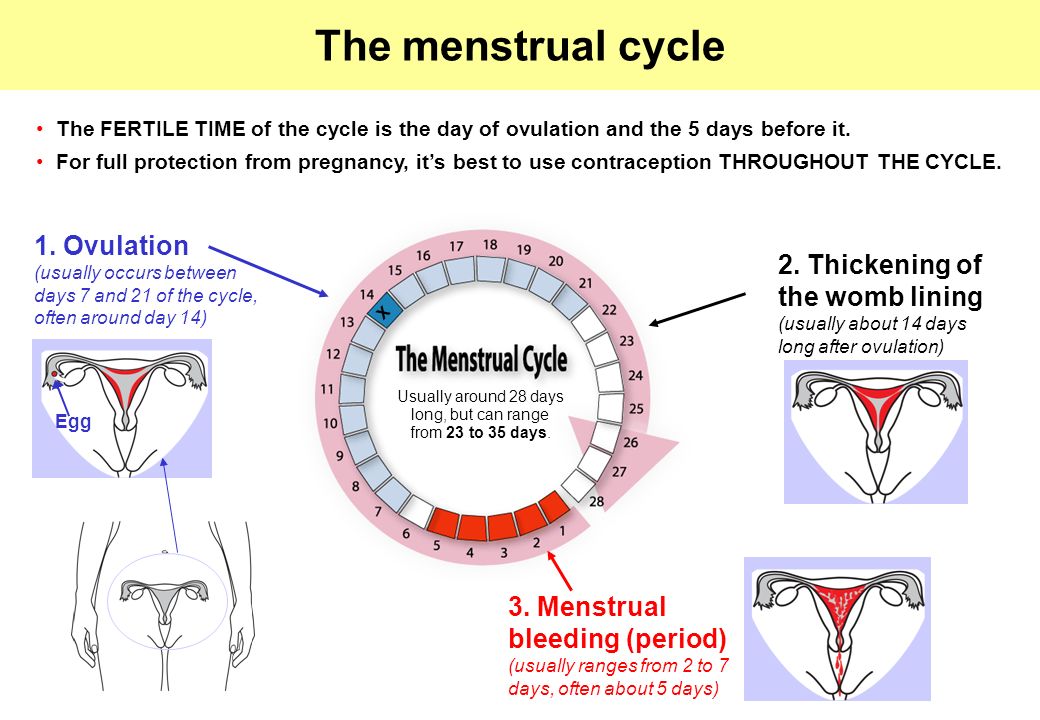
Cramping two days after ovulation
What to Expect and When to Test
At 1 to 3 days past ovulation (DPO), it’s still quite early to tell if you are pregnant or not. While some women do experience symptoms a few days after conception, most women do not — and most of the changes you will experience are related to changes in sex hormones during the luteal phase, not pregnancy changes.
At 1-3 DPO, the egg may be fertilized in the fallopian tubes 12-24 hours after ovulation. During 1-3 DPO it will migrate to implant in the uterine cavity. However, the fertilization and migration don’t cause a huge change in hormones during the early luteal phase, meaning you probably won’t experience specific symptoms associated with pregnancy.
Regardless of whether you are pregnant or not, your body and hormones will shift at 1 to 3 DPO. As a result, you might experience physical signs associated with the higher progesterone levels in your body after ovulation. Let’s find out what signs and symptoms you may experience at 1-3 DPO and what they mean, if anything.
What Happens to Your Body at 1-3 DPO?
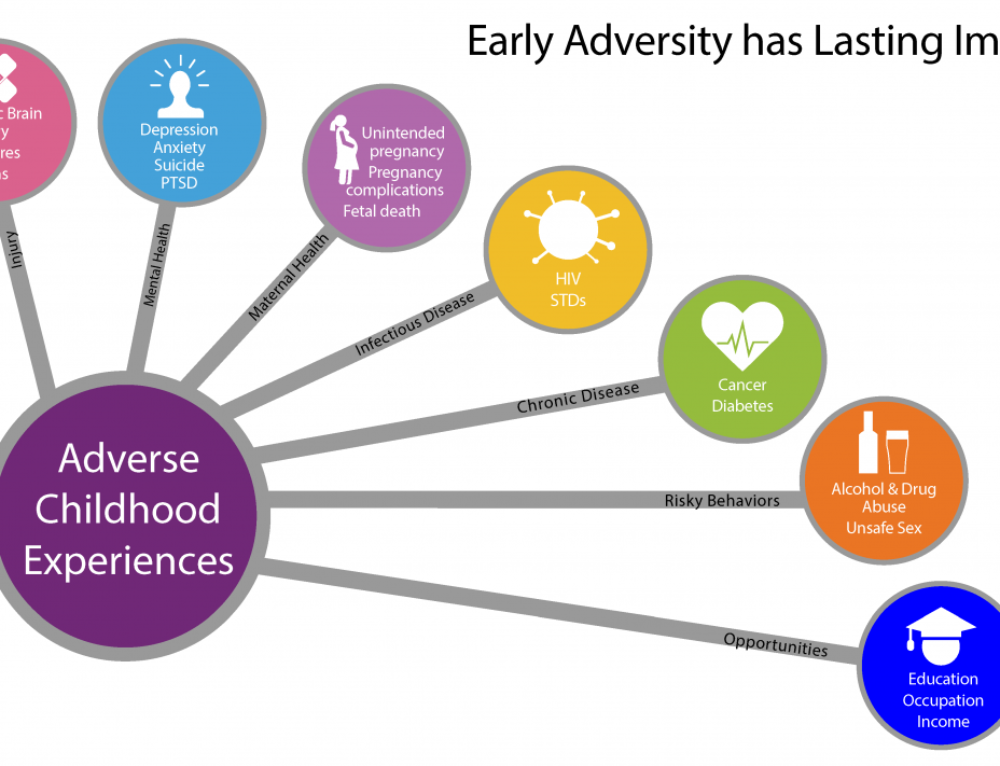
At 1 to 3 DPO, you are beginning the journey known as the “two-week wait” (TWW). This refers to the approximately two weeks it takes for the pregnancy hormone hCG to rise high enough to become detectable on a home pregnancy test. For the most accurate results, it’s not recommended to take a pregnancy test until the first day of your missed period.
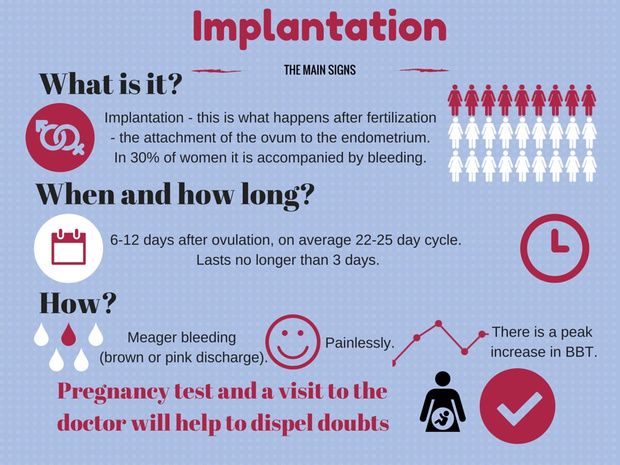
If you are pregnant, you may or may not experience symptoms at 1 to 3 DPO. If you aren’t pregnant, you could still also experience some early premenstrual symptoms around this time that are very similar to the symptoms of early pregnancy. Because many of these symptoms are the same, it can be confusing to tell whether you are pregnant or not this early in the game. If you are pregnant, you might find that these symptoms become more intense after implantation. This usually happens no earlier than 6 DPO and as late as 12 days DPO (8-10 DPO on average).
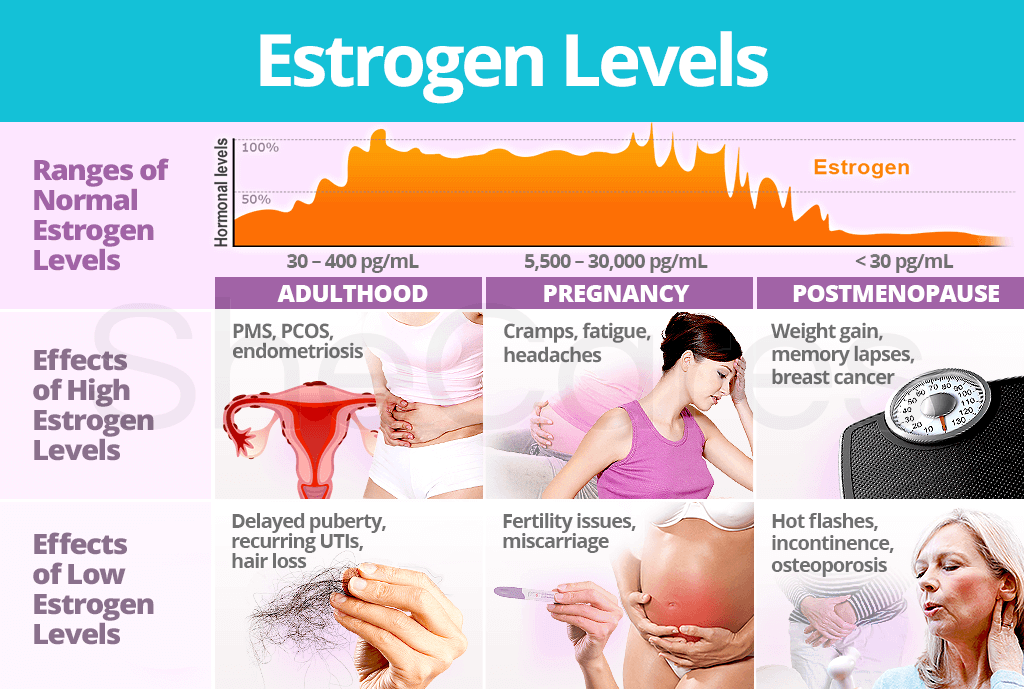
During early pregnancy, hormonal changes are responsible for many of the symptoms you may experience. These hormonal changes include rising levels of estrogen, progesterone, and the pregnancy hormone hCG. However, implantation does not occur earlier than 6-12 DPO, and these symptoms do not occur until implantation (more on DPO symptoms here).
These hormonal changes include rising levels of estrogen, progesterone, and the pregnancy hormone hCG. However, implantation does not occur earlier than 6-12 DPO, and these symptoms do not occur until implantation (more on DPO symptoms here).
At 1-3 DPO, you may start to experience cramping, fatigue, bloating, breast tenderness, and backaches. But, the symptoms are mostly related to hormonal changes in the luteal phase after ovulation happens. The symptoms are the same whether an egg was fertilized or not.
You might get tired of not knowing and feel tempted to test early. However, as frustrating as it can be to wait, make sure you stick out the entire TWW before taking a pregnancy test. Taking a pregnancy test too early can cause false-positive or false-negative results.
1 to 3 DPO is definitely too early for a pregnancy test to work — even the super-sensitive blood tests used in the doctor’s office may not be able to tell by this time. Both blood and urine tests work by detecting the pregnancy hormone hCG, which is not produced until after implantation at 6-12 DPO.
If you’re itching to take action, instead of taking a pregnancy test, you may want to consider tracking your hormonal changes with the Mira digital fertility tracker. Mira can help you identify rising levels of estrogen and progesterone after implantation to give you some idea of whether or not you are pregnant. You can continue to track with Mira until you are able to take a pregnancy test after the TWW is up — and, if you are not pregnant this cycle, you can also use Mira to more accurately pinpoint your ovulation to get pregnant during your next cycle.
What Pregnancy Symptoms Should You Be Feeling 1-3 Days Past Ovulation?
Because 1 to 3 DPO is so soon after conception, you shouldn’t panic if you don’t experience symptoms. If possible, try not to hyper-fixate on what your body is doing while also remaining aware of any changes you experience, especially if you are hoping to get pregnant.
Here’s what to look out for, without obsessing over it, at 1 to 3 DPO:
Cramping at 3 DPO
Yes, it is possible to experience cramping at 1-3 DPO, but it is mostly associated with hormonal changes after ovulation. Some women experience cramps during implantation, or the process of a fertilized embryo implanting in the uterine lining (a.k.a. the endometrium). This step is important to pregnancy because the developing fetus gets nutrients from the endometrium, but it does not occur until 6-12 DPO.
Some women experience cramps during implantation, or the process of a fertilized embryo implanting in the uterine lining (a.k.a. the endometrium). This step is important to pregnancy because the developing fetus gets nutrients from the endometrium, but it does not occur until 6-12 DPO.
These cramps can feel a lot like period cramps, which can be confusing. You might also experience some implantation bleeding or brown discharge during this time, no earlier than 10-14 DPO.
Between cramps and bleeding, it may be difficult to tell if you are getting your period early or if you are experiencing implantation. Keep an eye out for other symptoms of early pregnancy to help you tell the difference.
Fatigue at 3 DPO
Growing a baby is a lot of work and you might feel fatigued at 1-3 DPO. If you are pregnant, your body is going through a lot to prepare for the next nine months, beginning from the moment of conception. More likely, however, you are experiencing fatigue at 1-3 DPO due to hormonal changes associated with the luteal phase.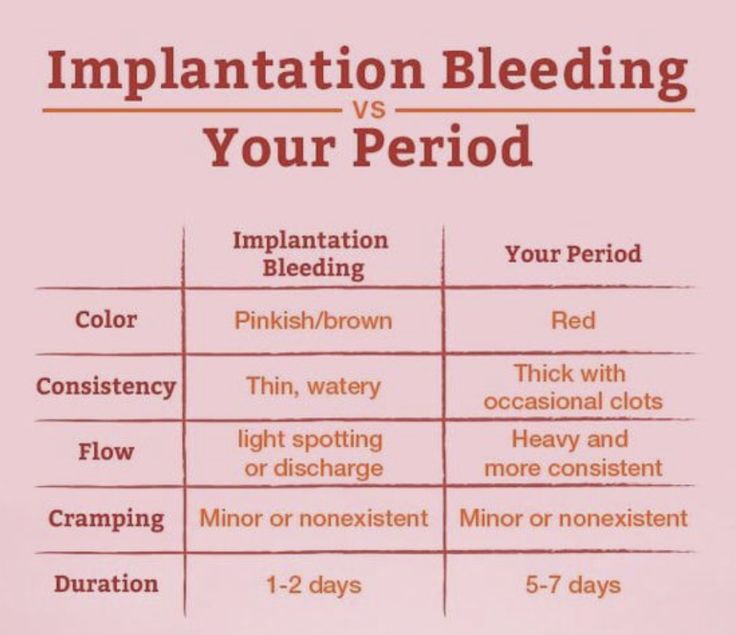 It is still too early to tell if you are fatigued due to pregnancy or not at 1-3 DPO.
It is still too early to tell if you are fatigued due to pregnancy or not at 1-3 DPO.
Bloating at 3 DPO
Yes, you may experience bloating at 1-3 DPO. Many women experience bloating in early pregnancy as their body begins developing excess progesterone which helps thicken the uterine lining to support the growing fetus.
But, at 1-3 DPO, this mostly occurs due to ovulation. When the egg is released from the follicle in the ovary, a small amount of fluid can also be released into the lining of the internal organs, especially the gut. This can lead to bloating, and so can rising levels of progesterone during the luteal phase of your cycle.
Breast Tenderness at 3 DPO
Yes, breast tenderness is a common symptom experienced at 1-3 DPO. It is associated with high levels of progesterone during the luteal phase. Breast tenderness can make your breasts feel heavy and swollen. You might also have extreme nipple sensitivity. All of these symptoms occur alongside the changes happening in your breasts as they prepare for lactation.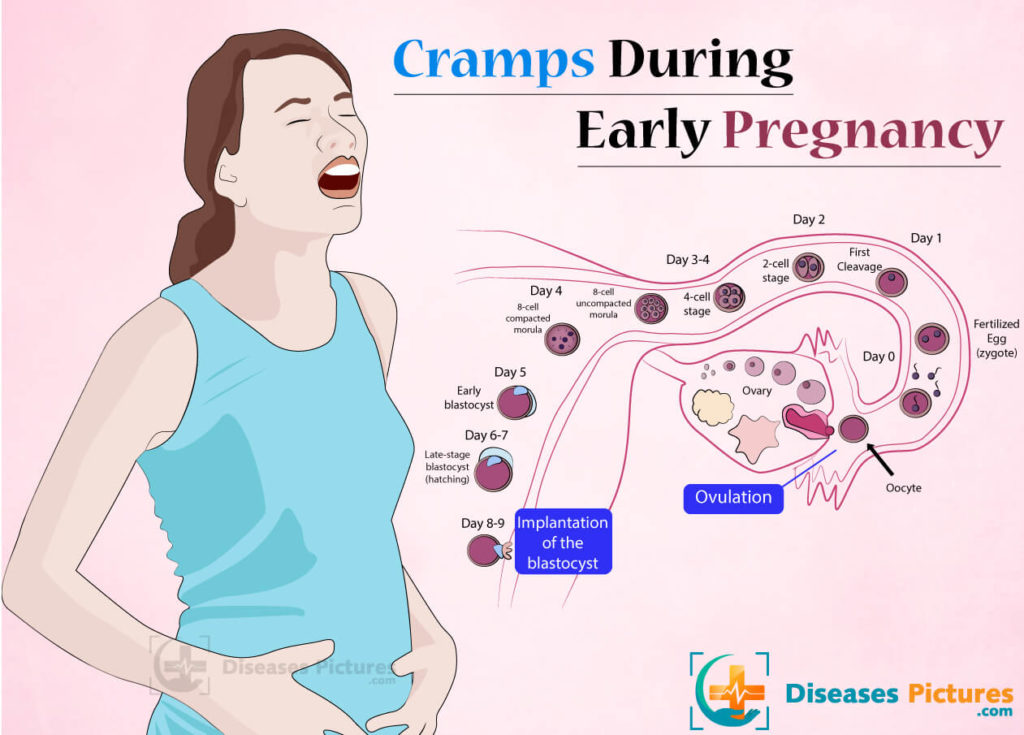
These changes in your breasts may be either an early symptom of pregnancy or a sign of rising progesterone during the luteal phase. Thus, at 1-3 DPO, it is difficult to distinguish whether breast tenderness is due to pregnancy or not.
Backaches at 3 DPO
Yes, backaches may happen at 1-3 DPO! Back pain is not often talked about, but it is a common sign of early pregnancy and can also appear due to hormonal changes during the luteal phase. These hormones loosen your joints to prepare the body for a future pregnancy and backaches may be a side effect.
You’re more likely to experience backaches in early pregnancy if you are overweight or if you have a history of back pain before pregnancy. But, at 1-3 DPO it is too early to distinguish whether a backache is due to early pregnancy or hormonal changes in the luteal phase.
Can You Take a Pregnancy Test at 1-3 DPO?
Pregnancy testing is a little like the story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears: you don’t want to test too early or too late! Testing too late might mean you make poor lifestyle choices, such as continuing to drink alcohol or failing to take prenatal vitamins because you don’t know you’re pregnant. Meanwhile, testing too early can lead to false-positive or false-negative results.
Meanwhile, testing too early can lead to false-positive or false-negative results.
False-negative test results usually result from taking a pregnancy test too early. Home pregnancy tests work by detecting the level of the pregnancy hormone hCG in your urine, which does not appear until after the implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus. Your hCG must cross a certain threshold for the pregnancy test to show a positive result. Even if you are pregnant, your hCG may not be high enough during the TWW for the pregnancy test to come out positive. If you take a test again on the first day of your missed period, you may find that the test comes back positive, even though you received a negative result before.
Ideally, you should not take a pregnancy test sooner than the first day of your missed period. By this point, your hCG levels should be high enough for a home pregnancy test to detect them. If you really cannot wait that long, your doctor may be willing to do a blood test that can detect pregnancy as early as 8-10 DPO.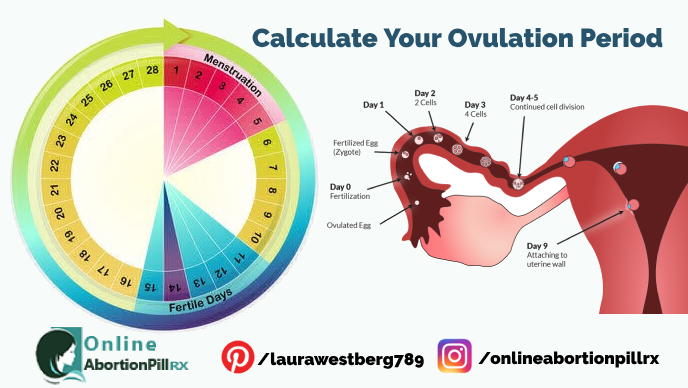 Unfortunately, many doctors will not perform a blood test before 14 DPO because it is recommended to wait until the first day of your missed period.
Unfortunately, many doctors will not perform a blood test before 14 DPO because it is recommended to wait until the first day of your missed period.
2 DPO: Symptoms, Signs & What to Expect
Ovulation is behind you. The TWW lies stretched out ahead. So what’s happening at 2 DPO and what are the symptoms?
So you’re at 2 DPO (that’s two days past ovulation, by the way ‒ one of the many abbreviations of the TTC community!).
Whether you’re feeling excited, nervous, or just plain tired, there’s no denying that these few days at the beginning of the TWW (two-week wait) can feel like they go on forever.
If it makes it any easier, here’s our guide to everything that’s going on with your body today, with help from embryologist and fertility expert, Navya Muralidhar.
In this article: 📝
- Do you feel anything 2 days after conception?
- What happens 2 days after ovulation?
- What are 2 DPO symptoms?
- Can implantation happen 2 days post-ovulation?
- Why do I have cramps 2 days after ovulation?
- Does progesterone rise 2 days after ovulation?
- Can you feel pregnant 2 days after ovulation?
- Can you get a positive test at 2 DPO?
Do you feel anything 2 days after conception?
At 2 DPO, you probably won’t feel anything different than you would on a normal day.
This doesn’t mean that there’s not a lot going on inside your body.
It’s more to do with the fact that, annoyingly, at this stage, 2 DPO symptoms ending in BFP (big fat positive on your pregnancy test) can be pretty similar (sometimes the same) as your normal post-ovulation symptoms in your menstrual cycle.
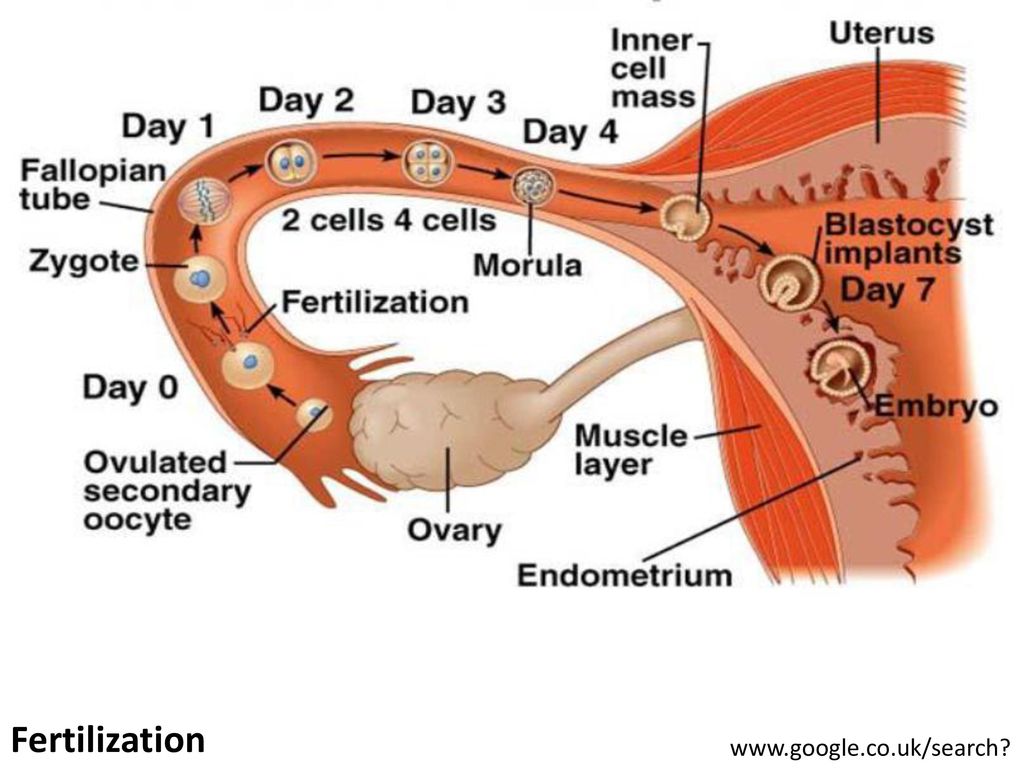
What happens 2 days after ovulation?
As soon as ovulation has taken place (usually between day 12 and day 16 of your cycle), your released egg begins traveling down the fallopian tube on its way to your uterus.
Here’s the difference from other months though.
If you’re not TTC, the egg will probably be reabsorbed into your body sometime around now.
But, if sperm was present at the time when the egg was released and hanging out at the ampulla of the fallopian tube, one sperm cell might fertilize the egg to form what’s known as a zygote.
In this case, at 2 DPO, the zygote will be continuing its slow journey towards the uterus, the cells dividing every 15 hours or so.
Once it gets there, it will hopefully (fingers crossed) implant and settle in for the next nine months sometime between 6 and 10 DPO.
What are 2 DPO symptoms?
Can you have symptoms at 2 DPO?
Yes, you can, but they’re pretty hard to distinguish from normal post-ovulation symptoms.
Each of these can also be signs that you’re in the normal luteal phase of your cycle, when your progesterone levels go up to thicken your uterus lining.
You might just be noticing them more because you’re paying more attention to your body than you ever have before.
But if you’re on the lookout for those early 2 DPO symptoms before BFP, here’s the most common:
- Tiredness: Yep, pregnancy fatigue can kick in even as early as 2 days post ovulation!
- Breast tenderness: Another early pregnancy sign that might also be your regular post-ovulation symptoms.
- Mood swings: Thanks, fluctuating hormones.
- Bloating: Yet another typical symptom that has you wondering “Is it PMS or pregnancy?”
- Back pain and pelvic pain: Some cramping can feel like back or pelvic pain.
- Nausea: Nausea at 2 DPO is a pretty common symptom, but whether it’s psychosomatic or an actual pregnancy symptom is still up for debate.
- Cramping: 2 DPO cramping is a bit early for implantation cramps, but it could also be yoru standard post-ovulation cramping, too.
- More discharge than usual: 2 DPO discharge is easy to overlook, but often, cervical mucus is one of the early indicators of pregnancy, even at 2 DPO.
- Cervix changes: If you’re checking how hard or soft your cervix is, you might notice it feeling a little softer than usual, before it hardens up ready for the mucus plug.
There’s no harm in tracking your 2 DPO symptoms, especially if you’ve been TTC for a while and you know your body well.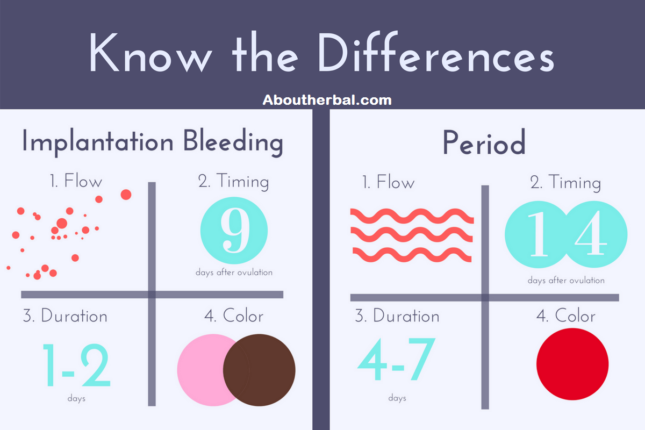
On the other hand, at this early stage, you might find that it’s better for your mental health to go with the flow and try to distract yourself from every new feeling as you wait out the TWW, until you can finally take a test.
Here are some of our Peanut TTC community sharing their 2 DPO symptoms:
- “I’ve got exhaustion at 2 DPO, I can barely keep my eyes open to function.” ‒ Allison
- “Had moderate cramps from 2-4 DPO (unusual for me), indigestion after eating between 5-8 DPO. Now sharp twinges in lower right abdomen 9-10 DPO.” ‒ Becky
- “2 DPO and my hips have become achy and painful and I’m cramping.” ‒ Megan
- “I’m 2DPO and getting cramps and sensitive nipples.” ‒ Katy
- “I know it’s way too early to even start thinking about symptoms, but I have had sore boobs and dizziness and nausea that comes and goes starting today ‒ 2 DPO.” ‒ Gaby
- “I have sore boobs, fatigue, and my lower abdomen feels so full at 2 days post ovulation.
 ” ‒ Aja
” ‒ Aja - “I’m 2 DPO and feeling bloated and have stomach cramps.” ‒ Sarah
Can implantation happen 2 days post-ovulation?
Not often, no.
Implantation usually happens between 6 to 12 DPO.
So if you’re spotting at 2 DPO, it’s not likely to be implantation bleeding ‒ it’s more likely to be ovulation bleeding.
Why do I have cramps 2 days after ovulation?
Cramping at 2 DPO (or at any time) can be one of the symptoms that worries every woman who’s TTC.
But cramping 2 days past ovulation, it isn’t an indication that you are or aren’t pregnant, and it doesn’t necessarily mean anything bad.
In about a week’s time, you might experience implantation cramps and spotting, as the embryo embeds itself in your uterine wall, but it would be pretty rare for this to happen before 3 DPO.
2 DPO cramps are more likely to be ovulation cramps.
Does progesterone rise 2 days after ovulation?
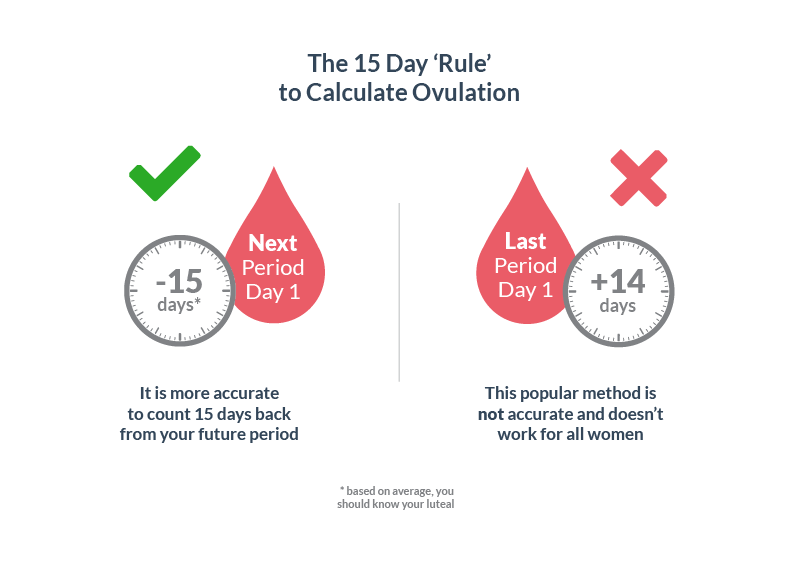
Yes, your progesterone levels will rise straight after ovulation, reaching their peak at about 5 to 9 DPO.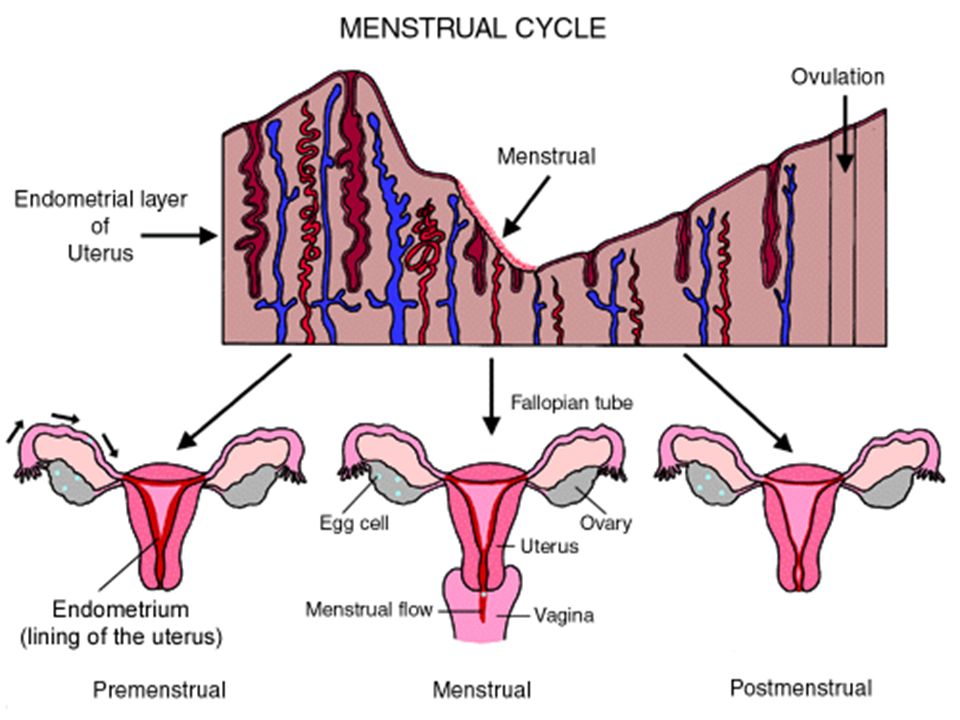
This is the case whether you’re pregnant or not ‒ rising progesterone at this point is essentially there to help with implantation, although if you are pregnant, they’ll keep rising until about 36 weeks pregnant.
Can you feel pregnant 2 days after ovulation?
It’s possible, but hard to tell at this stage.
On paper, the frustrating waiting game is going to continue for at least another week.
You won’t experience true pregnancy symptoms until after implantation because, before that point, your body really has no idea whether it’s pregnant or not.
In fact, it’s the process of implantation that triggers your body to start secreting the hormones that cause the classic symptoms of pregnancy, like nausea, changes to your breasts, and fatigue.
Lots of women swear that they just knew long before a pregnancy test confirmed their suspicions.
After all, no one knows our own bodies better than us.
Can you get a positive test at 2 DPO?
It’s incredibly rare to get a 2 DPO positive pregnancy test ‒ it’s a bit too early to get an accurate result.
If you get a 2 DPO negative pregnancy test, that doesn’t mean you’re not pregnant.
It takes just over a week to get your hCG levels high enough to show a positive pregnancy test result.
So if you’re looking at a 2 DPO BFN, don’t despair!
Wait a bit longer to take a pregnancy test ‒ about 10-14 DPO (although 14 DPO is best, the day after your next expected period) ‒ to get a more accurate result.
Basically, at 2 days after ovulation, everything is still up in the air, and intuition or no, there’s still that seemingly endless TWW until you can know for sure.
If you’re on 2 DPO, hang in there, be kind to yourself, and remember you can always talk all things TTC with other women in the Peanut community.
➡️ Read next: 3 DPO: Signs, Symptoms & What to Expect
why it occurs, causes, what to do and how to treat
Discomfort in the lower abdomen can haunt a woman not only during menstruation. One in five people experience ovulatory syndrome. This is when discomfort occurs in the middle of the cycle and can be sudden, acute or marked in the form of spasms. Read about why pain occurs during ovulation, how to deal with it, and when to see a doctor.
This is when discomfort occurs in the middle of the cycle and can be sudden, acute or marked in the form of spasms. Read about why pain occurs during ovulation, how to deal with it, and when to see a doctor.
Website editor
Tags:
Women Health
Massage
VOICE Tips
Causes of pain
ovulation
To understand the symptoms and causes of their occurrence, it is worthwhile to understand whether the pain during ovulation is typical and what happens to the female body during this period. nine0003
Do not self-medicate! In our articles, we collect the latest scientific data and the opinions of authoritative health experts. But remember: only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
How does the process of ovulation occur and can the stomach hurt at the same time?
Ovulation is the release of a developed egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube. It does not pass in every menstrual cycle and pain on the days of ovulation is a fairly common occurrence. Attachment of the fetal egg occurs 6-12 days after ovulation. As a rule, only one egg is released from the ovary during one ovulation. nine0003
Ovulation can be determined in several ways:
- using a calendar;
- using basal temperature charts;
- a special test from a pharmacy;
- Ultrasound.
Many women additionally focus on their well-being: during ovulation, many have pain in the lower abdomen. Of course, this sign cannot be considered the main one, it only supplements the data of the calendar, test or ultrasound. Determining the date of ovulation helps to plan the conception of a child, or to prevent unwanted pregnancy.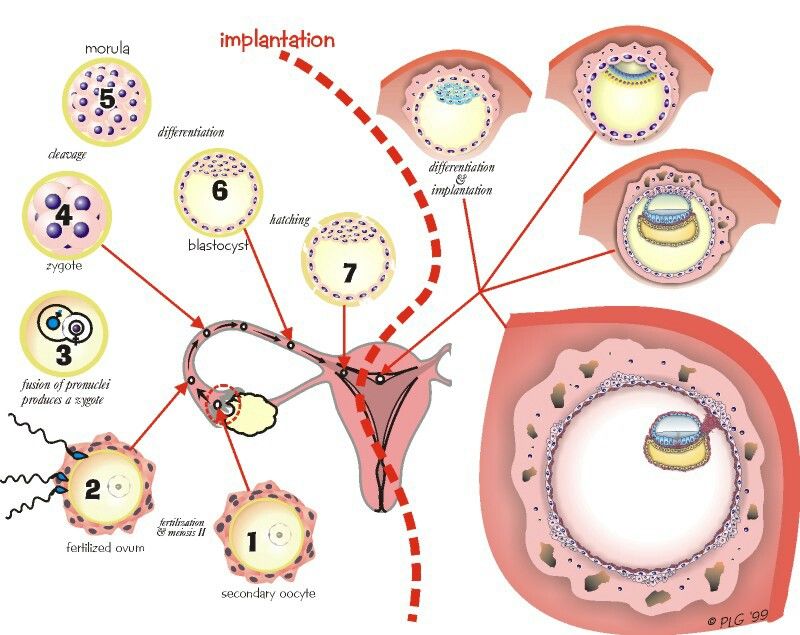 nine0003
nine0003
If fertilization does not occur during ovulation, the egg is absorbed by the lining of the uterus and is later expelled from the body during menstruation. After that, a new egg begins to mature in the ovary.
If the menstrual cycle is stable and lasts 28 days, ovulation will begin on days 10-12. The occurrence of ovulation may be accompanied by mild, less often strong, aching, pulling or dull pains in the lower abdomen. This is not such a rare problem: on women's forums, questions about unpleasant discomfort arise with frightening regularity. Someone shares that after ovulation, the stomach didn’t hurt at all, and someone has to stock up on analgesics in anticipation of the middle of the cycle. nine0003
Pain during ovulation and other symptoms
During ovulation, the lower abdomen often hurts, depending on the activity of the ovaries: on the left or right side. Sometimes there are sharp mood swings that accompany tearfulness, irritability and irritability. Thus, the body signals that it is ready for conception.
Thus, the body signals that it is ready for conception.
Another typical symptom is a discharge from the vulva, stretchy and slippery. They have the appearance of raw egg white, usually odorless, do not cause itching and irritation. Their color may change. In medicine, this is called cervical mucus. Discharge does not depend on whether the stomach hurts during ovulation or not. nine0003
Attention! If the discharge is accompanied by a pungent odor, burning, pain in the lower abdomen. At the same time, they acquire dark red, green or yellow hues. You need to see a doctor immediately. Such discharges are not normal and may indicate the development of a disease or an inflammatory process. The doctor will determine the cause of their occurrence and prescribe adequate treatment.
A relatively rare symptom is if the chest hurts after ovulation. But it still happens that during this period there are unpleasant sensations in the area of the mammary glands, the shade of the nipples changes.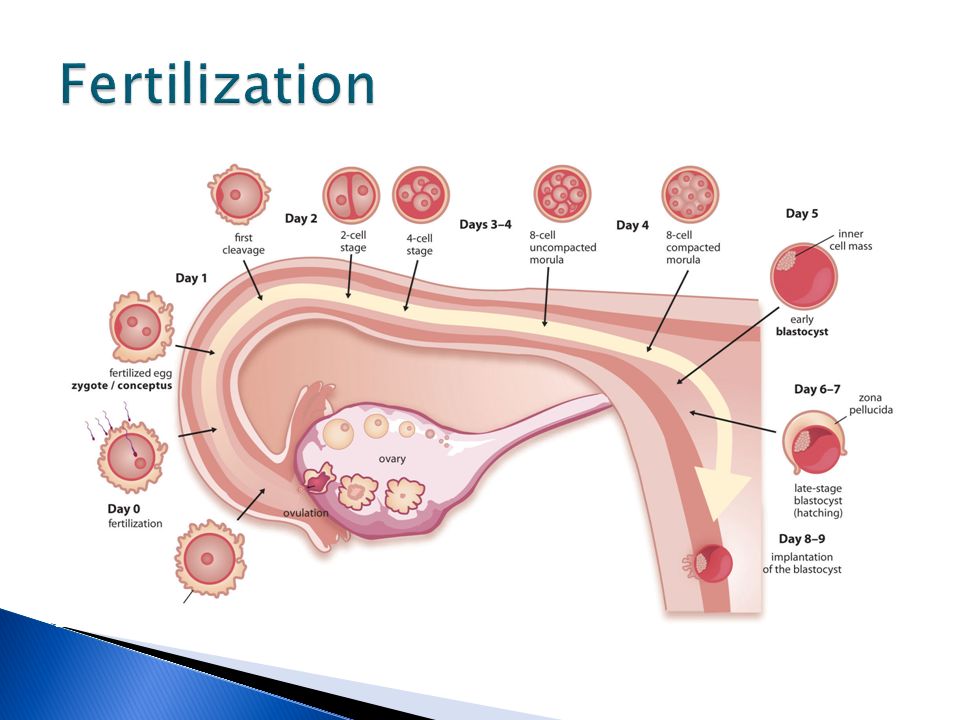 This is due to the swelling of the mammary glands. You should not be afraid of this symptom, such an indisposition is acceptable. nine0003
This is due to the swelling of the mammary glands. You should not be afraid of this symptom, such an indisposition is acceptable. nine0003
How common are ovulation pains and why are they dangerous? However, if you have not noticed such a condition before or the discomfort has become much more intense, you should contact a specialist. In these cases, the body may signal the onset of a serious illness. Below we have listed the symptoms that you should definitely pay attention to. nine0003
Not all women have pain in the lower abdomen after ovulation. In some cases, pain may radiate to the lower back. And sometimes the release of an egg from the ovary is extremely unpleasant and deprives women of working capacity, sometimes even leads to loss of consciousness.
Why does the stomach hurt before ovulation
The discomfort before the process begins is explained as follows. Pain before ovulation can occur when the vessels at the base of the follicle rupture when the egg is released. A hemorrhage occurs, the uterus begins to contract when fluid from the follicle enters it, which causes pain just below the navel. This is the most common cause for discomfort. nine0003
A hemorrhage occurs, the uterus begins to contract when fluid from the follicle enters it, which causes pain just below the navel. This is the most common cause for discomfort. nine0003
However, its appearance can also be an indicator of the development of various diseases. It is better not to self-medicate and you should not delay a visit to the doctor. If you are worried about pain during ovulation in the lower abdomen, you should discuss this issue with a gynecologist.
1. "Middle" pain
Most often, during ovulation, the lower abdomen hurts, and discomfort occurs only on one side, and this side can change in different cycles. Unpleasant sensations last from a few minutes to half an hour, may be accompanied by bloating and mild nausea. In medicine, it is called the German term Mittelschmerz ("middle" pain). nine0003
How to get rid of: if the sensations pass and the pain is not too severe, a warm bath and painkiller tablets are sufficient. If your health leaves much to be desired and literally folds you in half, it is better to meet with a doctor and discuss why pain occurs during ovulation. It may be worth discussing the use of low-dose hormonal contraceptives.
If your health leaves much to be desired and literally folds you in half, it is better to meet with a doctor and discuss why pain occurs during ovulation. It may be worth discussing the use of low-dose hormonal contraceptives.
2. Polycystic ovaries
In cases where the critical days are long and irregular, and there is a lot of hair on the body, the fact that you have a stomachache after ovulation may signal polycystic ovaries. Complications can be serious, from infertility to cancer, so you should see a doctor. nine0003
How to get rid of: After diagnosis, treatment varies, but usually includes a special diet and hormonal medication. If the treatment is chosen correctly, the stomach will no longer hurt after ovulation.
3. Inflammatory diseases of the pelvis
Often, pain in the lower abdomen after ovulation is the result of an infection such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. Before or during the process, discomfort in the pelvis is noted, which can even lead to hospitalization. nine0003
Before or during the process, discomfort in the pelvis is noted, which can even lead to hospitalization. nine0003
How to get rid of: most often the doctor prescribes antibiotics, and the infection goes away with pain.
4. Pain after caesarean section
It leaves a scar in any case, and pain can occur in that area during ovulation for a year after childbirth. In this case, the problem is not in the ovary, but in the scar itself, so the nature of the discomfort is different.
How to get rid of: special massage and physiotherapy prescribed by a doctor. nine0003
Pain during ovulation: when to rush to the doctor
Even if you have a rough idea of why your stomach hurts during ovulation, it is important to always listen to your body. Any of the following factors, and even more so their combination, should alert:
- Prolonged pain (more than a day).
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Dizziness, loss of consciousness.
- Purulent or profuse bleeding.
- Discharge with a strong odor, burning in the vulva. nine0032
- Pain when urinating.
- Rise in temperature, fever.
If painful ovulation is accompanied by these symptoms, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Photo: Getty Images
Painful ovulation - the norm or disease
Pain in the middle of the cycle, ovulatory syndrome - occurs in every fifth woman.
Mittelschmerz (pain in the middle of the cycle) was described in medical periodicals as early as 1940y.g.
How can ovulatory syndrome manifest itself?
During ovulation, a woman may experience a dull, sudden sharp or cramping pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, pain can be localized on the right or left, depending on which ovary ovulation occurs.
Pain may radiate to the lumbar region, sacrum, or groin and may be aggravated by strenuous exercise, sudden changes in body position, and sexual intercourse. These days, pain may be accompanied (or appear independently) by mild bloody discharge from the genital tract. nine0003
These days, pain may be accompanied (or appear independently) by mild bloody discharge from the genital tract. nine0003
In addition, some women experience weakness, rarely nausea and even vomiting.
For some women, pain may accompany every ovulation, for others it may occur occasionally.
The duration of pain can vary from a few minutes to 24 hours, but no more. This is one of the features that distinguishes "ovulatory syndrome is not a disease" from gynecological diseases (endometriosis, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs), manifested by pain.
What causes pain and spotting in the middle of the cycle?
The causes of pain during ovulation are:
- damage to the ovary wall at the time of ovulation
- irritation of the inner lining of the abdomen, resulting from the reflux of a small amount of blood from a burst follicle into the pelvic cavity.
- low pain threshold. Most women are able to easily tolerate unpleasant symptoms, but sometimes hypersensitivity can provoke subjective pain.
 nine0032
nine0032
Minor spotting is caused by the sudden change in sex hormone levels that accompanies ovulation.
Illness or not and what to do about it?
A natural question arises: “If ovulation is a physiological process, why is it accompanied by pain?”
According to an incomprehensible idea of nature in women, pain often accompanies many physiological (menstruation, childbirth) processes. Pain is associated with participation in events such as menstruation and ovulation of inflammatory substances (cytokines) and spasm of small vessels. The peculiarities of the exchange of pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as individual sensitivity to pain, explain the fact that some women do not feel ovulation at all, while others experience significant discomfort during a certain period of their life. nine0003
In the case of ovulatory syndrome, the line between the norm and the disease is very thin.
To answer the question of whether pain in the middle of the cycle is a problem requiring treatment, it is necessary to conduct an examination. In this case, ultrasound of the pelvic organs provides valuable information, which allows an experienced specialist to determine with high accuracy the presence or absence of such probable causes of pain as endometriosis, inflammatory tumors of the small pelvis, adhesive disease of the pelvic organs, functional ovarian cysts, tumors, anomalies in the development of the genital organs and other. nine0003
According to individual indications, the gynecologist can prescribe microbiological and hormonal tests.
So, if gynecological diseases are excluded, this is ovulatory syndrome.
If the pain associated with ovulation is mild, there is usually no need for treatment.
If the pain associated with ovulation is limiting your activities, your gynecologist will help you find the treatment that is best for you at that time in your life (pain medications and other options).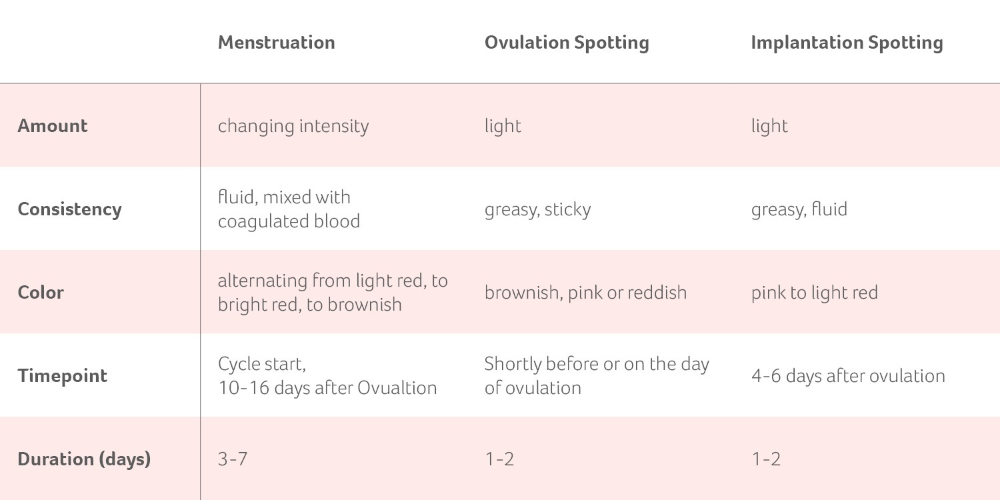 nine0003
nine0003
So is it necessary to go to the gynecologist for periodic or systematic pain in the middle of the cycle? – Definitely YES!
As already mentioned, ovulatory syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion: you need to conduct an examination to make sure that the cause of pain is not a gynecological pathology.
The experience of our specialists shows, especially in severe pain syndrome, a thorough examination using modern ultrasound devices, less often hysteroscopy allows us to identify previously undiagnosed problems: endometriosis, associated or unrelated adhesions in the pelvis, rare anomalies in the development of the genital organs. nine0003
Moreover, our experience with women with ovulatory syndrome shows that in the absence of endometriosis, adhesions and other morphological problems, hormonal imbalance is a common cause of pain, the correction of which led to a significant improvement in the quality of life of patients.
Does ovulatory syndrome affect the possibility of getting pregnant?
No evidence that mid-cycle pain impairs fertility or adversely affects pregnancy .