Carpal tunnel after baby
Carpal Tunnel Post Pregnancy | Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel post pregnancy is a common condition affecting new mothers. Carpal tunnel post pregnancy occurs due to an increased pressure on your median nerve at your wrist. Symptoms of carpal tunnel post pregnancy can include pins and needles, numbness, tingling, and pain in your arm, hand, and fingers. Your wrist has a space in it called the carpal tunnel. This is where your median nerve and nine tendons pass from your forearm into your hand. Carpal tunnel post pregnancy happens when pressure builds up from swelling in this tunnel. The increase in swelling puts pressure on your nerve, effectively causing a pinched nerve.
Fluid retention during your pregnancy can contribute to carpal tunnel post pregnancy. The fluid retention may disappear soon after your baby is born, however, many women report an increase in carpal tunnel symptoms after delivery. This is caused by continued early postpartum swelling and constant wrist bending required in caring for and feeding your baby. There may multiple contributing factors in you getting carpal tunnel post pregnancy, including arthritis, previous fractures or nerve irritation due to repetitive, prolonged, and/or vigorous wrist movements. In carpal tunnel post pregnancy numbness or tingling is mostly in your thumb, second, middle, and ring fingers. The symptoms are more likely to be experienced during the night but can occur during daily activities such as driving a car or feeding your baby. Postpartum mothers may sometimes notice their grip strength is weaker, some occasional clumsiness or an increased tendency to drop things.
What can you do about Carpal Tunnel Post Pregnancy?
At City Physiotherapy we will perform a thorough assessment of your wrist, symptoms, relevant medical history and body biomechanics. We will then give you treatment and provide you with valuable education and tools to minimise your symptoms. If left untreated, the pressure on your nerves will not magically go away by itself.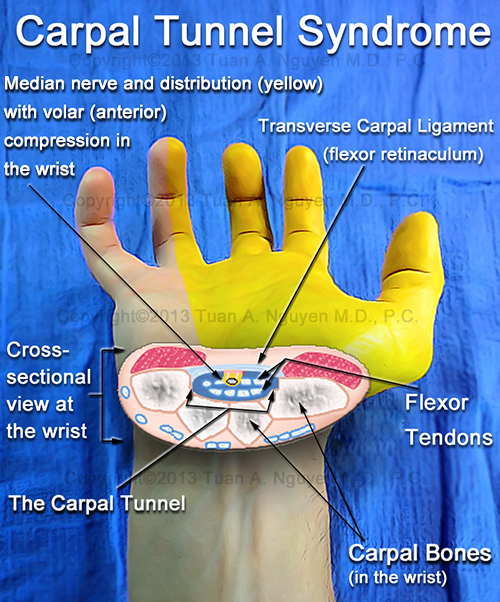 It is imperative to receive treatment as early as possible to help relieve the pressure on your nerve around the carpal tunnel, allowing for the swelling to reduce sooner.
It is imperative to receive treatment as early as possible to help relieve the pressure on your nerve around the carpal tunnel, allowing for the swelling to reduce sooner.
In the meantime you can:
- Try to maintain your wrist in a neutral position (not bent forward or backward) with your daily activities.
- Try using a supportive pillow to prop up your baby during feeding so you aren’t supporting the weight of your baby on your wrist.
- Don’t carry heavy washing baskets or bags of shopping. Try and get others to assist you where possible.
- Avoid a sustained pinch/grip, (ie over gripping cooking utensils when chopping or peeling or pegging out heaving washing such as wet towels and sheets – I find using a drying rack better as you don’t need to peg as much)
- Ensure you take regular rest and stretch breaks from daily activities to prevent overuse
Treatment can vary but may include, posture rehab strengthening exercises, taping or strapping for support, nerve glides, stretching, dry needling and other manual therapies.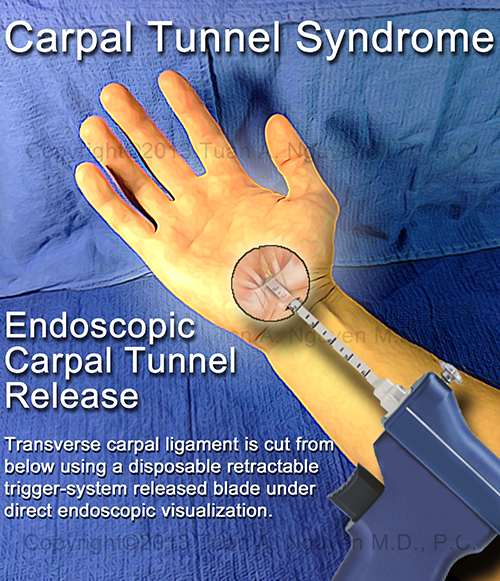 Our Physiotherapists can also fit you with a supportive wrist brace which you can wear during the day and also at night. This can be most helpful to minimise pressure on your median nerve and reduce swelling, which will help your carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms.
Our Physiotherapists can also fit you with a supportive wrist brace which you can wear during the day and also at night. This can be most helpful to minimise pressure on your median nerve and reduce swelling, which will help your carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms.
BACK TO BLOG
Treatment Search
If you know your injury or ailment, search or select from the dropdown list to the right. Alternatively click on the quick link buttons below to find out more.
Enter your injury or ailment
STAY CONNECTED
Follow us to stay connected and keep up to date with the latest physiotherapy, health & wellbeing tips from City Physiotherapy Adelaide.
Something is wrong.
Instagram token error.
Load More
See more on Instagram cityphysiotherapy
City Physiotherapy & Sports Injury Clinic Adelaide
City Physiotherapy & Sports Injury Clinic Adelaide
Postpartum carpal tunnel: Causes and treatment
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Carpal tunnel syndrome – a condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in your wrists and hands – is common during pregnancy and can sometimes linger after you give birth. There are many remedies for postpartum carpal tunnel, including splints, simple exercises, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medicines, and steroid shots. Carpal tunnel usually lets up on its own, but in some cases, you may need a minor surgical procedure to relieve pressure on your nerves. Call your provider right away if you notice sudden swelling in your hands, as this could be a sign of postpartum preeclampsia.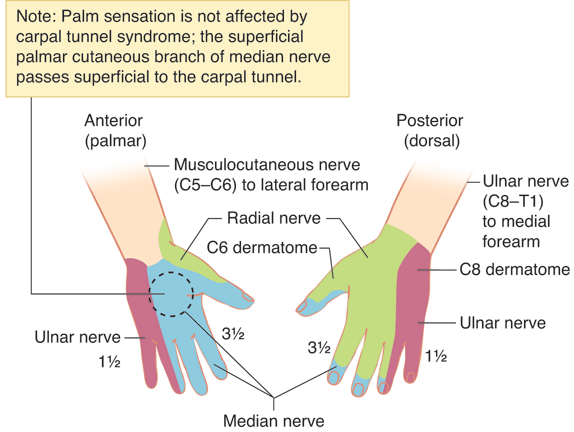
Photo credit: iStock.com / deng qiufeng
What is postpartum carpal tunnel?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in your hands, wrists, and arms. It's common during pregnancy, and sometimes lingers after you give birth, thanks to postpartum swelling that can compress the median nerve in your hand and trigger symptoms. (You can also develop carpal tunnel postpartum even if you didn't have symptoms during pregnancy.)
Research shows that almost 30 percent of pregnant women will develop carpal tunnel in pregnancy – and about 15 percent of moms will still have carpal tunnel a month after giving birth. Some experts believe that risk factors for carpal tunnel may include excessive weight gain during pregnancy and gestational diabetes. Most new moms find that the symptoms resolve on their own within three months, but for some, it can persist and even worsen.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Numbness, tingling, burning, and pain in your thumbs and fingers
- Shock-like sensations that travel down your arms to your thumbs and fingers
- Pain or tingling that shoots up your forearm.
 (The pain is usually worse at night, and can even disturb your sleep.)
(The pain is usually worse at night, and can even disturb your sleep.) - Hand weakness that makes it hard to do things, such as button clothes. You may also find yourself dropping things frequently.
If your hands or wrists ever swell up suddenly, call your healthcare provider right away – especially if the swelling is accompanied by a severe headache, changes in your vision, upper abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting, or shortness of breath. These are all potential symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia, a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is different than De Quervain's tenosynovitis, another common cause of wrist pain after pregnancy. De Quervain's is marked by inflammation of the tendon that runs down your forearm, through your wrist, and to your thumb. Many moms experience symptoms of De Quervain's, which are similar to postpartum carpal tunnel syndrome, since it can develop by overusing your wrist – to hold and feed a newborn, for example.
How to relieve postpartum carpal tunnel
Fortunately, there are many remedies that can help relieve some of the pain associated with postpartum carpal tunnel. Talk to your healthcare provider about what's best, which may include:
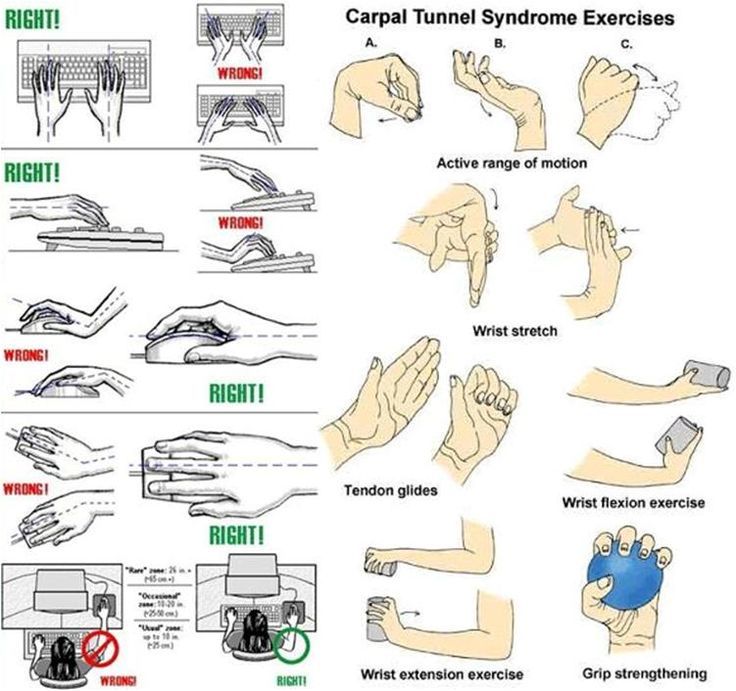
- Bracing or splinting. Wearing a wrist splint or brace works to keep your wrist in a neutral position, which reduces pressure on the median nerve.
- Hand exercises. Your provider may recommend certain exercises and stretches to help the median nerve move more freely within the carpal tunnel and improve range of motion. A short course of physical therapy may also help.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen can help relieve pain and inflammation during the postpartum period, though it's worth noting that they're not recommended during pregnancy. (It's best to talk to your provider before taking any pain medications, especially if you're breastfeeding.
 )
) - Steroid injections. These can temporarily relieve inflammation, and they’re safe for breastfeeding moms. If there's evidence of ongoing nerve damage though, surgery to repair the issue may be necessary.
You may have read that taking a daily dose of vitamin B6 can help alleviate carpal tunnel symptoms, but that's only true if you have a true B6 deficiency. If you're eating a healthy, balanced diet, you're getting the postpartum nutrients and vitamins you need.
Advertisement | page continues below
Will carpal tunnel after pregnancy go away on its own?
It depends. The pain usually goes away gradually as the swelling from pregnancy subsides. But if your carpal tunnel pain still persists even after the swelling resolves, you may need to wear a wrist splint or have a minor surgical procedure to relieve the pressure on your median nerve.
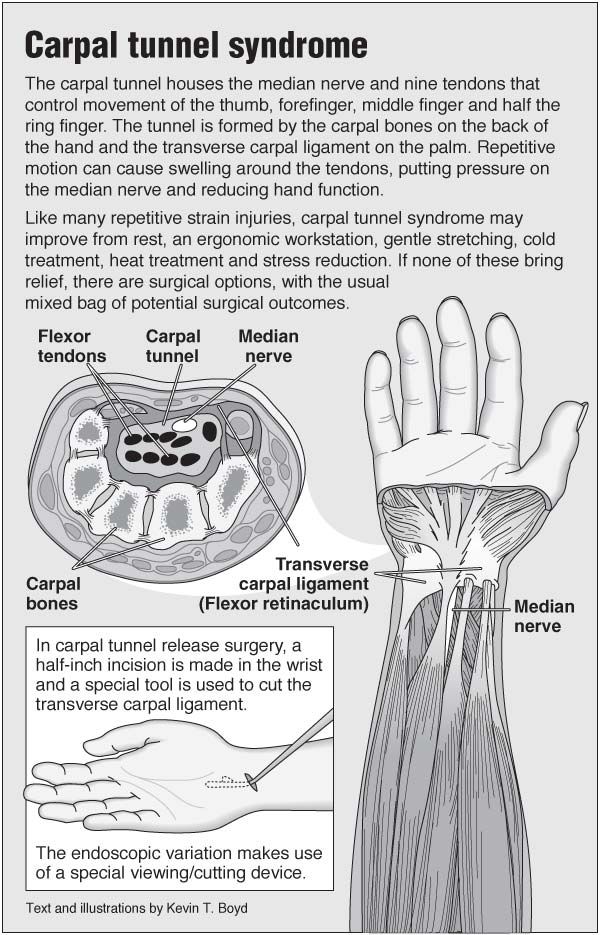
During the procedure, a small incision is made in your palm so the transverse carpal ligament, which pushes into the median nerve as the carpal tunnel swells and prevents it from functioning properly, can be cut.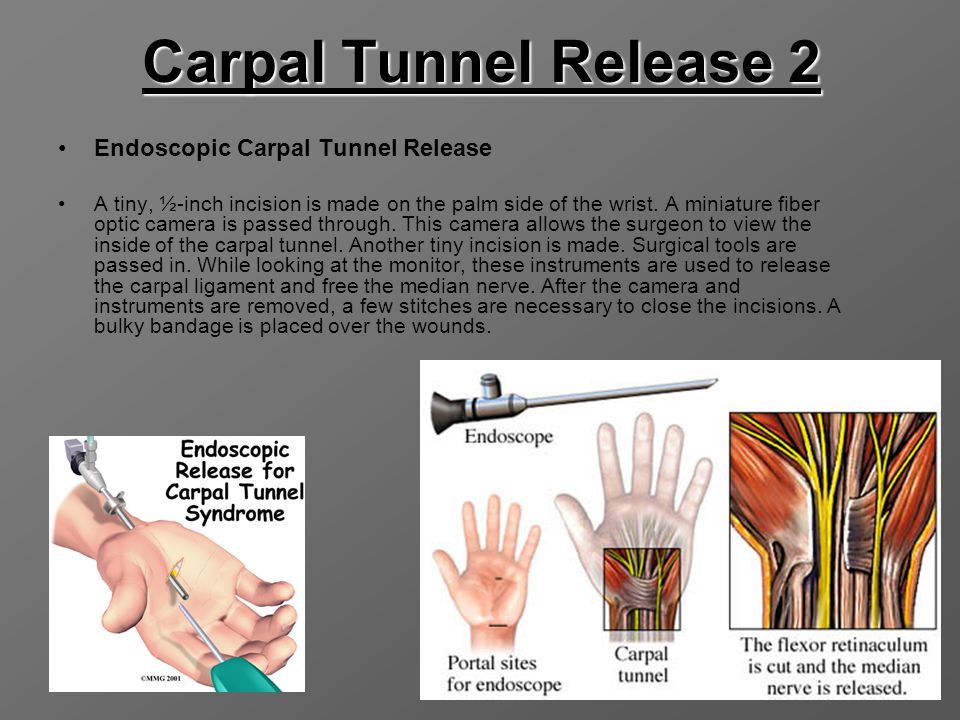 Once the ligament cut is made, pressure is alleviated, allowing the median nerve to do its job. The surgery isn't painful, but recovery can take several weeks.
Once the ligament cut is made, pressure is alleviated, allowing the median nerve to do its job. The surgery isn't painful, but recovery can take several weeks.
Because carpal tunnel can cause nerve damage, it's important to let your healthcare provider know about your pain. Bring it up at your postpartum checkup if you're still feeling soreness or tingles, and they can assess the appropriate next steps.
Read more:
Postpartum warning signs
How long does postpartum recovery last?
How to lose weight after pregnancy the healthy way
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Hallie Levine
Hallie Levine is an award-winning journalist who has covered health and wellness for more than 20 years. She lives with her three children in Fairfield, Connecticut.
Carpal tunnel syndrome - treatment, symptoms, causes, diagnosis
Carpal - this word comes from the Greek Karpos, which means "wrist". The wrist is surrounded by bundles of fibrous tissue, which normally performs a supporting function for the joint.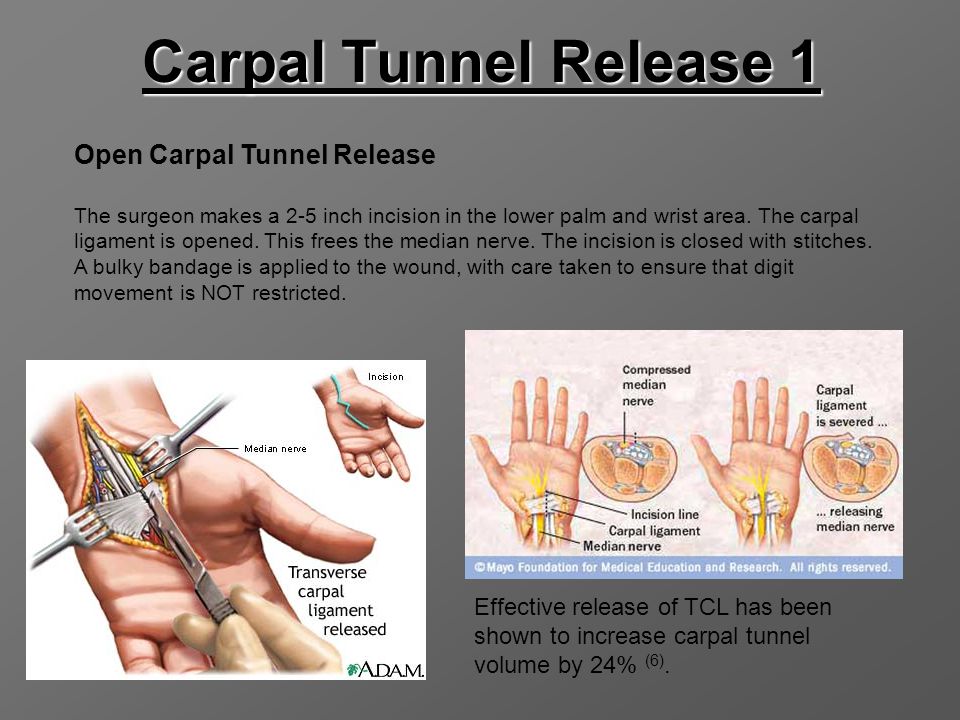 The confined space between these fibrous bands of fibrous tissue and the bony structures of the wrist is called the carpal tunnel. The median nerve, which runs through the wrist, provides sensation to the thumb, index, and middle fingers. Any condition that causes swelling or repositioning of tissues in the wrist can compress and irritate the median nerve. Irritation of the median nerve, in such cases, results in tingling and numbness of the thumb, index, and middle fingers, a condition known as "carpal tunnel syndrome."
The confined space between these fibrous bands of fibrous tissue and the bony structures of the wrist is called the carpal tunnel. The median nerve, which runs through the wrist, provides sensation to the thumb, index, and middle fingers. Any condition that causes swelling or repositioning of tissues in the wrist can compress and irritate the median nerve. Irritation of the median nerve, in such cases, results in tingling and numbness of the thumb, index, and middle fingers, a condition known as "carpal tunnel syndrome."
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Given the limited space of the carpal tunnel, any swelling in this area can put pressure on the median nerve, causing the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. There are many different causes leading to the development of this syndrome, but often the exact cause cannot be determined. Some people initially have an anatomically narrower carpal tunnel, which makes them more at risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. It is believed that this tendency can be genetically determined, and if there are cases of this syndrome in the family, then the likelihood of pressure on the median nerve increases significantly.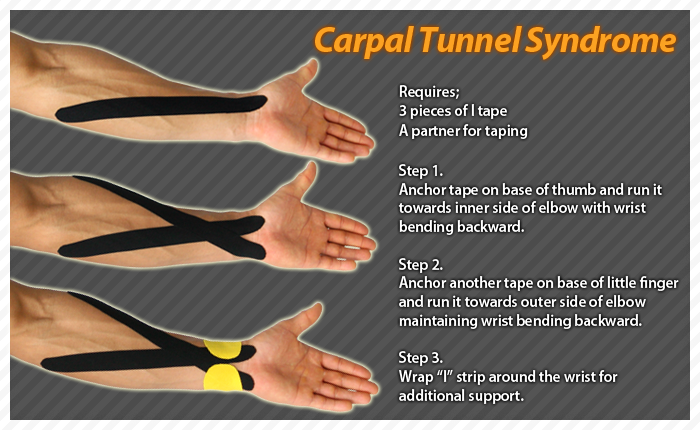 You are also more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if you are overweight, smoke, or drink too much alcohol. The same risk factor is age - the older the person, the higher the likelihood of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Women are more prone to this syndrome than men due to the narrower carpal tunnel. There is also a greater tendency to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if there was a wrist injury (rupture or sprain) or there are diseases such as:
You are also more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if you are overweight, smoke, or drink too much alcohol. The same risk factor is age - the older the person, the higher the likelihood of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Women are more prone to this syndrome than men due to the narrower carpal tunnel. There is also a greater tendency to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if there was a wrist injury (rupture or sprain) or there are diseases such as:
- diabetes mellitus
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- hypothyroidism
It is possible that hormones play a role in the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, as some women develop the syndrome during pregnancy or menopause. Hormones produced during pregnancy can lead to fluid retention, which in turn can cause swelling in the wrist. It is noted that the performance of certain activities can lead to the development of this syndrome. People who do a lot of heavy manual work or repetitive wrist movements, such as on an assembly line or working with their hands in cold temperatures, are also at greater risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.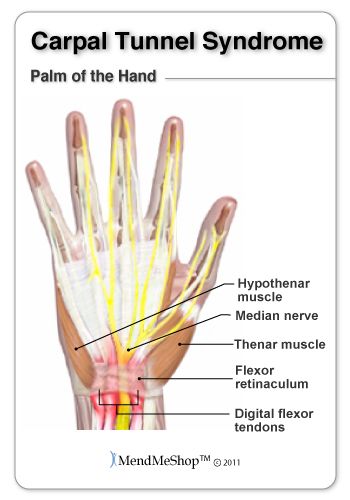 But the probability increases significantly if the load is combined with the presence of systemic diseases.
But the probability increases significantly if the load is combined with the presence of systemic diseases.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
Patients with carpal tunnel syndrome initially feel numbness and tingling in the hand along the median nerve innervation (thumb, index, middle, and part of the fourth fingers). These sensations are often more pronounced at night and may even lead to awakening from sleep. The reason for the worsening of symptoms at night may be due to the flexed position of the wrist during sleep and / or the accumulation of fluid around the wrist and hand while it is in a horizontal position. Carpal tunnel syndrome may be a temporary condition that resolves completely on its own, or symptoms may persist and progress.
As the syndrome progresses, patients may develop a burning sensation and/or spasms and hand weakness. Decreased grip strength can cause objects to fall out of the hand frequently. Sometimes sharp shooting pains can also be felt in the forearm. Chronic carpal tunnel syndrome can also lead to muscle atrophy in the hand, especially the muscles at the base of the thumb on the palmar surface.
Diagnosis
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be diagnosed based on the symptoms and characteristic areas of numbness in the hand. But at the same time, it is often necessary to exclude other possible causes of symptoms that mimic carpal tunnel syndrome. It could be neck, shoulder or elbow problems. The doctor examines the wrist to detect swelling, local temperature increase, tenderness, and discoloration. Sometimes pressing on the front of the wrist can produce a tingling sensation in the hand and is called the Tinel sign, which is characteristic of carpal tunnel syndrome. Symptoms can also be reproduced from time to time with forward flexion of the wrist (called the Phalen symptom). The final diagnosis can be made with ENMG. As a rule, with carpal tunnel syndrome, there is a slowdown in the conduction of a nerve impulse after the nerve passes through the wrist.
Testing of limb muscles, an electromyogram, is sometimes done to rule out or detect other conditions that may mimic carpal tunnel syndrome.
Laboratory tests may be performed in order to diagnose conditions associated with carpal tunnel. These tests include thyroid hormone testing, complete blood counts, blood sugar levels, etc. An x-ray of the hand may also be ordered to check for bony changes (abnormalities in the bones and joints of the wrist). MRI is necessary in cases where it is necessary to visualize changes in ligaments, cartilage.
Treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome
The choice of treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying disease that may be causing the symptoms.
In the first stage, treatment usually includes rest, immobilization of the wrist in a brace, and sometimes local cold. If the patient's profession is associated with a load on the wrist, then it is necessary to change activities for a while. In addition, it is possible to improve the ergonomics of the workplace, for example, you can adjust the computer keyboard and chair height and optimize the load on the hands. These measures, along with occasional periods of rest and wrist stretching, can actually prevent the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, which are caused by repetitive excessive motion of the wrist, from developing. If there are systemic diseases or injuries, then individual treatment of these diseases is carried out. In case of fractures, orthopedic correction (gypsum, orthosis) may be required. Overweight patients should be advised to reduce weight. In rheumatoid arthritis, specific treatment of the inflammatory autoimmune process is carried out. Swelling of the wrist, which may be associated with pregnancy, disappears after the birth of the child.
Medications
Several types of medications can be used to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is often prescribed in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome, and although the mechanism of therapeutic action is not entirely clear, nevertheless, many doctors note a certain effect of using this drug. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may also be helpful in reducing inflammation and reducing pain. But these drugs have side effects and therefore it is necessary to take this into account when prescribing them. Corticosteroids may also be used. They can be given orally or by injection into the affected wrist joint. Corticosteroids can lead to a rapid improvement in symptoms, but the side effects of these drugs prevent their use for a long time and in the presence of certain conditions (for example, in diabetes mellitus, their use may lead to a worsening of the condition). They should also not be used in the presence of infections. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy and acupuncture also provide a certain therapeutic effect. Most patients with carpal tunnel syndrome can be treated with conservative therapy. But sometimes chronic pressure on the median nerve can lead to permanent numbness and weakness. In order to avoid serious and permanent nerve and muscle damage, surgical treatment may be recommended in such cases.
Surgical intervention consists in excising the tissue that puts pressure on the median nerve. This surgical procedure is called carpal tunnel release. Currently, such an operation can be performed using endoscopic techniques, which allows for minimal tissue trauma and rapid restoration of nerve conduction. After surgical treatment, it is necessary to use exercise therapy to restore hand function.
Prognosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
Complications of carpal tunnel syndrome are rare and include atrophy and weakness of the muscles at the base of the thumb in the palm of the hand. This can become a permanent disorder if not treated on time. Such atrophy disrupts the motor skills of the hand and the performance of certain movements. As a rule, the prognosis for carpal tunnel syndrome is positive and it is possible to cure it conservatively or surgically.
Pregnancy carpal tunnel syndrome
26.02.2020
At the end of the second trimester of pregnancy many women suffer from hand numbness. Around the 26th week there is tingling, numbness and pain in the fingers, sometimes extending to the shoulder. This is carpal tunnel syndrome, which in pregnant women is associated with hormonal changes and water retention in the body.
As a result of stagnant fluid, compression of the nerves in the wrist reaches the fingers. The symptoms are worse especially at night. The pain can be so severe that it can wake the woman up or prevent her from getting a good night's sleep. Although carpal tunnel syndrome is a problem and usually resolves spontaneously 2-3 weeks after delivery .
How to deal with hand numbness in pregnant women?
A woman with carpal tunnel syndrome should avoid positions that cause pressure on her arm. Sometimes symptoms come from shaking the numb limb or placing it below the heart line (eg on the knee) or loosely lowering the arm (also during sleep).
People who have symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome should stop tasks that require repeating the same finger and hand movements. They include working on a computer (writing, graphic design), working on a production line, as well as embroidery, crocheting, or even peeling fruits and vegetables.
If it is not possible to completely eliminate these responsibilities, you should schedule frequent breaks. When working on a computer, you can take care of special pillows and ergonomic keyboards that will facilitate the correct positioning of the hand. The position of our body is also important for proper circulation. Avoid Crossbreeding feet and cross-legged position for prolonged sitting. It is better to rest with legs up .
Proper Diet
Diet , rich in magnesium and vitamin B6, is helpful in preventing and relieving symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. It is worth taking care of a variety of dishes based on poultry, fish, potatoes and milk. Other sources of vitamin B6 include nuts, beans, soybeans, avocados, sunflower seeds, eggs, and bananas.