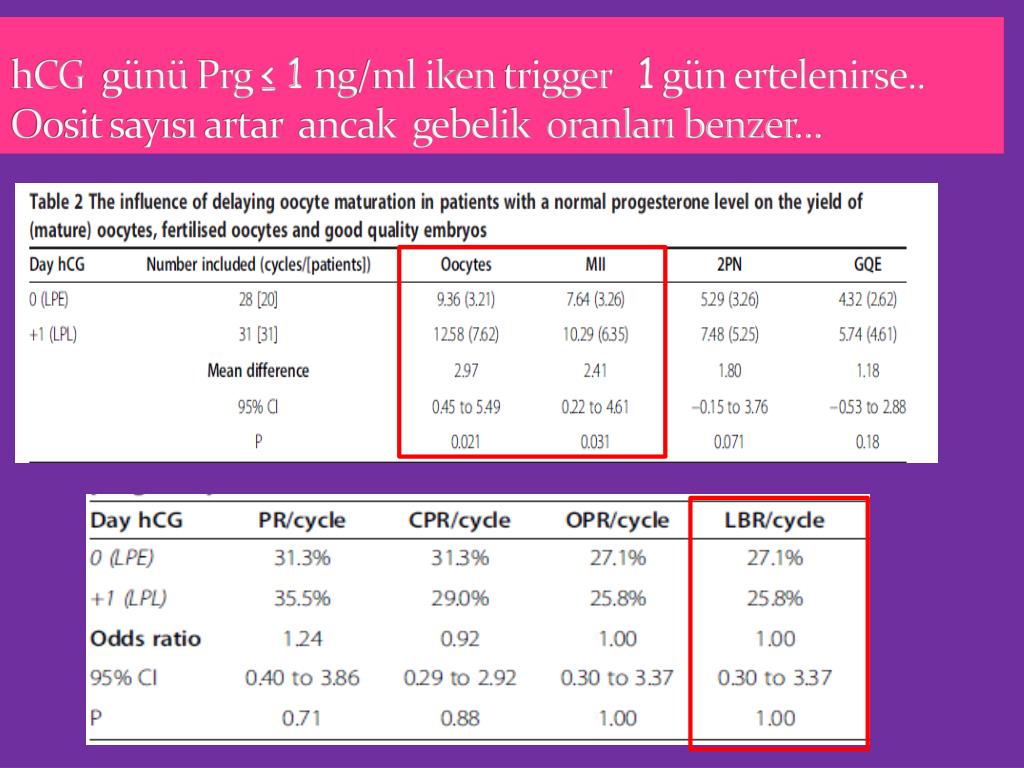
How can i get my hcg levels up
What causes Low HCG Levels in Early Pregnancy & How to increase HCG Levels in Pregnancy by Food
The HCG levels are checked by a doctor when a woman is unsure if she is pregnant. However, the absence of HCG in her blood does not always imply that she is not pregnant. For instance, she might be too early in her pregnancy for HCG levels to rise.
Every aspiring and would-be mom knows how important HCG is but do they understand what causes low HCG levels in early pregnancy? Here are all the details starting from the basics of HCG and then the causes of low Hcg and how to increase HCG levels during pregnancy by food.
What is HCG in pregnancy?Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is often referred to as the pregnancy hormone because it is produced by cells created in the placenta, which provides nourishment to the egg after it has been fertilised and attached to the uterine wall. A blood test may identify levels approximately 11 days after pregnancy, while a urine test can reveal levels 12-14 days after conception. HCG levels typically double every 72 hours for the first 8-11 weeks of pregnancy, then gradually fall and level out for the rest of the pregnancy.
HCG levels of more than five million (mIU/mL) international units per millilitre often suggest pregnancy. The first test score is considered to be the baseline level, which may range from 20 mIU/mL or even lower to 2,500 mIU/mL. Because of a medical practice known as "doubling time", the baseline level is crucial. During the first four weeks of a healthy pregnancy, HCG levels normally increase every two to three days. The levels will almost double every 96 hours after six weeks. Whether a woman's baseline level is more than 5 mIU/mL, her doctor may order a follow-up test to see if the number doubles.
Why does a doctor suggest an HCG injection during pregnancy?HCG injections are administered to pregnant women unless they are essential because the body of a pregnant woman needs high quantities of HCG to help sustain the pregnancy. Therefore, women with low HCG levels are given HCG injections during pregnancy.
Therefore, women with low HCG levels are given HCG injections during pregnancy.
"Low HCG levels may indicate a very early pregnancy or a pregnancy that ends in loss," Dr Lang, who is an Ob-Gyn at Baylor Obstetrics and Gynaecology at Children Pavillion for women in Texas, explains. Here are some other reasons for low HCG levels -
-
Miscalculated gestational age - Low HCG levels usually indicate a pregnancy that was considered to be between 6 and 12 weeks is not actually in that time period. Ultrasound and other HCG tests may be utilised to measure gestational age accurately.
-
Miscarriage - Low HCG levels might sometimes suggest that the woman has had or will have a miscarriage. If the pregnancy fails to produce a placenta, the levels may initially be normal but fail to increase.
-
Blighted egg - When an egg is fertilised, it adheres to the uterine wall but does not grow further.
 The gestational sac may produce HCG hormone, but the amount does not grow since the egg does not mature.
The gestational sac may produce HCG hormone, but the amount does not grow since the egg does not mature. -
Ectopic conception - Ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilised egg stays in the fallopian tube and develops there, which is fatal. Low HCG levels may be indicative of an ectopic pregnancy.
Although sometimes it's not possible for a woman to increase her HCG levels naturally, a few things can be considered to sustain normal pregnancy.
How to increase HCG levels in early pregnancy?HCG increases naturally in the body; however, if a woman's HCG is critically low, her doctor may prescribe medications or injections. A study claims that the HCG diet helps store energy for would-be mothers for the first trimester. Here's all about it-
The HCG diet severely restricts calories, generally to 500 per day but occasionally up to 1,500, according to Weinandy, an RD at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus..jpg) The HCG diet significantly decreases fat because of this stringent limitation, she says.
The HCG diet significantly decreases fat because of this stringent limitation, she says.
Here is a list of allowed foods, according to the HCG diet website:
-
Oranges, apples, strawberries, and red grapefruit are among the fruits available.
-
Vegetables that aren't starchy celery, Lettuce, onions, cabbage, cucumbers, and tomatoes are all options.
-
Chicken breast, shrimp, lean ground beef, white fish and lobster are all examples of lean meat.
The diet prohibits the following:
-
Fatty foods include fatty fish, nuts, and anything containing oil.
-
Potatoes, for example, are starchy vegetables.
-
Sugar of any form should not be included in the diet.
Although it is important to know what causes low HCG levels in early pregnancy, It is equally important to remember that It is normal for HCG to progress slowly during early pregnancy.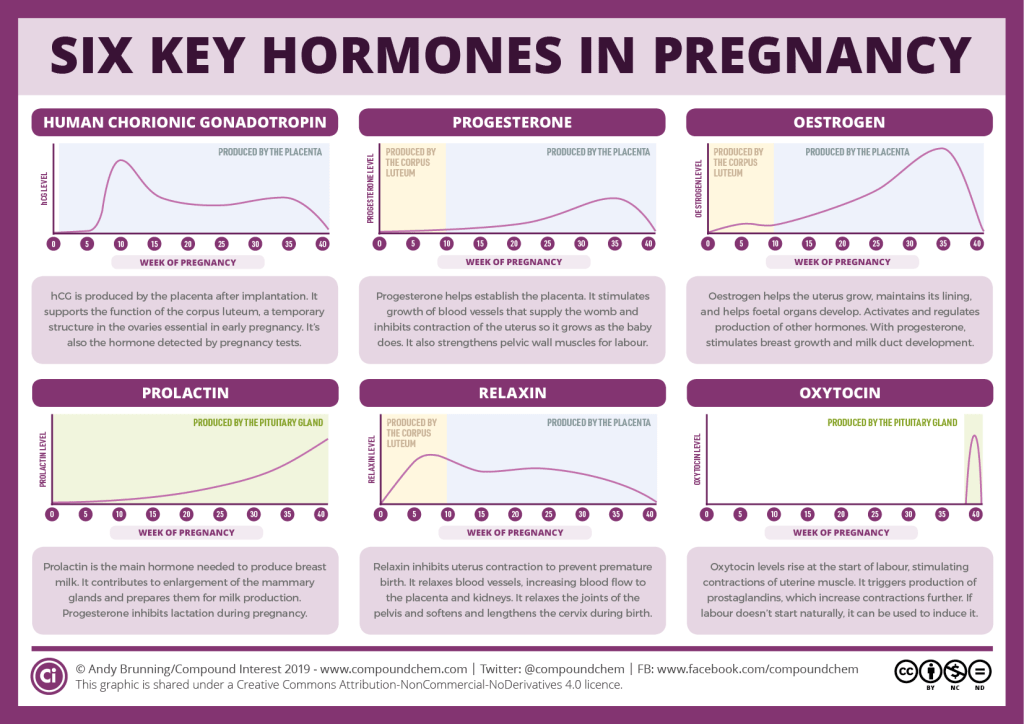 Also, some women have a healthy pregnancy throughout with not very high levels of HCG. Also, what works for one might not work for another. Food plays an important role in keeping a woman's hormones in balance, ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Follow the doctor's advice and make diet plans accordingly. Women should watch their symptoms, eat healthily and work as per their doctor's suggestions.
Also, some women have a healthy pregnancy throughout with not very high levels of HCG. Also, what works for one might not work for another. Food plays an important role in keeping a woman's hormones in balance, ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Follow the doctor's advice and make diet plans accordingly. Women should watch their symptoms, eat healthily and work as per their doctor's suggestions.
You may like: How to Increase Hcg Levels In Early Pregnancy Naturally? (mylofamily.com)
References:1. Clinical Pearl. (2018). Low hCG the Telltale Sign of Abnormal Pregnancy. journals.lww.com
2. Barjaktarovic M, Korevaar TI. (2017). Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentrations during the late first trimester are associated with fetal growth in a fetal sex-specific manner. NCBI
Trending Articles
Thumb Sucking | temper tantrums | swaddling | periods after delivery
Popular Articles
weight loss exercises for women | pregnancy walking | how to use cloth diapers | postpartum complications
Low hCG Levels: Causes, Treatments, and Symptoms
Low hCG Levels: Causes, Treatments, and Symptoms- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.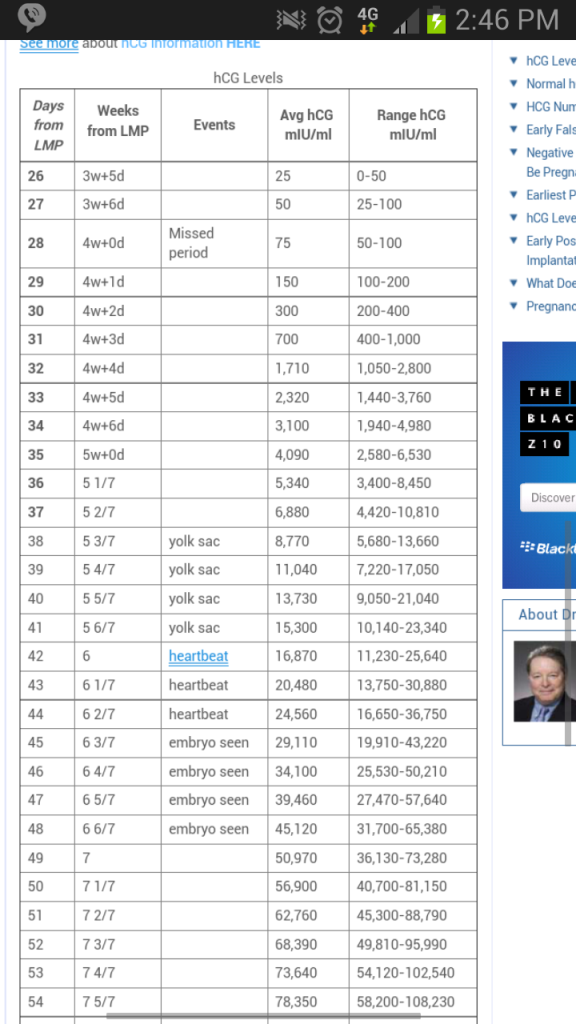 D. — By Becky Young on November 3, 2017
D. — By Becky Young on November 3, 2017
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.Was this helpful?
What is an hCG test?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced by your placenta once an embryo implants in the uterus.
The purpose of the hormone is to tell your body to continue to produce progesterone, which prevents menstruation from occurring. This protects the endometrial uterine lining and your pregnancy.
A pregnancy test can detect hCG in your urine if your levels are high enough. This is how the test identifies that you are pregnant. But only a blood test can give you a precise numerical hCG reading.
Purchase pregnancy tests here.
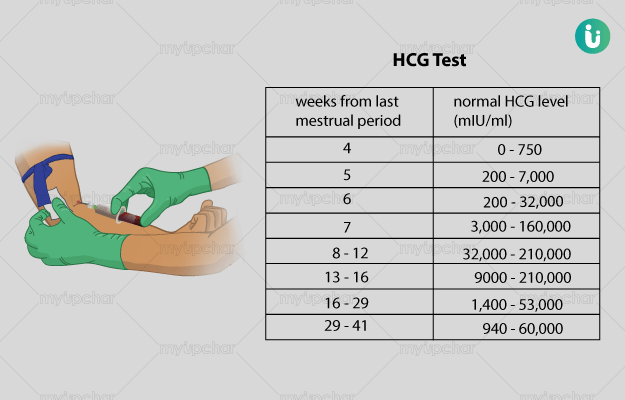
Standard hCG levels
Standard hCG levels vary quite massively from woman to woman. This is because hCG levels really depend on what is normal for you, how your body responds to pregnancy, as well as how many embryos you are carrying. The way a woman’s body reacts to pregnancy is entirely unique.
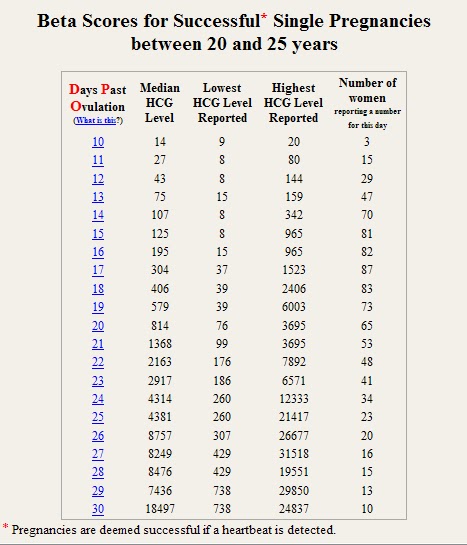
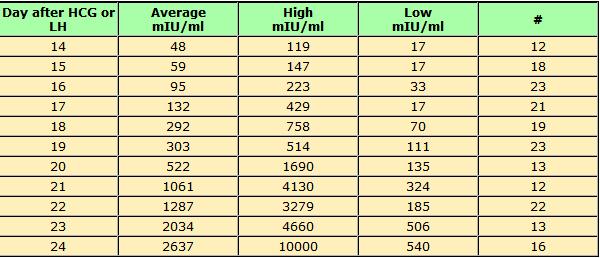
The table below gives you a guideline as to the normal wide range of hCG levels in each week of pregnancy. hCG levels are measured in milli-international units of hCG hormone per milliliter of blood (mIU/mL).
hCG levels usually consistently rise until around week 10–12 of your pregnancy, when the levels plateau or even decrease. This is the reason why pregnancy symptoms can be greater in the first trimester and ease off after this time for many women.
This is the reason why pregnancy symptoms can be greater in the first trimester and ease off after this time for many women.
In early pregnancy, hCG levels usually double every two to three days. Interestingly, when the measurements start off high they don’t expand at the same rate. If they start off more slowly, the increase ends up happening much quicker.
If your hCG levels fall below the normal range, your doctor may want you to have a blood test every two to three days to ensure the levels are increasing. A single measurement of your hCG level is not useful. To give an accurate indication, a series of hCG blood tests needs to be taken a couple of days apart and the readings compared. There is often variation with a rapid increase in numbers, especially in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Causes of low hCG levels
If your hCG levels fall below the normal range, it’s not necessarily a cause for concern. Many women have gone on to have healthy pregnancies and babies with low hCG levels. Most women don’t ever have cause to find out what their hCG levels are specifically.
Most women don’t ever have cause to find out what their hCG levels are specifically.
However, sometimes low hCG levels can be caused by an underlying problem.
Gestational age miscalculated
Typically, the gestational age of your baby is calculated by the date of your last menstruation. This can be easily miscalculated, particularly if you have a history of irregular periods or are unsure of your dates.
When low hCG levels are detected, it’s often because a pregnancy that was thought to be between 6 and 12 weeks is actually not that far along. An ultrasound and further hCG tests can be used to calculate the gestational age correctly. This is usually the first step when low hCG levels are detected.
Miscarriage
A miscarriage is a pregnancy loss that occurs before 20 weeks of gestation. Sometimes low hCG levels can indicate that you have had or will have a miscarriage. If the pregnancy fails to develop a placenta, then the levels may be normal initially but fail to rise. Common signs that you are experiencing a miscarriage are:
Common signs that you are experiencing a miscarriage are:
- vaginal bleeding
- abdominal cramps
- passing tissue or clots
- cessation of pregnancy symptoms
- discharge of white/pink mucus
Blighted ovum
This is when an egg is fertilized and attaches to the wall of your womb, but does not continue to develop. When the gestational sac develops, hCG hormone can be released, but the level does not rise since the egg doesn’t develop.
This occurs very early in pregnancy. Most women won’t even know that it’s taken place. Usually you’ll experience your normal menstruation symptoms and assume it’s your usual period. However, if you’re trying to conceive, you may do an early pregnancy test that could pick up the presence of hCG.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is when the fertilized egg remains in the fallopian tube and continues to develop. It’s a dangerous and life-threatening condition, as it may cause the fallopian tube to rupture and bleed excessively. Low hCG levels can help to indicate an ectopic pregnancy. At first the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy can be similar to those of a normal pregnancy, but as it progresses you can experience the following:
Low hCG levels can help to indicate an ectopic pregnancy. At first the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy can be similar to those of a normal pregnancy, but as it progresses you can experience the following:
- abdominal or pelvic pain that worsens with straining or movement (this can happen strongly on one side initially and then spread)
- heavy vaginal bleeding
- shoulder pain caused by internal bleeding (the bleeding aggravates the diaphragm and presents as pain at the tip of the shoulder)
- pain during intercourse
- pain during a pelvic examination
- dizziness or fainting due to internal bleeding
- symptoms of shock
How is it treated?
Unfortunately, there is nothing that can be done to treat low hCG levels, though low levels alone are not always a cause for concern.
If your low hCG levels have been caused by a miscarriage, it’s possible that you may need treatment if any pregnancy tissue is left inside your womb. If there’s no tissue retained, then you won’t require any treatment at all. If there is, then there are three treatment options available:
If there’s no tissue retained, then you won’t require any treatment at all. If there is, then there are three treatment options available:
- You can wait for the tissue to pass naturally.
- You can take medication to help you to pass the tissue.
- You can have it surgically removed.
Your doctor will discuss with you what the best course of action is.
The treatments for an ectopic pregnancy are similar. Medications are given to prevent the pregnancy from continuing to grow. If surgery is required, it’s standard for the doctors to remove the affected fallopian tube as well as the pregnancy.
What’s the outlook?
Low hCG levels alone are not necessarily a reason to be worried. There are many factors that affect the levels, and the normal range varies hugely between individual women. Your doctor will be able to monitor your hCG levels for you if you have concerns. Even if they remain low, there is nothing that you can do. It’s also important to remember that low hCG isn’t caused by anything you’ve done.
If your low hCG levels are due to a pregnancy loss, this doesn’t necessarily mean that you won’t be able to get pregnant and carry to term in the future. If you lose a fallopian tube due to an ectopic pregnancy, your fertility shouldn’t change significantly as long as your other tube is functioning. Even if it isn’t, reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization can help lead to successful pregnancy.
Last medically reviewed on November 3, 2017
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Fan J, et al. (2017). Advances in human chorionic gonadotropin detection technologies: A review.
ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/pubmed/29056064
nih.gov/pubmed/29056064 - Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG): The pregnancy hormone. (2017).
americanpregnancy.org/while-pregnant/hcg-levels/ - Lawrenz B, et al. (2017). Luteal phase serum progesterone levels after GnRH-agonist trigger – how low is still high enough for an ongoing pregnancy?
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29037085 - Matson PL, et al. (1990). Measurement of human chorionic gonadotropin during early pregnancy: A comparison of two immunoradiometric assays.
link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF01135683 - Schumacher A. (2017). Human chorionic gonadotropin as a pivotal endocrine immune regulator initiating and preserving fetal tolerance.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29039764
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Nov 3, 2017
Written By
Becky Young
Edited By
Phil Riches
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M. D. — By Becky Young on November 3, 2017
D. — By Becky Young on November 3, 2017
Read this next
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) Blood Test
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Get the facts on the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) blood test. Although it's often used to detect pregnancy, it has other uses such as detecting…
READ MORE
Can Taking Prometrium Vaginally Prevent Miscarriage?
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
Progesterone is known as the “pregnancy hormone.” Without enough progesterone, a woman’s body can’t continue to grow a fertilized egg. If you’ve…
READ MORE
How Many Eggs Are Women Born With? And Other Questions About Egg Supply
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
If you're looking to get pregnant, you may wonder how many eggs you have at various points in life.
 The short answer: It goes from millions to none.
The short answer: It goes from millions to none.READ MORE
How Does Clomid Work for Fertility?
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Clomid is also known as clomiphene citrate. It’s an oral medication that is often used to treat certain types of female infertility.
READ MORE
Your Guide to the Egg Donation Process
Medically reviewed by Fernando Mariz, MD
There are many reasons you might consider donating your eggs. Learn more about the egg donation process, including possible risks, legal…
READ MORE
What’s the Connection Between Your Biological Clock and Fertility?
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
The biological clock describes the pressure people may feel to get pregnant while at the peak of their reproductive years, before fertility declines.
READ MORE
How Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Affects Fertility and What to Do
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common cause of infertility. We'll discuss why and what you can do.
READ MORE
hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin, indications for the appointment, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
I confirm More
- INVITRO
- Library
- Laboratory...
- HCG, Chorionic...
ECO
Miscarriage
Pregnancy
2083 July 29
We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, β-hCG, beta-hCG, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
Chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced by the outer shell of the embryo, and is normally determined in the blood and urine of a woman only when pregnancy occurs.
Chorionic gonadotropin consists of two subunits - alpha and beta. The beta subunit (β-hCG) used for the immunometric determination of the hormone is unique. To monitor the course of pregnancy, the determination of the beta subunit of hCG is used. The level of beta-hCG in the blood as early as 6-8 days after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy (the concentration of β-hCG in the urine reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later than in the blood serum).
To monitor the course of pregnancy, the determination of the beta subunit of hCG is used. The level of beta-hCG in the blood as early as 6-8 days after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy (the concentration of β-hCG in the urine reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later than in the blood serum).
HCG has a multifaceted effect on the body of a pregnant woman: it affects the development of the embryo and fetus, stimulates the synthesis of estrogens and androgens by ovarian cells, promotes the functional activity of the chorion and placenta, and ensures the successful course of pregnancy.
The introduction of hCG into the body of non-pregnant women stimulates ovulation and the synthesis of sex hormones necessary for conception. In men, this hormone enhances the formation of seminal fluid, activates the production of gonadosteroids.
In early pregnancy and up to the 2nd trimester, β-hCG supports the production of hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy, and in male fetuses it stimulates cells responsible for the formation and development of the male reproductive system.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, beta-hCG, b-hCG, Human Chorionic)
Synonyms: Beta-hCG general. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
RUB 685
Add to cart
Indications for determining the level of hCG in women
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- Exclusion/confirmation of pregnancy, including ectopic (ectopic).
- Diagnosis of the state of the fetus at different stages of pregnancy.
- Assessment of the state of the placenta at different stages of pregnancy.
- Dynamic monitoring of fetal development during pregnancy, including in the diagnosis of malformations.
- Suspicion of the presence of neoplastic diseases of the reproductive system, such as hydatidiform mole (a rare pathology of the fetal egg, in which instead of developing the embryo, the chorionic villi grow), chorionepithelioma (a malignant tumor that develops from the epithelium of the villi of the fetal egg).
- Performing artificial termination of pregnancy.
Indications for determining the level of hCG in men:
The presence of suspicion of tumors of the testicles.
Deadline for this test is 1 working day, excluding the day of taking the biomaterial.
Rules for preparing for a blood test to determine the level of hCG
non-specific: it is enough to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol on the eve of the procedure, limit stress and intense physical activity for a week; blood donation is carried out on an empty stomach.
The determination of hCG in the blood is possible already on the 6-8th day after conception. The use of urinary test systems (rapid pregnancy tests) will be informative starting from the 7th day after the fertilization of the egg. To confirm the result, it is recommended to re-determine the level of the hormone a few days after the first analysis.
You can take a blood test for hCG (thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin, Thyroid StimulatingHormone, TSH) at the nearest INVITRO medical office. The list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory testing is presented in the "Addresses" section.
Reasons leading to high levels of β-hCG
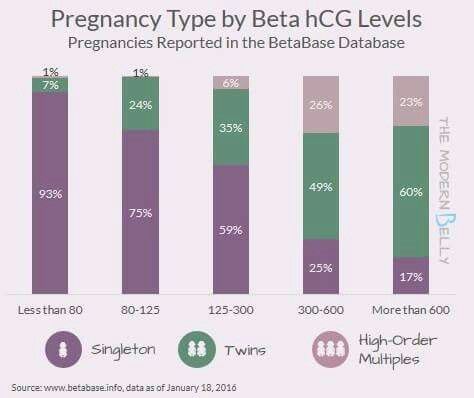
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Wrong timing of pregnancy.
- Pathological pregnancy: the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure, loss of protein in the urine (preeclampsia), convulsions (eclampsia), toxicosis.
- The presence of a pregnant woman with chronic diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus).
- Multiple fetal malformations (in this situation, the determination of the level of β-hCG together with other indicators, the so-called "triple test" is used. This study is used as a screening, and not for making a diagnosis.).
Reasons for fixing a decrease in the level of β-hCG
- Incorrectly established terms of pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Frozen pregnancy.
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Fetal or placental disorders (including placental insufficiency).
- Intrauterine fetal death (in this case, it is informative to determine the level of the hormone in the first and second trimesters).
During abortions, the level of β-hCG is also monitored, the dynamics of growth / fall of which can be used to judge the completeness of the manipulation.
Determining the level of hCG, in addition to establishing the fact of pregnancy in the early stages, is part of the screening examination of pregnant women in the first trimester, along with ultrasound.
2 040 RUB
Add to cart
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 3,090 Sign up
In gynecological practice, human chorionic gonadotropin is used to treat infertility, stimulate ovulation, and synthesize sex steroids. In urology, it is used in the treatment of cryptorchidism (undescended testicles) and infertility associated with impaired spermatogenesis.
Quantitatively, β-hCG is determined in the blood, for a qualitative determination, special test systems (pregnancy tests) are used, and in this case, urine serves as a biomaterial.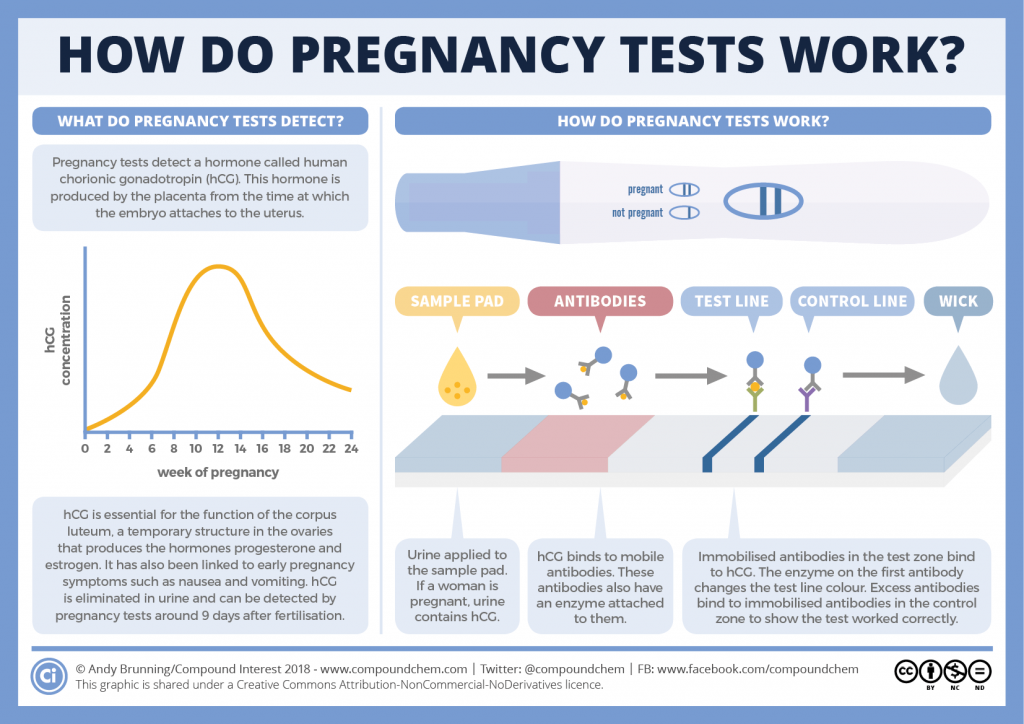
Quantitative determination of the level of hCG allows you to monitor the course of pregnancy in dynamics. To do this, obstetrician-gynecologists have developed tables for increasing the level of hCG, depending on the duration of pregnancy in weeks. The sensitivity of the determination is in the range of 1.2-1125000 mU/ml.
Reference values of hCG levels in dynamics by gestational age
| Pregnancy (weeks from conception) | HCG level (mU / ml) |
| 2 | 25–300 |
| 3 | 1500–5000 |
| 4 | 10000–30000 |
| 5 | 20000–100000 |
| 6–11 | 20000–>225000 |
| 12 | 19000–135000 |
| 13 | 18000–110000 |
| 14 | 14000–80000 |
| 15 | 12000–68000 |
| 16 | 10000–58000 |
| 17–18 | 8000–57000 |
| 19 | 7000–49000 |
| 20–28 | 1600–49000 |
| Men and non-pregnant women | 0–<5 mU/ml |
Values ranging from 5 to 25 mU / ml do not allow unambiguous confirmation or denial of pregnancy, therefore, a second study is required after two days.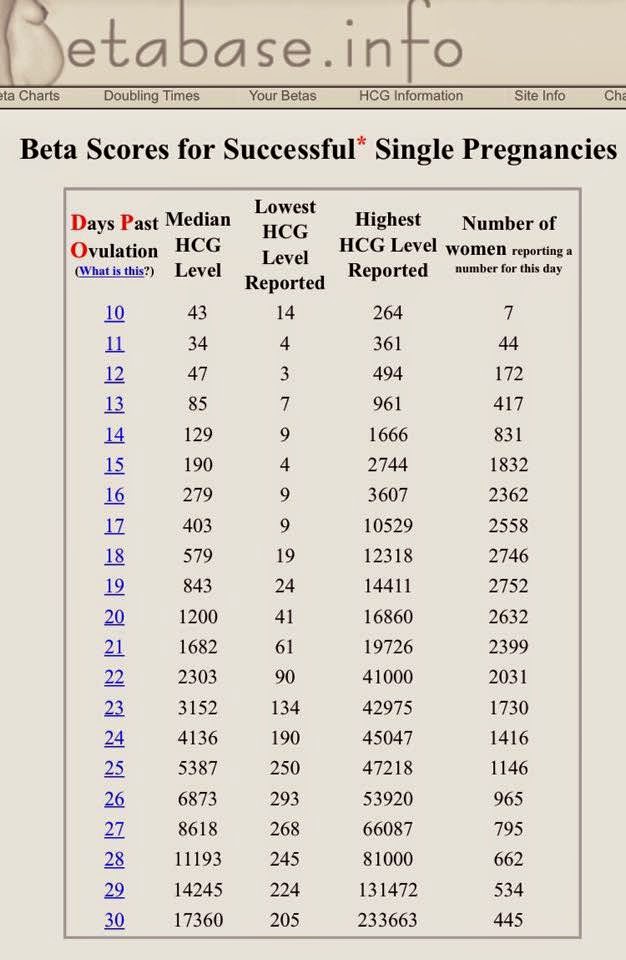
Since the hormone is produced by the placenta, during normal pregnancy, with placental pathology (for example, with fetoplacental insufficiency - a violation of the development of the fetus and placenta), with multiple pregnancies, the values of β-hCG will differ. With a normal pregnancy until the fifth week, the level of the hormone rises exponentially: every two days its concentration doubles, reaching a peak by the 11th week of gestation. Accordingly, in a multiple pregnancy, the level of β-hCG will be even higher than in a single pregnancy.
If the indicator deviates from the norm, additional ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus, appendages) is required.
US examination of pelvic organs (uterus, adnexa)
Ultrasound scanning of the organs of the female reproductive system to assess the shape and size, as well as exclude pathology.
RUB 2,590 Sign up
However, with a normal hCG value, additional examinations may also be needed:
- Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy (required to confirm pregnancy, clarify the term).
Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy
Examination to confirm pregnancy and determine the place of attachment of the ovum (to exclude ectopic pregnancy).
RUB 2,390 Sign up
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to assess the characteristics and confirm the normal development of the fetus.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 3,090 Sign up
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to confirm the presence of several fetuses, determine their characteristics; It is necessary for planning the subsequent actions of the doctor and the management of pregnancy.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
A study that allows you to evaluate the growth and development of fetuses, their position in the uterus, and make a plan for further pregnancy management.
RUB 3,990 Sign up
- Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week) - performed in case of suspected ectopic pregnancy.
Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week)
Additional ultrasound, which is prescribed in the presence of concomitant pathologies to monitor the condition of the fetus.
RUB 2,790 Sign up
- Lab tests to be performed in the first trimester are collected in the Pregnancy: 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) profile.

For professional assistance in interpreting the results, contact
obstetrician-gynecologist
.
Sources:
- www.invitro.ru
- Clinical guidelines "Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2021.
- Clinical guidelines "Premature birth". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2020.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
Recommendations
-
PSA (prostate specific antigen) test
7261 may 13
-
Human papillomavirus
14111 04 May
-
Alkaline phosphatase
13168 16 April
Show more
Similar articles
Heredity
Pregnancy
ECO
Research to determine biological relationship in the family: paternity and motherhood
You can perform molecular genetic studies that reveal predisposition to various diseases, and now also undergo studies to establish biological relationship in the family: paternity and motherhood.
More
ECO
Thrombophilia
Pregnancy
Thrombosis: extended panel 114GP
Thrombosis, extended panel: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the analysis, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Pregnancy
ECO
Physiological changes in blood parameters during pregnancy
Changes in the coagulogram of a pregnant woman is a physiological process associated with the appearance of the uteroplacental circulation. This process is associated with the evolutionary, adaptive reactions of the body of a pregnant woman. The body of a woman prepares for the costs during gestation and possible blood loss during childbirth. During the physiological course of pregnancy, the activity of the procoagulant link increases. Already at the 3rd month of pregnancy, fibrinogen rises (this is the factor I (first) of the plasma coagulation system) and reaches maximum values on the eve of childbirth. Therefore, gynecologists reasonably recommend monitoring this indicator during pregnancy (1 time per trimester, if there are deviations of these indicators more often, 1 time per week).
This process is associated with the evolutionary, adaptive reactions of the body of a pregnant woman. The body of a woman prepares for the costs during gestation and possible blood loss during childbirth. During the physiological course of pregnancy, the activity of the procoagulant link increases. Already at the 3rd month of pregnancy, fibrinogen rises (this is the factor I (first) of the plasma coagulation system) and reaches maximum values on the eve of childbirth. Therefore, gynecologists reasonably recommend monitoring this indicator during pregnancy (1 time per trimester, if there are deviations of these indicators more often, 1 time per week).
More
Hypogonadism
ECO
Menopause
Climax
Estradiol
Estradiol
More
ECO
Hypogonadism
Menopause
Climax
Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH, AMH, anti-Mullerian hormone)
Anti-Mullerian hormone: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Nothing found
Try changing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from list
Medical office not found
Try changing your query or select medical office from the list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
Nothing found
Please try editing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
Subscribe to our newsletters
Enter e-mail
I consent to processing of personal data
Subscribe
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics
Content
- Table of average hCG norms
- Table of average hCG norms for carrying twins
- Table of average hCG values after IVF with engrafted twins
- Guidelines for free β-hCG subunit
- Norm РАРР-А
- What if I am at high risk?
- How to confirm or deny the results of screening?
- The doctor says I need an abortion.
 What to do?
What to do?
One of the main tests during pregnancy is the study of the level of pregnancy hormone - hCG or human chorionic gonadotropin. If expectant mothers want to know if the hormone level is normal, we made a summary table of values
Table of average hCG norms:
| Gestation period | HCG in mU/ml | HCG in mIU/ml | HCG in ng/ml |
| 1-2 weeks | 25-156 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 2-3 weeks | 101-4870 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 3-4 weeks | 1100 – 31500 | 25-156 | - |
| 4-5 weeks | 2560 - 82300 | 101-4870 | - |
| 5-6 weeks | 23100 - 151000 | 1110 -31500 | - |
| 6-7 weeks | 27300 - 233000 | 2560 -82300 | - |
| 7-11 weeks | 20900 - 2 | 23100 -233000 | 23.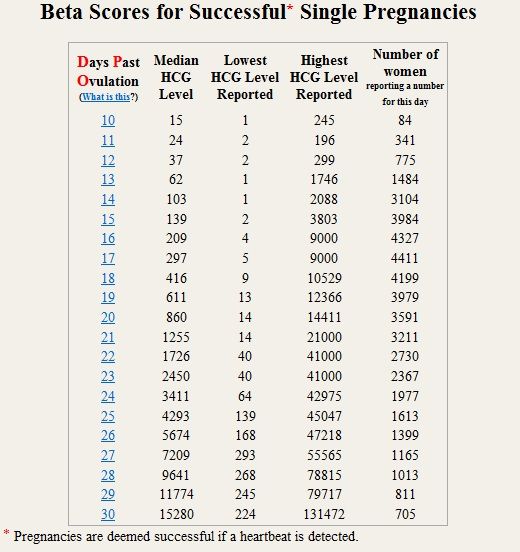 7 - 130.4 7 - 130.4 |
| 11-16 weeks | 6140 - 103000 | 20900 -103000 | 17.4 - 50.0 |
| 16-21 weeks | 4720 - 80100 | 6140 – 80100 | 4.67 - 33.3 |
| 21-39 weeks | 2700 - 78100 | 2700 -78100 | - |
Table of average hCG norms when carrying twins:
| Gestation period, weeks | Mean hCG concentration range (mU/ml) |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 – 112 |
| 2-3 weeks | 209 – 9740 |
| 3-4 weeks | 2220 - 63000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 5122 - 164600 |
| 5-6 weeks | 46200 - 302000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 54610 - 466000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 41810 - 582000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 12280 - 206000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 9440 – 160210 |
| 21-39 weeks | 5400 - 156200 |
Table of average hCG values after IVF with engrafted twins:
| Gestational age, weeks | HCG range, mU/ml |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 – 600 |
| 2-3 weeks | 3000 - 10000 |
| 3-4 weeks | 20000 – 60000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 5-6 weeks | 100000 - 400000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 100000 - 400000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 40000 – 120000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 20000 – 70000 |
| 21-39 weeks | 20000 – 120000 |
Free hCG β-subunit limits
Measuring free hCG β-subunit levels can more accurately determine the risk of Down syndrome in an unborn child than measuring total hCG.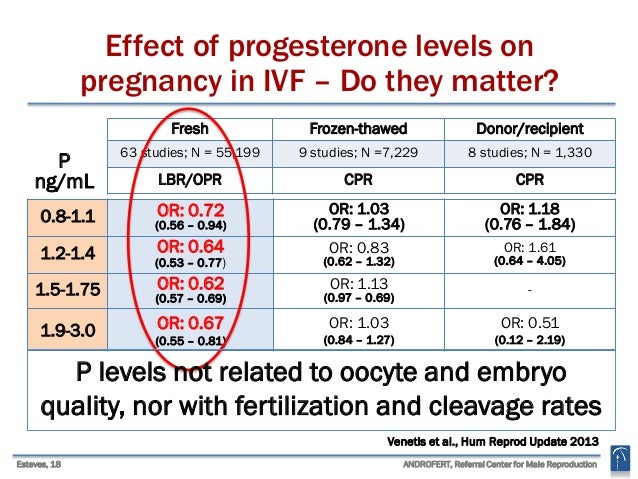
Norms for free β-hCG subunit in the first trimester:
| Gestational period, weeks | HCG in ng/ml |
|---|---|
| 9 weeks | 23.6 - 193.1 ng/ml, or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 10 weeks | 25.8 - 181.6 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 11 weeks | 17.4 - 130.4 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 12 weeks | 13.4 - 128.5 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 13 weeks | 14.2 - 114.7 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM.
If hCG is abnormal, then:
- If the free hCG β-subunit is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, then the child has an increased risk of Down syndrome.
- If the free hCG β-subunit is below normal for your gestational age, or is less than 0.5 MoM, then the baby is at increased risk of Edwards syndrome.
PAPP-A norm
PAPP-A, or "pregnancy-associated plasma protein A" as it is called, is the second indicator used in first trimester biochemical screening. The level of this protein constantly increases during pregnancy, and deviations in the indicator may indicate various diseases in the unborn child.
The norm for PAPP-A depending on the duration of pregnancy:
| Gestational age, weeks | HCG in ng/ml |
|---|---|
| 8-9 weeks | 0.17 - 1.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 9-10 weeks | 0.32 - 2.42 mU/mL, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 10-11 weeks | 0.46 - 3.73 mU/mL, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 11-12 weeks | 0.79- 4.76 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 12-13 weeks | 1. 03 - 6.01 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM 03 - 6.01 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 13-14 weeks | 1.47 - 8.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM.
If PAPP-A is abnormal:
- If PAPP-A is lower for your gestational age, or less than 0.5 MoM, your baby is at increased risk for Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome.
- If PAPP-A is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, but other screening values are normal, then there is no cause for concern.
Studies have shown that women with elevated PAPP-A levels during pregnancy are not at greater risk of fetal disease or pregnancy complications than other women with normal PAPP-A.
What if I am at high risk?
If your screening reveals an increased risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, then this is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy.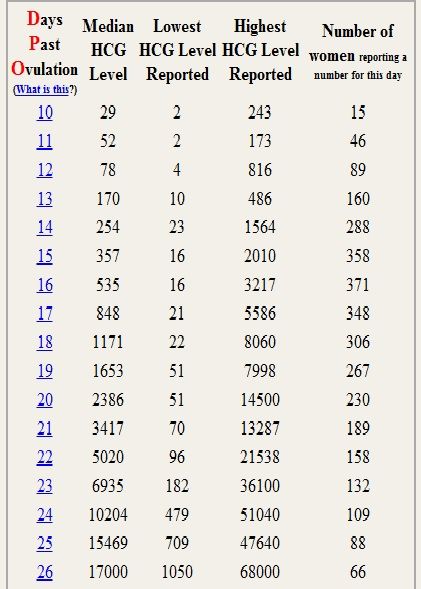 You will be referred for a consultation with a geneticist who, if necessary, will recommend examinations: chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis
You will be referred for a consultation with a geneticist who, if necessary, will recommend examinations: chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis
How to confirm or refute the screening results?
If you think that the screening was not done correctly, you should be re-examined at another clinic, but for this you need to retake all the tests and undergo an ultrasound. This method is possible only if the gestational age at the time of the examination does not exceed 13 weeks and 6 days.
The doctor says I need an abortion. What to do?
Unfortunately, there are times when a doctor strongly recommends or even forces an abortion based on screening results. Remember: no doctor has the right to such actions. Screening is not a definitive method for diagnosing Down syndrome and, based on poor results alone, a pregnancy should not be terminated.
Say that you want to consult a geneticist and undergo diagnostic procedures for Down syndrome (or other disease): chorionic villus biopsy (if you are 10-13 weeks pregnant) or amniocentesis (if you are 16-17 weeks pregnant).
The author of the article:
Ananyina Anna Alexandrovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Highest category
Work experience since 2010
Sign up
Eat more foods rich in iron: beef tongue, liver, buckwheat and oatmeal, prunes, dried apricots, green apples, etc. But diet alone will not work to raise hemoglobin.
Medical therapy with iron supplements is required. If the problem is associated with insufficient intake of iron into the body, one set of drugs is needed, if with absorption, another. The doctor must select drugs.
Injection therapy may be required for more severe anemia.
If there are no contraindications, natural childbirth is possible. Only an obstetrician-gynecologist should decide on the possibility of EP.
Get tested
- Chest X-ray
- KSR
- Hepatitis B HBsAg
- Hepatitis C Anti-HCV
- Rubella IgM
- Rubella IgG
- HIV
- B/P for flora and senses.
 - from throat
- from throat
Specialist consultation:
- General practitioner consultation
With an increase in the duration of pregnancy and the growth of the baby, the uterus increases - this can lead to increased tone. Sometimes tension arises in response to the movements of the child. Strong physical exertion, stress, overwork of a pregnant woman can also lead to increased tone.
In early pregnancy, uterine tone may be associated primarily with reduced progesterone production. In this case, the doctor prescribes the patient treatment with progesterone preparations.
Symptoms of increased tone
All pregnant women experience tone differently. Someone - like heaviness and tension in the lower abdomen. Others - as a pulling pain in the lumbar region. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, a woman can feel the tone by putting her hand on her stomach: the uterus becomes "stone", then relaxes.
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Specify the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Ph.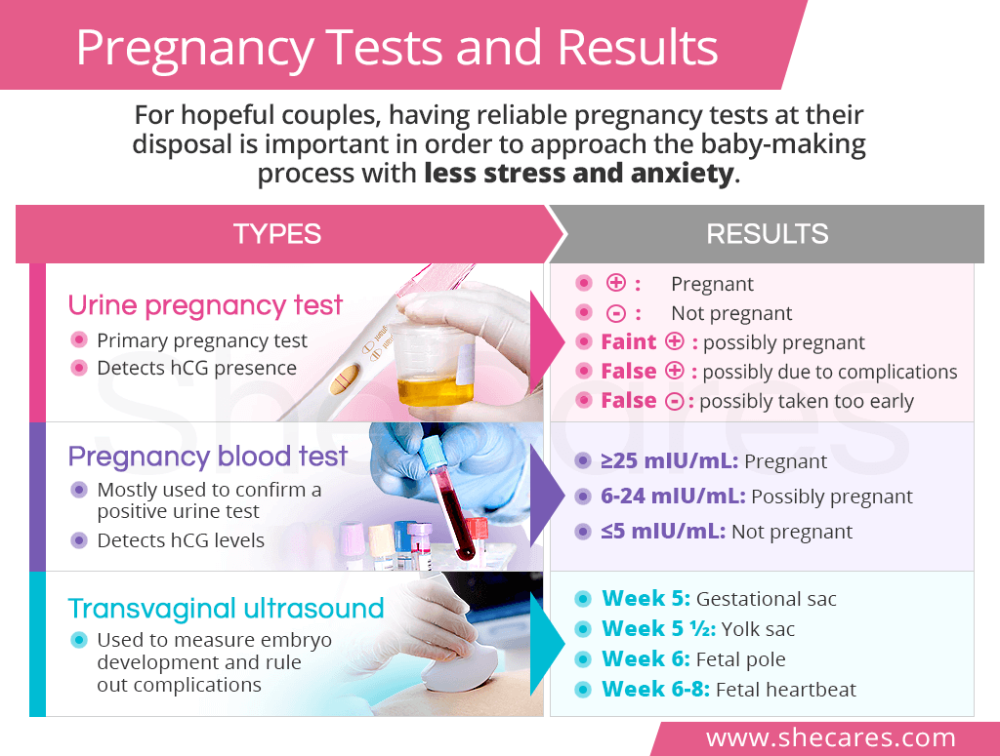 D.
D.
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Check the cost of admission
in Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Specify the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist / Gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the second category
Check the cost of admission
in Call-center
Mobile application of the clinic
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and much more.