
increased salivation;
-
itching and urge to keep hands, toys in mouth;
-
capriciousness of a child;
-
sleep disorder;
-
refusal to breast, bottle or complementary foods;
-
fever;
-
stool disorders;
-
runny nose.
The following will help you get through this period as comfortably as possible:
-
special teething rings that relieve itching, especially with a cooling effect;
-
local anesthetic dental gels;
-
antipyretic and analgesic preparations;
Gentle silicone fingertip massage to soothe and relieve your baby [6]
Baby Teeth Care
As soon as the first tooth erupts, don't put off going to the dentist. Schedule a visit (at least once every 3-4 months). And after the first birthday, it is also desirable to be observed by an orthodontist. If there are no problems, visits to him should be repeated once a year [7,8]
Schedule a visit (at least once every 3-4 months). And after the first birthday, it is also desirable to be observed by an orthodontist. If there are no problems, visits to him should be repeated once a year [7,8]
Proper care at home is important.
-
The milk teeth are suitable for an ultra-soft toothbrush with a small head.
-
Children's mouth rinses are used from about 4 years of age or from the time the child can spit.
-
Parents should supervise the brushing of preschool children's teeth and, if necessary, help and clean missed areas.
-
Adults should teach their children to rinse their mouths after eating from an early age.
-
Until the child has learned to spit on his own, toothpaste should not contain fluorides.
-
A bathroom timer or a favorite song helps you stick to the 2-minute brushing time.
-
Solid food should be included in the diet daily in sufficient quantities to properly form the bite and stimulate the gums.

These simple tips help keep baby teeth healthy from the very beginning until they are naturally replaced by permanent teeth.
List of sources
-
Izmestieva OV, Galaktionova M. Yu., Manashev GG Characteristics of exogenous and endogenous factors affecting the eruption of temporary teeth in children. 2012 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/harakteristika-ekzogennyh-i-endogennyh-faktorov-vliyayuschih-na-prorezyvanie-vremennyh-zubov-u-detey (date of access: 21.02.2020)
-
Galaktionova M. Yu., Izmest'eva OV Timing of eruption of temporary teeth and the nature of feeding children in the first year of life. 2012 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sroki-prorezyvaniya-vremennyh-zubov-i-harakter-vskarmlivaniya-detey-pervogo-goda-zhizni (date of access: 02/21/2020)
-
Iordanishvili AK, Korovin NV, Serikov AA Anatomical and topometric characteristics of the jaws during eruption and retention of wisdom teeth.
 2017 //https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/anatomo-topometricheskie-harakteristiki-chelyustey-pri-prorezyvanii-i-retentsii-zubov-mudrosti (Accessed: 02/21/2020)
2017 //https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/anatomo-topometricheskie-harakteristiki-chelyustey-pri-prorezyvanii-i-retentsii-zubov-mudrosti (Accessed: 02/21/2020) -
Bimbas E. S., Saipeeva M. M., Shishmareva A. S. Terms of eruption of permanent teeth in children of primary school age. 2016 //https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sroki-prorezyvaniya-postoyannyh-zubov-u-detey-mladshego-shkolnogo-vozrasta (date of access: 02/21/2020)
-
Shilova N., Berzina S., Brinkmane A., Dulevska I., Umbraszko S., Briede I. Timing and sequence of eruption of primary teeth and factors influencing them. 2017 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sroki-i-posledovatelnost-prorezyvaniya-molochnyh-zubov-i-vliyayuschie-na-nih-faktory (date of access: 02/21/2020)
-
Bogdanova NA, Zueva TE How to help a child with teething? A new look at an old problem. 2019 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/kak-pomoch-rebenku-pri-prorezyvanii-zubov-novyy-vzglyad-na-staruyu-problemu (date of access: 02/21/2020)
-
Ayupova FS Tactics of treatment of children with anomalies in the eruption of permanent posterior teeth.