Does being pregnant cause headaches
Headaches during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Headaches during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content9-minute read
Listen
If you have a severe headache during pregnancy that is not usual for you, seek medical help immediately.
Key facts
- It’s common to get mild headaches in the first few months of pregnancy because of hormonal changes.
- If you usually suffer from migraines, they may get better, worse, change or stay the same when you’re pregnant.
- Headaches during pregnancy may be triggered by poor sleep, stress, dehydration, low blood sugar or eye strain.
- If your headache doesn’t settle with simple measures (for example, rest and rehydration), you can take paracetamol.
- A headache after 20 weeks can be a sign of pre-eclampsia, which is a serious pregnancy condition that needs medical attention – see your doctor or midwife.
Does pregnancy cause headaches?
Many people get mild headaches when they are pregnant. Headaches can often be triggered by a change in hormones. They are more common in the first few months of pregnancy.
If you usually suffer from migraines, you might notice a change when you’re pregnant. There’s a good chance that your migraines will improve after the first trimester. This may be because your oestrogen level starts to stabilise. However, some people don’t notice a change, or may get worse migraines during pregnancy. You also might notice different changes from one pregnancy to the next.
Headaches can develop for many different reasons — it’s not always because of pregnancy hormones.
Why else might I get headaches during pregnancy?
Besides hormonal changes, there are many triggers that cause headaches in general, but might occur more often when you’re pregnant, such as:
- not getting enough sleep
- withdrawal from caffeine — such as in coffee, tea or cola drinks
- low blood sugar from not eating regularly
- dehydration
- feeling stressed, anxious or depressed
- eye strain — especially as your eye muscles relax during pregnancy
Many of these triggers can cause tension headaches, which are very common. The pain is usually mild and on both sides of your head.
The pain is usually mild and on both sides of your head.
Some of these triggers can cause migraines, which are more severe and mostly occur on one side of your head. If you have migraines, you might also feel sick or vomit and be sensitive to light or sound.
Pre-eclampsia
If you start getting frequent headaches after 20 weeks of pregnancy, this could be a sign of a more serious pregnancy condition called pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is when you have high blood pressure that affects your kidneys and sometimes other parts of your body. If you have a pre-eclampsia headache, you may find that simple pain-relieving medicines like paracetamol don’t help.
It’s very important to tell your doctor or midwife if you are getting headaches in the second half of pregnancy, or if your headaches are very severe.
If you have a severe headache during pregnancy, call your doctor or midwife. It could be something more serious.
Health conditions
Just like when you’re not pregnant, a headache can sometimes be a sign of other health conditions, including:
- infections, such as an ear infection or flu
- sinusitis
- problems with your teeth
- an aneurysm or stroke
What can I do to treat a headache when I’m pregnant?
If you have a headache, you could try:
- having a nap, or resting with your eyes closed
- drinking water
- having something to eat
- putting a cold or heat pack on your forehead or the back of your neck
- asking someone to give you a gentle neck massage
If you need to take medicine for pain relief, paracetamol is safe during pregnancy. Pain-relieving medicines can actually cause headaches if you take them too often, so don’t take paracetamol more than 3 times a week.
Pain-relieving medicines can actually cause headaches if you take them too often, so don’t take paracetamol more than 3 times a week.
When you’re pregnant, avoid anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen or aspirin and medicines that contain caffeine.
What can I do to prevent headaches during pregnancy?
If you find you are getting mild headaches often, it’s a good idea to:
- getting more sleep
- drink at least 8 cups of water a day
- go to pregnancy yoga classes or do some other type of exercise
- learn relaxation or stress management techniques
- don't go more than 4 hours without eating
- avoid processed foods
- see an optometrist for an eye check
What can I do if I suffer from migraines during pregnancy?
If you suffer from migraines, try to avoid things that may trigger migraines for you. People have different triggers for migraines, so it’s important to learn what your personal triggers are. Keep a headache diary, and see if your triggers include:
Keep a headache diary, and see if your triggers include:
- specific foods such as chocolate, or food additives such as caffeine or MSG
- bright or flickering lights, strong smells and loud sounds
- not enough sleep, or too much sleep
- skipping meals
- computer or movie screens
- strenuous exercise
- emotional triggers such as arguments or stress
Check with your doctor, pharmacist or midwife before you take a medicine for your migraine, to make sure it’s safe during pregnancy.
Paracetamol is the safest option for pain relief. If paracetamol doesn’t help and you need something stronger, ask your doctor about if you can take codeine. Try not to take codeine often, as you could become dependent on it and your baby could have withdrawal symptoms after they are born.
Most triptans (migraine medicines) are not considered safe in pregnancy. If you don’t get relief from paracetamol and codeine, you may be able to take sumatriptan occasionally. This medicine is available from a pharmacist and requires a prescription. Speak with your doctor or pharmacist before using it to help you understand the risks and the benefits of this medicine during pregnancy.
This medicine is available from a pharmacist and requires a prescription. Speak with your doctor or pharmacist before using it to help you understand the risks and the benefits of this medicine during pregnancy.
You can take metoclopramide if you suffer from nausea or vomiting with migraines.
Acupuncture can help treat migraines. Talk to your doctor or midwife first to check it’s safe for you. Make sure to tell your acupuncturist that you’re pregnant, so they can avoid certain points that shouldn’t be used in pregnancy.
When should I see a doctor?
See your doctor or midwife if you have symptoms of pre-eclampsia, including:
- a headache that doesn’t get better with paracetamol
- severe pain below your ribs
- heartburn that doesn’t disappear after taking antacids
- sudden swelling in your face, hands or feet
- blurred vision
Headaches can sometimes be a sign of other serious health conditions. Contact your doctor straightaway if you have:
- a sudden severe headache
- a change in your usual headaches
- your first-ever migraine
- a headache together with fever, neck stiffness, sensitivity of your eyes to light, drowsiness or weakness of your arm or leg
- a recent head injury
CHECK YOUR SYMPTOMS — If you are feeling unwell and not sure what to do next, check your symptoms using the healthdirect Symptom Checker tool.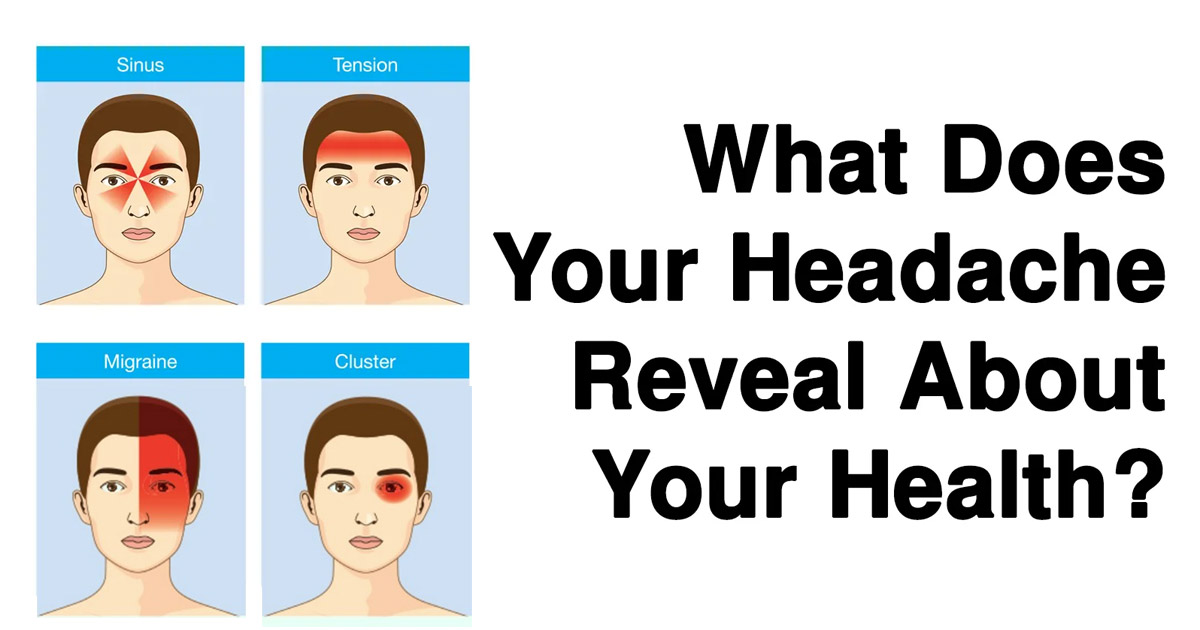
- Speak with your doctor or midwife, particularly if you have any concerns about pre-eclampsia.
- For more information about headaches, visit Migraine and Headache Australia.
- For more information about medicines you can take during pregnancy, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Tommy’s (Headaches in pregnancy – should I be worried?), NSW Government (Having a baby), Migraine & Headache Australia (Adults and headache), Migraine & Headache Australia (Migraine), Migraine & Headache Australia (Headache triggers), Migraine & Headache Australia (Headache treatment – no absolute cure), Migraine & Headache Australia (What is headache?), Migraine & Headache Australia (Tension headache), RANZCOG (Pre-eclampsia and high blood pressure in pregnancy), Royal Women's Hospital (Medicines in pregnancy), NSW Health (Migraine in pregnancy and breastfeeding), RANZCOG (Q&A: severe headache in the third trimester), Migraine & Headache Australia (Self-Care & Trigger Management)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
Need more information?
Common discomforts during pregnancy
Your body has a great deal to do during pregnancy. Sometimes the changes taking place will cause irritation or discomfort, and on occasions they may seem quite alarming.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Treatment of Headache - Migraine & Headache Australia
There is no absolute cure for headache, but many effective treatments exist which can prevent and treat different headache types.
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Adults and Headache - Headache Australia
Studies confirm that tension-type headache and migraine are more common in women while cluster headache, a rare form of headache, is more common in men.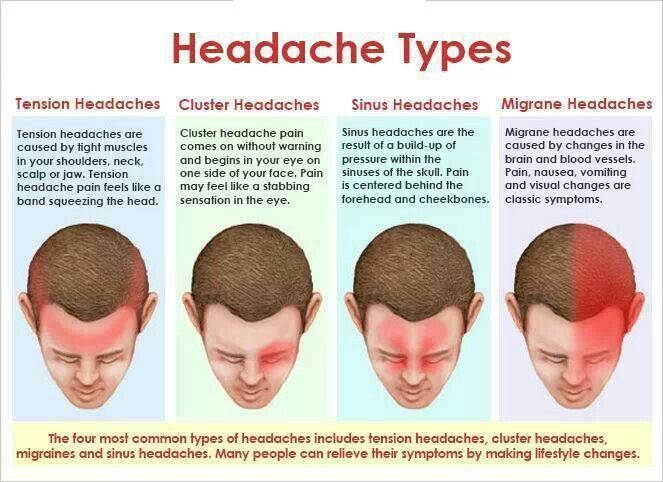
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Tension-type Headache - Migraine & Headache Australia
Tension-type headache is one of the most common everyday headaches. It causes a dull, non-throbbing pain and can be caused by stress.
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Migraine Management Tips - Headache Australia
It’s important to be organized and informed about your migraine attacks and how they impact your life. Here are some migraine management tips to assist.
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Six ways to manage migraine without drugs | The George Institute for Global Health
We’ve all heard of the crushing headache pain that comes with migraine but did you know that one in every seven people experience them, three in every four people with migraine are females, and migraine is the number one cause of disability in young people? With so many people affected worldwide, you’d think modern medicine would have developed a solution by now but unfortunately there’s still no definite cure for migraine.
Read more on The George Institute for Global Health website
Mumps and pregnancy
Find out about mumps and its symptoms, how it spreads, how to manage it at home, and how to avoid mumps if you’re planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Stress and pregnancy
Stress is a normal response to major life changes but there are things you can do to reduce pregnancy-related stress. Learn more here about how it affects you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Toxaemia of pregnancy (pre-eclampsia) - MyDr.com.au
Pre-eclampsia, also known as pre-eclamptic toxaemia, or just toxaemia, occurs in pregnancy, causing problems for the baby and mother.
Read more on myDr website
Warning signs during pregnancy
Most changes in your body are likely to be a normal part of pregnancy, but some signs may indicate things are not going well. Learn how to recognise them and know when you should seek help.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
What Causes Them and What You Can Do
If you’re pregnant and having headaches, you’re not alone. A medical review reports that 39 percent of pregnant and postpartum women have headaches.
Though during pregnancy you may have a different kind of headache than you usually do, most headaches during pregnancy aren’t harmful.
Headache pain during the first trimester of pregnancy may happen for different reasons than headaches in the second or third trimester. In some cases, headache pain may be a sign of other health problems during pregnancy.
Tell your doctor about any headache you have during, before, and after pregnancy. Keep a journal to record how often you have headaches and how serious the pain is. Additionally, record any other symptoms you have.
Most headaches during pregnancy are primary headaches. This means that the headache pain happens by itself. It’s not a sign or symptom of another disorder or a complication in the pregnancy. Primary headaches include:
- tension headaches
- migraine attacks
- cluster headaches
About 26 percent of headaches during pregnancy are tension headaches. Tell your doctor if you have chronic headaches or migraine during pregnancy or if you have a history of migraine.
Some women with a history of migraine get fewer migraine attacks during pregnancy. Migraine has also been linked to complications that happen later in pregnancy or after the birth of your baby.
Migraine has also been linked to complications that happen later in pregnancy or after the birth of your baby.
Secondary headaches are a caused by a complication in the pregnancy, such as high blood pressure.
Headache pain may vary from one person to the next. You may have:
- dull ache
- throbbing or pulsating pain
- severe pain on one or both sides
- sharp pain behind one or both eyes
Migraine pain may also include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- seeing lines or flashes of light
- blind spots
First trimester
Tension headaches are common in the first trimester of your pregnancy. This may happen because your body is undergoing several changes at this time. These changes may trigger headache pain:
- hormonal changes
- higher blood volume
- weight changes
Common causes of headache pain during the first trimester of pregnancy also include:
- dehydration
- nausea and vomiting
- stress
- lack of sleep
- caffeine withdrawal
- poor nutrition
- low blood sugar levels
- too little physical activity
- sensitivity to light
- changes in vision
Some foods may also cause headaches. Your trigger foods may change during pregnancy. Common foods that may cause headaches in some people include:
Your trigger foods may change during pregnancy. Common foods that may cause headaches in some people include:
- dairy
- chocolate
- cheese
- yeast
- tomatoes
Second and third trimester
Headaches during your second and third trimester may have different causes. These include:
- extra weight
- posture
- too little sleep
- diet
- muscle strain and tightness
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
High blood pressure
Headaches during your second or third trimester of pregnancy may be a sign that you have high blood pressure. About 6 to 8 percent of pregnant women ages 20 to 44 in the United States have high blood pressure.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) warns that this treatable condition can cause serious complications for both mother and baby. This is most common after week 20 of pregnancy.
If you’re pregnant, high blood pressure can raise the risk of:
- stroke
- preeclampsia
- eclampsia
- low oxygen flow to the baby
- preterm delivery, before 37 weeks
- placental abruption
- low baby birth weight, which is less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces
Treatment for hypertension during pregnancy
Your doctor may prescribe medication to treat your high blood pressure. You’ll also need to cut down on salt and add more fiber to your daily diet. Regular exercise is also very important to help balance your blood pressure.
You’ll also need to cut down on salt and add more fiber to your daily diet. Regular exercise is also very important to help balance your blood pressure.
Other causes of headache during pregnancy include common infections and more serious illnesses:
- sinus infection
- low blood pressure
- blood clots
- bleeding
- sickle cell anemia
- brain tumor
- aneurysm
- stroke
- heart conditions
- meningitis or encephalitis
Talk to your doctor before taking your regular headache pain medication during pregnancy. Don’t take aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin etc.).
The CDC warns that these pain relief drugs can be harmful to your growing baby, especially if taken during the first trimester. Many women may take acetaminophen (Tylenol) during pregnancy. However, some studies suggest there may be effects from taking acetaminophen as well.
Your doctor can recommend alternative medications to treat headache during pregnancy and natural headache remedies, such as:
- drinking plenty of water
- rest
- ice pack
- heating pad
- massage
- exercise and stretching
- essential oils, such as peppermint, rosemary, and chamomile
When to see your doctorSee your doctor if you have any headache pain at all during pregnancy.
Get urgent medical attention if you have:
- fever
- nausea and vomiting
- blurred vision
- severe pain
- headache that lasts longer than a few hours
- frequent headache pain
- fainting
- seizure
Your doctor may recommend tests and scans to find out the cause of your headaches. These include:
- checking your blood pressure
- blood test
- blood sugar test
- vision test
- ultrasound of the head and neck
- heart or head scan
- checking eye health with a scope
- spine puncture
Headache pain during pregnancy is common. You may have tension headaches during your first trimester of pregnancy. This may happen because of the many changes that you’re going through in a short period.
Headache pain may happen in the second and third period of your pregnancy for other reasons. Some causes of headaches in your mid to late pregnancy may be serious.
High blood pressure is a serious cause of headache pain during pregnancy.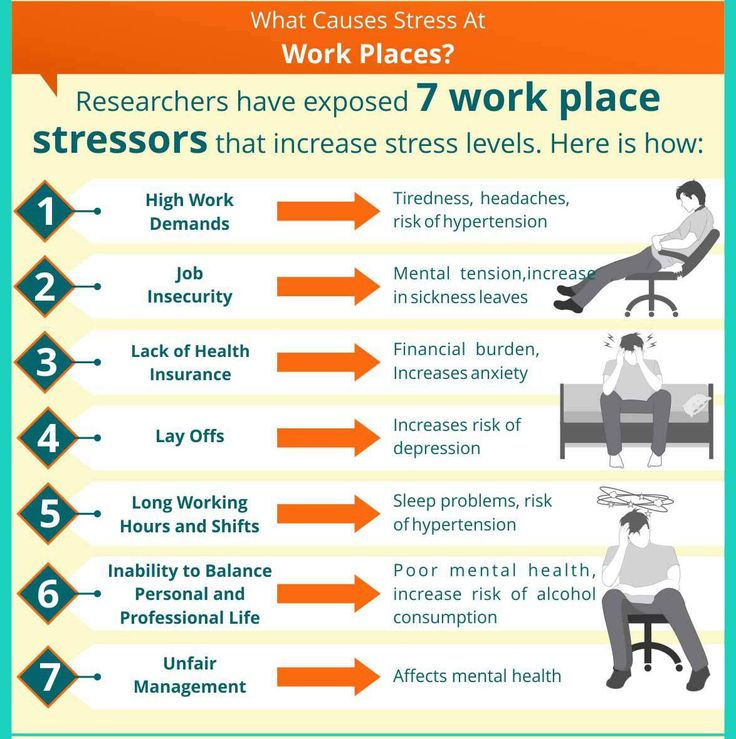 You can have high blood pressure at any time in your pregnancy. You may not have any symptoms at all. Check your blood pressure at least once a day with a home monitor.
You can have high blood pressure at any time in your pregnancy. You may not have any symptoms at all. Check your blood pressure at least once a day with a home monitor.
Tell your doctor if you have headaches at any time in your pregnancy. Let your doctor know right away if you have a personal or family history of migraine, high blood pressure, seizures or diabetes.
Take all medications and treatment exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all diet and exercise advice carefully. See your doctor for all follow-up and regular check-ups. Most causes of headaches during pregnancy are treatable or preventable with the right care.
For more pregnancy guidance and weekly tips tailored to your due date, sign up for our I’m Expecting newsletter.
Headache during pregnancy: where does it come from and how to get rid of it
November 14, 2020 Likbez Health
Sometimes you just need to get some sleep, and sometimes you need to call an ambulance immediately.
When to call an ambulance
Call 103 or 112 urgently if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- sudden and severe headache;
- consciousness becomes confused or completely lost;
- pain worsens over 5 minutes; nine0012
- flies, spots flash in the eyes;
- throbbing and noisy in the ears;
- speech has become slurred, words are drawn out;
- arms and legs weaken, convulsions set in;
- the muscles of the neck are very stiff, it is impossible to reach the chest with the chin;
- fever of 39 °C or more;
- increased heart rate at rest;
- severe shortness of breath;
- the child pushes without stopping or stops abruptly;
- leaking water or blood; nine0012
- lower abdomen hurts, as if contractions had begun.
Why pregnant women can get headaches
Pregnancy headaches are not always life threatening. But the doctor needs to be told about it in any case. If the symptom appeared for the first time and does not hurt much, postpone the conversation until a scheduled visit. If your headache is recurring or gets worse, it's best to make an appointment as soon as possible. The gynecologist will decide what needs to be done or refer you to another doctor.
If the symptom appeared for the first time and does not hurt much, postpone the conversation until a scheduled visit. If your headache is recurring or gets worse, it's best to make an appointment as soon as possible. The gynecologist will decide what needs to be done or refer you to another doctor.
There are many causes of headaches. Scientists have found that in pregnant women in 57% of cases it is primary, that is, not associated with other diseases. The most common are migraines and tension headaches. nine0003
Everything else is a secondary headache caused by various pathologies. Usually it is high blood pressure and infections. But there are also more dangerous reasons.
1. Stress and fatigue
A pregnant woman's body experiences increased stress, because it has to work for two. If at the same time the expectant mother is exposed to stress, strong feelings or sleeps little, she develops a tension headache.
Discomfort lasts from 30 minutes to several days. The head hurts in the forehead, occiput, both temples. But there is no feeling that they put on a tight hoop or helmet. The pain does not get worse when bending over, walking, or climbing stairs, bright lights, or sounds. nine0003
The head hurts in the forehead, occiput, both temples. But there is no feeling that they put on a tight hoop or helmet. The pain does not get worse when bending over, walking, or climbing stairs, bright lights, or sounds. nine0003
What to do
Tension headache can go away on its own: just get some fresh air or sleep. Sometimes pleasant emotions help, which distract from experiences.
If the pain persists for 2-3 consecutive days, see a doctor. He will select painkillers that are safe for the child.
2. Medications
Any medicine that enters the stomach or bloodstream can cause headaches even if the dosage is correct. In pregnant women, this often occurs due to drugs for high blood pressure, heart disease, antibiotics, anticonvulsants. nine0003
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for headaches may cause the opposite effect: the pills do not remove, but provoke symptoms.
What to do
If your head hurts a few hours after taking the medicine, you need to see a doctor to change the medicine. Do not drink non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for more than 3-5 days. If they do not help, you need to tell the doctor about it.
Do not drink non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for more than 3-5 days. If they do not help, you need to tell the doctor about it.
3. Love for coffee or rejection of it
Coffee can cause headaches during pregnancy. Unpleasant symptoms occur if you drink more than 3-4 cups a day.
Abrupt refusal of coffee is also harmful. It is worth finding out about pregnancy and stopping brewing a fragrant drink, and after 1-2 days, aching pain will appear in the temples and the back of the head.
What to do
Coffee is best avoided during pregnancy. If a headache occurs a day after this, you can drink a small cup of the drink and wait a day again. Gradually, the dependence on coffee will pass. nine0003
Coffee drinkers can reduce their drink intake to 1-2 cups per day.
4. Infection with fever
Acute viral (usually ARVI) or bacterial (eg, streptococcal tonsillitis) infections cause fever and headache. This is a normal reaction to foreign microorganisms.
But any infection is dangerous for pregnant women. It can cause fetal defects, growth retardation and even miscarriage. And with meningitis, especially listeriosis, there is a threat to the life of the mother. nine0003
What to do
If you have a headache with fever, call your doctor. He will prescribe safe medications or give you a referral to the hospital if a severe infection is suspected. In this case, you need strong antibiotics, droppers to maintain the body and sometimes hormones.
5. Preeclampsia and preeclampsia
After 20 weeks, preeclampsia may develop in pregnant women. This is a disease in which one of three symptoms or a combination of them may appear: high blood pressure, edema, and protein in the urine. nine0003
Without proper treatment, preeclampsia turns into preeclampsia. The pressure rises sharply, the head and lower abdomen hurt unbearably, the baby pushes unusually hard or, on the contrary, suddenly calms down. Preeclampsia can lead to placental abruption, damage to the liver and other organs, bleeding, and even seizures. Without urgent medical care, the fetus and mother die.
Without urgent medical care, the fetus and mother die.
What to do
When the first signs of preeclampsia appear, the pregnant woman is hospitalized to find treatment. After that, she is discharged home under the supervision of her gynecologist. nine0003
But if her health worsens, the doctor again sends the woman to the hospital, where she is prescribed medication to reduce pressure, special drips to keep her body functioning. If improvement does not occur within a day, a caesarean section is performed.
6. Migraine
One of the causes of migraine is a change in estrogen levels. But the disease very rarely appears due to pregnancy. On the contrary, in 70% of women, the symptoms subside dramatically after conception. Nevertheless, migraines torment many. nine0003
It may begin with an aura: flashes of light, spots before the eyes, tingling in the hands or numbness of half of the face, sometimes tinnitus. Each symptom can last from 20 minutes to an hour.
A migraine attack develops after the aura. In this case, one side of the head hurts and throbs, nausea or vomiting appears. A woman is irritated by bright lights, loud noises, smells. They make the pain worse.
Seizures last from a few hours to a week or more. After a migraine, there is a feeling of severe fatigue, exhaustion, and an awkward turn of the head can return the pain. nine0003
What to do
Any medication for migraine during pregnancy must be prescribed by a doctor. In some cases, drugs from the group of beta-blockers are used.
Studies have shown that frequent migraine in pregnancy is associated with a lack of magnesium. The doctor will help you choose the appropriate type of vitamin and mineral complex and its dosage.
7. Cerebral vascular disease
Hormone problems in some pregnant women increase blood clotting, which increases the risk of thrombosis, stroke or bleeding in the meninges. These conditions are very dangerous: a woman can die within a few minutes or remain disabled.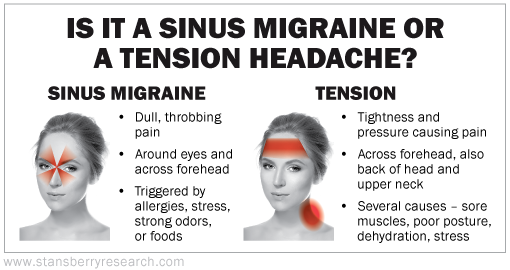 nine0003
nine0003
Vascular involvement is always accompanied by several symptoms:
- severe headache on one side;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions.
What to do
Urgently call an ambulance. The pregnant woman must be laid or seated so that she does not hit when she falls. You can't give medicine! You can only open the window so that there is more air in the room.
Which treatment the doctor prescribes depends on the specific disease. These can be drugs that reduce blood clotting and dissolve blood clots. In some cases, urgent surgery is needed. nine0003
8. Brain tumors
Studies show that progesterone and estrogen during pregnancy can trigger or accelerate the growth of tumors in the brain. Symptoms of the disease appear slowly, over several months, and depend on the size and location of the tumor.
Headache may gradually increase, then vision, speech, hearing deteriorate, limbs go numb and convulsions appear. Sometimes it is difficult for a woman to keep her balance.
Sometimes it is difficult for a woman to keep her balance.
What to do
If a pregnant woman often has a headache, or she forgets what she wanted to buy in the store and how to cook her favorite borscht, confuses her way home, you need to go to a neurologist. First, he will prescribe standard treatment, simple and safe medicines, rest, good sleep.
If this does not help, the symptoms persist or worsen, a deep examination is needed. The pregnant woman will be sent for an MRI of the brain. This procedure is safe for the fetus. If the diagnosis is confirmed, surgery may be required. nine0003
What to do if the doctor cannot find the cause of the pain
If you have been examined and the doctor cannot tell you why your head hurts and diagnoses you with vascular dystonia, this is cause for concern. There is no such disease.
Seek another doctor. Perhaps he uses new diagnostic methods that will help to deal with the problem and choose a treatment.
How to avoid pregnancy headaches
Experts recommend:
- Avoid triggers.
 For example, if you notice that certain foods, smells, or situations cause headaches, try not to encounter them.
For example, if you notice that certain foods, smells, or situations cause headaches, try not to encounter them. - Protect yourself from stress, do not worry about trifles.
- Move more. During pregnancy, walk every day in the fresh air and do special exercises for expectant mothers.
- Eat right. Try to eat a lot of vegetables and fruits, dairy products, drink at least 2.4 liters of liquid. Every day, the menu should include fish, poultry or lean meat. And it is better not to buy sweet, fast food and other junk food. nine0012
- Follow the daily routine. You need to sleep at least 8 hours a day and go to bed no later than 22-23 hours in order for melatonin to be produced normally.
- Learn to relax. Learn simple meditation techniques or breathing exercises.
Read also 🧐
- How pregnancy develops by week
- How to calculate the duration of pregnancy
- What rights does a pregnant woman have at work
- 7 best sex positions for pregnant women
- How to recognize a miscarriage and what to do next
Pregnancy headache
Authors: A. Yu. Limanskaya, Yu.V. Davydova
Yu. Limanskaya, Yu.V. Davydova
nineteen.01.2017
A.Yu. Limanskaya
Tension headache and migraine are the most common types of headaches (30-78% and 15% respectively). According to the WHO, primary headache is in general in 10th place among all conditions leading to disability, and in women, in 5th place. In 16% of patients, episodic tension-type headache becomes chronic. The economic loss in Western Europe and North America due to headache-related disability is estimated at $17-20 billion a year. To date, there is a trend towards an increase in the incidence of headache in young people. nine0206
Yu.V. Davydova
The International Headache Society defines migraine as a throbbing, unilateral headache associated with nausea, sensitivity to light, sound, and turning of the head.
In a broader sense, this pathology can be considered as a hereditary disease in which physiological changes (whether external, such as changes in weather conditions, or internal, such as changes in sleep patterns) often cause stereotypical attacks with migraine symptoms, as defined above. Migraine occurs three times more often in women than in men, with the highest rates in women during active childbearing age, peaking at 27% at age 41 years. To date, there is no evidence that migraine itself affects fertility or the course of pregnancy, but the quality of life in pregnant women with migraine is significantly reduced. nine0003
According to some researchers, migraine and tension-type headache in pregnant women are risk factors for the development of arterial hypertension and preterm birth (F. Facchinetti et al., 2009). Pregnancy can provoke the occurrence of diseases accompanied by headache (preeclampsia, thrombosis of the cerebral arteries, compression of the brain as a result of the presence of tumors). Relevant today is the rapid diagnosis of pathology and an adequate choice of therapeutic and obstetric tactics for the treatment of headaches in pregnant women due to the great medical and social significance of the problem. nine0003
Relevant today is the rapid diagnosis of pathology and an adequate choice of therapeutic and obstetric tactics for the treatment of headaches in pregnant women due to the great medical and social significance of the problem. nine0003
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is defined by the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (APLA) associated with an increased risk of thrombosis or recurrent spontaneous abortions. The most serious complications can occur in secondary APS against the background of inflammatory systemic autoimmune diseases. Studies conducted in neurological clinics have found that it is migraine, and not headache of all types, that is significantly associated with APLA in patients with systemic autoimmune pathology. However, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), headache is significantly associated with positive APLA titers. Also in this group, cerebral ischemic lesions were significantly more common. nine0003
During pregnancy, a woman may experience many health problems. For example, a headache during pregnancy occurs quite often, at different times of the day and for various reasons. Oddly enough, but a woman's frequent headache may be a sign of pregnancy, which she does not yet know about.
For example, a headache during pregnancy occurs quite often, at different times of the day and for various reasons. Oddly enough, but a woman's frequent headache may be a sign of pregnancy, which she does not yet know about.
More than 80% of women sooner or later complain of a headache during pregnancy. Even if a woman was absolutely healthy before pregnancy, then during the bearing of a child she gets a headache. Sometimes it becomes so strong that it is difficult to endure. Headache can occur at any time during pregnancy, but it tends to be most common during the first and third trimesters. nine0003
There are factors that can cause headaches during pregnancy.
1. Hormonal changes: The state of the nervous system depends on the woman's hormonal status, that is, on the quantity and quality of hormones produced.
2. Hypotension during pregnancy is associated with the predominance of progesterone over other hormones; the vasodilating effect of progesterone leads to a decrease in blood pressure, cerebral hypoxia and, as a result, to headache. nine0003
nine0003
3. Arterial hypertension and preeclampsia cause headache as a result of generalized vasospasm and circulatory disorders in the central nervous system.
4. Nutritional factors - cold food or eating foods containing tyramine and phenylamine (nitrogen compounds that can affect blood vessels) can cause headache attacks; pregnant women who are prone to migraine headache should be careful in consuming the following foods: chocolate, nuts, yogurt, chicken liver, avocados, citrus fruits, bananas, canned and pickled foods, Japanese cuisine, tea, coffee, cola, sausages, red wine, cheese. nine0003
5. Hunger headache occurs as a result of a decrease in blood glucose levels and impaired supply of nutrients to the brain.
6. Overweight.
7. Eye strain or prolonged forced stay in the same uncomfortable position.
8. Allergic reactions.
9. Dehydration of the body.
Dehydration of the body.
10. Exacerbation of chronic diseases - spine, especially osteochondrosis, due to increased load during pregnancy, static and dynamic loads often cause headaches; neurocirculatory asthenia as a cause of vasospasm and as a consequence of the appearance of a feeling of heaviness in the head, mood lability and headache.
11. Occurrence of infectious and other diseases such as: meningitis, encephalitis, sinusitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis and certain ophthalmic pathologies; the characteristic manifestations of this headache are its intensity and the lack of effect of pain medications. nine0003
12. Stress factor. Lability of the nervous system, ups and downs in mood, excitement, psycho-emotional stress, depression - all this can cause a headache.
13. Changing weather conditions. During pregnancy, fluctuations in atmospheric pressure can lead to headaches.
14. Physical stimuli - flickering light, noise, strong odors.
15. Weekend headache. nine0206 If you sleep longer than usual during the day, the cause of headache can be, for example, venous congestion.
16. Indoor climate: too dry or warm air, a lot of tobacco smoke.
The most common form of headache during pregnancy is migraine, which is accompanied by visual impairment, gastrointestinal disorders, nausea, vomiting, photoreaction, and various vestibular disorders.
In the United States, 28 million people aged 12 and older suffer from migraine, of which 21 million are women aged 25-55. In about 25% of families, one of its members suffers from migraine. nine0003
A feature of migraine pain is known to be severe, throbbing pain, predominantly hemicrania, often preceded by aura and marked photoreaction.
It is noteworthy that about 15% of women who have never experienced migraine before, first encounter it with the onset of pregnancy.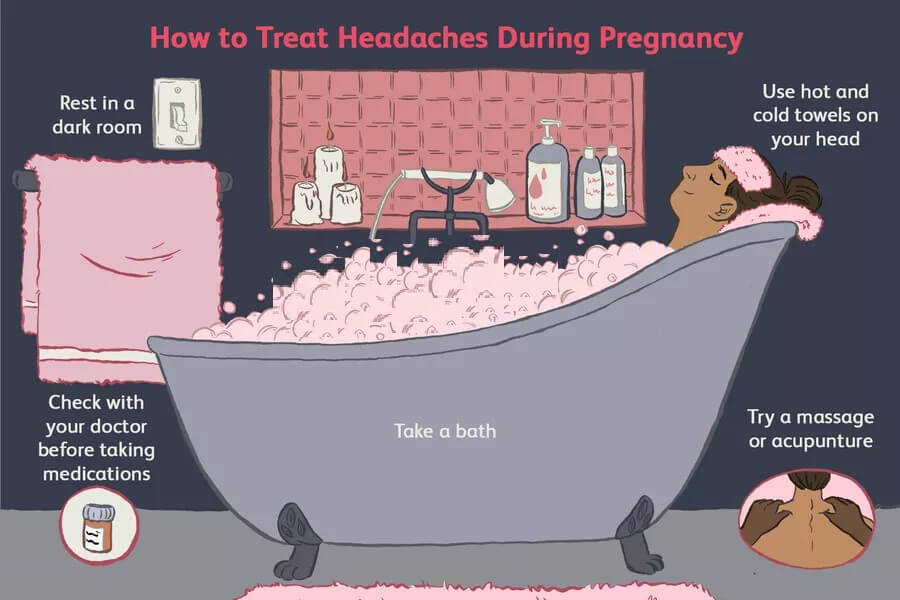 On the other hand, there are cases when during pregnancy a woman completely stops migraine attacks. In this case, this is due to changes in hormonal status and the absence of ovulation and menstruation. nine0003
On the other hand, there are cases when during pregnancy a woman completely stops migraine attacks. In this case, this is due to changes in hormonal status and the absence of ovulation and menstruation. nine0003
The occurrence of migraine in women under the influence of hormonal changes is possible throughout the entire menstrual cycle. The positive effect of pregnancy on migraine is observed in 55-90% of women during the gestation period, regardless of the type of migraine. The relief of headache symptoms during pregnancy and their possible worsening after childbirth is likely due to uniformly high and stable estrogen levels during pregnancy and their rapid decline after childbirth.
Another type of headache in pregnancy is tension headache. As a rule, it is characterized by medium intensity, unlike migraine, it often covers the entire head. The pain of tension squeezes the head like a hoop, or causes a pulling sensation; occurs mainly as a result of stress or overexertion.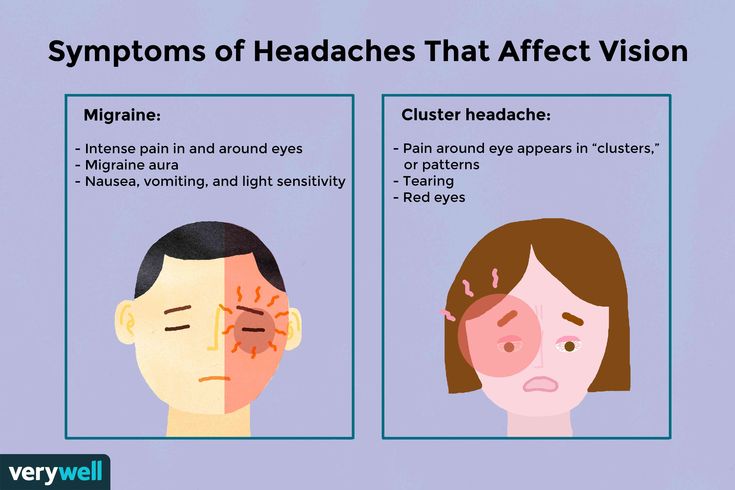 nine0003
nine0003
- If a woman has frequent headaches before pregnancy, the risk of developing preeclampsia increases by 2.4 times
- If a woman is diagnosed with migraine before pregnancy, the risk of developing preeclampsia increases by 3.5 times migraine attacks are observed in the early stages - the risk of developing preeclampsia increases 4 times
Pregnancy headache treatment
A pregnant woman needs medical advice when:
- headache has become almost constant, and has recently changed its character;
- headache in the morning and all day;
- pain is constantly localized in a certain area of the head;
- headache is accompanied by other symptoms - impaired vision, hearing, speech, motor functions, sensitivity, etc.;
- Pain accompanies high or low blood pressure.
Doctor's prescriptions depend on the underlying cause of the headache. Sometimes several factors influence at once, so it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. If the headache bothers you regularly, you should contact a neurologist for a specific examination. nine0003
If the headache bothers you regularly, you should contact a neurologist for a specific examination. nine0003
Primary therapy during pregnancy - non-drug (relaxation, sleep, massage). For the treatment of acute migraine attacks, paracetamol (1000 mg) is considered the drug of choice, preferably in the form of suppositories. The table shows data on the possibility of using a number of drugs for the treatment of headache during pregnancy.
The risks associated with the use of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) and ibuprofen are considered relatively low if the drugs are taken episodically and removed in the last trimester. nine0003
Information on the safety of triptan treatment during pregnancy is available for only a few drugs in this group (sumatriptan, naratriptan and rizatriptan). According to information databases containing information on pregnancy outcomes in women who received these drugs, there were no facts indicating serious risks to the mother and fetus.
With some triptans (sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, naratriptan), there is currently a possibility of a small increase in preterm birth, so triptans are acceptable in severe migraine in exceptional cases. However, data on the use of triptans continues to accumulate and there is not yet sufficient evidence for the safety of the use of triptans during pregnancy. nine0003
However, data on the use of triptans continues to accumulate and there is not yet sufficient evidence for the safety of the use of triptans during pregnancy. nine0003
Dihydroergotamine and ergotamine tartrate are contraindicated in pregnant women.
Headache definitely cannot be tolerated, it must be correctly diagnosed, differentiated and treated.
The American Academy of Neurology recommends a brain scan in the following cases (if pregnant, only MRI is recommended)
- if, in the presence of a headache, a neurological deficit occurs or any, even short-term, changes in the neurological status; nine0305 - if the headache has atypical manifestations and does not fit into the strict framework of establishing a diagnosis of migraine;
- if there is a proven immunodeficiency;
- a sudden severe headache in women for the first time.
- Number:
- Thematic issue "Gynecology, Obstetrics, Reproductology" No.
 4 (24), chest 2016
4 (24), chest 2016
Effective therapy of complication of vaginess is the price of nutrition, which is not turbulent for a skin practitioner. It is based on the current settings, the main directions for the improvement of the normal excess of vaginess and the preservation of superfluous blood flow in the system "mother - placenta - baby", prevention of fetal development, restoration of the vessel endothelium and a change in the level of resistance to insulin. Behind Danami Doslizhen, I am a normal strategist of the normal overbird, I will be recognized as a sign of the tsi categorical additives, yaki may at his own stocks, l-arginin, folіvu, puhno, sireno, tan, zero, zero, zero, zero, zero, zero-tan.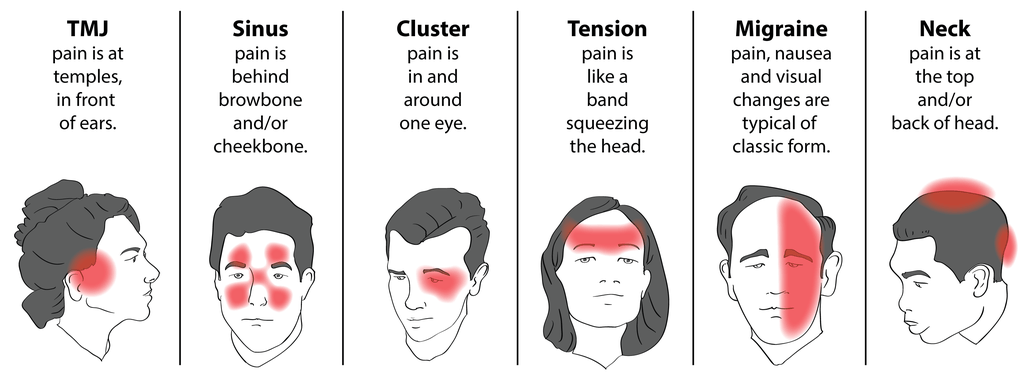 ... nine0003
... nine0003
11/20/2022 Obstetrics / gynecology The use of antiseptics in the treatment of vaginal infections in various etiologies
Such antiseptics are an alternative to antibiotic therapy in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis due to a wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity, low toxicity and high bioavailability from tissues. The Recommendations present the advantages and disadvantages of the main antiseptic products available today, which can be stasted for the treatment of vaginitis in various etiologies. ... nine0003
11/20/2022 Obstetrics/gynecology Aspects of treatment of pain syndrome in endometriosis
Pain syndrome in endometriosis is headache, for which patients go to the doctor.



:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/674814/chart_01_large.0.png)