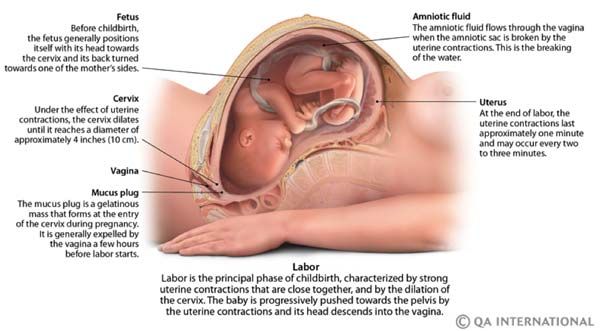
Fetus in sac
Amniotic fluid Information | Mount Sinai
Amniotic fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the unborn baby (fetus) during pregnancy. It is contained in the amniotic sac.
Amniocentesis is used to determine the health of an unborn baby. Amniotic fluid contains cells that are normally shed from the fetus. Samples of these cells are obtained by withdrawing some amniotic fluid. The chromosome analysis of these cells can be performed to determine abnormalities. In addition, the cells may be cultured and analyzed for enzymes, or for other materials that may indicate genetically transmitted diseases. Other studies can be done directly on the amniotic fluid including measurement of alpha-fetoprotein.
Amniotic fluid not only protects the fetus from injury and temperature changes, it also is circulated by the fetus every 3 hours.
Polyhydramnios may occur when a fetus cannot swallow a normal amount of amniotic fluid due to a gastrointestinal, neurological, or other problem.
Amniotic fluid surrounds the growing fetus in the womb and protects the fetus from injury and temperature changes. It also allows for freedom of fetal movement and permits musculoskeletal development. The amniotic fluid can be withdrawn in a procedure called amniocentesis to check for chromosomal defects or other abnormalities.
Information
While in the womb, the baby floats in the amniotic fluid. The amount of amniotic fluid is greatest at about 34 weeks (gestation) into the pregnancy, when it averages 800 mL. About 600 mL of amniotic fluid surrounds the baby at full term (40 weeks gestation).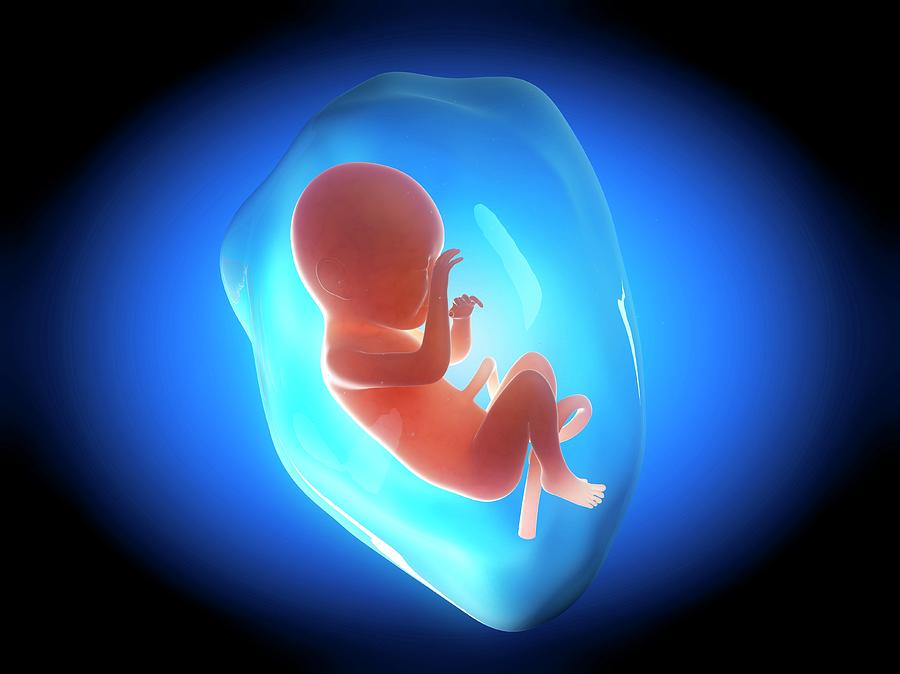
The amniotic fluid constantly moves (circulates) as the baby swallows and "inhales" the fluid, and then releases it.
The amniotic fluid helps:
- The developing baby to move in the womb, which allows for proper bone growth
- The lungs to develop properly
- Prevents pressure on the umbilical cord
- Keep a constant temperature around the baby, protecting from heat loss
- Protect the baby from outside injury by cushioning sudden blows or movements
Too much amniotic fluid is called polyhydramnios. This condition can occur with multiple pregnancies (twins or triplets), congenital anomalies (problems that exist when the baby is born), or gestational diabetes.
Too little amniotic fluid is known as oligohydramnios. This condition may occur with late pregnancies, ruptured membranes, placental dysfunction, or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal amounts of amniotic fluid may cause the health care provider to watch the pregnancy more carefully.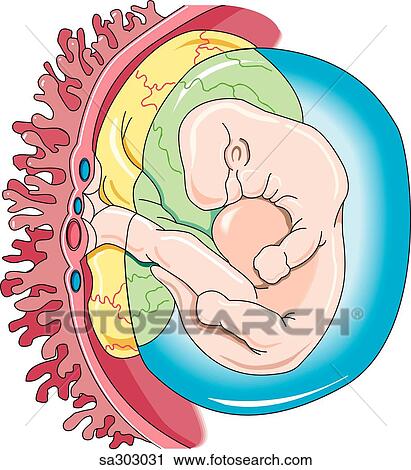 Removing a sample of the fluid through amniocentesis can provide information about the sex, health, and development of the fetus.
Removing a sample of the fluid through amniocentesis can provide information about the sex, health, and development of the fetus.
Burton GJ, Sibley CP, Jauniaux ERM. Placental anatomy and physiology. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 1.
Gilbert WM. Amniotic fluid disorders. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 28.
Ross MG, Beall MH. Amniotic fluid dynamics. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 4.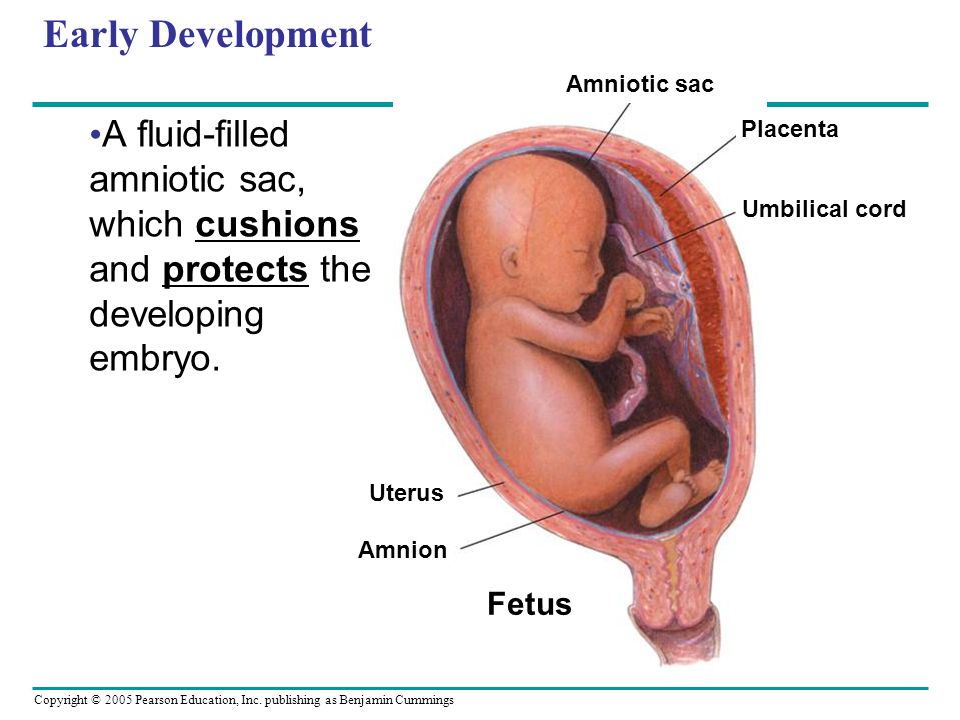
Last reviewed on: 12/3/2020
Reviewed by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Color, Smell, Function & Disorders
Overview
Amniotic fluid is a water-like substance that surrounds and protects a fetus (unborn baby) during pregnancy.What is amniotic fluid?
Amniotic fluid is a water-like substance surrounding the fetus in your uterus. The fetus grows inside an amniotic sac filled with amniotic fluid during pregnancy. The amniotic sac forms around 12 days after you become pregnant. When your water breaks (a sign of labor), your amniotic sac breaks and amniotic fluid leaks from your vagina.
Amniotic fluid is more than just a liquid the fetus floats in. Amniotic fluid contains nutrients, hormones, antibodies and other fluids to help keep the fetus healthy and protected. Amniotic fluid is constantly circulating because the fetus swallows it, then urinates it out. Having too little or too much amniotic fluid could cause problems for a pregnant person or the fetus.
Amniotic fluid is constantly circulating because the fetus swallows it, then urinates it out. Having too little or too much amniotic fluid could cause problems for a pregnant person or the fetus.
Function
What does amniotic fluid do?
Amniotic fluid has an important job in the uterus. It helps with fetal growth and development. Among other things, it:
- Protects the fetus from infection.
- Cushions the fetus's movements and helps it move.
- Helps the fetus's muscles and bones develop.
- Prevents the umbilical cord from getting compressed.
- Helps the fetus's digestive and respiratory systems develop.
- Regulates fetal body temperature.
- Protects it from your movements (like a fall or sudden blow).
Why is amniotic fluid important?
Amniotic fluid is necessary for a healthy pregnancy and helps prepare the fetus baby for the outside world. It acts as a cushion to protect them from your movements. This same cushion allows them to move freely and develops their muscles and bones. The fluid prevents the umbilical cord from compressing. The umbilical cord transports oxygen and nutrients from you to the fetus and could become squished without amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid contains antibodies to help strengthen the fetal immune system. The fetus practices breathing and swallows amniotic fluid to help develop its lungs and digestive system.
This same cushion allows them to move freely and develops their muscles and bones. The fluid prevents the umbilical cord from compressing. The umbilical cord transports oxygen and nutrients from you to the fetus and could become squished without amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid contains antibodies to help strengthen the fetal immune system. The fetus practices breathing and swallows amniotic fluid to help develop its lungs and digestive system.
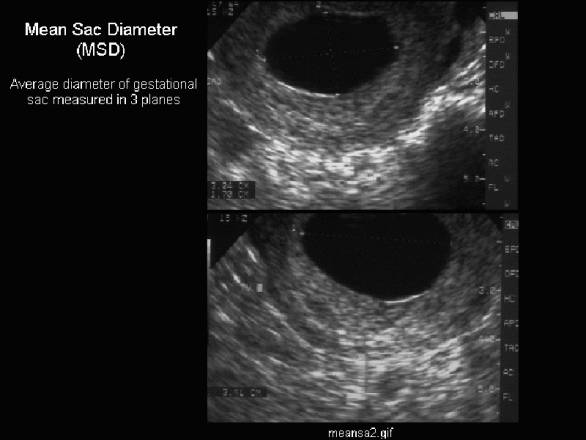
How is amniotic fluid measured?
Healthcare providers measure amniotic fluid using ultrasound. They measure pockets of amniotic fluid in specific areas of the amniotic sac, then calculate the total volume of fluid.
Anatomy
What color is amniotic fluid?
Amniotic fluid is mostly clear but can be a pale yellow like the color of straw. Amniotic fluid that's tinted brown or green means the fetus has passed meconium (their first poop) in your uterus.
Meconium in amniotic fluid can cause complications if the fetus breathes it in. In severe cases, the fetus may develop meconium aspiration syndrome and need immediate treatment after birth.
In severe cases, the fetus may develop meconium aspiration syndrome and need immediate treatment after birth.
What does amniotic fluid smell like?
Amniotic fluid should be odorless. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice a foul smell as it could be meconium-stained or mean there is an infection.
Is amniotic fluid sticky?
No, amniotic fluid isn't sticky. If you feel sticky vaginal discharge, it might be your mucus plug.
What creates amniotic fluid?
Amniotic fluid is mostly water for the first half of pregnancy. The fetus's pee makes up most of the amniotic fluid after about 20 weeks of pregnancy. This is because, like adults, the fetus will swallow liquid and pee it out.
How many liters of amniotic fluid is normal?
It depends on how far you are in your pregnancy. Your amniotic fluid levels peak at 34 to 36 weeks and then slowly decrease as you reach your due date (40 weeks). At its peak, there is a little less than 1 liter of fluid in the amniotic sac.
Conditions and Disorders
What are signs of leaking amniotic fluid?
Some pregnant people leak amniotic fluid during pregnancy. Amniotic fluid is clear, thin and odorless. It can have a hint of color (brown, green or yellow are most common). It's common for pregnant people to leak urine, so some people have difficulty distinguishing amniotic fluid from pee. Inspecting your underwear for smells or color can help you determine what it is. Urine has a unique smell and may be easier to control than amniotic fluid.
If you feel a strong gush of fluid from your vagina, it could be your water breaking. But there is an increase in vaginal secretions late in pregnancy, so it can be hard to tell the difference. Contact your healthcare provider if you believe your water has broken or if you're confused about what is leaking from your vagina.
What happens when you have low amniotic fluid?
Low amniotic fluid is called oligohydramnios. Low amniotic fluid affects about 4% of pregnant people. Several factors can contribute to low amniotic fluid. Some of them are:
Several factors can contribute to low amniotic fluid. Some of them are:
- Congenital conditions that affect your baby's kidneys or urinary tract.
- Going more than two weeks past your due date.
- Gestational diabetes.
- Growth-restricted babies.
- Early rupture of membranes.
- Problems with the placenta.
- Twins that share the same placenta.
What are the complications of low amniotic fluid?
Low amniotic fluid in the first six months of pregnancy is generally more dangerous. These complications could include miscarriage, physical deformities of the developing baby including lungs that don’t develop properly or premature birth.
If you're diagnosed with oligohydramnios in the last trimester (weeks 28 to 40) of pregnancy, complications could include:
- Umbilical cord compression.
- Fetal growth restriction.
- Respiratory issues.
- Increase risk of cesarean delivery.
How is low amniotic fluid treated?
It depends on how far along you are in your pregnancy. If you're close to full term (37 weeks of pregnancy), your healthcare provider may schedule an induction or monitor you more closely until delivery.
If you're close to full term (37 weeks of pregnancy), your healthcare provider may schedule an induction or monitor you more closely until delivery.
What happens if you have too much amniotic fluid?
Too much amniotic fluid is called polyhydramnios. It's a rare condition that causes symptoms like swollen feet, breathlessness or constipation.
Moderate to severe polyhydramnios could be caused by:
- A congenital condition affecting the fetus's ability to swallow.
- Gestational diabetes.
- Carrying identical twins with transfusion syndrome (TTTS).
- Problems with the fetus's stomach.
- Issues with the placenta.
What are the complications of too much amniotic fluid?
If you have too much amniotic fluid in your uterus, it can put pressure on neighboring organs. This can cause pregnancy complications, especially if the condition shows itself early into the pregnancy. Other complications include:
- Preterm labor or preterm birth.
- The fetus is becoming too large.
- Postpartum hemorrhage.
- Stillbirth.
How do doctors treat high amniotic fluid?
Polyhydramnios is usually not treated unless it's necessary. Your healthcare provider may schedule additional appointments to check on the size of the fetus. In severe cases, medication can control fetal urine production while in your uterus. Your provider may also recommend early induction, bed rest, or draining a small amount of amniotic fluid.
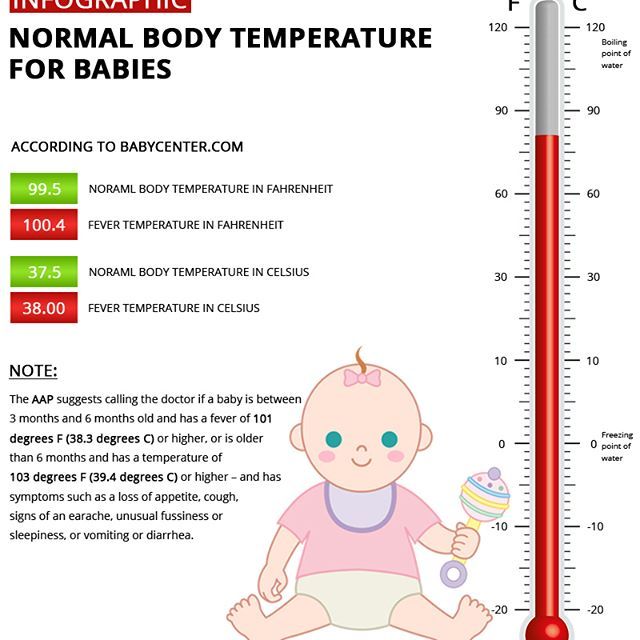
Care
Can drinking water increase amniotic fluid?
No one is entirely sure if drinking more water can increase amniotic fluid. Some healthcare providers will recommend a pregnant person increase their water intake if their fluid is low. There's no harm in drinking more water during pregnancy but talk to your provider first to see what they recommend.
Can a baby live without amniotic fluid?
No. A fetus needs some amniotic fluid in the uterus to survive. However, the exact amount of amniotic fluid it needs depends on its gestational age and other factors.
Can a baby drink amniotic fluid?
Yes, a fetus drinks amniotic fluid in the uterus. This helps them practice swallowing and develops their digestive system.
Does a baby breathe in amniotic fluid?
The fetus baby practices breath-like movements in amniotic fluid in your uterus. This helps with fetal lung development and teaches it how to breathe outside the uterus. Fetuses begin practicing breathing amniotic fluid in the first trimester.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Amniotic fluid helps a fetus grow and protects it from injury and infection. Fetuses swallow and practice breathing amniotic fluid, then pee it out. Some pregnant people have too much or too little amniotic fluid. Your healthcare provider may monitor you more closely or perform additional ultrasounds if this happens to you. If you're concerned about your pregnancy or experience fluid leaking from your vagina, don't hesitate to talk to your provider.
Physalis - useful properties and calorie content, use and preparation, benefits and harms
Diet tables
Table No. 1: for ulcers and gastritis (5) Table No. 2: for gastritis, colitis and liver diseases (5) Table No. 3: for intestinal diseases (5)
1: for ulcers and gastritis (5) Table No. 2: for gastritis, colitis and liver diseases (5) Table No. 3: for intestinal diseases (5)
PP recipes
PP breakfasts ( 74) PP lunch (56) PP dinner (74) PP desserts (75) Low glycemic meals (30)
Recipes for children
Recipes for children 2-3 years old (428) Recipes for children from 3 years (950) Recipes for children 1-2 years old (176)
By type of dish
Pastries and desserts (1913) Main dishes (1800) Appetizers (1048) Salads (747) Cocktails (389) Soups (352) Breakfasts (344) Pasta (136) Marinades (76) Sandwiches (76) Pizza (58) Bouillons (2)
National cuisine
Russian (357) Italian (200) French (105) Georgian (67) American (65) European (52) Ukrainian (43)Japanese (39)English (31)Mexican (30)Spanish (24)Uzbek (22)Greek (19)Indian (19)Chinese (19)) other cuisines
By time
from 3 to 10 minutes (1101) from 10 to 25 minutes (2654) from 25 minutes to 1 hour (3833) from 1 to 2 hours (575) more than 2 hours (201) several days (14)
Preferences
Vegetarian dish (321) Lenten menu (488) Children's menu (215) Low calorie dish (135) In a slow cooker (33) In a bread machine (11) Steamed (33)
For the holiday
Favorite recipes (161)Birthday (104)Valentine's Day (85)Shrovetide (118)Recipes for the New Year 2021 (308)Christmas (35)Picnic (27)Halloween (8)March 8 (56) Great Lent (225)Easter Recipes (46)
Article
SelectedVoice Navigator Project -Using Agreement Politics of Privacy
Return back
F
Physalis
description of the family, frequent representatives of the family, frequent representatives of the family, frequent representatives of the family. This is a perennial herbaceous plant up to 1 m high with a lignified stem at the base. A distinctive feature of all types of physalis is the fruit-berry, enclosed in a sheath-case, similar to a Chinese paper lantern. This cap is formed by fused sepals, which grow noticeably faster than the fruit; when fully ripe, its color changes. Physalis flowers are yellow, orange, rarely white, sometimes lilac. The fruit is a fleshy yellow-green or yellow-orange berry, similar to a tomato, tasting from very pleasant to burning bitter. Among the many forms and types of physalis, there are two of its edible forms - vegetable and strawberry.
This is a perennial herbaceous plant up to 1 m high with a lignified stem at the base. A distinctive feature of all types of physalis is the fruit-berry, enclosed in a sheath-case, similar to a Chinese paper lantern. This cap is formed by fused sepals, which grow noticeably faster than the fruit; when fully ripe, its color changes. Physalis flowers are yellow, orange, rarely white, sometimes lilac. The fruit is a fleshy yellow-green or yellow-orange berry, similar to a tomato, tasting from very pleasant to burning bitter. Among the many forms and types of physalis, there are two of its edible forms - vegetable and strawberry.
Common names: emerald berry, ground cranberry, bubble cherry, sleepy grass, purse, dog cherries, Jewish apple, sleepy dope.
Distribution
This plant is found in light forests, on forest edges, in ravines, among shrubs, as a weed in gardens, orchards. In many places, physalis has been introduced into cultivation as a vegetable or ornamental plant.
Physalis is widely distributed in Iraq, Bulgaria, the Baltic States, the Caucasus, Central Asia. In our country, the most famous representative of this plant is a decorative Chinese lantern (or immortelle), its fruits are inedible and even toxic.
Applications
Edible varieties of Physalis have been used in both cooking and medicine. Jam is made from fruits, fillings for pies, candied fruits are made, sauces, marinades, pickles are prepared, and berry varieties with a high dry matter content and sugar content are dried for raisins, which almost do not differ from the real one. Physalis juice as a seasoning is added to meat and fish. Boiled physalis fruits make an excellent decoration for cakes.
Benefits
All parts of physalis contain many biologically active substances. Carbohydrates, sugars, pectins, organic acids, carotenoids, ascorbic acid, tannins, micro and macro elements were found in fruits. The leaves contain carotenoids, esters, steroids, cholesterol, phenolcarbolic acids, flavonoids.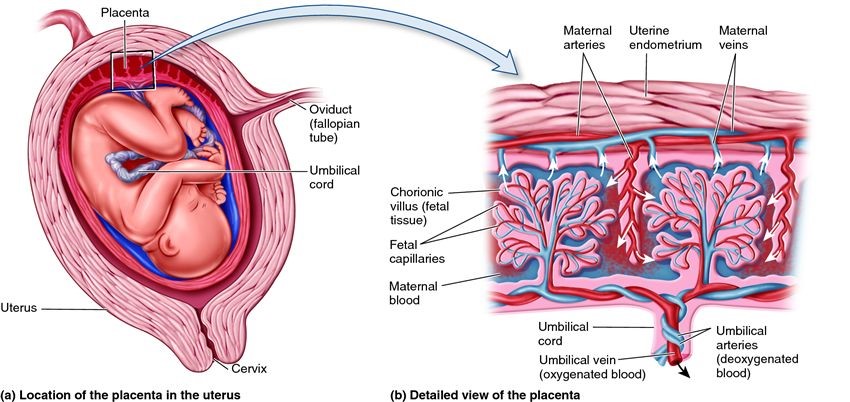 Alkaloids were found in the roots, and fatty oil was found in the seeds.
Alkaloids were found in the roots, and fatty oil was found in the seeds.
Physalis fruits have antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, hemostatic, analgesic, diuretic, choleretic effects. Fresh fruits and juice from them are used for diseases of the respiratory tract, hypertension, dermatoses, dysentery. An aqueous infusion or decoction of the fruit is used for cystitis, urolithiasis, hepatitis, bronchitis, edema, ascites, gout, rheumatism, bruises.
A decoction of the roots is used as an antitussive and analgesic. Tea made from dried leaves and cases of physalis is useful for hypertension.
Attention! Physalis, which grows wild in central Russia, is unsuitable for food due to the high content of toxic substances.
Calorie content and nutritional value of physalis
Calorie content of physalis - 53 kcal.
Physalis nutritional value: proteins - 1.9 g, fats - 0.7 g, carbohydrates - 11. 2 g with spinach and physalis
2 g with spinach and physalis
10 minutes
Olga Chernykh
Mini-cakes with mango
1 hour 30 minutes
Ksenia
Asparagus in a creamy sauce with jamon 9003 100003
PHYSALIS OR BUBBLE GRASS | Science and life
Science and life // Illustrations
Science and life // Illustrations
The fruit of the physalis is in a sheath of fused sepals. The calyx in the first time after flowering grows faster than the fruit. When fully ripe, it dries up and changes its color.
Ornamental physalis is a perennial plant with bright orange "lanterns". It is good to put a vase with dried plants in the darkest corner of the apartment.
Physalis is extraordinarily productive: every flower in it necessarily sets a fruit.
Fruits of strawberry physalis - amber color, sour-sweet, weight 5 - 10 g. They are tasty fresh and smell of strawberries.
They are tasty fresh and smell of strawberries.
Physalis variety Confectioner.
‹
›
View full size
Physalis is not one of those plants that can be said to grow in abundance in our gardens, but those few enthusiasts who grow this vegetable curiosity fully enjoy peculiar beauty, taste and benefits of its fruits.
It was the funny look of the fruit that gave rise to many names in Russia, among them there are such as dog cherries, bubble grass, sleepy dope. Physalis got its scientific name because of the shape of the calyx of the flower (from the Greek physao - to inflate, physalis - bubble).
Indeed, the calyx of the flower grows strongly and takes the form of a bubble, inside of which there is a round, multi-seeded, shiny orange berry, the size of a cherry. By the time the fruit ripens, the color of the calyx changes from green to bright orange.
Physalis originates from Central and South America, where it grows wild and propagates by self-sowing like a weed. This culture is very popular in Mexico, Guatemala, Peru, Venezuela, Colombia. In these countries, a large number of productive varieties adapted to cultivation on the plains and in the mountains have been bred.
This culture is very popular in Mexico, Guatemala, Peru, Venezuela, Colombia. In these countries, a large number of productive varieties adapted to cultivation on the plains and in the mountains have been bred.
In Russia, physalis became known almost simultaneously with tomatoes - at the beginning of the 19th century. century, but the culture was not widespread. In those days, dishes from physalis was only occasionally served at ceremonial Russian dinners as a dessert.
A large collection of plants of the nightshade family, including physalis, was collected and brought in 1925-1926 during the expedition of N. I. Vavilov. The seeds were sown on experimental plantations of the All-Union Institute of Plant Growing, located in different climatic zones of the country. And it turned out that physalis can be grown almost everywhere, although it grew best in southern Russia and the Far East. They tried to use the collected fruits in the confectionery industry, but it all ended with the fact that they became the raw material for obtaining natural citric acid.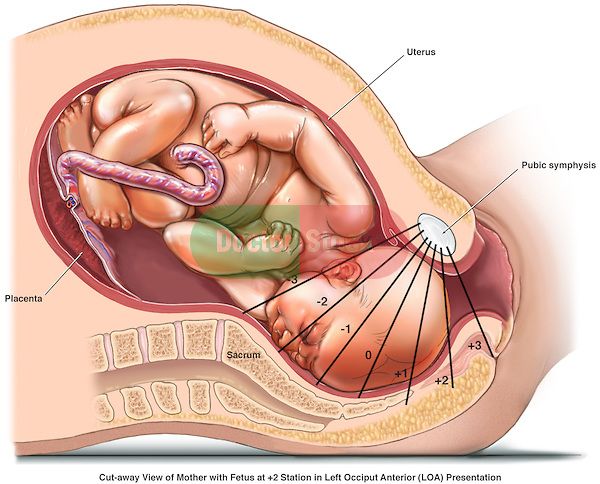 Gradually, interest in this vegetable crop dried up.
Gradually, interest in this vegetable crop dried up.
Once again, physalis was remembered during the Great Patriotic War, when the Soviet Union received several tons of seeds of this plant under Lend-Lease. But, unfortunately, this did not help him become a common culture, and for the time being, physalis firmly established itself only in the areas of amateur gardeners.
FRUITS FOR EVERY TASTE
There are vegetable, strawberry and decorative physalis.
Vegetable physalis is descended from shade-tolerant and cold-resistant Mexican plants. These are strongly branching plants with elongated-ovate leaves. Depending on the variety, the tops are yellowish, green, dark green and purple.
The plants are cross-pollinating, the flowers are relatively large, yellow, with dark purple bases of the petals. Mature fruits are large, of various colors: yellowish, green, yellow-green, bright yellow, yellow-violet and violet, weighing 30-80 g. Their surface is covered with a sticky waxy coating, bitter taste.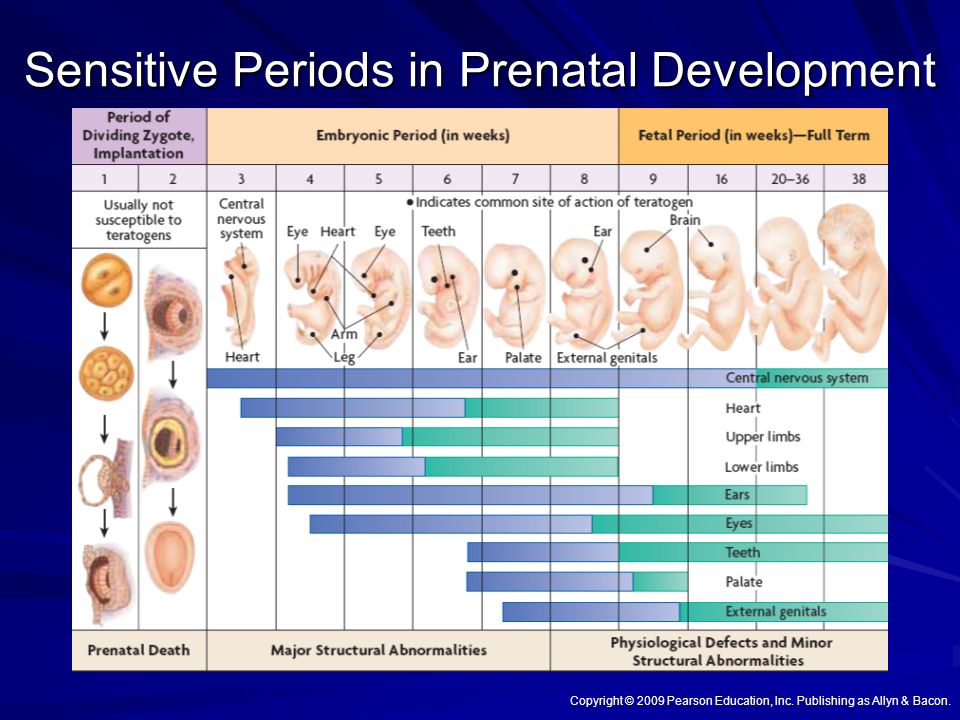
Strawberry, or berry, physalis comes from South American self-pollinating plants; it has densely pubescent stems and oval, slightly corrugated, dark green with yellow leaves. The flowers are smaller than those of the vegetable physalis, pale yellow, with brown speckles at the base of the petals. The berries are medium-sized, yellow or bright orange, sweet and sour-sweet, with a strawberry taste, weighing 5-10 g. There is no sticky waxy coating on them. Strawberry physalis is sometimes referred to as raisinberry or ground cranberry by gardeners.
Very popular with gardeners and florists is decorative, or garden, physalis. It is represented by several types of tall and low plants with green and crimson shoots, large and small bell-shaped drooping flowers with a red, white, blue corolla and "lanterns" of various sizes, yellow, orange, red or hazel. Grow decorative physalis as a border plant; it not only looks good in the garden, but can also be an unconditional decoration of any winter bouquet.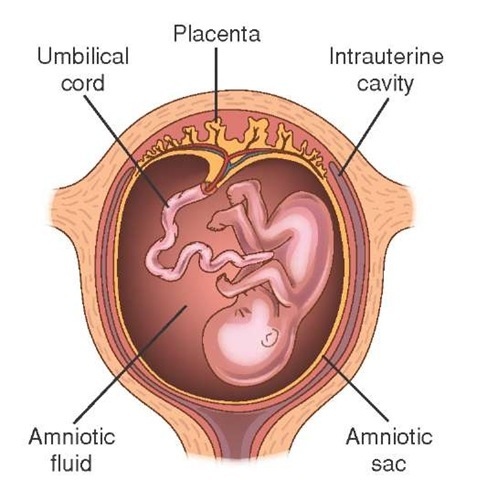 To do this, the stems with "flashlights" are cut off before the color of the boxes begins to change, and without any pretreatment they are hung to dry in a warm room.
To do this, the stems with "flashlights" are cut off before the color of the boxes begins to change, and without any pretreatment they are hung to dry in a warm room.
DIETARY PRODUCT
The immature fruits of physalis contain toxic substances (glycoalkaloids), which disappear by the time they reach full maturity.
In mature fruits, 3-6% sugars, 1-2.5% proteins, tannins, pectin substances, flavonoids, organic acids (citric, malic, succinic, tartaric), steroid and wax-like compounds, bitterness, essential oils and a complex of vitamins were found: provitamin A (total carotenoids), vitamins B 1 , B 2 , B 12 , C, P, PP with all the necessary macro- and microelements.
Physalis fruits are considered a valuable dietary product with a balanced composition of biologically active substances that have a diuretic, choleretic, antispasmodic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and anthelmintic effect. They can be used for diseases of the urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system, and due to the high content of pectin, as a component that binds and removes microbial toxins, heavy metals, radionuclides and excess cholesterol from the human body.
The balanced complex of nutrients, vitamins and microelements contained in physalis makes it possible to consider it as a means of restoring the body's ability to heal itself. That is why it is especially useful for people who have had long-term severe illnesses.
Before eating, the fruits of vegetable physalis, freed from covers, are washed with hot water or blanched for 2-3 minutes to remove sticky waxy substances that have a not very pleasant smell and bitter taste. Physalis is added to salads, vegetable soups and canned vegetables. Delicious sauces, caviar, candied fruits, jams and sweets are made from fruits, they are pickled and salted, getting a great snack. Strawberry physalis is used to make jam, marmalade, jams, candied fruits, compotes, jelly, sweets. Since the fruits of this species are devoid of a waxy coating, they are simply washed, but not blanched. You can also dry them using, like raisins, somewhat less sweet than real ones.
Any physalis, due to the high content of pectin, has gelling properties.
Gardener - note
PHYSALIS IN THE GARDEN
Modern varieties of physalis are well adapted to the climatic conditions of Russia, they can be grown in open ground wherever tomatoes grow. The best temperature for growth is 18-25°C. Plants withstand autumn frosts down to -2°C.
Strawberry physalis, unlike vegetable physalis, is more demanding on heat. Its seeds begin to germinate at a temperature not lower than 15 ° C, and the plant itself develops well only with a short southern day. Under the conditions of a long northern day, the growing season is extended and ripe fruits can be obtained only when this species is grown through seedlings.
Physalis succeeds on all soils, except for acidic and excessively moist. Grows better when making humus or compost with the addition of superphosphate. It should not be planted on soils that are abundantly manured, otherwise the plants will grow strong tops, and the formation and ripening of fruits will be delayed.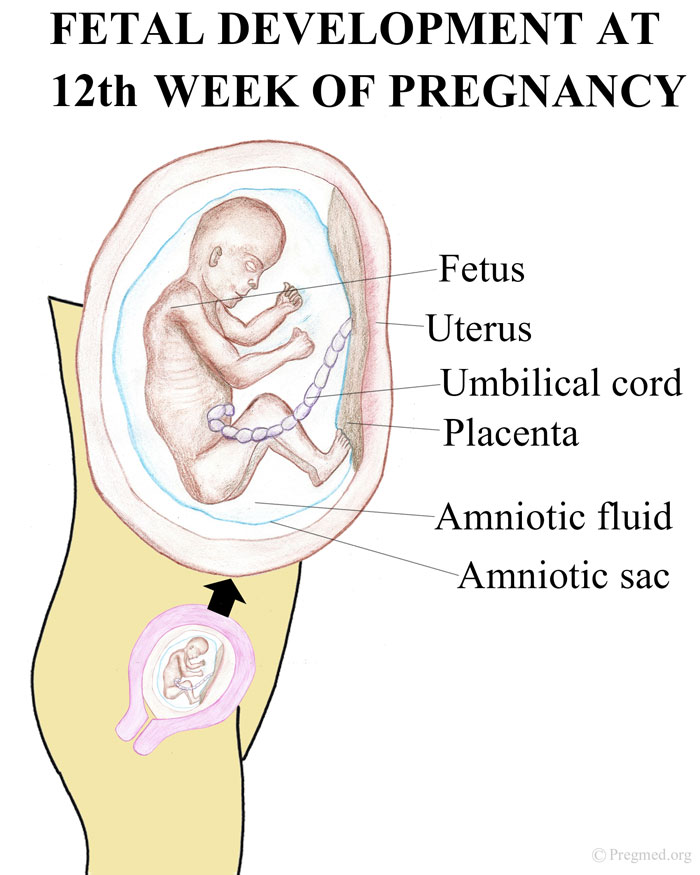
You should not plant it where eggplants, peppers, tomatoes, potatoes were grown - it will develop poorly due to one-sided depletion of the soil. In addition, all these are related crops and they suffer from the same diseases and pests. The best predecessors of Physalis: pumpkin, cabbage, legumes and root plants.
Physalis care is the same as for tomatoes. But physalis do not stepchild, because the main crop is formed on the side branches.
The signs of fruit ripening are the drying of the caps and the acquisition by them of the color characteristic of this variety. Ripe fruits fall off, in dry weather they can lie without spoiling for 7-10 days. Physalis can be harvested once a week, starting with fallen and ripe fruits, and then plucking well-developed greens. The removed fruits are stored in a dry room in small slatted boxes. At a temperature of 12-14 ° C, mature physalis lies for 1-2 months. At a higher temperature, it ripens and deteriorates faster: at a temperature of 25-30 ° C, it takes 1-2 weeks to ripen.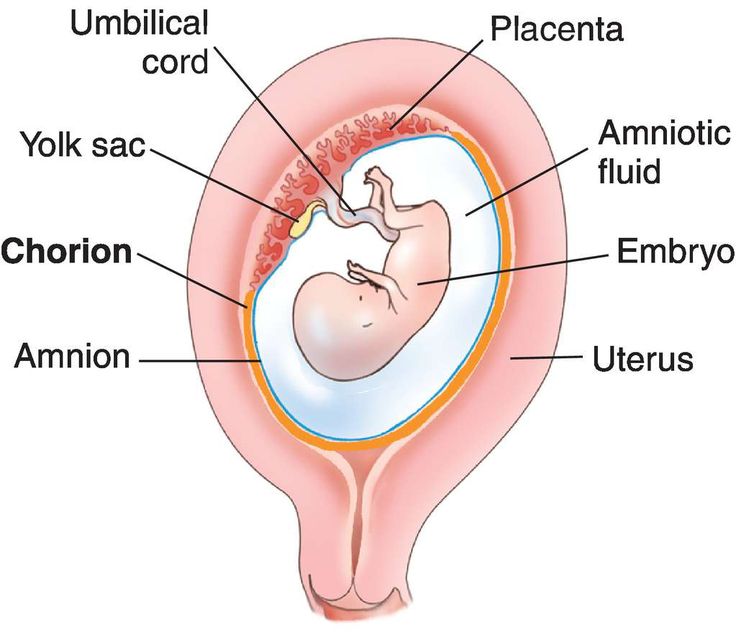
Note to the hostess
NOT ONLY DELICIOUS JAM
Sauce
1 kg mature physalis, 4 onions, finely chopped, 1.5 cups granulated sugar, 1.5 cups vinegar, 1 tsp. chopped ginger, 2 tsp. salt, cayenne pepper to taste.
Wash the fruits and pierce with a thick needle in several places. Mix all the ingredients, bring to a boil, add the fruits and cook over low heat for 45 minutes, stirring constantly. Pour hot into steam-sterilized bottles and, after cooling, close with a cork.
PHYSALIS, PICKLED
500 g of physalis fruit, 2-3 buds of cloves, bay leaf, a piece of hot pepper, marinade (50 g of salt, 50 g of granulated sugar, 1 tsp of vinegar essence per 1 liter of water).
Peel the fruits from the shell, remove plaque with hot water, wipe, chop and place tightly in jars. Add cloves, hot pepper and bay leaf. Pour marinade, sterilize for 20 minutes and roll up the lids.
PHYSALIS SALTED
1 kg of physalis, 50 g of spices (dill, horseradish, garlic, red pepper, black currant leaf, tarragon, basil, mint, parsley, celery).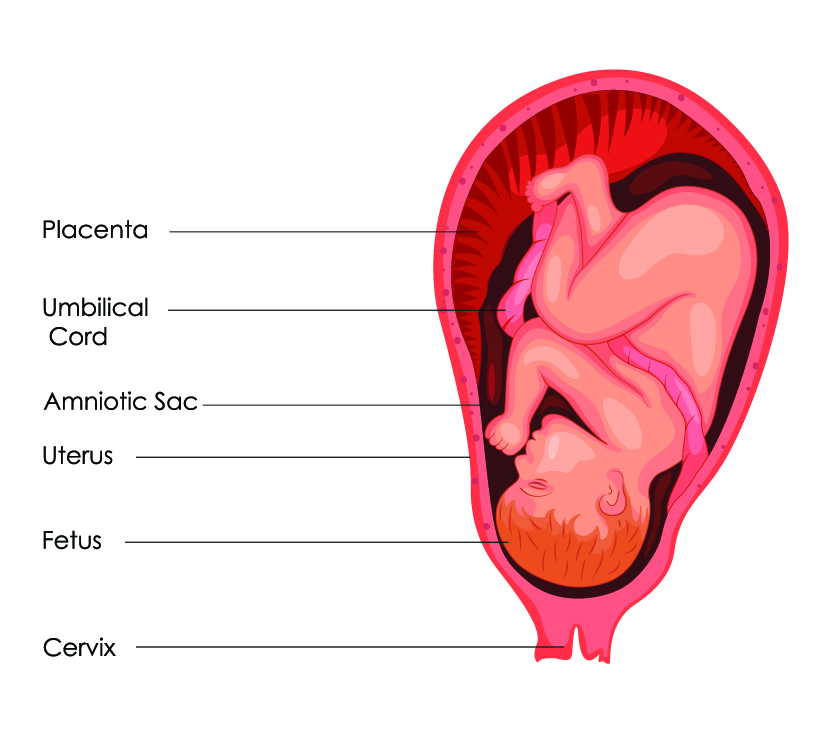
Brine: for 1 liter of water 60 g of salt.
Peel the physalis fruits from the shell, remove the plaque and put in jars with spices. Pour in brine, cover with a clean cloth and leave for 7-10 days at room temperature for fermentation. Mold that appears during fermentation is recommended to be removed. After the appearance of a sour taste, the brine is drained, filtered, boiled, poured into jars again and rolled up. Store in refrigerator or cellar.
IKRA
500 g of physalis, 200 g of onions, 200 g of carrots, 100 g of parsley or celery roots, salt, sugar, ground black pepper, bay leaf, finely chopped garlic, dill and parsley to taste.
Physalis fruits, onions and roots are peeled, chopped and fried on a vegetable oil. Add to taste salt, sugar, ground black pepper, bay leaf, finely chopped garlic, dill and parsley. Well warmed mixture carefully mix until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
Chilled caviar is served on the table.
JAM
1 kg of physalis fruit, 1 kg of sugar.
Peel the physalis fruits from the shell and remove the plaque. The smallest ones - pierce in several places, medium ones - cut in half, large ones - into 4 parts, put in an enamel bowl and pour hot syrup over. After the syrup has cooled, cook in several stages. Add a few clove buds or pieces of ginger before the last stage of cooking to add flavor.
CANDIED
Heat the finished jam and pour on a sieve, allowing the syrup to drain. Put the fruits on a baking sheet and dry in the oven at a temperature of 35-40 about C. In a well-ventilated kitchen, you can dry without heating.
Sprinkle dried fruits with sugar and store in jars with lids.
CANDIES
Carefully cut the caps of the physalis fruits with thin scissors so that when the film is folded back, a star is obtained. Dip each fruit into melted chocolate and leave on a sheet of paper until it hardens.