Chances of delivering early with fourth pregnancy
Fourth Pregnancy: What to Expect
Fourth Pregnancy: What to ExpectMedically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Jessica Timmons on November 11, 2018
Your fourth pregnancy
For many women, the fourth pregnancy is like riding a bike — after experiencing the ins and outs three times before, both your body and your mind are intimately familiar with the changes pregnancy brings.
While every pregnancy is unique and different, the general mechanics will be the same. Still, there will likely be a few differences between pregnancy number one and pregnancy number four. Here’s what to expect.
Physical changes
Women experiencing pregnancy for the first time typically show later than they do in subsequent pregnancies. Blame it on the first baby — your uterus and abdominal muscles were much tighter before they stretched to accommodate a growing passenger.
As your uterus grew, it expanded out of the pelvis into the abdomen, stretching your abdominals and eventually becoming that baby bump.
The result? Many women will show earlier during their fourth pregnancy than they did with subsequent pregnancies. And for a fourth-time mom, early can mean somewhere around the 10th week.
During a first pregnancy, many women notice breast changes. With those changes comes extreme tenderness, which can be an early indication of pregnancy.
For second-, third-, or fourth-time moms, your breasts might not be quite as tender. They might not change in size as significantly as they did the first time.
Pregnancy symptoms
That “feeling” about pregnancy that experienced moms have comes from, well, experience! Women who have been through a previous pregnancy tend to notice signs and symptoms that they might have missed the first time around.
It can be easy to mistake breast tenderness for an impending menstrual cycle, or morning sickness for a stomach bug. But fourth-time moms are more likely to recognize pregnancy symptoms than first-timers.
Other parts of pregnancy are more recognizable, too. Many women experiencing pregnancy for the first time mistake the movements of their tiny baby for something like gas. Moms on their second, third, or fourth pregnancies are far more likely to recognize those little flutters for what they are.
Many women experiencing pregnancy for the first time mistake the movements of their tiny baby for something like gas. Moms on their second, third, or fourth pregnancies are far more likely to recognize those little flutters for what they are.
You might notice that you’re much more tired during a subsequent pregnancy. It’s no wonder — you will probably have at least one other small child to look after. This probably means less opportunity to rest, something you likely did during your first pregnancy.
Your partner might not pamper you quite as much, either, thinking that you’re a pro by now. If you’re on your fourth pregnancy, you’re at least five years older, too. The age difference alone can make you feel more tired.
The age difference is one of the biggest contrasts between first and fourth pregnancies. Having a baby when you’re older means you have a greater likelihood of twins. This is because hormonal changes as you age increase the chance that more than one egg is released during ovulation.
Being an older mom also means a greater risk of having a baby with a chromosomal defect. Doctors are more likely to recommend genetic testing in a fourth pregnancy than they might with a first.
Labor and delivery
One of the benefits of subsequent pregnancies is a shorter labor. For many women, labor is faster the second, third, or fourth time. On the flip side, you may notice that Braxton-Hicks contractions begin earlier in your pregnancy, and that you have more of them.
It’s a common misconception that your first delivery experience will dictate any deliveries that follow. Just like every baby is different, so is every pregnancy.
Complications
If you had complications with a previous pregnancy, including gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, hypertension, or premature birth, you could be at an increased risk for these issues.
If you had a cesarean delivery in the past, you are also at a higher risk for complications. It’s important to speak with your doctor about previous pregnancies, so you know what to look for going forward. Women with a previous cesarean delivery can still have a vaginal delivery on a subsequent pregnancy.
Women with a previous cesarean delivery can still have a vaginal delivery on a subsequent pregnancy.
Other experiences that can worsen with subsequent pregnancies include back pain and varicose veins. While a sore back is a common pregnancy woe, it can be even more painful if you’re carrying around young children.
Varicose and spider veins also tend to get worse from one pregnancy to the next. If you suffer from vein issues, try wearing support hose from the beginning. Also remember to elevate your feet and legs when you can.
If you had hemorrhoids, constipation, or incontinence during a previous pregnancy, try being proactive to avoid the same problems this time. Make sure to eat lots of fiber, drink plenty of water, and get regular exercise.
Don’t forget daily Kegel exercises, either. While you might not be able to prevent these symptoms, you may be able to keep them to a minimum.
The takeaway
For many women, one of the biggest advantages to a fourth pregnancy is experience. First-time moms can have a lot of emotional stress from the unknown and the many changes to come.
First-time moms can have a lot of emotional stress from the unknown and the many changes to come.
Second-, third-, and fourth-time moms already know what to expect from pregnancy, labor, recovery, and beyond. That knowledge can make you feel more secure as you begin another pregnancy.
Will labor be the same as my previous pregnancies? Not necessarily. A baby’s size and placement in your uterus will have the biggest effect on your labor experience, no matter what number pregnancy this is.
Last medically reviewed on November 12, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Harms RW. (2017). Pregnancy week by week.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-answers/second-pregnancy/faq-20115105 - Hunt S, et al. (2018). Vaginal birth after cesarean. DOI:
10.1016/S1751-4851(18)30030-8 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Twin pregnancies: what multiples mean for mom.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/twin-pregnancy/art-20048161 - Silver RM. (2012). Implications of the first cesarean: perinatal and future reproductive health and subsequent cesareans, placentation issues, uterine rupture risk, morbidity, and mortality. DOI:
10.1053/j.semperi.2012.04.013
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Nov 12, 2018
By
Jessica Timmons
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Jessica Timmons on November 11, 2018
D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Jessica Timmons on November 11, 2018
related stories
How to Dilate Faster During Labor: Is It Possible?
7 Nutritious Fruits You’ll Want to Eat During Pregnancy
Weird Early Pregnancy Symptoms No One Tells You About
Tips on How to Conceive Twins
Stroke Risk Factors and Prevention
Read this next
How to Dilate Faster During Labor: Is It Possible?
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
As you approach your due date and delivery, you might be wondering how to speed up the process. Here’s what you need to know about inducing labor and…
READ MORE
7 Nutritious Fruits You’ll Want to Eat During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R.D.
Fruit is a healthy choice to eat throughout your pregnancy.
 Here are benefits and ideas for how to add more fruit to your diet.
Here are benefits and ideas for how to add more fruit to your diet.READ MORE
Weird Early Pregnancy Symptoms No One Tells You About
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
You might be surprised by certain symptoms that the first trimester of pregnancy can bring. Get the facts on 10 unusual symptoms, such as tasting…
READ MORE
Tips on How to Conceive Twins
Medically reviewed by University of Illinois
Giving birth to multiples is more common today than ever. Here’s a look at factors that influence why a couple might have twins.
READ MORE
Stroke Risk Factors and Prevention
Medically reviewed by Seunggu Han, M.D.
A stroke occurs when blood flow is blocked to a part of the brain.
 Brain cells become deprived of oxygen and begin to die. As brain cells die, people…
Brain cells become deprived of oxygen and begin to die. As brain cells die, people…READ MORE
Does Swaddling Increase the Risk of SIDS?
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Is swaddling safe, or is it a risk factor for SIDS? Here's what the most recent research says.
READ MORE
Antidepressants in Pregnancy Aren't Linked to Increased Neurological Issues in Children
A cohort study of antidepressant use in pregnancy found that the rate of neurological disorders in children born to those who took antidepressant…
READ MORE
These Guided Pregnancy Journals Will Help You Document All the Feels
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
The pregnancy and postpartum periods are full of emotions (rightfully so!), and these pregnancy journals are a great place to document it all.

READ MORE
What You Need to Know If You’re Having a High Risk Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
A high risk pregnancy is any pregnancy that comes with increased health risks for either the pregnant parent, the fetus, or both.
READ MORE
What Are Conjoined Twins?
Conjoined twins are identical twins who are born connected and likely share one or more organs. We explain how they develop and when separation is…
READ MORE
Fourth Pregnancy: What to Expect
Fourth Pregnancy: What to ExpectMedically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Jessica Timmons on November 11, 2018
Your fourth pregnancy
For many women, the fourth pregnancy is like riding a bike — after experiencing the ins and outs three times before, both your body and your mind are intimately familiar with the changes pregnancy brings.
While every pregnancy is unique and different, the general mechanics will be the same. Still, there will likely be a few differences between pregnancy number one and pregnancy number four. Here’s what to expect.
Physical changes
Women experiencing pregnancy for the first time typically show later than they do in subsequent pregnancies. Blame it on the first baby — your uterus and abdominal muscles were much tighter before they stretched to accommodate a growing passenger.
As your uterus grew, it expanded out of the pelvis into the abdomen, stretching your abdominals and eventually becoming that baby bump.
The result? Many women will show earlier during their fourth pregnancy than they did with subsequent pregnancies. And for a fourth-time mom, early can mean somewhere around the 10th week.
During a first pregnancy, many women notice breast changes. With those changes comes extreme tenderness, which can be an early indication of pregnancy.
For second-, third-, or fourth-time moms, your breasts might not be quite as tender. They might not change in size as significantly as they did the first time.
They might not change in size as significantly as they did the first time.
Pregnancy symptoms
That “feeling” about pregnancy that experienced moms have comes from, well, experience! Women who have been through a previous pregnancy tend to notice signs and symptoms that they might have missed the first time around.
It can be easy to mistake breast tenderness for an impending menstrual cycle, or morning sickness for a stomach bug. But fourth-time moms are more likely to recognize pregnancy symptoms than first-timers.
Other parts of pregnancy are more recognizable, too. Many women experiencing pregnancy for the first time mistake the movements of their tiny baby for something like gas. Moms on their second, third, or fourth pregnancies are far more likely to recognize those little flutters for what they are.
You might notice that you’re much more tired during a subsequent pregnancy. It’s no wonder — you will probably have at least one other small child to look after. This probably means less opportunity to rest, something you likely did during your first pregnancy.
This probably means less opportunity to rest, something you likely did during your first pregnancy.
Your partner might not pamper you quite as much, either, thinking that you’re a pro by now. If you’re on your fourth pregnancy, you’re at least five years older, too. The age difference alone can make you feel more tired.
The age difference is one of the biggest contrasts between first and fourth pregnancies. Having a baby when you’re older means you have a greater likelihood of twins. This is because hormonal changes as you age increase the chance that more than one egg is released during ovulation.
Being an older mom also means a greater risk of having a baby with a chromosomal defect. Doctors are more likely to recommend genetic testing in a fourth pregnancy than they might with a first.
Labor and delivery
One of the benefits of subsequent pregnancies is a shorter labor. For many women, labor is faster the second, third, or fourth time. On the flip side, you may notice that Braxton-Hicks contractions begin earlier in your pregnancy, and that you have more of them.
It’s a common misconception that your first delivery experience will dictate any deliveries that follow. Just like every baby is different, so is every pregnancy.
Complications
If you had complications with a previous pregnancy, including gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, hypertension, or premature birth, you could be at an increased risk for these issues.
If you had a cesarean delivery in the past, you are also at a higher risk for complications. It’s important to speak with your doctor about previous pregnancies, so you know what to look for going forward. Women with a previous cesarean delivery can still have a vaginal delivery on a subsequent pregnancy.
Other experiences that can worsen with subsequent pregnancies include back pain and varicose veins. While a sore back is a common pregnancy woe, it can be even more painful if you’re carrying around young children.
Varicose and spider veins also tend to get worse from one pregnancy to the next. If you suffer from vein issues, try wearing support hose from the beginning. Also remember to elevate your feet and legs when you can.
If you suffer from vein issues, try wearing support hose from the beginning. Also remember to elevate your feet and legs when you can.
If you had hemorrhoids, constipation, or incontinence during a previous pregnancy, try being proactive to avoid the same problems this time. Make sure to eat lots of fiber, drink plenty of water, and get regular exercise.
Don’t forget daily Kegel exercises, either. While you might not be able to prevent these symptoms, you may be able to keep them to a minimum.
The takeaway
For many women, one of the biggest advantages to a fourth pregnancy is experience. First-time moms can have a lot of emotional stress from the unknown and the many changes to come.
Second-, third-, and fourth-time moms already know what to expect from pregnancy, labor, recovery, and beyond. That knowledge can make you feel more secure as you begin another pregnancy.
Will labor be the same as my previous pregnancies? Not necessarily.A baby’s size and placement in your uterus will have the biggest effect on your labor experience, no matter what number pregnancy this is.
Last medically reviewed on November 12, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Harms RW. (2017). Pregnancy week by week.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-answers/second-pregnancy/faq-20115105 - Hunt S, et al. (2018). Vaginal birth after cesarean. DOI:
10.1016/S1751-4851(18)30030-8 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Twin pregnancies: what multiples mean for mom.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/twin-pregnancy/art-20048161 - Silver RM. (2012). Implications of the first cesarean: perinatal and future reproductive health and subsequent cesareans, placentation issues, uterine rupture risk, morbidity, and mortality. DOI:
10.1053/j.semperi.2012.04.013
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Nov 12, 2018
By
Jessica Timmons
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Jessica Timmons on November 11, 2018
related stories
How to Dilate Faster During Labor: Is It Possible?
7 Nutritious Fruits You’ll Want to Eat During Pregnancy
Weird Early Pregnancy Symptoms No One Tells You About
Tips on How to Conceive Twins
Stroke Risk Factors and Prevention
Read this next
How to Dilate Faster During Labor: Is It Possible?
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
As you approach your due date and delivery, you might be wondering how to speed up the process.
 Here’s what you need to know about inducing labor and…
Here’s what you need to know about inducing labor and…READ MORE
7 Nutritious Fruits You’ll Want to Eat During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R.D.
Fruit is a healthy choice to eat throughout your pregnancy. Here are benefits and ideas for how to add more fruit to your diet.
READ MORE
Weird Early Pregnancy Symptoms No One Tells You About
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
You might be surprised by certain symptoms that the first trimester of pregnancy can bring. Get the facts on 10 unusual symptoms, such as tasting…
READ MORE
Tips on How to Conceive Twins
Medically reviewed by University of Illinois
Giving birth to multiples is more common today than ever.
 Here’s a look at factors that influence why a couple might have twins.
Here’s a look at factors that influence why a couple might have twins. READ MORE
Stroke Risk Factors and Prevention
Medically reviewed by Seunggu Han, M.D.
A stroke occurs when blood flow is blocked to a part of the brain. Brain cells become deprived of oxygen and begin to die. As brain cells die, people…
READ MORE
Does Swaddling Increase the Risk of SIDS?
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Is swaddling safe, or is it a risk factor for SIDS? Here's what the most recent research says.
READ MORE
Antidepressants in Pregnancy Aren't Linked to Increased Neurological Issues in Children
A cohort study of antidepressant use in pregnancy found that the rate of neurological disorders in children born to those who took antidepressant…
READ MORE
These Guided Pregnancy Journals Will Help You Document All the Feels
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
The pregnancy and postpartum periods are full of emotions (rightfully so!), and these pregnancy journals are a great place to document it all.
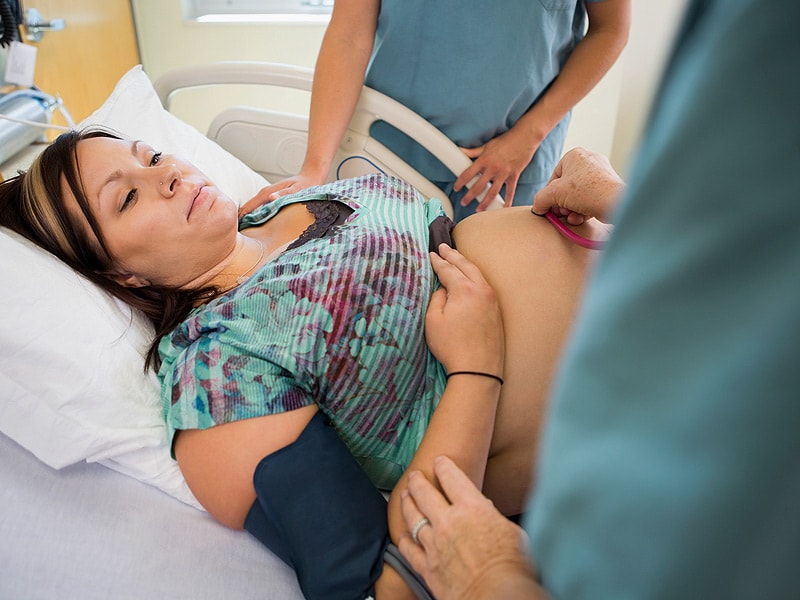
READ MORE
What You Need to Know If You’re Having a High Risk Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
A high risk pregnancy is any pregnancy that comes with increased health risks for either the pregnant parent, the fetus, or both.
READ MORE
What Are Conjoined Twins?
Conjoined twins are identical twins who are born connected and likely share one or more organs. We explain how they develop and when separation is…
READ MORE
Premature birth statistics
Premature births are those that occur between 22 and 37 weeks of gestation (from 154 to less than 259 days). Preterm birth is divided according to gestational age into very early preterm birth - 22-27 weeks, early preterm birth - 28-33 weeks and preterm birth - 34-37 weeks, which is associated with the peculiarities of obstetric tactics and outcomes of preterm birth [11]. According to the results of scientific studies, about 5% of preterm births occur at a gestational age of up to 28 weeks, about 15% - at 28-31 weeks, about 20% - at 32-33 weeks, 60-70% - at 34-37 weeks [16 ].
According to the results of scientific studies, about 5% of preterm births occur at a gestational age of up to 28 weeks, about 15% - at 28-31 weeks, about 20% - at 32-33 weeks, 60-70% - at 34-37 weeks [16 ].
Over the past 50 years, despite progress in the provision of medical care, including the widespread use of beta-agonists as tocolytic agents since the 70s of the XX century, the frequency of preterm birth has not changed [1] and is 5-10%, changing from region to region, is not the same in different countries; in developed countries has increased in recent years as a result of the use of new reproductive technologies [15]. According to the literature [11], at the beginning of the 21st century, this figure in the United States was 10.1%, in England - 7.8%, in France - 7.2%, in Germany - 9-10%, in Hungary - 10%. In Norway, the rate of preterm birth varies by region from 5 to 7.8%, averaging 7%. In the United States in 1981, this figure was 9.5%, and in 2005 - 12.7% [16] and differs in different ethnic groups: in the United States and Great Britain, African American and Afro-Caribbean women had preterm births in 16- 18% of women compared to 5-9% of white women. In East Asia, Spain, rates of prematurity are low, in South Asia, including the Indian subcontinent, the rate of birth of children with low birth weight is high, due to a decrease in fetal growth, but the percentage of preterm births is not increased [16]. According to the research results of R. Goldenberg et al. (2008), in the US, about 20-25% of pregnant women smoke, of which 12-15% continue to smoke during pregnancy, nicotine is known to increase the risk of preterm birth.
In East Asia, Spain, rates of prematurity are low, in South Asia, including the Indian subcontinent, the rate of birth of children with low birth weight is high, due to a decrease in fetal growth, but the percentage of preterm births is not increased [16]. According to the research results of R. Goldenberg et al. (2008), in the US, about 20-25% of pregnant women smoke, of which 12-15% continue to smoke during pregnancy, nicotine is known to increase the risk of preterm birth.
According to ICD-10, “Premature birth” has an independent heading O 60 - the onset of labor (spontaneous) before 37 completed weeks of pregnancy [5]. Registration of preterm births in our country is carried out according to the annual statistical reporting form of the Ministry of Health of Russia No. 32 "Report on medical care for pregnant women, women in labor and puerperas." In the Russian Federation, until recently, the registration of preterm birth was carried out from 28 weeks of pregnancy, and in economically developed countries - from 22 weeks. In this regard, the indicators of perinatal losses were not comparable.
In this regard, the indicators of perinatal losses were not comparable.
The following frequency of preterm births (28-37 weeks of pregnancy) was registered in the Russian Federation: 2008 - 3.6% of the total number of births, 2009 - 4.1%, 2010 - 3.8%, 2011 - 3.9%. In connection with the transition in 2012 of Russia to the birth registration criteria recommended by WHO (fetal weight 500 g or more, gestational age 22 weeks or more) [6], the proportion of preterm births at 22-37 weeks in 2012 was 4.3% [8].
The etiology and pathogenesis of preterm labor are not fully understood. Premature birth at 22-27 weeks of gestation (fetal weight from 500 to 1000 g) is most often caused by isthmic-cervical insufficiency, infection of the lower pole of the fetal bladder and its premature rupture. Premature birth with a gestational age of 28-33 weeks (fetal weight 1000-1800 g) and preterm birth with a gestational age of 34-37 weeks (fetal weight 1900-2500 g and more) are due to various reasons: the woman's age (up to 20 years and over 35 years), preeclampsia, multiple pregnancy, etc. The highest percentage of abortion occurs at 34-37 weeks of gestation, while at 22-27 weeks of gestation this figure is 12 times lower. High morbidity and mortality in premature newborns is noted in the early stages - 22-33 weeks of gestation.
The highest percentage of abortion occurs at 34-37 weeks of gestation, while at 22-27 weeks of gestation this figure is 12 times lower. High morbidity and mortality in premature newborns is noted in the early stages - 22-33 weeks of gestation.
Preterm birth is a multifactorial process. In the 70s and 80s. of the last century, the world scientific community discussed articles on the identified social risk factors for preterm birth, among which the frequency of preterm birth was higher among residents of the northern and remote areas; among visiting women in remote areas, it was 18%, since they are not adapted to extreme conditions; in large cities, near airfields, major highways, the frequency of preterm birth is higher; in women working 42 hours a week, the frequency of preterm birth was 8.5%, and in women working less than 42 hours a week - 4.5%; among women using several modes of transport on their way to work, premature births were observed in 22%, with a lower load - in 6. 3%; in women engaged in physical labor, combining work and study, premature births occurred 2 times more often; in women younger than 20 and older than 40, the percentage of preterm births is higher, etc. [16].
3%; in women engaged in physical labor, combining work and study, premature births occurred 2 times more often; in women younger than 20 and older than 40, the percentage of preterm births is higher, etc. [16].
Women with preterm labor are 2.5 times more likely to have them again in their next pregnancy. The study of all these factors makes it possible to predict the likelihood of preterm birth in women who do not have clinical signs of the disease. This is not about the early detection of the disease, but about the forecast of the degree of probability of its development. Among the risk factors, the interval between births plays an important role: successive pregnancies and childbirth deplete the mother's body, reduce its resistance, thereby contributing to an increase in morbidity.
Significant progress in the study of preterm labor was achieved by the French scientist E. Papernik [12]. A group of researchers under his leadership managed to reduce the frequency of preterm birth by 2-2. 5 times (1969-1984). Thanks to taking into account the influence of socio-demographic, professional and household factors, perinatal mortality has significantly decreased in European countries. According to E. Papernik [12], the preterm birth prevention program can be implemented only if the work is well organized, both in the medical part and in the social part.
5 times (1969-1984). Thanks to taking into account the influence of socio-demographic, professional and household factors, perinatal mortality has significantly decreased in European countries. According to E. Papernik [12], the preterm birth prevention program can be implemented only if the work is well organized, both in the medical part and in the social part.
P.G. Martynenko, V.G. Volkov [3] based on a retrospective analysis of the birth histories of 25,297 puerperas in obstetric institutions in the Tula region during 2006-2008. revealed that the main risk factors for early preterm birth (22-31 weeks) are multiple pregnancies (75.8%) and isthmic-cervical insufficiency (54.9%). The presented materials testify to the social orientation of risk factors for preterm birth. In this regard, preterm birth is not only a medical but also a social problem.
Pregnancy and preterm birth itself are associated with a significant number of complications, and maternal and fetal outcomes with increased levels of reproductive losses. It is preterm birth that determines the level of perinatal morbidity and mortality. The problem of preterm birth is of great social importance, given the high cost of nursing low birth weight children. The average cost of nursing a 500 g baby is over $150,000, and only 44% of them survive. With a child weighing 1251-1500 g, the average cost of nursing is approximately US$ 30,000 and the survival rate is 97% [11, 12]. The total cost of medical care for premature newborns is 16.9 billion dollars a year. This is 10% of all childhood costs and 35% of all newborn costs.
It is preterm birth that determines the level of perinatal morbidity and mortality. The problem of preterm birth is of great social importance, given the high cost of nursing low birth weight children. The average cost of nursing a 500 g baby is over $150,000, and only 44% of them survive. With a child weighing 1251-1500 g, the average cost of nursing is approximately US$ 30,000 and the survival rate is 97% [11, 12]. The total cost of medical care for premature newborns is 16.9 billion dollars a year. This is 10% of all childhood costs and 35% of all newborn costs.
Ola Didrik Zaugstad, a well-known neonatologist and author of a study in the field of problems related to newborns and premature babies [17], believes that to date, not enough is known about the causes of preterm birth. At the same time, he notes the following causes of premature birth: bleeding during pregnancy, stress, pregnancy complications, hard physical work, cervical weakness, multiple pregnancies, early discharge of water, heredity.
When analyzing the mechanisms of development of preterm birth, four main causes of preterm birth were identified:
- infection - acute, chronic, systemic, ascending, bacterial and / or viral;
- maternal and/or fetal stress due to extragenital pathology, pregnancy complications and placental insufficiency;
- thrombophilic disorders leading to placental abruption, thrombosis in the placenta;
- overstretching of the uterus with multiple pregnancy, polyhydramnios, with malformations of the uterus, infantilism [10, 12].
The high incidence of pregnancy complications and preterm birth itself is responsible for significant neonatal morbidity and mortality in newborns. Premature babies account for 60-70% of cases of early neonatal mortality, 50% of neurological diseases [17]. Stillbirth in preterm birth is observed 8-13 times more often than in timely. In developed countries, the mortality of children weighing 1000-1500 g at birth has decreased from 50 to 5%, the mortality of children weighing 500-1000 g - from 90 to 20% [9].
Preterm infant survival has improved significantly with the development of intensive neonatal care. Although most premature babies survive, they are at increased risk of neurological, respiratory, and gastrointestinal complications. The shorter the gestational age at the time of delivery, the higher the risk of morbidity and mortality for the child.
Finnish scientists [2] calculated that the decrease in perinatal mortality is due to 40% improvement in social living conditions, 35% - the development of the country's economy and 30% - medical organizational measures.
The infant mortality rate in Russia under the new birth criteria [6], according to Rosstat, increased from 7.4 to 8.7‰ (by 17.6%). The perinatal mortality rate increased from 7.17 in 2011 to 10.0 per 1000 live births and stillbirths in 2012 (by 39.7%): the stillbirth rate - from 4.5 to 6.34‰ (by 40. 9%), and early neonatal mortality - from 2.7 to 3.6‰ (by 33.3%). The level of perinatal mortality in obstetric hospitals in 2012 increased by 45. 1%, mainly due to accounting for children weighing 500-999 g, and amounted to 9.75 per 1000 live births and stillbirths - against the level of 6.72% in 2011 for children weighing 1000 g or more. According to L.P. Sukhanova [7], in obstetric hospitals of the 2nd level, 53.2% of preterm births and 50.3% of births in the period of 22-27 weeks are carried out.
1%, mainly due to accounting for children weighing 500-999 g, and amounted to 9.75 per 1000 live births and stillbirths - against the level of 6.72% in 2011 for children weighing 1000 g or more. According to L.P. Sukhanova [7], in obstetric hospitals of the 2nd level, 53.2% of preterm births and 50.3% of births in the period of 22-27 weeks are carried out.
The severity of the contingent of women with early preterm birth is evidenced by the high frequency of their operative delivery and forced obstetric hysterectomy during all years. Thus, according to the average annual indicator for 5 years, the frequency of hysterectomy in the process of abortion in women with a gestational age of 22-27 weeks is 18.6 times higher than the rate in childbirth (28.4) per 1000 interruptions in the period of 22-27 weeks against 1.53 per 1000 deliveries at 28 weeks or more. The frequency of small cesarean section (307.0 per 1000 interruptions in the period of 22-27 weeks according to the average annual rate for 2008-2012) is 1. 4 times higher than the rate in the period of 28 weeks or more (219,2 per 1000 births) - with higher mortality in short gestations. The frequency of complications during small caesarean section (0.55 per 100 operations) is higher than in the period of 28 weeks or more (0.35) [7].
4 times higher than the rate in the period of 28 weeks or more (219,2 per 1000 births) - with higher mortality in short gestations. The frequency of complications during small caesarean section (0.55 per 100 operations) is higher than in the period of 28 weeks or more (0.35) [7].
Russian researchers [13] showed an increased risk of maternal mortality associated with preterm birth. Thus, the leading causes of death of women in preterm birth were preeclampsia (26.6%), extragenital diseases (23.4%), bleeding (21.9%) and sepsis (12.4%). In the group of women who died during timely delivery, the 1st place in the structure of causes of death was occupied by bleeding (25.8%), 2nd by sepsis (22.3%), 3rd by uterine rupture (18.2%) , 4th - extragenital diseases (9.9%).
According to M.E. Matveenko [4], the primary medical documentation for 82 cases of maternal death in multiple pregnancy, which occurred spontaneously in 81 women, in 1 woman after IVF and PE, was subjected to clinical analysis. After childbirth, 93.9% died, of which 48.7% died after premature birth.
After childbirth, 93.9% died, of which 48.7% died after premature birth.
Among the mothers who died in 2008 in Russia, women in labor and childbirth accounted for 69.4%, of which 31.3% died during premature births. The study showed that preterm birth, with a frequency of 3.4% in the population, is responsible for 21.7% of maternal deaths. In this regard, the prevention of preterm birth is a reserve for reducing maternal mortality [13].
The tactics of managing and treating the threat of preterm birth takes into account the possible causes of preterm birth and is determined by: gestational age, the condition of the mother and fetus, the presence of a whole amniotic sac, the nature of the contractile activity of the uterus, the degree of changes in the cervix, the presence of bleeding and its severity [12]. The main tasks in the management of women with the threat of preterm labor are the prolongation of pregnancy to the optimal term of labor, timely prevention and correction of emerging complications, monitoring the condition and development of the fetus, the correct choice of the method of delivery, rational management of labor and the postpartum period [1]. Therapy to prevent preterm birth, methods of delivery in them, the effectiveness or danger of interventions that do not have the necessary evidence base are set out in the Cochrane Guidelines, as well as in the clinical protocol for preterm birth [1, 14]. Knowledge of these documents will change the priorities in the national obstetric service from excessive "obstetric aggression" towards preventive basic care, based on the basic principle of perinatal obstetrics - ensuring the safety of women and children.
Therapy to prevent preterm birth, methods of delivery in them, the effectiveness or danger of interventions that do not have the necessary evidence base are set out in the Cochrane Guidelines, as well as in the clinical protocol for preterm birth [1, 14]. Knowledge of these documents will change the priorities in the national obstetric service from excessive "obstetric aggression" towards preventive basic care, based on the basic principle of perinatal obstetrics - ensuring the safety of women and children.
In order to understand the causes and earlier treatment of preterm birth, rather than their consequences, the issue of introducing markers of preterm birth into clinical practice is currently being urgently raised. It is known that preterm birth is accompanied by an imbalance of pro- and anti-angiogenic factors, which is, apparently, the result of the activity of certain alleles. With the progress of molecular biology, it became possible to isolate the DNA of almost any protein from biological fluids (amniotic fluid, urine, cervical mucus, vaginal discharge, serum, plasma, saliva) using polymerase chain reaction. An attempt is being made to find molecular predictors of premature development of labor, which will allow choosing a rational etiologically and pathogenetically substantiated therapy.
An attempt is being made to find molecular predictors of premature development of labor, which will allow choosing a rational etiologically and pathogenetically substantiated therapy.
Thus, preterm birth is a medical and social problem and is associated with a woman's low socioeconomic and educational status, often stress, hard physical labor. The frequency of preterm birth in the world ranges from 5 to 10%. The role of infection, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, multiple pregnancy, aggravated obstetric and gynecological history in the occurrence of preterm labor was studied. However, in 40-50% of cases, the cause of preterm birth cannot be established. It is known that women with preterm birth are at risk of high reproductive losses. Recently, the search for predictors of preterm birth has been of particular interest in order to identify risk groups for the development of this complication and prevent its development, which is the subject of our scientific study.
Pregnancy: Terrible word THREAT! Let's save ourselves!
Our today's conversation will touch upon recommendations for a pregnant woman who is faced with such a complication of pregnancy as a threatened abortion.
Pregnancy is a physiological process for the female body. If a woman is young (18-30 years old) and healthy, then, as a rule, pregnancy proceeds without complications. Recently, in the world and in our country, there has been a sharp deterioration in the health of women of reproductive age.
Complications of pregnancy can be divided into 3 groups for a better understanding of the reader (these are not standards).
- Firstly, the complications associated with the pregnancy itself, if it were not for this condition, then there would be no complication - the threat of termination of pregnancy (the threat of premature birth).
- Secondly, these are complications associated with a disease (for example, rubella) that occurred during pregnancy.

- Thirdly, these are complications that arose in a woman who suffered from a particular disease before pregnancy (perhaps the first exacerbation of this disease is associated with pregnancy).
The most unpleasant psychological and physical complications are threatened miscarriage . If this happens in the early stages, then the term is used, the threat of termination of pregnancy ", if in the later stages (after 28 weeks), then " the threat of premature birth.
What to do if there is a threat of termination of pregnancy
In some countries, including Russia, it is customary to keep a pregnancy of any term; accordingly, if a woman notes spotting during pregnancy, then she immediately should see a doctor during the day or call the emergency team at night. But the question of the expediency of maintaining pregnancy with the onset of bleeding up to 12 weeks remains open, because. it is known that 70-80% of pregnancies terminated during this period are associated with chromosomal pathologies, sometimes incompatible with life. Those. It can be said that the body itself corrects its mistakes.
it is known that 70-80% of pregnancies terminated during this period are associated with chromosomal pathologies, sometimes incompatible with life. Those. It can be said that the body itself corrects its mistakes.
Reasons for termination of pregnancy
Termination of pregnancy may also be associated with cervical incompetence . Those. its upper part may not be tightly closed, i.e. unable to play the role of a "castle". This condition may be caused by trauma during previous births or during abortions ( even if it was a single ). In this case, treatment is carried out in a hospital, and in the future, pregnancy is observed by an outpatient doctor. A woman can be stitched on the cervix if such a diagnosis is made at 16-20 weeks or a special retaining ring is placed if complaints appear later than this period. The suture or ring is removed at the time of the onset of labor, i.e. with the appearance of regular contractions or the outflow of amniotic fluid. However, this procedure can be performed two weeks before the expected date of birth.
However, this procedure can be performed two weeks before the expected date of birth.
Termination of pregnancy may be associated with the hormonal status of a woman , therefore hormones play a leading role in the treatment of this complication. In order to clarify the diagnosis in the antenatal clinic, they can take the so-called “threat smear” (this is not a 100% confirmation of the diagnosis). Of course, hormones play one of the main roles in the regulation of pregnancy. The problem of treatment of miscarriage is very complex and multifaceted. I repeat that in our country it is customary to preserve early pregnancy. For this purpose, hormone therapy is used, based on the physiological and pathogenetic processes of the onset and development of pregnancy. A woman diagnosed with threatened miscarriage or threatened miscarriage is admitted to the hospital for appropriate therapy in severe condition, or may be observed on an outpatient basis and given hormonal therapy, as in inpatient treatment.
Symptoms of a threatened miscarriage
As for the threat of preterm labor, the first symptoms may not be bloody discharge, but simply heavy discharge (sometimes a woman thinks that she has urinary incontinence). This may be a signal that the integrity of the fetal bladder is broken. Of course, in this case, you should immediately consult a doctor. If it is daytime, then a doctor of antenatal clinic is enough. At night, it is better to call an ambulance or get to the maternity hospital on your own.
In later pregnancy there may also be spotting . The reason for them may be a low-lying placenta and constant uterine contractions (uterine tone). It is the tone of the uterus that can cause placental abruption and, accordingly, bleeding. Contacting a doctor should be in the same mode as described above.
Special mention should be made of ectopic pregnancy . This condition can also be associated with the threat of termination, only the consequences of the termination of an ectopic pregnancy can adversely affect the woman's health. An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg attaches itself outside the uterine cavity. This place is most often tubes, but an ectopic pregnancy can also be found directly in the ovary or in the abdominal cavity. The diagnosis of "ectopic pregnancy" requires immediate surgical intervention. The scope of the operation and operative approach (cavitary or laparoscopic) can only be decided in a hospital setting and depends on many factors, including complications that have arisen at the time of admission to the hospital. Very often, an ectopic pregnancy occurs when there is a malfunction of the villi that are in the tubes and push the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. It is impossible to predict this state. However, it can occur most often in chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
This condition can also be associated with the threat of termination, only the consequences of the termination of an ectopic pregnancy can adversely affect the woman's health. An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg attaches itself outside the uterine cavity. This place is most often tubes, but an ectopic pregnancy can also be found directly in the ovary or in the abdominal cavity. The diagnosis of "ectopic pregnancy" requires immediate surgical intervention. The scope of the operation and operative approach (cavitary or laparoscopic) can only be decided in a hospital setting and depends on many factors, including complications that have arisen at the time of admission to the hospital. Very often, an ectopic pregnancy occurs when there is a malfunction of the villi that are in the tubes and push the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. It is impossible to predict this state. However, it can occur most often in chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
What to do in case of termination of pregnancy
If the pregnancy could not be maintained, then the question arises about the reasons for this situation. After what happened, an examination is necessary, which will include an examination of both spouses. It is necessary to obtain the results of a histological examination and consult a geneticist . A woman will be examined by a gynecologist for infections or hormonal disorders, a man needs to consult a urologist (andrologist) for the same examination.
Sometimes it is very difficult to find the cause, but this is not a reason to despair. Subsequent pregnancies can pass without complications, and the first unsuccessful attempt is quickly forgotten. With a successful examination , it is recommended to plan the next pregnancy in 4-6 months .
Everything that we have talked about should draw attention to the health of a pregnant woman and help her navigate in the event of a particular situation. A desired pregnancy is a joyful state for a woman and her family. The task of the doctor is to prevent and, as far as possible, solve the problem with a positive result.
A desired pregnancy is a joyful state for a woman and her family. The task of the doctor is to prevent and, as far as possible, solve the problem with a positive result.
Doctors of the Center for Fetal Medicine are one of the leading specialists in prenatal diagnostics, candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest categories with a narrow specialization and extensive experience in prenatal medicine.
All ultrasound examinations in the center are carried out according to the international standards FMF (Fetal Medicine Foundation) and ISUOG (International Society for Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology).
Ultrasound doctors have international certificates from the Fetal Medicine Foundation (Fundamental Medicine, UK), which are are confirmed annually.
We take care of the most complex cases and, if necessary, it is possible to consult with specialists from King's College Hospital, King's College Hospital (London, UK).