Carpal tunnel in early pregnancy
Carpal tunnel syndrome and pregnancy
Carpal tunnel syndrome and pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs when swelling in your wrist presses on a nerve and causes pain in your hand.
- It’s common in pregnancy and usually goes away after your baby is born.
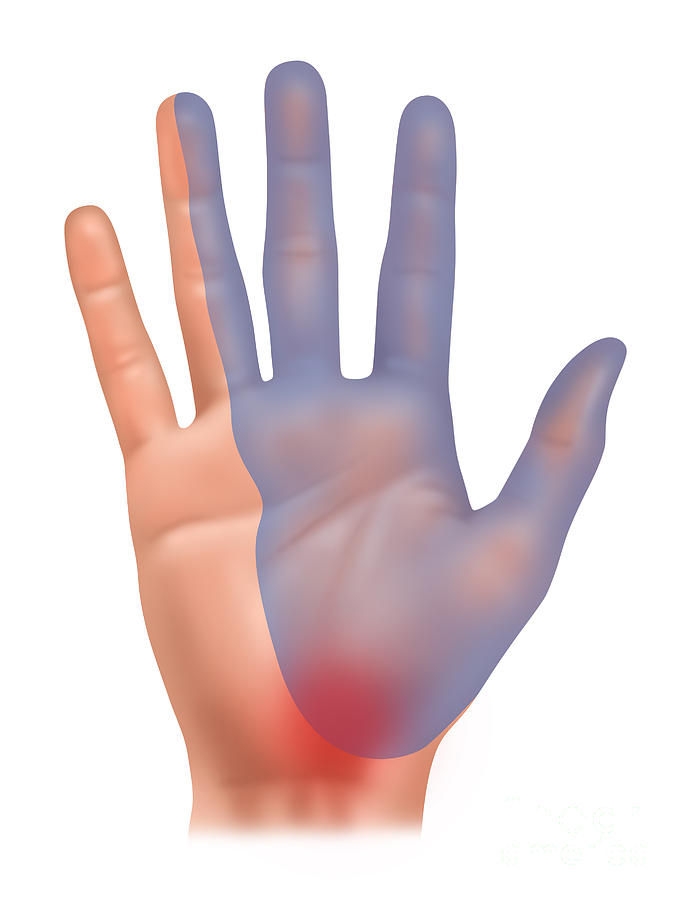
- It can cause pain, numbness and tingling in your thumb, index finger and middle finger. It can also cause weakness in your hand and pain going up your arm.
- You can modify your daily activities to reduce your pain.
- See a physiotherapist or occupational therapist to learn exercises and get a special wrist splint fitted to help relieve pain.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
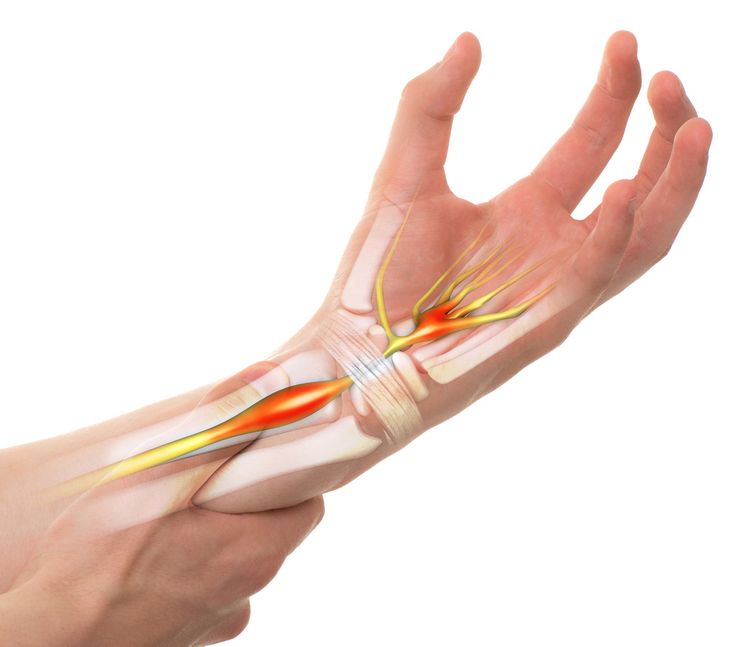
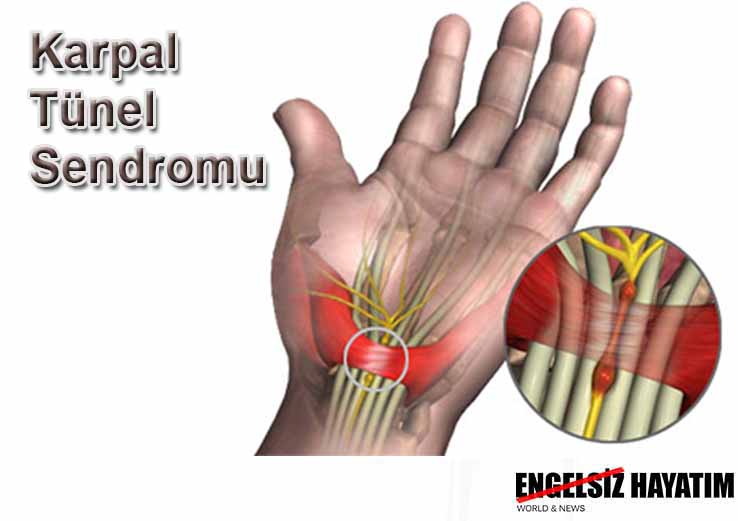
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs as a result of swelling around the nerves of your wrist. It can cause numbness, tingling or pain in one or both of your hands.
If you are pregnant, you’re particularly susceptible to the disorder. Up to 5 out of every 10 people who are pregnant develop carpal tunnel syndrome.
What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
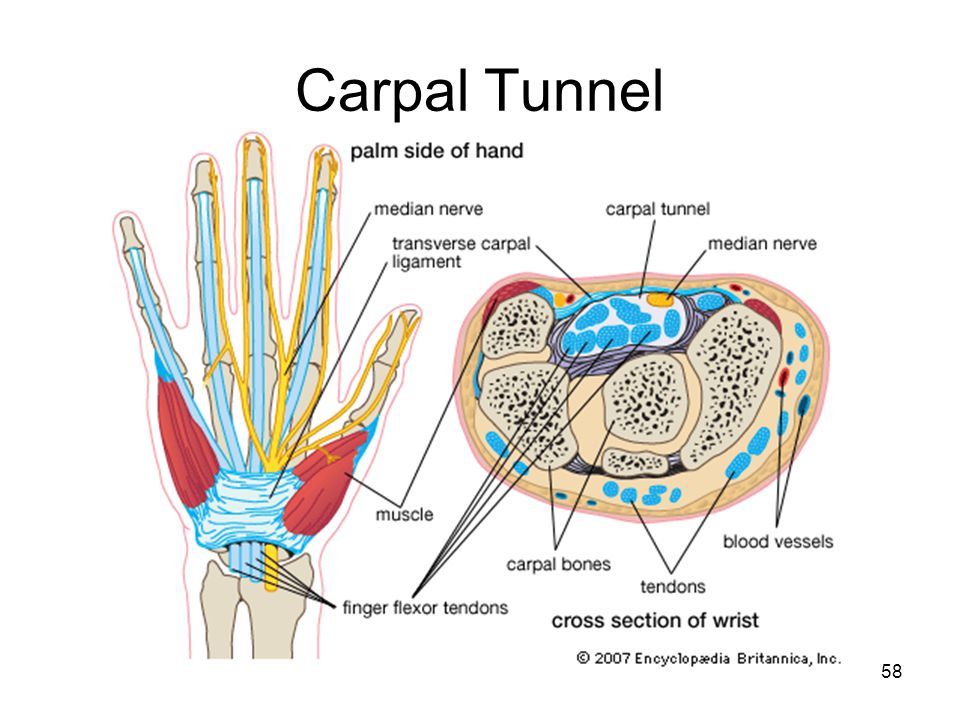
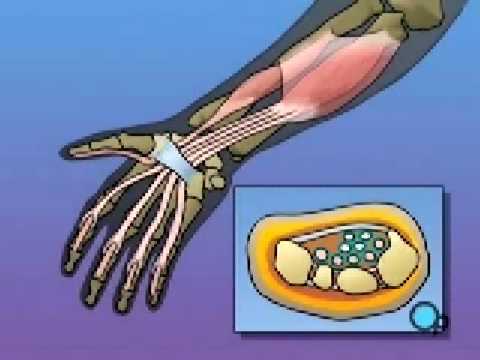
The carpal tunnel is a passage in your wrist that contains tendons and a nerve, called the median nerve, that run through the base of your hand. The carpal tunnel can swell and press against this sensitive nerve, causing pain.
While pregnancy is one cause, other common causes include arthritis or repetitive hand movements, which may occur in some jobs. Visit this healthdirect page for information about carpal tunnel syndrome unrelated to pregnancy.
How does pregnancy cause carpal tunnel syndrome?
When you are pregnant, your hormones cause fluid to build up in your body, which can cause swelling.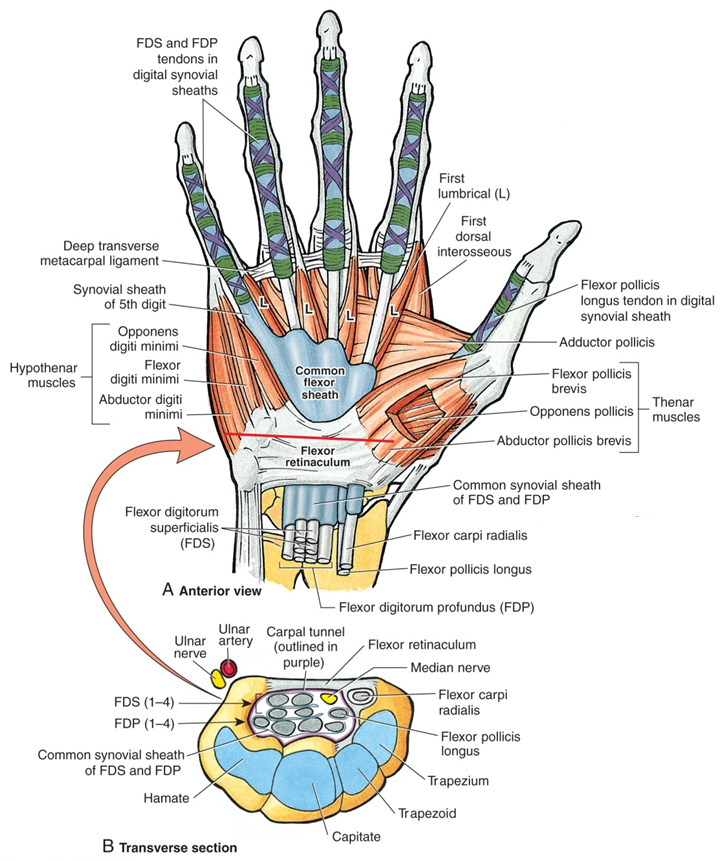 This can lead to swelling within the carpal tunnel.
This can lead to swelling within the carpal tunnel.
The condition is more common in the third trimester, but it can also happen in the first and second trimesters or after you give birth. In most cases, symptoms will go away after your baby is born.
What are the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Common symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness of your hand
- difficulty with hand coordination
- pain spreading to your arm or shoulder
You will probably feel the symptoms most in your thumb, index finger and middle finger. Symptoms can get worse at night.
The intensity of symptoms can vary from mild irritation or occasional soreness, to severe pain. Symptoms may stop you from sleeping or make it difficult to perform regular tasks such as working, getting dressed, cooking or caring for your baby.
Things that may make your symptoms worse include:
- repeating the same hand movements frequently
- keeping your hands in the same position for an extended time
- supporting your weight with straightened arms
Swelling may be a sign of high blood pressure in pregnancy.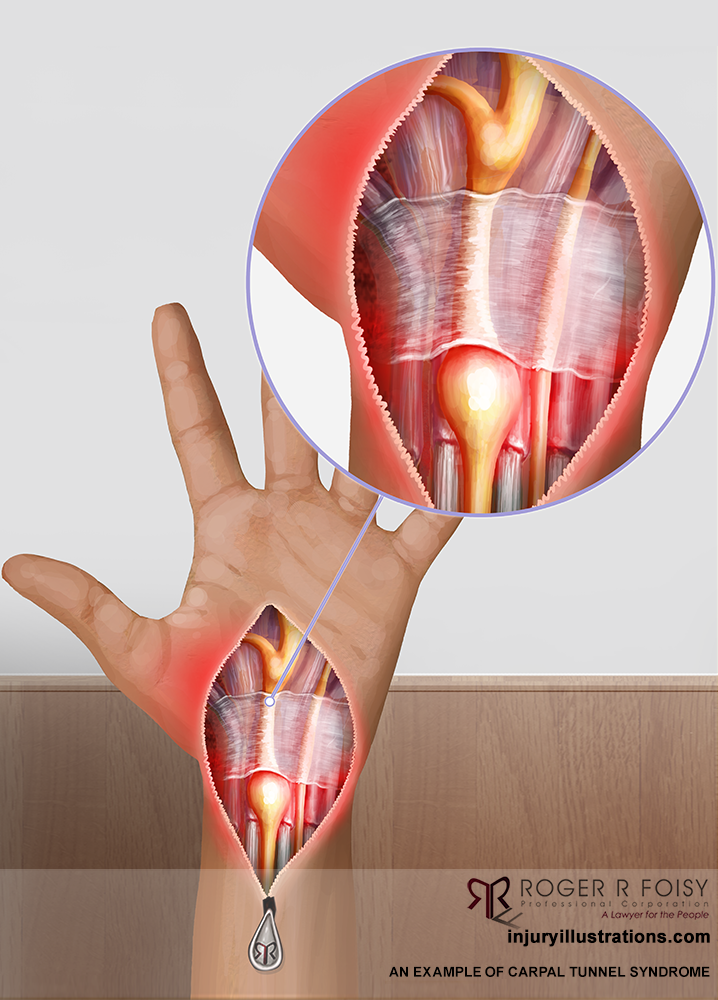 If your hands or feet are more swollen than usual, speak to your doctor or midwife.
If your hands or feet are more swollen than usual, speak to your doctor or midwife.
What can I do to relieve carpal tunnel syndrome?
You may find that your pain is reduced by the following:
- Keep your hands elevated as much as you can.
- Keep your wrists in a neutral position (not bent forwards or backwards), as much as you can.
- Maintain good posture in your arms and wrists while working at a desk and take breaks every 20 minutes.
- Sleep on the side of your less affected hand.
- Put an ice pack on your wrist or run cold water over your hand.
Here are some things you should avoid:
- Avoid any repeated movements that make your pain worse.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects.
- Avoid tasks where you do the same movement repeatedly.
- Don’t bend your wrist as far as it can go.
Here are some things you can do to relieve general swelling in your body:
- Lie down whenever you can, with your feet elevated.
- Cut down on salt in foods.
- Elevate your legs when you’re sitting down.
- Wear compression socks or stockings.
Are there any treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Treatment options include physiotherapy or occupational therapy. This may involve fitting you with a splint to keep your wrist in the best position to reduce strain. The splint must be adjusted to fit your wrist in order to be protective and supportive. You should wear your splint at night to keep your wrist in the right position while you’re asleep.
Your therapist will be able to tell you how best to protect your wrist at home, including exercises and resting positions.
You can try fluid drainage massage to reduce the swelling in your hand. You can do this by lifting your arm up and using your other hand to sweep gently along your skin from your fingers towards your shoulder. Be careful not to sweep the other way.
There are other treatments available for carpal tunnel syndrome, such as a cortisone injection into your wrist or even surgery.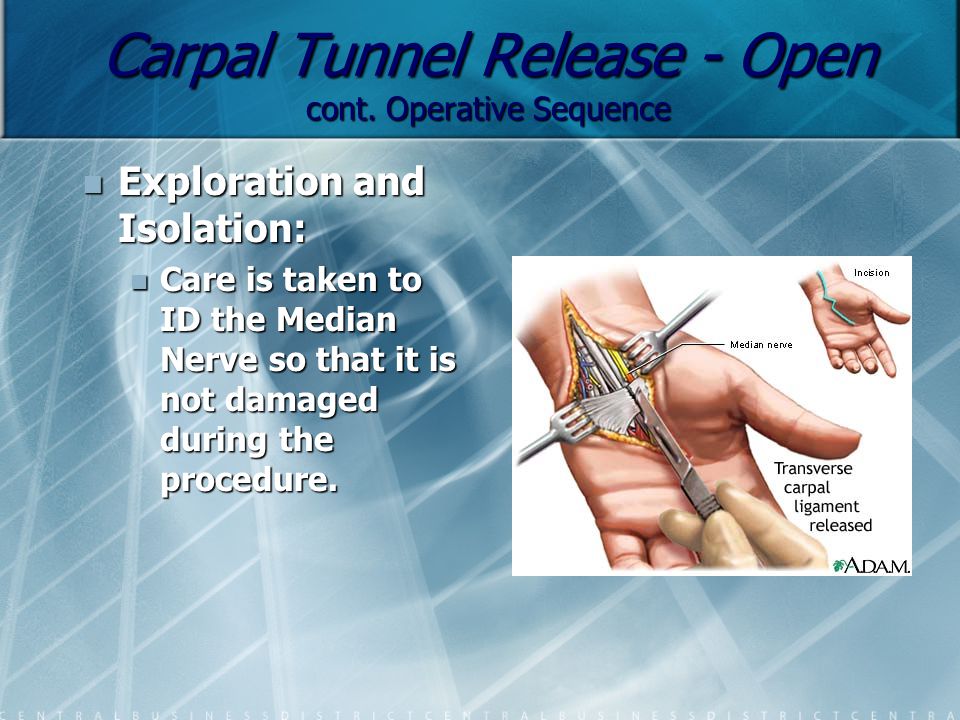
Will I still have pain after my baby is born?
Carpal tunnel syndrome tends to ease, and often disappears, after birth. If you still have pain after your baby is born, you may need to change the way you use your wrist. This might affect how you use your hand to hold and care for your baby, including how you feed your baby.
Speak to your physiotherapist, occupational therapist or lactation consultant for strategies and tips on how to minimise strain on your wrist while holding your newborn. It’s a good idea to continue using your splint, if you have one.
Sources:
Royal Women’s Hospital (Pregnancy-related carpal tunnel syndrome), Australian Government Department of Health (Carpal tunnel syndrome), Western Australia Department of Health (Carpal tunnel syndrome), Western Sydney local Heath District (Fact Sheet Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Physiotherapy advice after pregnancy
- Swelling during pregnancy
Need more information?
Carpal tunnel syndrome - Better Health Channel
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be caused by repetitive hand movements, pregnancy and arthritis.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Carpal tunnel syndrome - MyDr.com.au
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a progressive and painful condition where the median nerve is compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel.
Read more on myDr website
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a disorder of the hand caused by pressure on the median nerve as it runs through the wrist.
Read more on WA Health website
Pregnancy - signs and symptoms - Better Health Channel
All women experience pregnancy differently, and you will experience different symptoms at different stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Working during pregnancy
UnIess your doctor tells you it is unsafe, it is possible to work while pregnant. Get some tips on managing and making adjustments to your work and career.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Diabetes and getting pregnant - MyDr.com.au
How will having diabetes affect your pregnancy and your baby? And what planning do you need to do first?
Read more on myDr website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.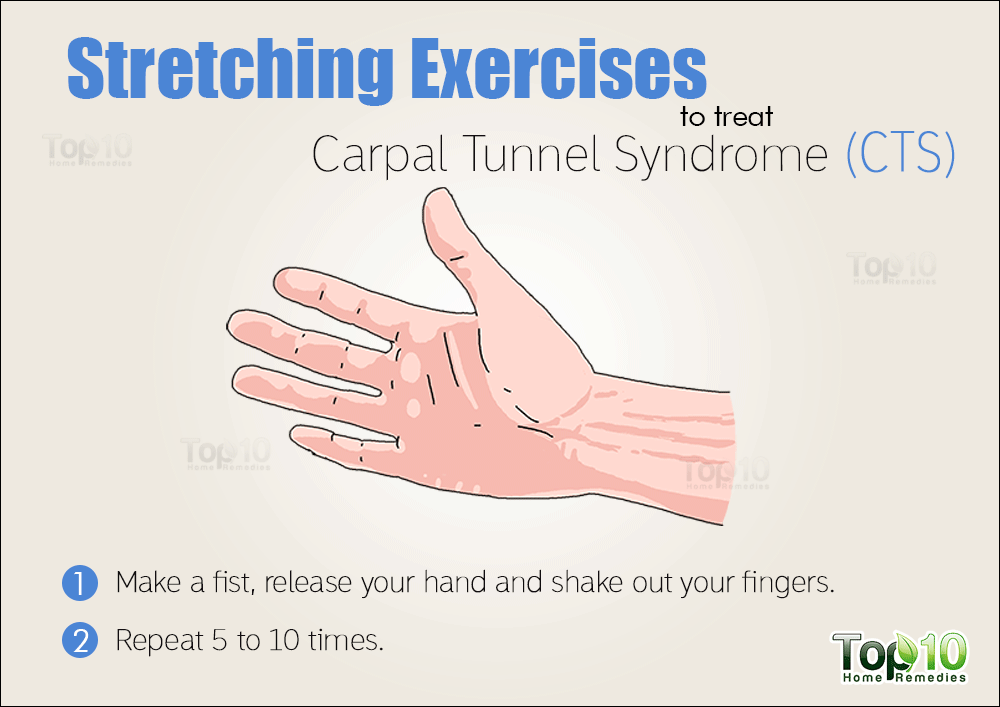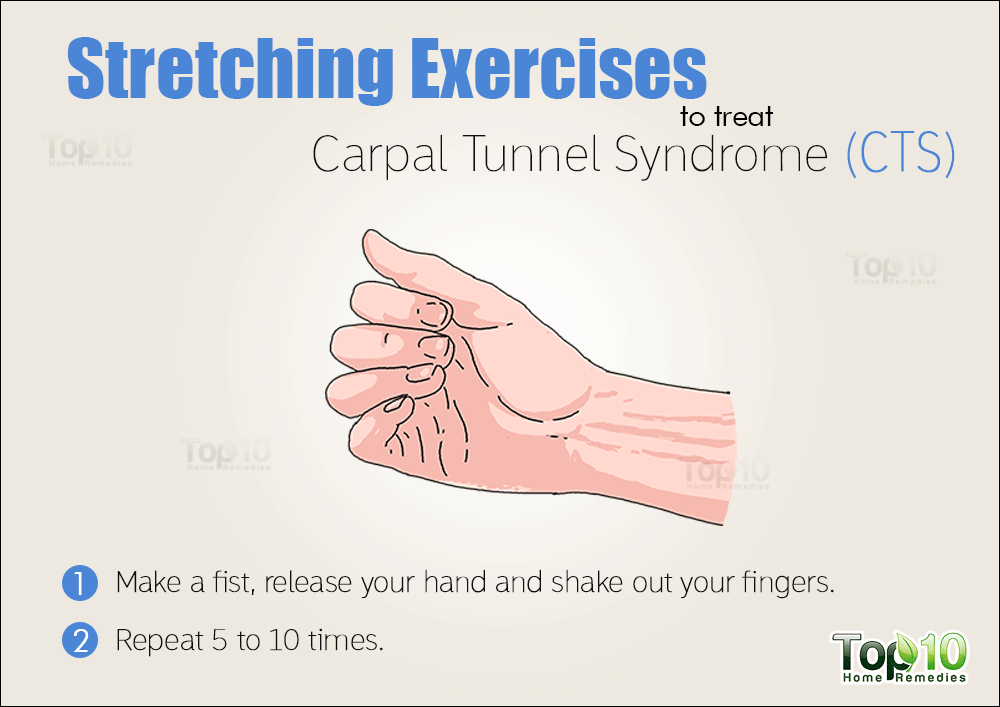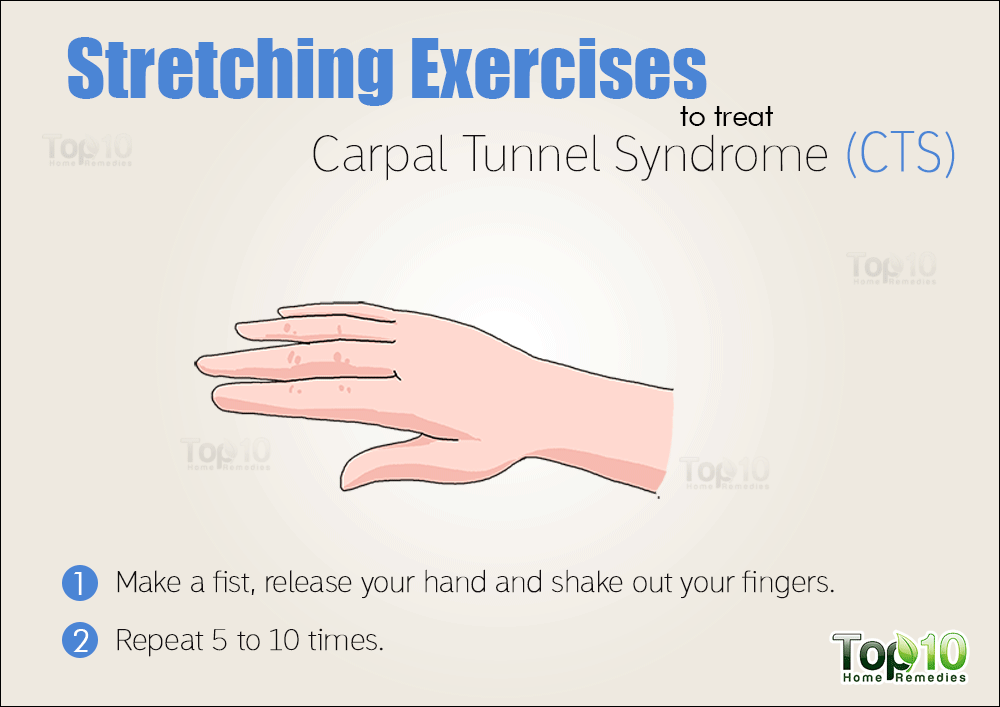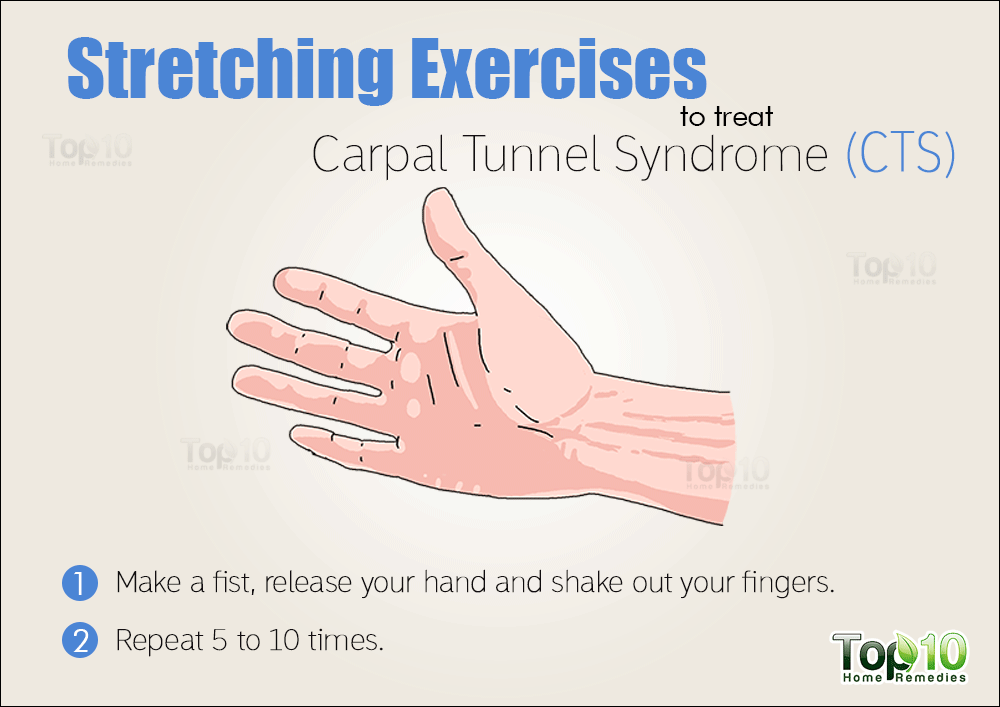
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Carpal tunnel syndrome and pregnancy go hand in hand | Your Pregnancy Matters
×
What can we help you find?Refine your search: Find a Doctor Search Conditions & Treatments Find a Location
Appointment New Patient Appointment
or Call214-645-8300
MedBlog
Your Pregnancy Matters
October 20, 2020
Your Pregnancy Matters
Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M. D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
Swelling – everywhere – is one of the most common symptoms of pregnancy. Patients often notice extra puffiness in their face, legs, and feet. But for some women, swelling manifests inside the wrist, resulting in carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
Approximately 4% of adults in the general population have carpal tunnel syndrome, but 31% to 62% of pregnant patients have it. Many patients notice symptoms after 30 weeks' gestation.
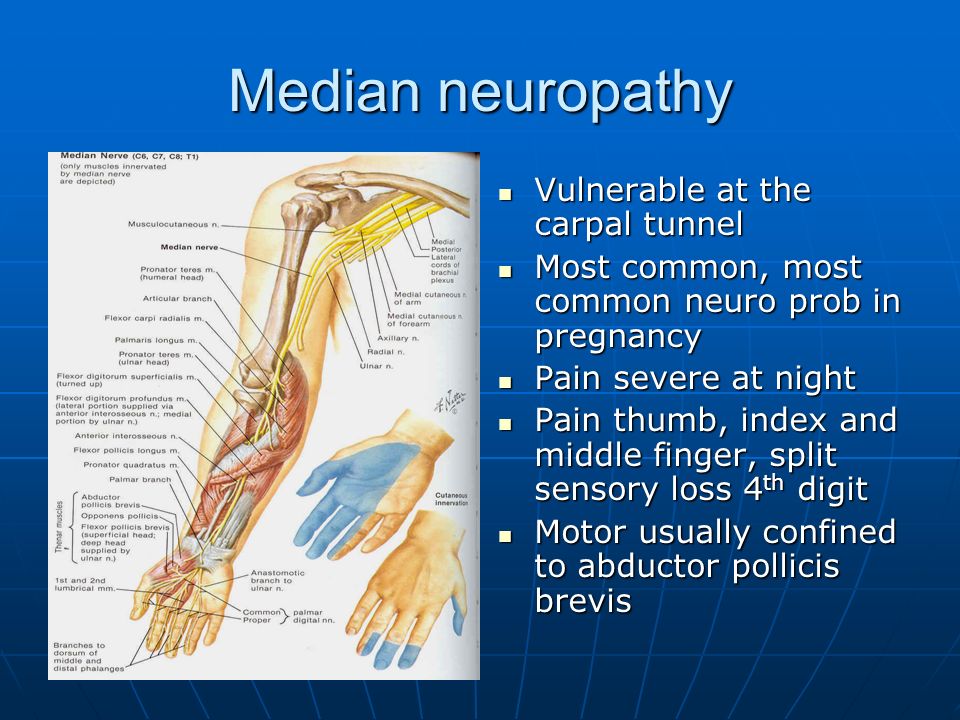
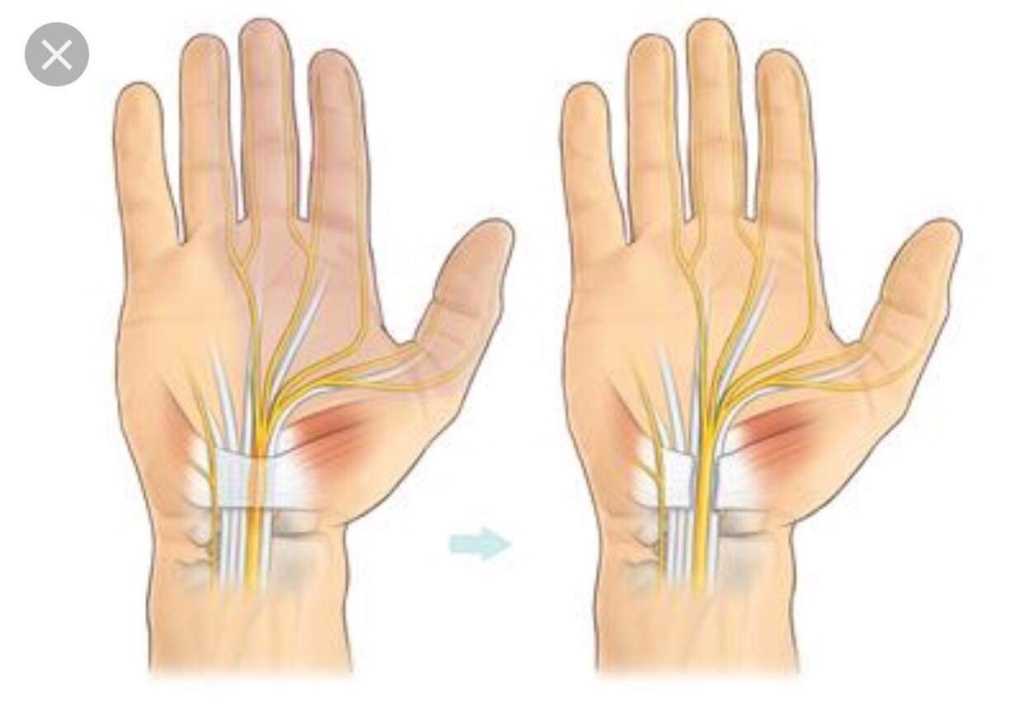
During pregnancy, your blood volume doubles. That extra fluid increases pressure and swelling in the blood vessels throughout your body. In tight spaces such as the carpal tunnel area of the wrist – through which nine tendons and one nerve pass – the swelling can compress the median nerve, which runs to the hand.
The median nerve gives sensation to the palm-side surface of thumb, index, and middle fingers, and half the ring finger. It's also responsible for helping to move the muscles in the hand that bend your fingers.
Nerve compression can cause pain, tingling, and numbness in the wrist and hand, which may increase when you're trying to sleep. Pregnancy may be the first time CTS symptoms arise or the last straw that causes a woman to see her doctor for ongoing symptoms.
The good news is that pregnancy-safe treatment is available, and symptoms typically subside for many patients after the baby arrives.
I've invited my colleague, Rupali Kumar, M.D., from UT Southwestern's Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PM&R) team to discuss CTS symptoms and treatment options.
Carpal tunnel symptoms in pregnancy
Dr. Rupali KumarWhen the median nerve is compressed during pregnancy, symptoms present as they would in any patient:
● Numbness and tingling
● Burning sensation
● Pain in the wrist or hand
At the onset of CTS, symptoms may come and go. But when numbness or weakness occurs frequently or constantly, that's a potential sign of nerve damage.
But when numbness or weakness occurs frequently or constantly, that's a potential sign of nerve damage.
In severe cases, patients may have weakened grip strength or decreased finger dexterity. For example, you might have trouble picking up small objects with your fingers, opening jars, or buttoning clothes.
Related reading: 5 weird pregnancy symptoms you might not know about
Diagnosing carpal tunnel in pregnancy
We often can diagnose CTS by talking with you about your symptoms and medical history. If your symptoms are severe, we may recommend an electrodiagnostic study (EMG) to confirm the diagnosis and measure nerve function in the arm, wrist, and hand. An EMG can tell us whether you have nerve damage, how severe it is, and whether it might be reversible with intervention.
The doctor will attach small electrode stickers to your hand and arm in different places and apply low levels of electrical stimulation to gauge the nerve activity. The doctor may also insert a fine acupuncture-like needle in certain areas of the arm and hand to test muscle electrical activity.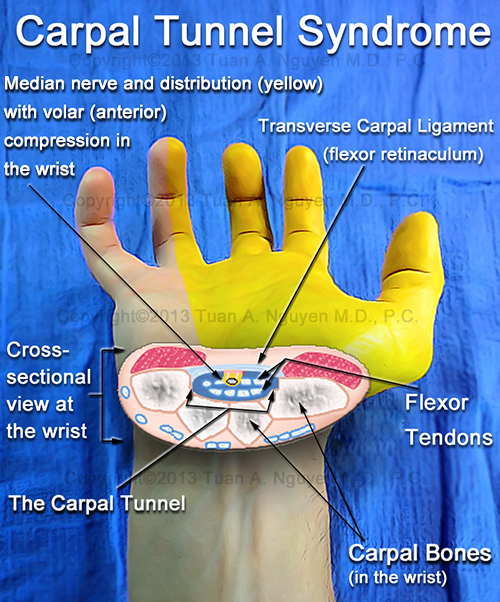 The study can be a little uncomfortable, but should not cause lasting pain.
The study can be a little uncomfortable, but should not cause lasting pain.
Pregnancy-safe treatment options
With CTS, it's best to start with the most conservative therapies. That's especially true in pregnancy. Here is a list of carpal tunnel treatment options that are safe for pregnancy, from least to most invasive.
Splinting
The first-line treatment is to immobilize the wrist in a neutral position to limit the range of flexion or extension. We use a neutral wrist splint with a metal bar inside that prevents the wrist from moving up, down, or side-to-side but allows the fingers to move.
Splinting gives the median nerve a break and can help alleviate swelling, which can allow mild to moderate nerve damage to heal. However, it's tough to wear a splint all day and do everyday activities. Your doctor may recommend wearing it while sleeping and as much as you can during the day.
Occupational therapy
Hand and wrist therapy can sometimes help relieve symptoms and prevent further nerve damage. A PM&R doctor or occupational therapist can create a personalized plan for you.
A PM&R doctor or occupational therapist can create a personalized plan for you.
Therapy may include wrist and finger range of motion and strengthening movements, massage, and nerve gliding techniques. We may also recommend desensitization to decrease nerve pain, including alternating hot and cold water baths.
Medication
Topical numbing agents can relieve symptoms, but these ointments won't get to the root of the problem. Some patients may benefit from pain relief injections, which include a combination of steroids and a local anesthetic injected around the median nerve under ultrasound guidance.
However, if there are other therapies to try, we typically avoid prescribing steroids during pregnancy to avoid side effects.
Check with your Ob/Gyn before using any over-the-counter or prescribed topical medications. Our PM&R doctors will consult with your Ob/Gyn prior to recommending medication during pregnancy.
Surgery, in severe cases
Carpal tunnel release surgery is reserved for severe cases. In this procedure, a surgeon will cut the ligament that presses on the carpal tunnel, making more room for the median nerve and tendons. This usually improves function and pain.
Generally, we recommend waiting until after pregnancy to have surgeries that are not urgent. If wrist pain or hand weakness severely limits your daily function, talk with your Ob/Gyn about the risks and benefits of having carpal tunnel surgery prior to delivery.
When will symptoms improve?
After delivery, your fluid levels and the extra pressure in your blood vessels will decrease. As such, your symptoms will likely improve or resolve.
That being said, new mothers use their hands and wrists nearly constantly. Lifting, changing, and feeding the new baby may lead to worsened or new hand and wrist symptoms.
Let your Ob/Gyn know as soon as symptoms begin. If we catch carpal tunnel early enough, we can start conservative treatments to reduce the risk of nerve damage or lingering symptoms.
After pregnancy, keep an eye on your wrist health. You'll be lifting your baby a lot and making repetitive motions, which can lead to tendinopathies related to overuse.
Even if your new aches and pains don't seem overtly pregnancy-related, let your Ob/Gyn know. Pregnancy does strange things to the body, and your provider can help you find relief from painful or annoying symptoms.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
More in: Your Pregnancy Matters
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
October 11, 2022
Prevention; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
October 4, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Meitra Doty, M.
 D.
D.
September 27, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
September 20, 2022
Men's Health; Women's Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Yair Lotan, M.
 D.
D.
September 6, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
August 29, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Patricia Santiago-Munoz, M.D.
August 23, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
August 11, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Emily Adhikari, M.
 D.
D.
August 2, 2022
More Articles
carpal tunnel syndrome
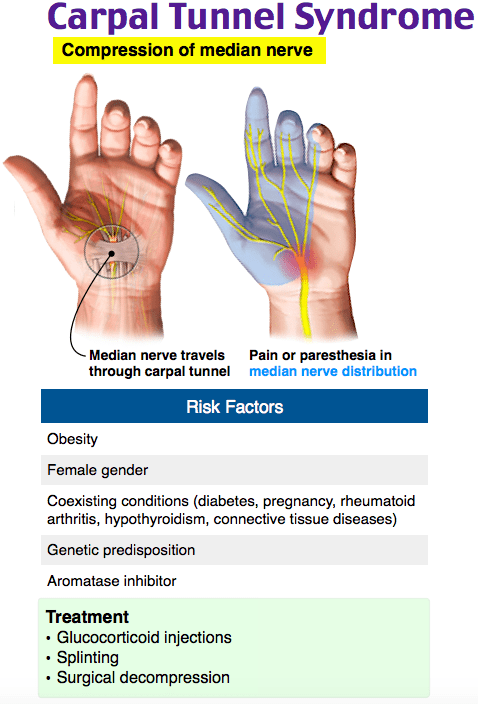
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition where compression occurs in the carpal (carpal) canal of the median nerve. Compression or trauma can provoke it.
The concept of carpal tunnel syndrome is not universal for the wrist area, this condition can also manifest itself in other anatomical areas where the nerves lie quite superficially and close to the bone structures at the same time. The syndrome under consideration manifests itself in the form of a decrease or lack of sensitivity in the thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger, as well as a violation of motor function in them.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common pathology and occurs in 1-3% of the population, and mainly in people whose occupation is associated with fine, monotonous motor skills of the hand.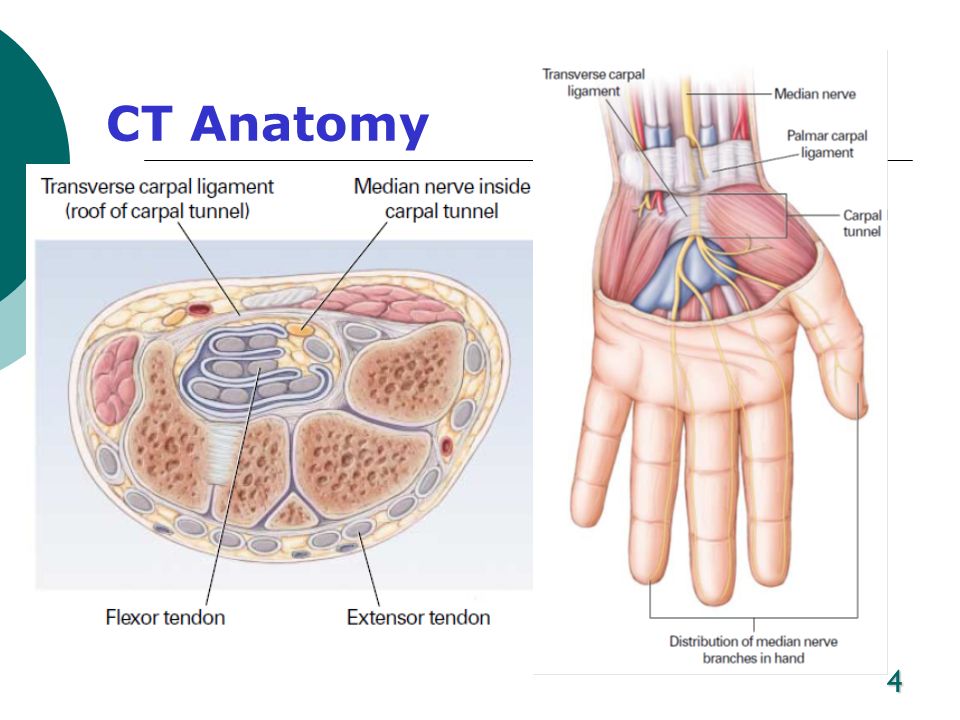 Half of all those suffering from this syndrome are people whose type of employment is associated with the use of a computer. Also, this disease can be considered an occupational pathology in musicians, tailors, office workers, etc. The syndrome occurs in the active working-age population at an already mature age (40-60 years), and in 105 cases even at a younger age. The researchers concluded that active PC users have a 15% higher risk of developing the syndrome, especially women.
Half of all those suffering from this syndrome are people whose type of employment is associated with the use of a computer. Also, this disease can be considered an occupational pathology in musicians, tailors, office workers, etc. The syndrome occurs in the active working-age population at an already mature age (40-60 years), and in 105 cases even at a younger age. The researchers concluded that active PC users have a 15% higher risk of developing the syndrome, especially women.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
The median nerve in the hand passes through a tunnel formed by the transverse ligament and carpal bones of the hand. To provoke compression of the nerve in the canal can:
-
Traumatic injuries of the hand. Bruises, sprains, sprains, fractures can cause swelling of the ligaments and muscles, or even displacement of the bones of the wrist. All this can compress the nerve in the canal and cause a violation of its function. With proper treatment, all these processes are reversible, but if timely and correct assistance is not provided, then muscle and ligament contractures, as well as bone deformities, may already be irreversible.
-
Arthrosis, arthritis and other pathological articular processes of various etiologies and genesis. Edema and inflammatory reactions caused by these pathologies, up to tissue necrosis, can also cause nerve compression. With the permanent course of inflammation and the progression of degenerative-dystrophic processes, the articular surfaces of the wrist lose their properties and wear out, resulting in deformation and compression of the nerve in the canal by already bone structures.
-
Inflammation of tendons or tendovaginitis. Inflammation can be septic (caused by microorganisms) and aseptic (caused by exercise, hypothermia, etc.). Diseases such as purulent wounds of the hand, including panaritiums, improper technique for taking blood from a finger, etc., can provoke septic inflammation. Non-infectious inflammation can be caused by chronic traumatic stress, for example, frequent monotonous motor skills of the hand, static load on it, temperature injury.

-
Diseases that lead to water retention in the body can cause swelling of the extremities and, as a result, lead to an increase in soft tissue volume and compression of the median nerve. Violation of the water and electrolyte composition can cause: pregnancy, taking hormonal contraceptives, menopause, kidney disease, etc.
-
Rare, but tumors of nervous tissue and median nerve in particular. Most of these are benign neoplasms (schwannomas, neurofibromas, perineuromas), but there are also malignant ones arising from the nerve sheaths. With its growth, the tumor compresses the nerve, which leads to its damage.
-
Diabetes mellitus. Under the influence of the protein kinase C enzyme, sorbitol and fructose accumulated in the course of the disease begin to break down in nerve tissues. Because of this, as well as because of the violation of the trophism of neurons and their processes, aseptic inflammation of the nerves and surrounding tissues occurs.
 Edema increases, which in turn leads to compression of the nerves, including the median one.
Edema increases, which in turn leads to compression of the nerves, including the median one. -
Acromegaly. As a result of prolonged and intensive growth of a person suffering from acromegaly, processes of disproportionate growth of bone and soft tissues occur. The median nerve can be entrapped in a narrowed carpal tunnel due to increased bone volume and narrowing of its lumen.
-
Congenital malformations . The transverse carpal ligament may be thickened from birth, and there is also poor production of tendon lubrication. One of the factors predisposing to carpal tunnel syndrome can be an anatomical feature of the structure, the so-called "square wrist".
Carpal tunnel symptoms
-
Finger numbness. The syndrome under consideration, as a rule, develops gradually and, in general, the lesion manifests itself unilaterally. Basically, the pathological process occurs in the limb that is leading, for right-handers, the right hand, and for left-handers, the left hand.
 Carpal tunnel syndrome develops gradually. However, a bilateral process can also be observed, with diseases of the endocrine system, pregnancy, etc.
Carpal tunnel syndrome develops gradually. However, a bilateral process can also be observed, with diseases of the endocrine system, pregnancy, etc. -
Paresthesia . Manifested in the form of tingling sensations and loss of sensation in the fingers. Appear in the morning, after waking up and disappear within a few hours. But over time, these manifestations become more stable and intense and may already become permanent. This can lead to a violation of the normal function of the limb: strength, dexterity, etc., the patient has to change hands when performing actions, give rest to the affected limb. Particular inconvenience is caused by manipulations requiring static tension of the limb.
-
Pain. When the disease manifests itself, a burning and tingling sensation may appear in the hand, which is rather quickly eliminated by lowering the limb down and shaking it. The blood flow in the arm resumes, and the pain disappears.
 As a rule, this happens during sleep due to the static position of the hand, or during monotonous work performed by the limb. Pain is not characteristic of any specific joints and is common. With the progression of the disease, pain can cover not only the fingers, but the entire hand and arm up to the elbow joint, which often makes it difficult to make a diagnosis. The patient cannot perform his duties because the pains may occur during the daytime.
As a rule, this happens during sleep due to the static position of the hand, or during monotonous work performed by the limb. Pain is not characteristic of any specific joints and is common. With the progression of the disease, pain can cover not only the fingers, but the entire hand and arm up to the elbow joint, which often makes it difficult to make a diagnosis. The patient cannot perform his duties because the pains may occur during the daytime. -
Loss of dexterity and strength. Over time, if the disease is not treated, the limb begins to lose strength and dexterity in movements. It is difficult for the patient to hold objects in his hands, especially small ones, as if they fall out spontaneously. The ability to perform fine motor skills is lost (grabbing small things, opposing the thumb, etc.).
-
Reduced sensitivity. Over time, the patient may begin to notice that he does not distinguish the temperature of objects well, stops feeling touches or even injections.
 There is a painful burning sensation in the hand, numbness.
There is a painful burning sensation in the hand, numbness. -
Muscle atrophy. In advanced forms of the syndrome, atrophy of the musculoskeletal apparatus of the arm may develop, muscles and ligaments not only lose strength, but also decrease in size. Over time, the brush deforms and takes on a shape resembling a monkey's paw.
-
Skin discoloration. Due to the fact that when the innervation of the hand is disturbed, there is also a violation of the nutrition of skin cells, a change in the color of the skin occurs, they become lighter and unevenly colored.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
For an accurate diagnosis, a consultation with a neurologist is necessary. In this case, the doctor conducts a number of specific tests, and laboratory and instrumental methods of research can also be used.
Tests for carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Tinel test. In the narrowest part of the carpal tunnel, on the side of the palm, when tapping, unpleasant tingling sensations occur.

- Phalen test. Wrist flexed to its maximum for a minute or less causes pain and paresthesia.
- Cuff test. Place the cuff from the blood pressure monitor on the forearm and inflate as much as possible. Within one minute, with a positive test and the presence of the syndrome, a feeling of numbness and tingling appears.
- Raised hands test. The upper limbs are lifted vertically upwards and held in this position for one minute. With a positive result, discomfort appears after 30-40 seconds.
All of the above tests can be done at home, and if you have at least one positive test, be sure to consult a doctor.
Of the instrumental research methods, the following are used:
- electroneuromyography;
- x-ray examinations;
- MRI;
- ultrasound.
To identify the causes of the disease, the patient is prescribed a blood and urine test:
- blood biochemistry;
- blood and urine test for sugar;
- thyroid-stimulating hormone test;
- clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, antistreptolysin-O;
- blood test for circulating immune complexes;
- blood test for antistreptokinase.

Carpal tunnel treatment
The most important thing in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is the observance of measures to prevent the development of the disease. Even with the best and highest quality treatment, preventive measures are indispensable, because the effect may simply not be achieved.
- Preventive measures for carpal tunnel syndrome. When the first signs of the disease occur, it is necessary to firmly fix the hand so that there is no possibility of movement in the joint and, as a result, injury to the nerve. The fixator can be applied by a doctor or, for temporary use, purchase an elastic bandage from a pharmacy. Within two to three weeks, you should avoid activities that aggravate the symptoms of the disease. Also, to reduce swelling, it is recommended to apply cold in the wrist area for 2-3 minutes 2-3 times a day. In the subsequent period, treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the course of the pathological process and its severity.
 If necessary, the treatment is based on the treatment of the underlying disease (traumatic injury, hypothyroidism, diseases of the urinary system, diabetes mellitus, etc.) that causes compression of the nerve in the canal.
If necessary, the treatment is based on the treatment of the underlying disease (traumatic injury, hypothyroidism, diseases of the urinary system, diabetes mellitus, etc.) that causes compression of the nerve in the canal. -
Topical treatment. Includes the use of compresses, the introduction of medicines into the canal cavity. These procedures allow you to quickly ease the painful manifestations and relieve local inflammation.
- Medical therapy. Drug therapy in each case is selected individually depending on the underlying or concomitant disease. In this case, B vitamins, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vasodilators, diuretics, anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants, glucocorticosteroids, antidepressants, etc. are often prescribed.
- Physiotherapy. Can be used both in drug therapy and in the postoperative period during rehabilitation. In this case, they apply: acupuncture; manual therapy techniques; ultraphonophoresis; shock wave therapy.
 Before using physiotherapy procedures, it is necessary to consult a specialist for contraindications.
Before using physiotherapy procedures, it is necessary to consult a specialist for contraindications.
Surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
If for 6 months or more conservative therapy does not give the desired effect, then it makes sense to think about the surgical resolution of the disease. The main task of surgery is to relieve pressure on the median nerve by widening the carpal tunnel.
Most operations are performed under local anesthesia. The following methods are used:
-
Open access: through the incision (5mm) in the area of the carpal tunnel dissect the carpal ligament.
-
Endoscopic surgery. There are two types of endoscopic intervention, through two incisions and through one. In the first case, an endoscope is inserted into one incision, and the ligament is cut into the second instrument. In the second case, both instruments are inserted one hole at a time.
At the end of the surgical intervention, a plaster cast is applied to the arm to immobilize the limb.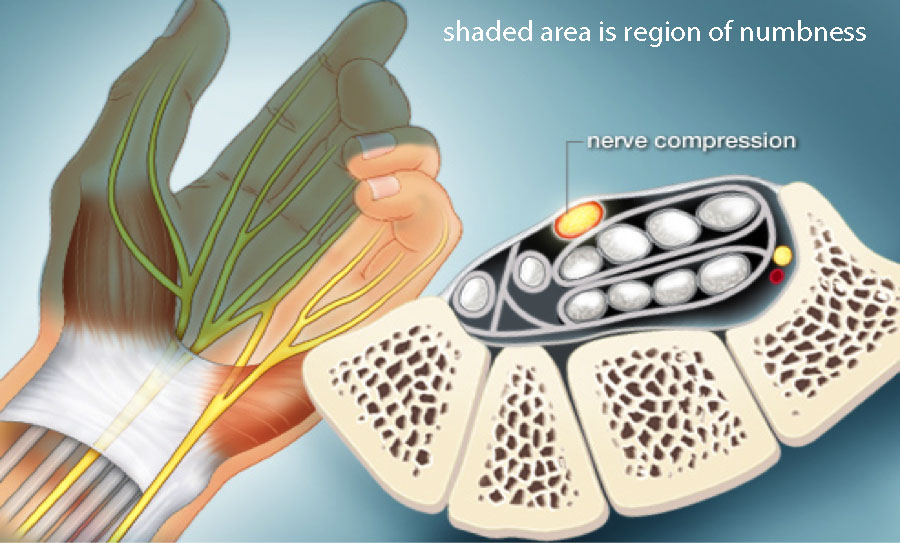 After removing the plaster, a course of physical therapy and physiotherapy is carried out. As a rule, complete restoration of the function of the hand occurs within six months. After recovery, the patient can return to work, subject to the protective regimen, so as not to provoke a relapse of the disease. In the modern world, where computer technology has already been introduced everywhere, the pathology we are considering is becoming more and more common. Timely and qualified assistance, and prevention in the event of carpal tunnel syndrome, allows you to fully and with sufficient persistence achieve remission.
After removing the plaster, a course of physical therapy and physiotherapy is carried out. As a rule, complete restoration of the function of the hand occurs within six months. After recovery, the patient can return to work, subject to the protective regimen, so as not to provoke a relapse of the disease. In the modern world, where computer technology has already been introduced everywhere, the pathology we are considering is becoming more and more common. Timely and qualified assistance, and prevention in the event of carpal tunnel syndrome, allows you to fully and with sufficient persistence achieve remission.
Carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy
02/26/2020
At the end of the second trimester of pregnancy many women suffer from hand numbness. Around the 26th week there is tingling, numbness and pain in the fingers, sometimes extending to the shoulder. This is carpal tunnel syndrome, which in pregnant women is associated with hormonal changes and water retention in the body.
As a result of stagnant fluid, compression of the nerves in the wrist reaches the fingers. The symptoms are worse especially at night. The pain can be so severe that it can wake the woman up or prevent her from getting a good night's sleep. Although carpal tunnel syndrome is a problem and usually resolves spontaneously 2-3 weeks after delivery .
How to deal with hand numbness in pregnant women?
A woman with carpal tunnel syndrome should avoid positions that cause pressure on her arm. Sometimes symptoms come from shaking the numb limb or placing it below the heart line (eg on the knee) or loosely lowering the arm (also during sleep).
People who have symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome should stop tasks that require repeating the same finger and hand movements. They include working on a computer (writing, graphic design), working on a production line, as well as embroidery, crocheting, or even peeling fruits and vegetables.
If it is not possible to completely eliminate these responsibilities, you should schedule frequent breaks. When working on a computer, you can take care of special pillows and ergonomic keyboards that will facilitate the correct positioning of the hand. The position of our body is also important for proper circulation. Avoid Crossbreeding feet and cross-legged positions for prolonged sitting. It is better to rest with your legs up .
Proper Diet
Diet , rich in magnesium and vitamin B6, is useful in preventing and relieving symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. It is worth taking care of a variety of dishes based on poultry, fish, potatoes and milk. Other sources of vitamin B6 include nuts, beans, soybeans, avocados, sunflower seeds, eggs, and bananas. Magnesium deficiency can be supplemented by such foods: parsley, pumpkin seeds, dill, dark chocolate, buckwheat or cocoa.
A woman should also reduce her intake of salt, coffee and tea (not to mention smoking and alcohol!).