Diagram of baby development
Pictures of Fetal Development Month-by-Month
Reviewed by Amita Shroff, MD on February 24, 2021
You're pregnant. Congratulations! Are you curious how big your developing baby is, what your baby looks like as it grows inside you, and when you'll feel it move? Take a peek inside the womb to see how a baby develops from month to month.
Fertilization happens when a sperm meets and penetrates an egg. It's also called conception. At this moment, the genetic makeup is complete, including the sex of the baby. Within about three days after conception, the fertilized egg is dividing very fast into many cells. It passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it attaches to the uterine wall. The placenta, which will nourish the baby, also starts to form.
At this point the baby is developing the structures that will eventually form their face and neck. The heart and blood vessels continue to develop. And the lungs, stomach, and liver start to develop. A home pregnancy test would show positive.
The baby is now a little over half an inch in size. Eyelids and ears are forming, and you can see the tip of the nose. The arms and legs are well formed. The fingers and toes grow longer and more distinct.
The baby measures about 2 inches and starts to make its own movements. You may start to feel the top of your uterus above your pubic bone. Your doctor may hear the baby's heartbeat with special instruments. The sex organs of the baby should start to become clear.
The baby now measures about 4.3 to 4.6 inches and weighs about 3.5 ounces. You should be able to feel the top of your uterus about 3 inches below your belly button. The baby's eyes can blink and the heart and blood vessels are fully formed. The baby's fingers and toes have fingerprints.
The baby weighs about 10 ounces and is a little more than 6 inches long. Your uterus should be at the level of your belly button. The baby can suck a thumb, yawn, stretch, and make faces. Soon -- if you haven't already -- you'll feel your baby move, which is called "quickening.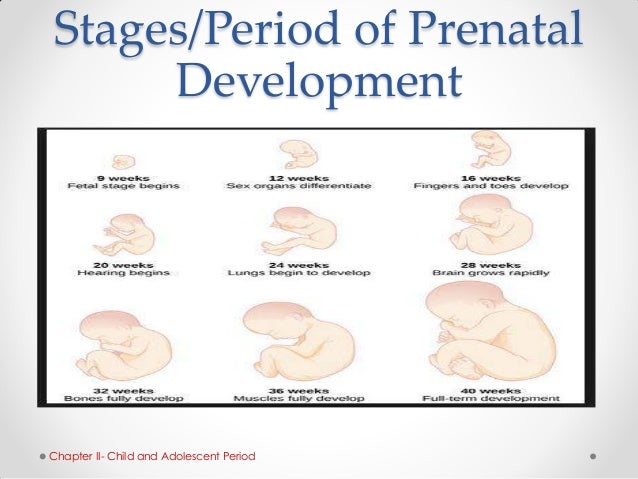 "
"
An ultrasound is usually done for all pregnant women at 20 weeks. During this ultrasound, the doctor will make sure that the placenta is healthy and attached normally and that your baby is growing properly. You can see the baby's heartbeat and movement of its body, arms, and legs on the ultrasound. You can usually find out whether it's a boy or a girl at 20 weeks.
Shown here is a 2D ultrasound (inset) contrasted with a 4D ultrasound, both at 20 weeks.
The baby weighs about 1.4 pounds now and responds to sounds by moving or increasing their pulse. You may notice jerking motions if they hiccup. With the inner ear fully developed, the baby may be able to sense being upside down in the womb.
The baby weighs about 2 pounds, 6 ounces, and changes position often at this point in pregnancy. If you had to deliver prematurely now, there is a good chance the baby would survive. Ask your doctor about preterm labor warning signs. Now is the time to register for birthing classes.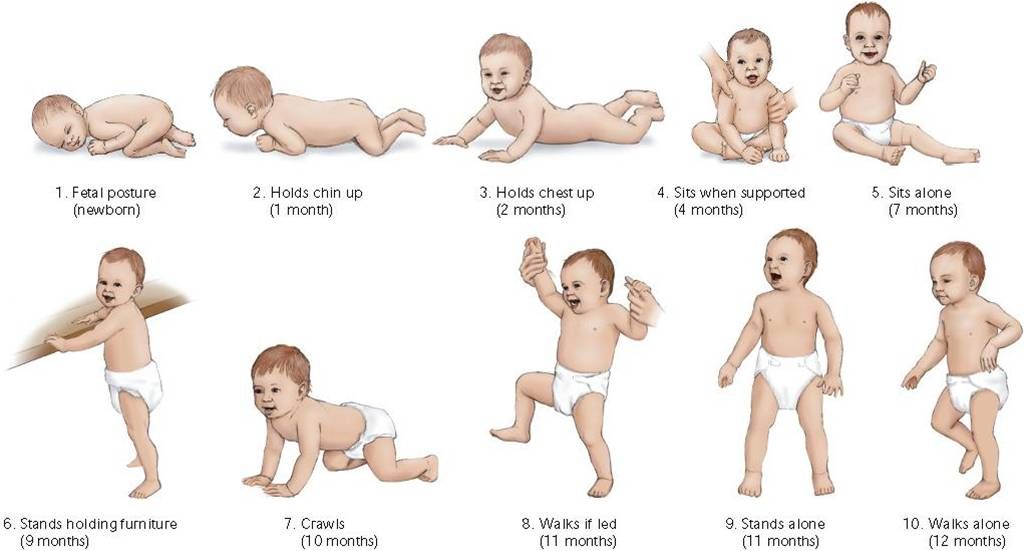 Birthing classes prepare you for many aspects of childbirth, including labor and delivery and taking care of your newborn.
Birthing classes prepare you for many aspects of childbirth, including labor and delivery and taking care of your newborn.
The baby weighs almost 4 pounds and is moving around often. The baby's skin has fewer wrinkles as a layer of fat starts to form under the skin. Between now and delivery, your baby will gain up to half their birth weight. Ask your doctor how to do a fetal movement chart. Think about breastfeeding. You may notice a yellowish fluid leaking from your breasts. That is colostrum, and it happens to get your breasts ready for making milk. Most women go to the doctor every two weeks at this stage of pregnancy.
Babies differ in size, depending on many factors, such as gender, the number of babies being carried, and size of the parents. So your baby's overall rate of growth is as important as the actual size. On average, a baby at this stage is about 18.5 inches and weighs close to 6 pounds. The brain has been developing rapidly. Lungs are nearly fully developed.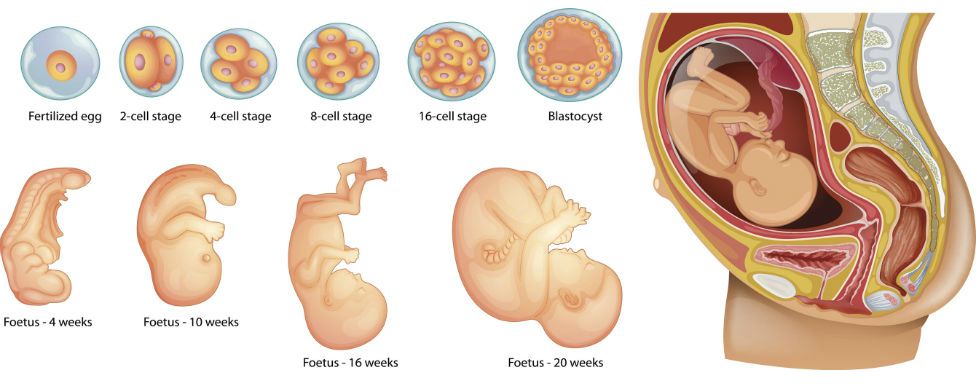 The head is usually positioned down into the pelvis by now. Your baby is considered at 'term' when they are 37 weeks. They are an early term baby if born between 37-39 weeks, at term, if they're 39-40 weeks and late term if they're 41-42 weeks.
The head is usually positioned down into the pelvis by now. Your baby is considered at 'term' when they are 37 weeks. They are an early term baby if born between 37-39 weeks, at term, if they're 39-40 weeks and late term if they're 41-42 weeks.
A mother's due date marks the end of their 40th week. The delivery date is calculated using the first day of their last period. Based on this, pregnancy can last between 38 and 42 weeks with a full-term delivery happening around 40 weeks. Some post-term pregnancies -- those lasting more than 42 weeks -- are not really late. The due date may just not be accurate. For safety reasons, most babies are delivered by 42 weeks. Sometimes the doctor may need to induce labor.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
(1) Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake – All rights reserved.
(2) Dr. David M. Phillips / Visuals Unlimited / Getty Images
(3) 3D4Medical.com / Getty Images
(4) Copyright © Scott Camazine / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
(5) Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake – All rights reserved.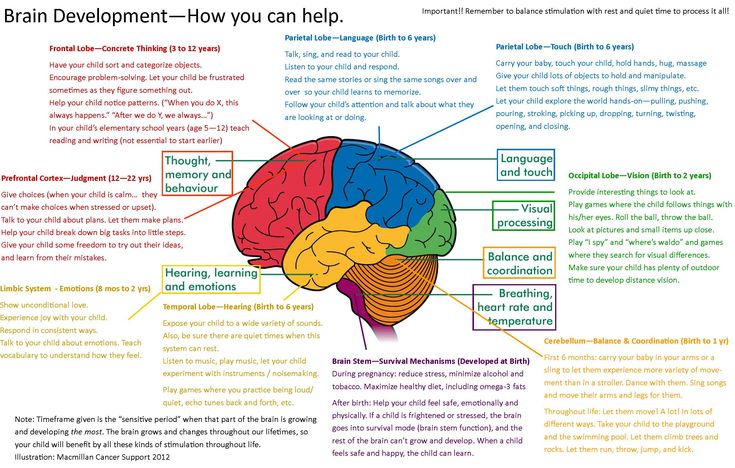
(6) Nestle / Petit Format / Photo Researchers, Inc.
(7) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(8) a) Dr.Benoit/Mona Lisa. Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake -- All rights reserved. b)Vincenzo Lombardo / Photographer's Choice / Getty Images
(9) Dr. Benoit/Mona Lisa. Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
(10) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(11) Jose Manuel Gelpi Diaz / iStockphoto
(12) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(13) © Yoav Levy / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
SOURCES:
American Academy of Family Physicians.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: "How Your Baby Grows During Pregnancy."
KidsHealth.org: "Pregnancy Calendar."
March of Dimes: "Prenatal Care – Ultrasound."
US Department of Health and Human Services Office of Women’s Health: "Pregnancy: Breast Changes."
© 2021 WebMD, LLC.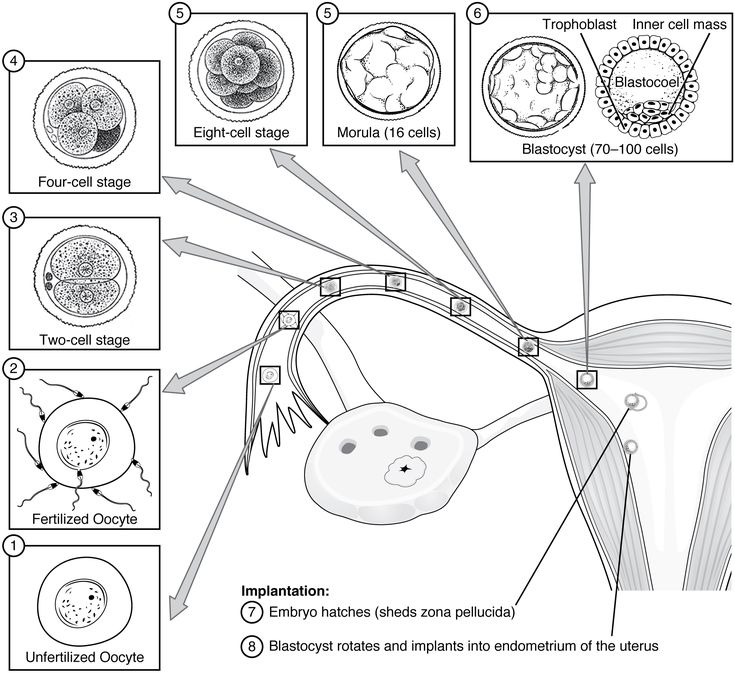 All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
Fetal development: Month-By-Month Stages of Pregnancy
When does a pregnancy start?
The start of pregnancy is actually the first day of your last menstrual period. This is called the gestational age, or menstrual age. It’s about two weeks ahead of when conception actually occurs. Though it may seem strange, the date of the first day of your last period will be an important date when determining your due date. Your healthcare provider will ask you about this date and will use it to figure out how far along you are in your pregnancy.
How does conception work?
Each month, your body goes through a reproductive cycle that can end in one of two ways. You will either have a menstrual period or become pregnant. This cycle is continuously happening during your reproductive years — from puberty in your teen years to menopause around age 50.
In a cycle that ends with pregnancy, there are several steps.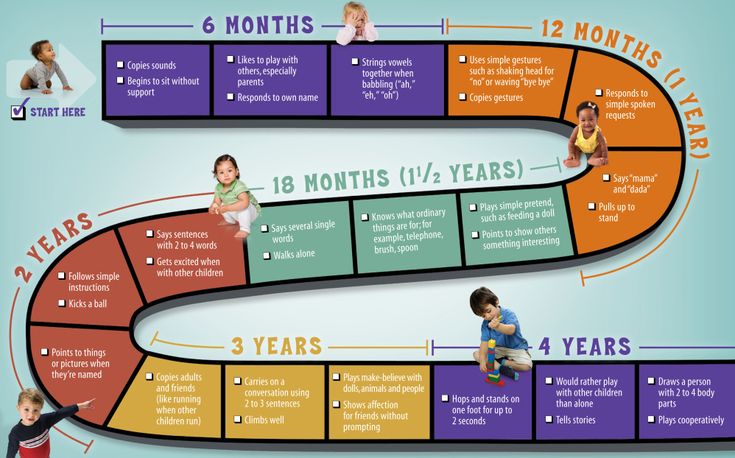 First, a group of eggs (called oocytes) gets ready to leave the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small, fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Think of these follicles as small containers for each immature egg. Out of this group of eggs, one will become mature and continue on through the cycle. This follicle then suppresses all the other follicles in the group. The other follicles stop growing at this point.
First, a group of eggs (called oocytes) gets ready to leave the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small, fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Think of these follicles as small containers for each immature egg. Out of this group of eggs, one will become mature and continue on through the cycle. This follicle then suppresses all the other follicles in the group. The other follicles stop growing at this point.
The mature follicle now opens and releases the egg from the ovary. This is ovulation. Ovulation generally happens about two weeks before your next menstrual period begins. It’s generally in the middle of your cycle.
After ovulation, the opened (ruptured) follicle develops into a structure called the corpus luteum. This secretes (releases) the hormones progesterone and estrogen. Progesterone helps prepare the endometrium (lining of the uterus). This lining is the place where a fertilized egg settles to develop. If you don’t become pregnant during a cycle, this lining is what is shed during your period.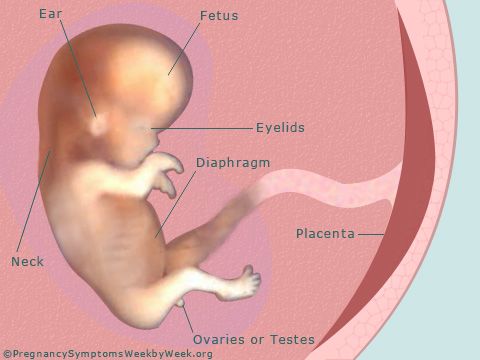
On average, fertilization happens about two weeks after your last menstrual period. When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating of the egg to prevent other sperm from entering.
At the moment of fertilization, your baby’s genetic make-up is complete, including its sex. The sex of your baby depends on what sperm fertilizes the egg at the moment of conception. Generally, women have a genetic combination of XX and men have XY. Women provide each egg with an X. Each sperm can be either an X or a Y. If the fertilized egg and sperm is a combination of an X and Y, it’s a boy. If there are two Xs, it’s a girl.
What happens right after conception?
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg begins rapidly dividing into many cells. It remains in the fallopian tube for about three days after conception. Then the fertilized egg (now called a blastocyte) continues to divide as it passes slowly through the fallopian tube to the uterus. Once there, its next job is to attach to the endometrium.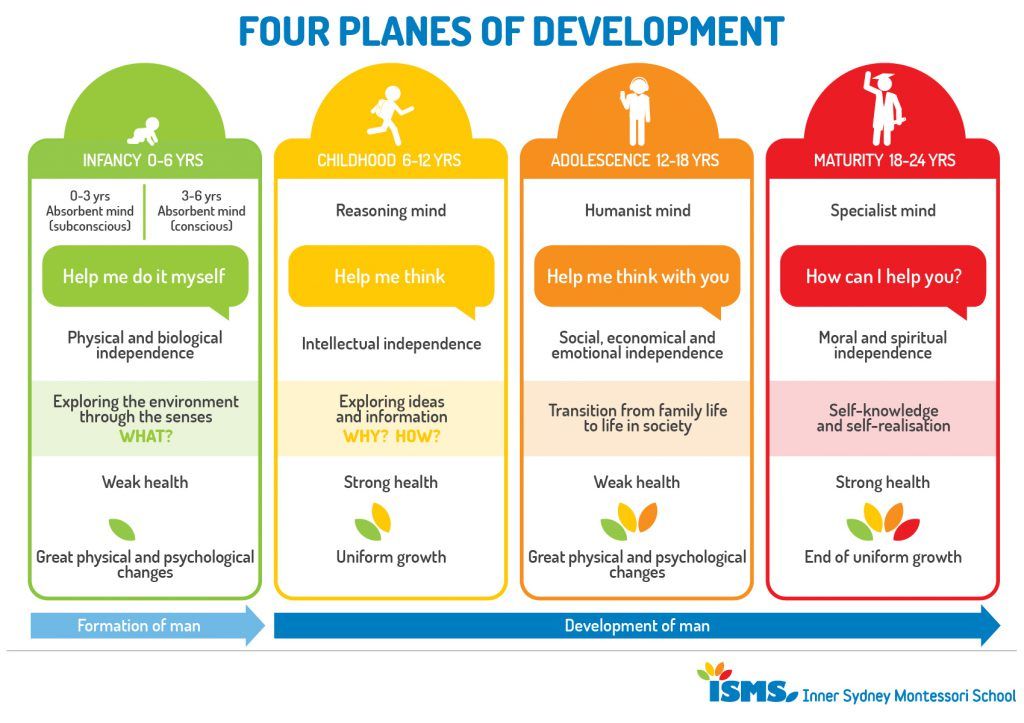 This is called implantation.
This is called implantation.
Before implantation though, the blastocyte breaks out of its protective covering. When the blastocyte makes contact with the endometrium, the two exchange hormones to help the blastocyte attach. Some women notice spotting (slight bleeding) during the one or two days when implantation happens. This is normal and isn’t something you should worry about. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix (the opening between your uterus and birth canal) is sealed by a plug of mucus.
Within three weeks, the blastocyte cells ultimately form a little ball, or an embryo. By this time, the first nerve cells have formed.
Your developing fetus has already gone through a few name changes in the first few weeks of pregnancy. Generally, it's called an embryo from conception until the eighth week of development. After the eighth week, it's called a fetus until it’s born.
How early can I know I’m pregnant?
From the moment of conception, the hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) will be present in your blood. This hormone is created by the cells that form the placenta (food source for the growing fetus). It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
This hormone is created by the cells that form the placenta (food source for the growing fetus). It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
When should I reach out to my healthcare provider about a new pregnancy?
Most healthcare providers will have you wait to come in for an appointment until you have had a positive home pregnancy test. These tests are very accurate once you have enough hCG circulating throughout your body. This can be a few weeks after conception. It’s best to call your healthcare provider once you have a positive pregnancy test to schedule your first appointment.
When you call, your healthcare provider may ask you if you are taking a prenatal vitamin. These supplements contain folic acid. It’s important that you get at least 400mcg of folic acid each day during a pregnancy to make sure the fetus's neural tube (beginning of the brain and spine) develops correctly.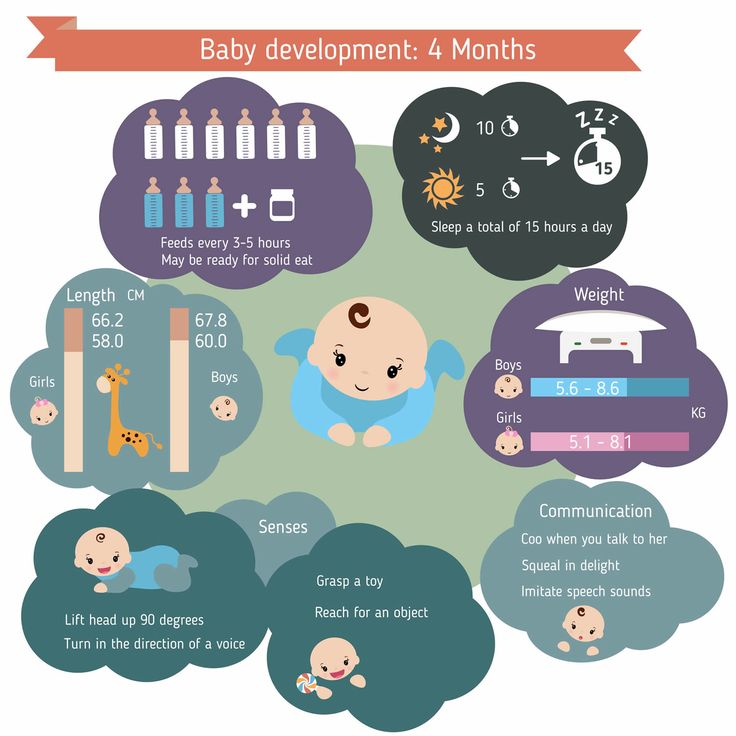 Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
What’s the timeline for fetal development?
The fetus will change a lot throughout a typical pregnancy. This time is divided into three stages, called trimesters. Each trimester is a set of about three months. Your healthcare provider will probably talk to you about fetal development in terms of weeks. So, if you are three months pregnancy, you are about 12 weeks.
You will see distinct changes in the fetus, and yourself, during each trimester.
Traditionally, we think of a pregnancy as a nine-month process. However, this isn’t always the case. A full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, or 280 days. Depending on what months you are pregnant during (some are shorter and some longer) and what week you deliver, you could be pregnant for either nine months or 10 months. This is completely normal and healthy.
This is completely normal and healthy.
Once you get close to the end of your pregnancy, there are several category names you might hear regarding when you go into labor. These labels divide up the last few weeks of pregnancy. They’re also used to look out for certain complications in newborns. Babies that are born in the early term period or before may have a higher risk of breathing, hearing or learning issues than babies born a few weeks later in the full term time frame. When you’re looking at these labels, it’s important to know how they’re written. You may see the week first (38) and then you’ll see two numbers separated by a slash mark (6/7). This stands for how many days you currently are in the gestational week. So, if you see 38 6/7, it means that you are on day 6 of your 38th week.
The last few weeks of pregnancy are divided into the following groups:
- Early term: 37 0/7 weeks through 38 6/7 weeks.
- Full term: 39 0/7 weeks through 40 6/7 weeks.
- Late term: 41 0/7 weeks through 41 6/7 weeks.
- Post term: 42 0/7 weeks and on.
Talk to your healthcare provider about any questions you may have about gestational age and due date.
Stages of Growth Month-by-Month in Pregnancy
First trimester
The first trimester will span from conception to 12 weeks. This is generally the first three months of pregnancy. During this trimester, the fertilized egg will change from a small grouping of cells to a fetus that is starting to have a baby’s features.
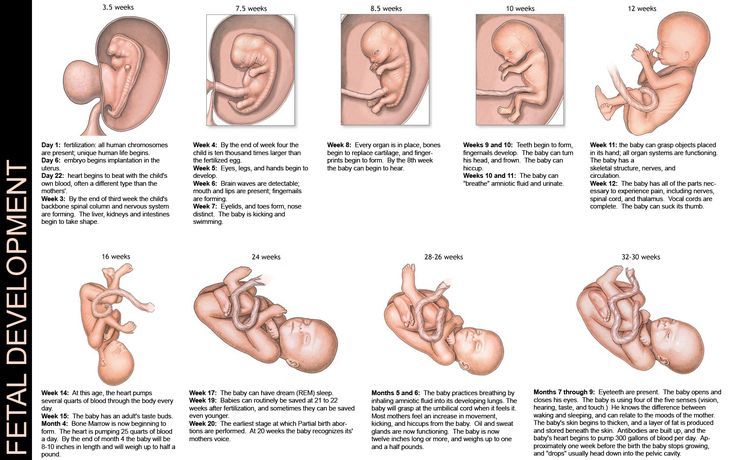
Month 1 (weeks 1 through 4)
As the fertilized egg grows, a water-tight sac forms around it, gradually filling with fluid. This is called the amniotic sac, and it helps cushion the growing embryo.
During this time, the placenta also develops. The placenta is a round, flat organ that transfers nutrients from the mother to the fetus, and transfers wastes from the fetus. Think of the placenta as a food source for the fetus throughout your pregnancy.
In these first few weeks, a primitive face will take form with large dark circles for eyes. The mouth, lower jaw and throat are developing. Blood cells are taking shape, and circulation will begin. The tiny "heart" tube will beat 65 times a minute by the end of the fourth week.
By the end of the first month, the fetus is about 1/4 inch long – smaller than a grain of rice.
Month 2 (weeks 5 through 8)
Facial features continue to develop. Each ear begins as a little fold of skin at the side of the head. Tiny buds that eventually grow into arms and legs are forming. Fingers, toes and eyes are also forming.
The neural tube (brain, spinal cord and other neural tissue of the central nervous system) is well formed now. The digestive tract and sensory organs begin to develop too. Bone starts to replace cartilage.
The head is large in proportion to the rest of the body at this point. At about 6 weeks, a heartbeat can usually be detected.
After the 8th week, healthcare providers refer to it as a fetus instead of an embryo.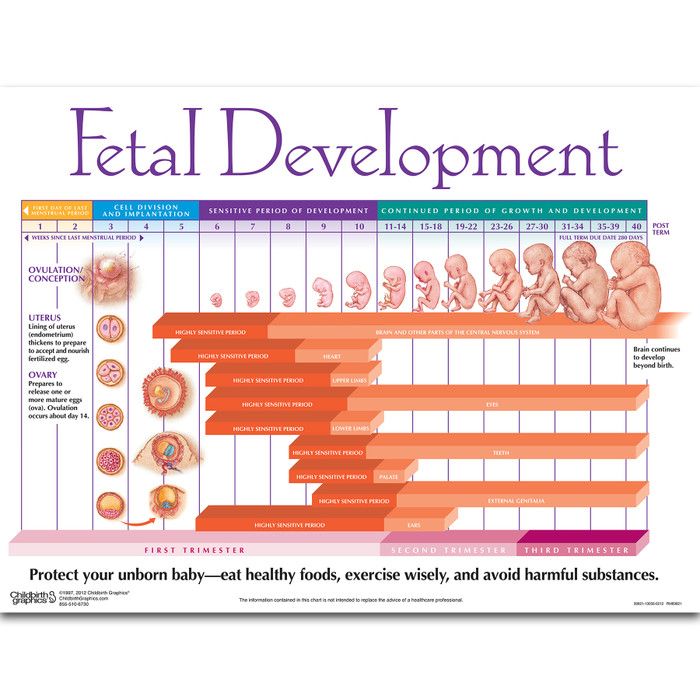
By the end of the second month, the fetus is about 1 inch long and weighs about 1/30 of an ounce.
Month 3 (weeks 9 through 12)
The arms, hands, fingers, feet and toes are fully formed. At this stage, the fetus is starting to explore a bit by doing things like opening and closing its fists and mouth. Fingernails and toenails are beginning to develop and the external ears are formed. The beginnings of teeth are forming under the gums. The reproductive organs also develop, but sex is still difficult to distinguish on ultrasound.
By the end of the third month, the fetus is fully formed. All the organs and limbs (extremities) are present and will continue to develop in order to become functional. The circulatory and urinary systems are also working and the liver produces bile.
At the end of the third month, the fetus is about 4 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce.
Since the most critical development has taken place, your chance of miscarriage drops considerably after three months.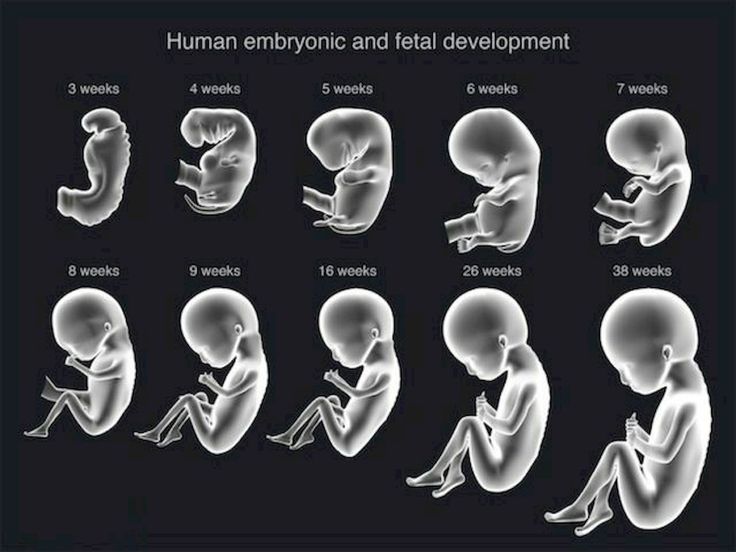
Second trimester
This middle section of pregnancy is often thought of as the best part of the experience. By this time, any morning sickness is probably gone and the discomfort of early pregnancy has faded. The fetus will start to develop facial features during this month. You may also start to feel movement as the fetus flips and turns in the uterus. During this trimester, many people find out whether their baby will be designated male or female at birth. This is typically done during an anatomy scan (an ultrasound that checks physical development) around 20 weeks.
Month 4 (weeks 13 through 16)
The fetal heartbeat may now be audible through an instrument called a doppler. The fingers and toes are well-defined. Eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails and hair are formed. Teeth and bones become denser. The fetus can even suck his or her thumb, yawn, stretch and make faces.
The nervous system is starting to function. The reproductive organs and genitalia are now fully developed, and your doctor can see on ultrasound if the fetus will be designated male or female at birth.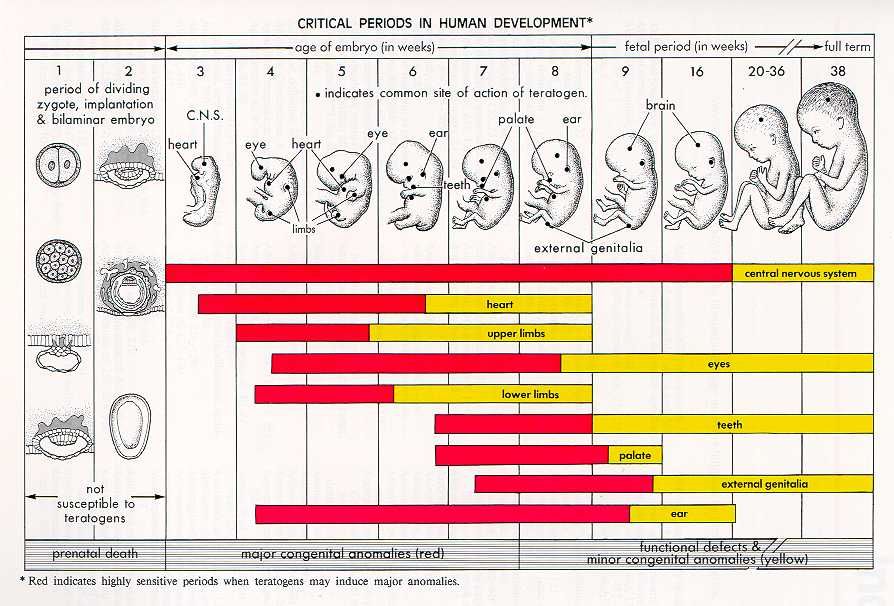
By the end of the fourth month, the fetus is about 6 inches long and weighs about 4 ounces.
Month 5 (weeks 17 through 20)
At this stage, you may begin to feel the fetus moving around. The fetus is developing muscles and exercising them. This first movement is called quickening and can feel like a flutter.
Hair begins to grow on the head. The shoulders, back and temples are covered by a soft fine hair called lanugo. This hair protects the fetus and is usually shed at the end of your baby's first week of life.
The skin is covered with a whitish coating called vernix caseosa. This "cheesy" substance is thought to protect fetal skin from the long exposure to the amniotic fluid. This coating is shed just before birth.
By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs from 1/2 to 1 pound.
Month 6 (weeks 21 through 24)
If you could look inside the uterus right now, you would see that the fetus's skin is reddish in color, wrinkled and veins are visible through translucent skin.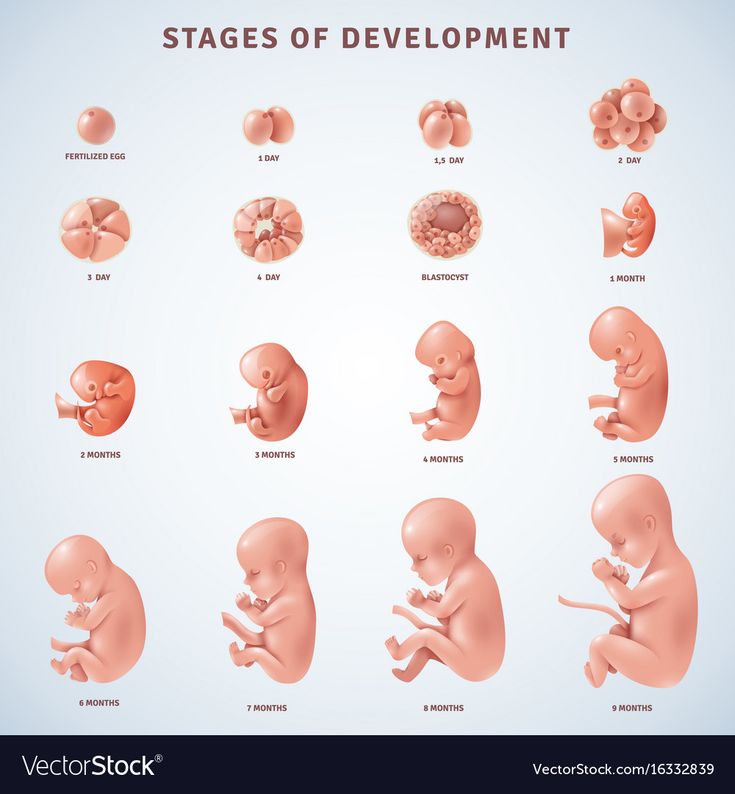 The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The fetus responds to sounds by moving or increasing the pulse. You may notice jerking motions if the fetus hiccups.
If born prematurely, your baby may survive after the 23rd week with intensive care.
By the end of the sixth month, the fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs about 2 pounds.
Month 7 (weeks 25 through 28)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. At this point, hearing is fully developed. The fetus changes position frequently and responds to stimuli, including sound, pain and light. The amniotic fluid begins to diminish.
If born prematurely, your baby would be likely to survive after the seventh month.
At the end of the seventh month, the fetus is about 14 inches long and weighs from 2 to 4 pounds.
Third trimester
This is the final part of your pregnancy. You may be tempted to start the countdown till your due date and hope that it would come early, but each week of this final stage of development helps the fetus prepare for birth. Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Remember, even though popular culture only mentions nine months of pregnancy, you may actually be pregnant for 10 months. The typical, full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, which can take you into a tenth month. It’s also possible that you can go past your due date by a week or two (41 or 42 weeks). Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely as you approach your due date. If you pass your due date, and don’t go into spontaneous labor, your provider may induce you. This means that medications will be used to make you go into labor and have the baby. Make sure to talk to your healthcare provider during this trimester about your birth plan.
Month 8 (weeks 29 through 32)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. You may notice more kicking. The brain developing rapidly at this time, and the fetus can see and hear. Most internal systems are well developed, but the lungs may still be immature.
The fetus is about 18 inches long and weighs as much as 5 pounds.
Month 9 (weeks 33 through 36)
During this stage, the fetus continues to grow and mature. The lungs are close to being fully developed at this point.
The fetus has coordinated reflexes and can blink, close the eyes, turn the head, grasp firmly, and respond to sounds, light and touch.
The fetus is about 17 to 19 inches long and weighs from 5 ½ pounds to 6 ½ pounds.
Month 10 (Weeks 37 through 40)
In this final month, you could go into labor at any time. You may notice that less movement because space is tight. At this point, The fetus's position may have changed to prepare for birth. Ideally, it's head down in your uterus. You may feel very uncomfortable in this final stretch of time as the fetus drops down into your pelvis and prepares for birth.
Your baby is ready to meet the world at this point. They are about 18 to 20 inches long and weigh about 7 pounds.
Child development by months to a year: child development calendar and table
02/22/2020 Reading time: 5 min 63955 nine0010
Concern for the health and well-being of their child is natural for all parents. But the greatest concern is experienced by moms and dads in the 1st year after the birth of the baby. During these 12 months, a child goes through a truly huge journey from a helpless newborn to a child who actively explores the world around him and knows how to interact with it.
Each stage of this path has its own characteristics, and the table of child development by months, which shows the main indicators of height and weight, will help to partly understand them.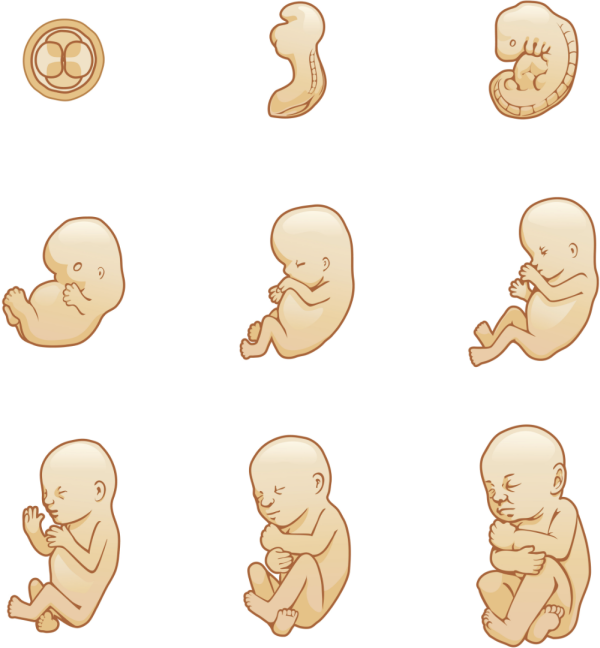 nine0010
nine0010
| Age (months) | Height (cm) | Body weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Newborn | 49.0 - 54.0 | 2.6 - 4.01 |
| one | 52.0 - 55.0 nine0034 | 3.0 - 4.3 |
| 2 | 55.0 - 57.0 | 4.5 - 5.0 |
| 3 | 58.0 - 60.0 | 4.0 - 6.0 |
| 4 | 60.0 - 63.0 | 4.5 - 6.5 nine0034 |
| five | 63.0 - 67.0 | 6.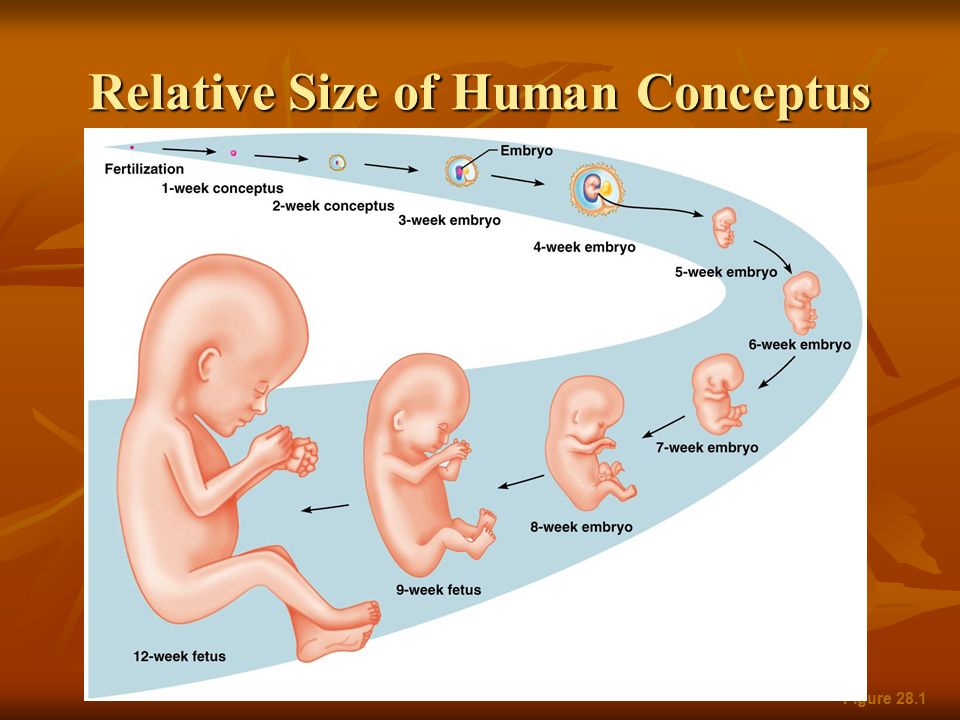 5 - 7.5 5 - 7.5 |
| 6 | 65.0 - 69.0 | 7.5 - 7.8 |
| 7 | 67.0 - 71.0 | 8.0 - 8.8 |
| eight nine0034 | 71.0 - 72.0 | 8.4 - 9.4 |
| nine | 72.0 - 73.0 | 9.4 - 10.0 |
| 10 | 73.0 - 74.0 | 9.6 - 10.5 |
| eleven | 74.0 - 75.0 nine0034 | 10.0 - 11.0 |
| 12 | 75.0 - 76.0 | 10. 5 - 11.5 5 - 11.5 |
The development of the child by months, or rather the main physical parameters of growth and weight gain, given in the table, can be attributed to the average, since they do not take into account the individual characteristics of the baby's body. In any case, every month of life is a new achievement for the child! nine0010
1st month
At the age of one month, the baby is already trying to raise his head for a few seconds when he is in a position on his stomach. Responds well to loud sounds and bright lights. In response to loud and sharp sounds or bright light, the baby “protects itself” - waves its arms and then presses them to the body.
2nd month
When you hold the baby in your arms so that his body is in an upright position, you will see that he briefly tries or can hold his head. The child is no longer afraid of sounds and light, but tries to smoothly follow the object of interest to him.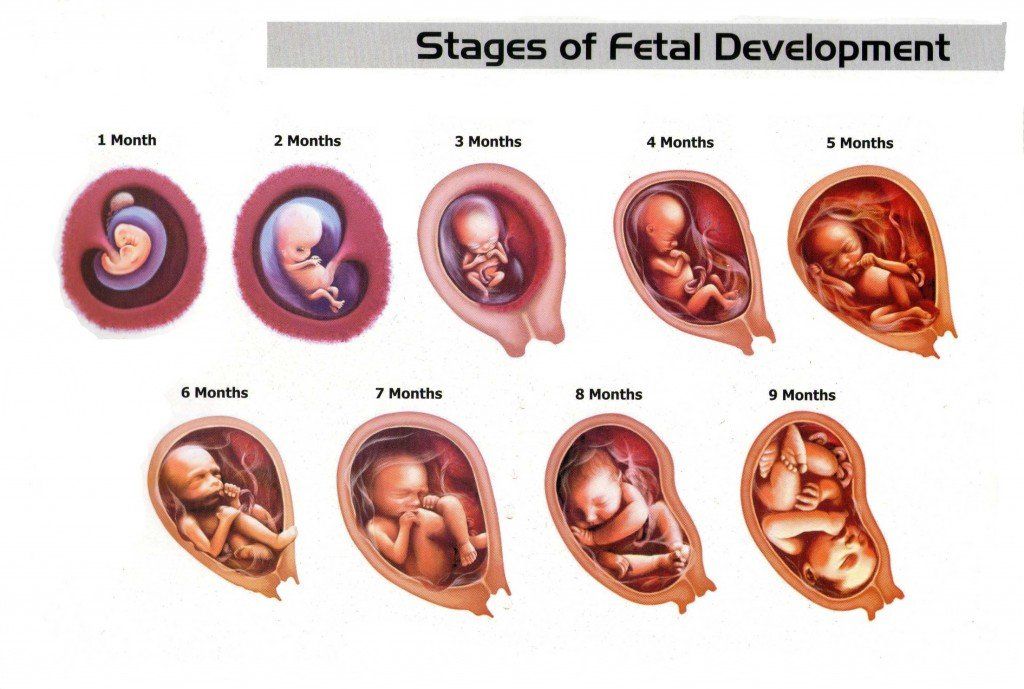 Moving objects that are within his reach, he tries to grab with his fingers, however, this does not always work out. nine0143
Moving objects that are within his reach, he tries to grab with his fingers, however, this does not always work out. nine0143
3rd month
Now the baby holds his head in an upright position. And in the position on the stomach, he is already able to lean on his elbows and try to lift the upper part of the body. He makes attempts to roll over, grab a sheet, reach for toys, but his coordination is not very good yet, and not all attempts are successful.
4th month nine0010
At this age, the baby already knows how to push off well with his feet when you hold him upright. His toys evoke a vivid emotional response. Interested, the baby raises its head and reaches for a bright object in an attempt to grab it.
5th month
The child rolls over from his back to his stomach and attempts to rise on his own to take a sitting position.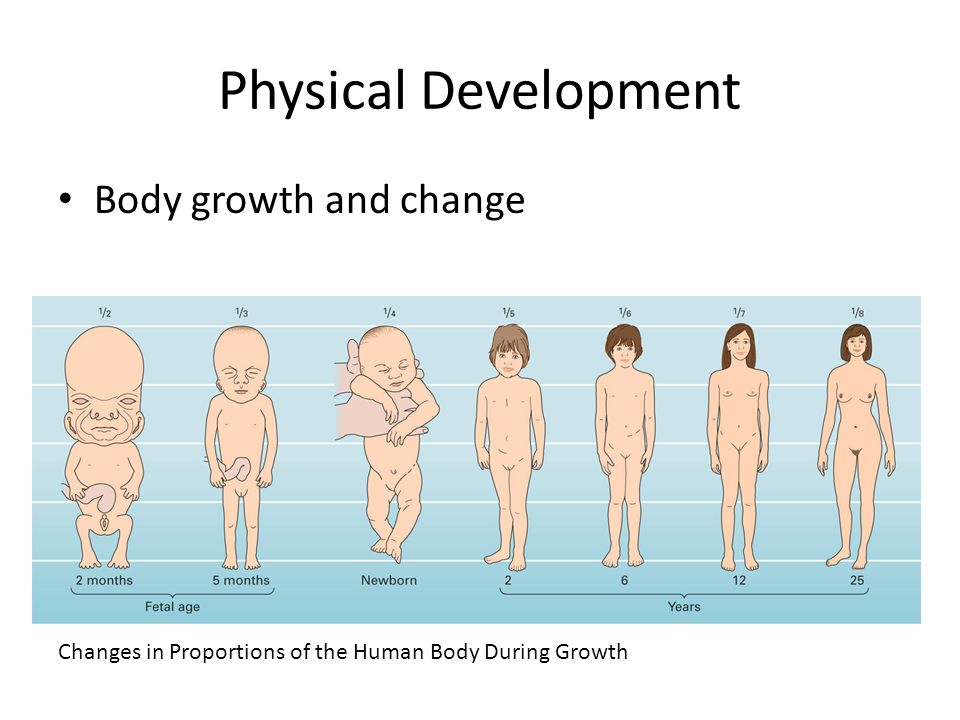 But it cannot stay there for long. But he already firmly holds the object of interest to him in his hand and carefully studies it, distinguishes close people from strangers and begins to understand the emotions of his mother by the intonations in her voice. nine0010
But it cannot stay there for long. But he already firmly holds the object of interest to him in his hand and carefully studies it, distinguishes close people from strangers and begins to understand the emotions of his mother by the intonations in her voice. nine0010
6th month
The kid learned not just to sit, but to sit down on his own. It easily rolls over from stomach to back and vice versa. Taking the child by the handles, you can observe how he is already consciously, and not reflexively, trying to walk. He reaches for a fallen toy, and if he manages to get it, he picks it up without outside help.
7th month
This is the age when it is no longer enough for the baby to sit still. He actively masters crawling, and, leaning on furniture or other durable objects, he can stand. The surrounding world interests the baby more and more. He recognizes objects well (especially favorite ones), and studying his own reflection in the mirror becomes one of the most exciting activities. nine0010
nine0010
8th month
At this age, the child can play with his favorite toys for a long time. You can play "Ladushki" with him. He shows a wide range of emotions - from fear to joy, and holding the hands of mom or dad, he can quite confidently step over his legs on the floor.
9th month
Now the baby not only knows how to get up on his own and move around, relying on furniture, he can even refuse the help of adults and try to do everything himself. But here it is important to take into account the peculiarities of the development of the child and not rush him with the first independent steps. nine0010
10th month
This is the age when the baby is no longer enough to show emotions with facial expressions. Now he knows how to do it with the help of monosyllabic words, hand movements. He perfectly imitates everything he sees and hears: the gestures of his parents, their intonation, their activities. Can engage in simple actions for a long time: open and close a chest of drawers or closet doors, throw and pick up a toy, and so on.
Can engage in simple actions for a long time: open and close a chest of drawers or closet doors, throw and pick up a toy, and so on.
11th month nine0010
Communication skills have developed to the extent that the baby is able to express his agreement and disagreement, approval and disapproval with the right gestures and facial expressions. Refusing something, he shakes his head and nods in agreement. He already knows what sounds animals make, and when asked to show something or do something, he usually willingly agrees.
12th month
The child is interested in absolutely everything that happens around: the noise of traffic outside the window, the movement of water during bathing, more complex toys. He knows how to perform difficult tasks expressed in words: at the request he closes or opens the door, brings the necessary items from another room. nine0014 All kids are different, and if some of the described skills appear a little earlier or a little later, do not worry and get upset! You can always ask your pediatrician about all the features of a child's development.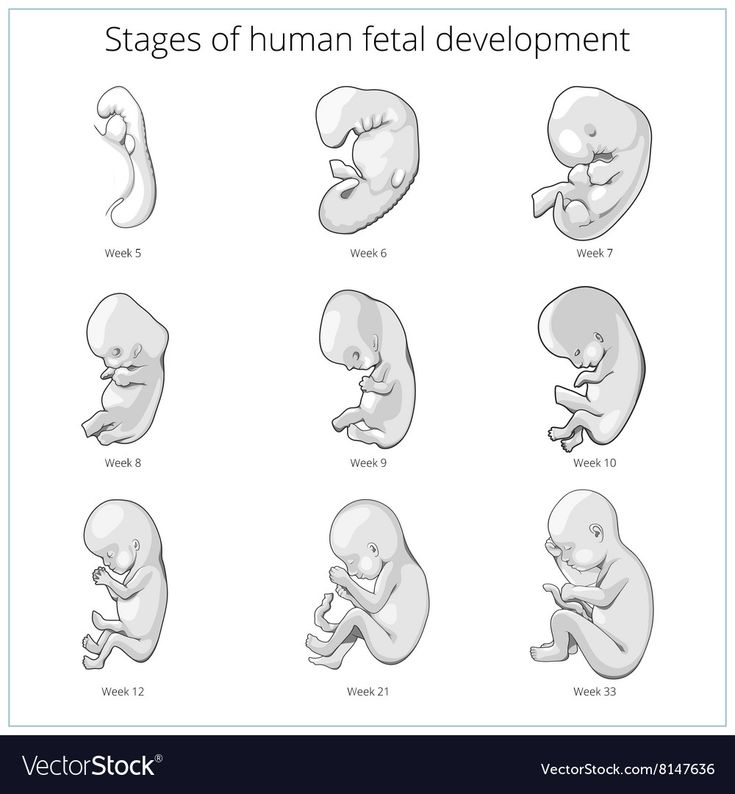
(7 ratings; article rating 4.9)
Child Development Calendar from Health of the Nation
The Child Development Calendar from the Health of the Nation medical center is a convenient system that tells parents by months how the baby is developing. nine0010
Child development by months
Newborn
How does the baby behave in the first weeks of life? Should I be worried if he sleeps 18 hours a day? What you need to know about the features of feeding the crumbs, and what recommendations for care should be followed?
Read more
nine0244 1 month
What happens to a child at the age of one month, how his behavior changes.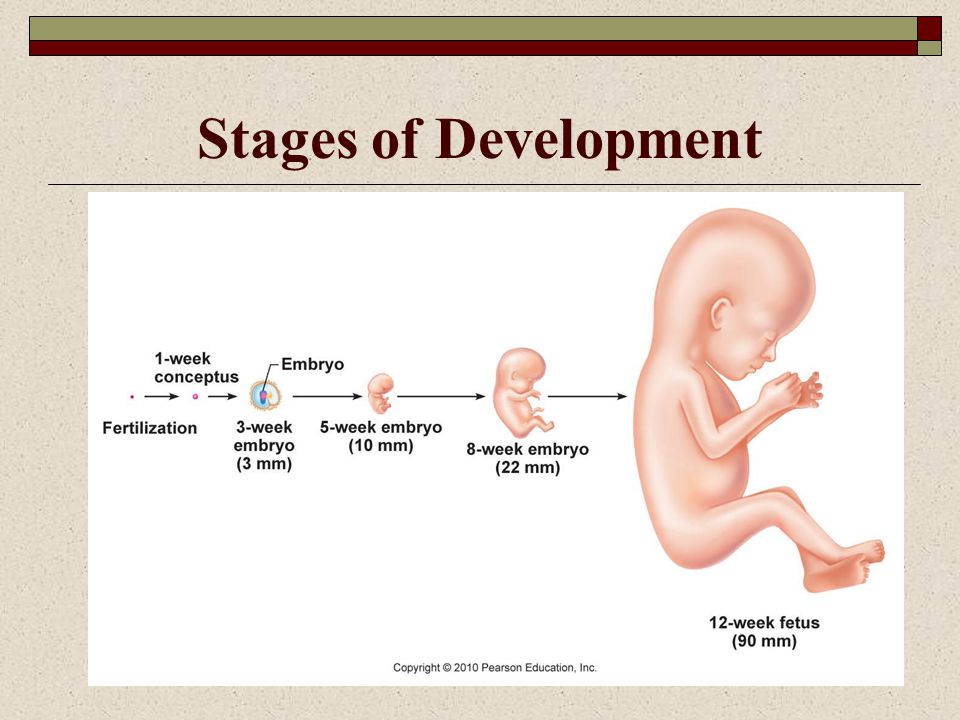 Features of development and the emergence of new actions. What you need to know about nutrition, daily care. Planned visits to doctors and testing.
Features of development and the emergence of new actions. What you need to know about nutrition, daily care. Planned visits to doctors and testing.
Read more
2 months
What happens in the life of a child at the age of 2 months? What behaviors should be taken into account? The appearance of the first emotions of the baby, the development of the vocal apparatus. nine0010
More details
3 months
What discoveries do parents expect when a child turns 3 months old? The emergence of new skills, the first conscious manifestation of emotions and desires. What you need to know about the features of feeding?
Read more
4 months
What happens to a 4 month old baby? The first serious games and interaction with the outside world.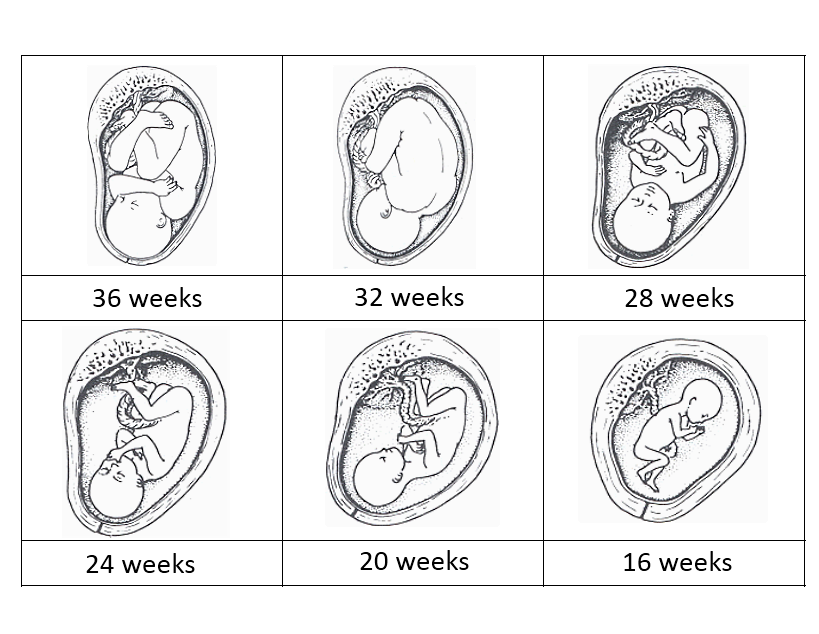 What you need to know about the features of feeding, and what recommendations for care should be followed?
What you need to know about the features of feeding, and what recommendations for care should be followed?
Read more
5 months
Transition period from horizontal position. What you need to know about the features of feeding crumbs? What should parents of a five-month-old baby be prepared for? nine0010
More details
6 months
What did the baby learn at 6 months of age? How critical is the discrepancy with accepted norms? What you need to know about the features of feeding crumbs, how to introduce the first complementary foods?
Read more
7-9 months
What happens to a 7-9 month old baby? The baby begins to sit, crawl or even take the first steps.