Does everyone experience morning sickness
No Morning Sickness? You Don't Need to Worry
For many women, one of the first signs of pregnancy (sometimes even before a missing period!) is failing to keep food down.
While it’s commonly called morning sickness, for most pregnant women this intense nausea has no time limits. Hitting morning, noon, and night, it’s enough to throw you for a mental loop.
One way that some women are able to keep sane and ride the waves of morning sickness is holding onto the hope that this discomfort means their baby is growing.
What if you’re not feeling your stomach churning though? Is your baby still growing and healthy? Does not having morning sickness mean anything about the health (or sex) of your baby?
Don’t worry, we won’t leave you in limbo 9 months waiting for an answer to these questions. Just keep reading on…
For a percentage of people, morning sickness is simply a pregnancy symptom they never experience. In and of itself, the lack of nausea and vomiting doesn’t mean anything is wrong.
It’s estimated 70 to 80 percent of pregnant people experience nausea and/or vomiting. So that’s still 20 to 30 percent who don’t have morning sickness at all!
If you find yourself pregnant without any nausea, you may feel lucky, confused, or even worried. Because morning sickness is such a commonly discussed first trimester symptom, it can seem odd if you don’t have it.
Many people experience morning sickness in the first 4 months of their pregnancy. Factors that contribute to the nausea include heightened hormones and lowered blood sugar. If you are pregnant with multiples or worn down from illness, stress, or traveling, you may experience morning sickness to a higher degree.
Nausea in pregnancy can range from light, infrequent experiences of nausea to extreme hyperemesis, with frequent vomiting which may require hospitalization for IV hydration and nourishment. A study from 2018 found that there may be a genetic component to experiencing hyperemesis.
If you’ve been very nauseous in prior pregnancies, take heart that just because you’ve experienced morning sickness in the past there’s no guarantee you’ll experience it again. (For better or worse, morning sickness can vary from pregnancy to pregnancy.)
(For better or worse, morning sickness can vary from pregnancy to pregnancy.)
Whether you’re trying to win the gender reveal party guessing games or are just dying of impatience waiting for your test results, you may want to know whether you have a girl or boy on the way.
You might have heard that decreased morning sickness means you’re having a boy. This is based on the belief that hormone levels are higher when carrying a baby girl.
The logic behind this is that higher hormone levels can cause increased nausea. Thus, girl babies are rumored to come with days of intense morning sickness, and being pregnant with baby boys should be smooth sailing in comparison.
However the science to support this theory is limited. One study from 2019 found that those carrying a female fetus or twins were more likely to experience nausea and vomiting during pregnancy than those carrying a single, male fetus.
However, the researchers noted that other factors, including the age of the mother, whether she smoked, and her BMI prepregnancy also affected chances.
Ultimately, you can’t determine the sex of your baby by whether or not you have morning sickness. The only way to really know if you’re having a boy or girl before delivery is through a chromosome test or ultrasound.
Miscarriage is a very real concern for many women (and their partners). Anything that indicates a pregnancy is not proceeding as expected can set off warning bells.
Since morning sickness is such a common pregnancy symptom in the first trimester, not feeling ill might raise some red flags for you. So should we praise nausea and vomiting as signs of a healthy pregnancy?
There is some research to indicate nausea and vomiting may indicate a reduced risk of pregnancy loss.
In order to get a better picture of how nausea and vomiting may be related to miscarriage, researchers in a 2016 study relied on hCG confirmed pregnancies (think positive urine tests) instead of ultrasound confirmed pregnancies.
This allowed researchers to begin testing for miscarriages earlier and identify more miscarriages. It also allowed them to track women’s nausea with more accuracy throughout the first trimester.
It also allowed them to track women’s nausea with more accuracy throughout the first trimester.
No study is perfect, and this 2016 study was fairly homogenous making it difficult to generalize the results. All the same, this study represents a large step forward in morning sickness and miscarriage research.
The study found that for women who had experienced miscarriage once or twice before, morning sickness was very common during the first trimester and related to a reduced chance of losing the pregnancy by 50 to 75 percent.
There are many theories about why nausea and vomiting in pregnancy are connected to a reduces miscarriage risk. One theory is that it is part of an evolutionary advantage to encourage eating carbohydrate rich foods and to rid the body of any potential toxins that may be harmful to the baby.
Another theory is that the vomiting is related to the body’s increasing hCG levels or markers of viable placenta tissue. More research will need to be done on all these theories in the future as many questions still remain.
While this means that you may welcome nausea and vomiting as a reassuring sign, keep in mind that, as mentioned earlier, it’s estimated that up to 80 percent of pregnant people experience morning sickness. That means there are still many healthy pregnancies that occur with no morning sickness whatsoever.
If you’re newly pregnant and not feeling any morning sickness, you may begin to worry.
But before allowing nightmare pregnancy scenarios to start filling your mind, consider taking a deep breath and pausing for a minute to think about other pregnancy symptoms you might be feeling. (Believe it or not, it can actually be calming to think about all the other ways this pregnancy has you hurting!)
Remember also that every pregnancy is different when it comes to morning sickness. Just because you’ve had it before doesn’t mean that you have to go through it again. Many factors including your hormones, level of rest, and diet can all play a role in how nauseous you feel.
If you ever feel like something isn’t right with your body or pregnancy, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor. They can offer you an exam, guidance, or even just some reassurance that you and your baby are doing just fine.
If you do suffer a miscarriage during your pregnancy, there are support groups and therapists available online and locally who can help you process your emotions.
When does morning sickness start?
Nausea is a well-known symptom of pregnancy, affecting at least 70% of expecting mothers. Also called morning sickness, nausea usually begins at around six weeks, peaks between weeks 8-11, and typically fades near the end of the first trimester. However, some women experience nausea as both a second trimester and third trimester symptom.
The early weeks of pregnancy can be an exciting and confusing time. You’re beginning a journey that involves many physical and emotional changes,, and you don’t always know how you’ll feel from one day to the next. But we’re here to help you understand the changes you’re going through, and morning sickness can be one of the most noticeable.
But we’re here to help you understand the changes you’re going through, and morning sickness can be one of the most noticeable.
Below, we cover what to expect and what you can do to find some relief from this common pregnancy symptom.
What is morning sickness and what are the symptoms?
Morning sickness is a feeling of nausea, sometimes also accompanied by vomiting. It can be one of the earliest signs of pregnancy for many women, appearing a couple weeks after a positive pregnancy test.
Despite being called morning sickness, nausea in pregnancy can happen at any time of day. Women often feel the most nauseous on an empty stomach, which is most apparent when you wake up after not eating all night, hence how it got its name.
Symptoms of morning sickness frequently occur on their own, but can also be triggered by certain foods, smells, heat, stress and other factors. The feeling can range from slight queasiness, like being a little carsick, to more intense nausea and vomiting.
Can you be pregnant and not have morning sickness?
Morning sickness is made out to be very common in movies and television, and it is. But it’s also possible to be pregnant without experiencing it. Three out of 10 pregnant women don’t experience morning sickness, so it’s not rare or concerning if that’s the case.
The same goes for aversions to certain foods or smells. Every pregnancy is unique, so not every pregnant woman will experience the same symptoms. If you think you could be pregnant but aren’t experiencing morning sickness or other symptoms, taking a pregnancy test is the only way to find out for sure.
What causes morning sickness?
While the exact cause isn't well understood, many doctors believe morning sickness happens because of hormones. The pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) reaches its highest level around the same time morning sickness is most severe. And, increases in the hormones estrogen and progesterone can make it harder for your body to digest food, adding to stomach discomfort.
When does morning sickness start?
If you’re one of the many pregnant women who experience morning sickness, you may start feeling nauseous somewhere around the sixth week of your pregnancy, typically two weeks after your first missed period. Symptoms may appear gradually or seem to happen overnight.
Is it normal to be nauseous all day when pregnant?
Don’t be fooled by the name. Morning sickness doesn’t only happen in the morning, and it’s very normal for it to last all day. No two women experience it in the same way. Also, some women who had morning sickness in their first pregnancy may not have any nausea at all in their second, and vice-versa.
When does morning sickness end?
Morning nausea usually peaks between weeks 8-11, and typically fades by the end of the first trimester. However, some women can experience nausea in their second trimester, and some even notice nausea near the end of pregnancy.
If your morning sickness lasts beyond your first trimester, you may be more sensitive to the effects of hormonal changes during pregnancy. Or you may just have a more delicate stomach. But it’s a good idea to bring up your morning sickness with your doctor or midwife to learn about your options for relief.
Or you may just have a more delicate stomach. But it’s a good idea to bring up your morning sickness with your doctor or midwife to learn about your options for relief.
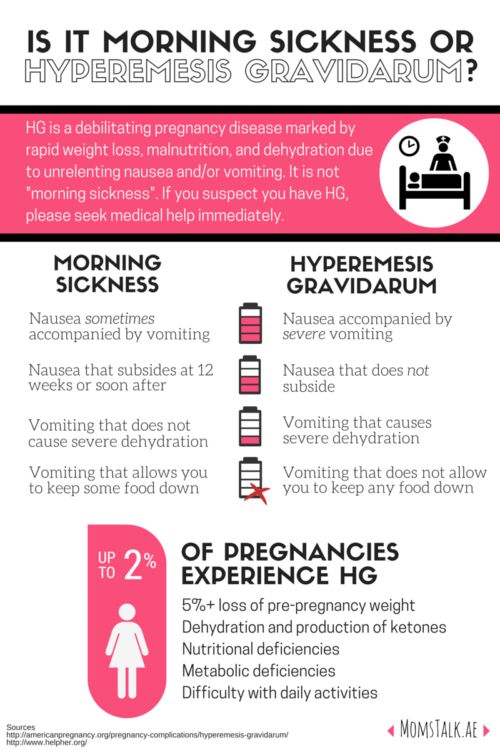
Hyperemesis gravidarum (HG)
If you’re throwing up more than two to three times a day and aren’t able to keep anything down, you may have hyperemesis gravidarum (HG), a form of severe morning sickness. Some cases can be treated with pressure-point wristbands, like those worn to prevent motion sickness. In other cases, you might need medication, bed rest or intravenous (IV) fluids to help reduce or eliminate symptoms.
Many women tolerate morning sickness because they know that nausea in pregnancy is very common, however they may not realize that severe vomiting is not as normal and requires attention. That’s why it’s important to know the signs of HG. Talk to your care provider right away if you are vomiting so much that you:
- Become persistently dehydrated
- Can’t keep any foods or liquids down for 24 hours
- Feel weak, dizzy or faint and/or lightheaded
- Lose three or more pounds in a week
It’s important to know what’s normal and what’s not. If you have any concerns about your morning sickness, our experienced team of OB-GYNs and midwives can help you get personalized care that’s right for you.
If you have any concerns about your morning sickness, our experienced team of OB-GYNs and midwives can help you get personalized care that’s right for you.
Is morning sickness bad for the baby?
It’s natural to wonder about whether your nausea and loss of appetite could be harmful to your baby. But rest assured, if you’re still able to eat and stay hydrated, your baby will still get all their needed nutrients. In rare and severe cases of morning sickness, your doctor or midwife will work to ensure that you and baby are getting the necessary nutrition and hydration to stay healthy.
What can I do to find relief from pregnancy nausea?
You don’t have to tough it out and wait for the day your morning sickness subsides. There are plenty of simple, safe and effective strategies you can try to combat nausea.
Eat smaller meals throughout the day
Having an empty stomach for too long can make anyone feel sick. Eating small snacks throughout the day in between larger meals can keep you from feeling queasy. But remember, eating too much can make you feel just as nauseous. It’s all about finding a balance that will keep you feeling good.
But remember, eating too much can make you feel just as nauseous. It’s all about finding a balance that will keep you feeling good.
Avoid trigger foods
Some food and drinks are difficult to digest and may make you feel sicker. Try to stay away from caffeine, acidic foods such as tomatoes, and greasy or spicy foods.
Iron supplements can also contribute to nausea and constipation, so talk to your doctor or midwife if you’re taking one.
Try the B.R.A.T. diet
If you can’t seem to find anything that agrees with you, try these foods that are bland and easy to digest: bananas, rice, applesauce and toast.
Stay hydrated
Drink a lot of fluids. In addition to water, sports hydration drinks, broth and juice can help replace nutrients that you may lose from vomiting.
Consume ginger
Eating and drinking foods with ginger can help calm the feelings of nausea. Easy options include ginger ale, ginger hard candy, ginger lollipops or ginger tea.
Take a vitamin B6 supplement
Though it may already be present in your prenatal vitamin, taking additional vitamin B6 has shown to be effective in reducing nausea during pregnancy. You can take up 25 to 50 mg of vitamin B6 per day, but it’s best to talk to your care provider before taking additional supplements.
Wear a wristband
As mentioned above, there are a variety of wristbands available over the counter that are designed to prevent motion sickness. They work by applying pressure to specific pressure points that can help ease nausea.
Experiment with different temperatures
You may have an easier time eating or drinking cold foods and beverages, or your stomach may feel calmer after a hot meal. Room temperature or warm food and drinks can sometimes cause nausea.
Keep a morning sickness record
What time of day does nausea strike? What are you doing when it does? By tracking your symptoms, you just might identify triggers that make you queasy – like certain foods or smells – so you can avoid them going forward.
Pack the essentials
If morning sickness does end up causing you to vomit, you can make it easier by carrying a few supplies with you. Feeling prepared by bringing a toothbrush and toothpaste, mouthwash, a backup shirt and even a plastic bag can give you peace of mind and make morning sickness feel more manageable.
Ask your doctor or midwife about finding relief from pregnancy nausea
These remedies may not work for everyone, and there are other solutions for more persistent symptoms. Talk to your care provider about anti-nausea medications that are safe to take while pregnant.
While morning sickness can be a challenging part of any pregnancy, it’s also a sign that your body is doing what it needs to support your growing baby. That said, you shouldn’t have to suffer through pregnancy nausea that interferes with your daily life and your ability to be present at work or with family.
Fortunately, there’s help available to make your pregnancy a bit smoother and more comfortable. If you’d like to explore your options for improving symptoms of pregnancy nausea, our women's health experts are here to help.
If you’d like to explore your options for improving symptoms of pregnancy nausea, our women's health experts are here to help.
Why do you feel sick in the morning on an empty stomach
Nausea in the morning on an empty stomach is most common in pregnant women due to intoxication, but it is not uncommon for males or even children to have this problem
Do not worry too much if you have encountered such a problem once, it is likely that this is a banal poisoning. But, if nausea in the morning on an empty stomach does not go away, you should immediately consult a doctor. Some people are used to dealing with this problem with folk remedies and medicines and they really get better, but it is worth considering that most likely the disease or pathology itself continues to develop. And as a result, it will turn into a more serious form. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of morning sickness and prescribe the most effective treatment. nine0004
nine0004
Possible diseases
Most often, morning sickness on an empty stomach may indicate the presence of the following diseases: unpleasant symptoms. This is due to inflammatory processes in the duodenum 12. The patient can also be tormented by: burning, bloating during and after eating, heartburn. nine0013 Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) - also characterized by nausea in the morning, as well as after eating fatty or fried foods. This disease is easily confused with gastritis due to the similarity of symptoms, but with pancreatitis, the patient begins to have problems with stools and an unpleasant, bitter taste in the mouth.
 nine0014
nine0014 Other causes of nausea in the morning
After excluding the above diseases from the list of causes, the following causes can be considered:
- Pregnancy. Intoxication and nausea in the morning is often found in pregnant women, especially in the early stages. This is a normal reaction of the body to significant changes and hormonal changes. It is very important to completely exclude drugs for the treatment of the digestive tract during pregnancy. These funds can have an extremely negative impact on the health of the patient, the unborn child and the course of pregnancy. Therefore, you will have to endure this ailment and get by with folk remedies, but be sure to consult your doctor. nine0014
- Migraine. Morning sickness on an empty stomach may precede a severe headache. You will most likely still feel a lot of noise and increased sensitivity to smells.
- High blood pressure (hypertension). The problem of morning sickness can be accompanied by headache and dizziness.
 If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk starting this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke.
If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk starting this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke. - Cardiovascular disease - rarely, nausea on an empty stomach occurs with heart failure or developing myocardial infarction. If nausea is accompanied by pain, a feeling of heaviness and tightness behind the sternum, numbness or tingling in one half of the body, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible, as this may be an incipient myocardial infarction. nine0014
- Increased intracranial pressure - Nausea and regurgitation in infants can occur when pressure increases inside the ventricles of the brain.
What to do if you feel sick in the morning
It is important to understand that regular morning sickness is a signal of the presence of a pathology or disease and it is highly undesirable to self-medicate. Be sure to consult a doctor for an examination, but if you don’t have such an opportunity at the moment, there are several effective ways that will help reduce or temporarily get rid of this problem:
- Medicines.
 You need to be very careful and you must be sure that morning sickness is not the cause of pregnancy or an intestinal disease.
You need to be very careful and you must be sure that morning sickness is not the cause of pregnancy or an intestinal disease. - Ginger root, mint and lemon drinks. You can make infusions of these products for maximum effect, simply by adding them to a glass and boiling water, after 15 minutes you will have a very effective and safe (in the absence of allergies) remedy for morning sickness. YOU can also just add them to hot tea. nine0014
- Medicinal collection - if nausea relentlessly torments you in the morning, you can try a collection of mint, oak bark and celandine. To prepare the drink, take 1 tsp of mint leaves, dried oak bark and chopped celandine, pour 0.5 l of boiling water and boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. After the broth is cooled and filtered, take 1 tablespoon 3-5 times a day before meals.
- During pregnancy. There are some little tricks you can use. For example, do not get out of bed quickly, drink plenty of fluids. Eliminate fatty and heavy foods from your diet.
 Eat small meals several times a day. nine0014
Eat small meals several times a day. nine0014
You might be interested
90,000 causes, treatment, prevention. How to get rid of nausea?Causes of nausea
Nausea may indicate the presence of diseases, but in some cases it occurs in apparently healthy people. This unpleasant sensation is more common in women, but men have their own risk factors.
Non-disease causes of nausea include the following situations.
- Overeating and eating fatty foods. This is due to the inability of the body to process a large amount of "heavy" food. nine0014
- Psychogenic reactions: stress, neurosis, anxiety. With psychogenic nausea, it is enough to feel an unpleasant smell or see something unpleasant, to remember the emotions experienced.
- Motion sickness or motion sickness. This type of nausea is associated with irritation of the receptors of the vestibular apparatus during movement.
- Pregnancy. Nausea during pregnancy is one of the first manifestations of toxicosis.
 Morning sickness most often appears at 6-7 weeks and most often stops at 12-13 weeks. nine0014
Morning sickness most often appears at 6-7 weeks and most often stops at 12-13 weeks. nine0014 - Exposure to toxic fumes from chemicals, smoke, etc.
- Side effects of drugs. Nausea may occur as an adverse reaction of the body to certain medications, such as antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, etc.
- Sun or heat stroke.
- Increased body temperature.
Nausea can be a symptom of many gastrointestinal disorders. These include:
- diseases requiring urgent surgical intervention: acute pancreatitis, appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, enteritis, colitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, nonspecific ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, irritable bowel syndrome, chronic cholecystitis;
- intestinal infections - salmonellosis, dysentery, enterovirus, rotavirus infections, helminthiases, food poisoning, etc.
 ; nine0014
; nine0014 - liver diseases - hepatitis, cirrhosis;
- foreign body of the esophagus, stomach;
- food allergy.
Nausea may develop in some diseases of other organs and systems.
- Traumatic brain injury, brain tumors, encephalitis, meningitis, stroke, etc.
- Diseases of the inner ear: labyrinthitis, Meniere's disease.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system: myocardial infarction, hypertension.
- Diseases of the endocrine system: phenylketonuria (impaired metabolism of amino acids), diabetic ketoacidosis (impaired carbohydrate metabolism, in which acetone accumulates in the blood), thyrotoxicosis (excess thyroid hormones). nine0014
- Renal failure.
- Migraine.
- When receiving chemotherapy.
Nausea treatment
Since nausea is most often a symptom of an illness, it is important to identify and eliminate the underlying cause. If the cause is not associated with the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the harmful factors.
Tablets
Different medications may be used depending on the underlying cause.
- in case of motion sickness or seasickness - the antihistamine Dramina. nine0014
- For nausea associated with the work of the gastrointestinal tract - drugs that improve the motility of the stomach and intestines and contribute to the rapid evacuation of food.
- For neurogenic nausea - sedatives, tranquilizers.
In case of nausea and vomiting, it is important to drink plenty of fluids in order to restore fluid loss and normalize the balance of water and electrolytes in the body.
We tell you what is actually the most common cause of stomach gastritis, what are the symptoms of the disease and what is the modern approach to effective treatment
Folk remedies
Mineral water, for example, Borjomi, Narzan, Essentuki, Jermuk, helps to eliminate the feeling of nausea, you can also try tea with lemon. Also eliminates discomfort 1 teaspoon of soda dissolved in a glass of water.
Folk remedies for nausea include a decoction of dill seeds, potato juice, and an infusion of basil leaves.
Prevention
Prevention of nausea is based on the elimination of its causes. It is necessary to follow certain rules of prevention. nine0004
- More time outdoors during pregnancy.
- Eat little and often.
- Avoid fatty and fried foods.
- Drink more fluids.
Popular Questions and Answers
Why is nausea dangerous?
Nausea is characterized by a peculiar feeling of pressure in the epigastrium and an unpleasant sensation in the mouth. It may be accompanied by pallor of the face, salivation, dizziness, low blood pressure, general weakness, and sometimes pre-syncope. nine0004
Nausea can be a manifestation of acute and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach diseases, pancreatitis, etc.), but it also occurs with hypertensive crises, toxicosis of pregnant women, kidney failure, with sun or heat stroke, motion sickness or "seasickness" and other diseases.