Can you have mozzarella cheese when pregnant
Can You Eat Mozzarella in Pregnancy? Isn’t It a Soft Cheese?
If you’re a cheese lover, the recommendation to avoid certain soft cheeses during pregnancy may feel downright demoralizing. No mold-ripened Roquefort, no fresh Camembert, no imported gorgonzola? What’s a cheese-ophile to do?
With some soft cheeses a no-go for 9 months, you may wonder if you can drown your sorrows in some stretchy mozzarella — only to hear buzz that fresh mozz might also be unsafe in pregnancy.
Fortunately, there’s good news about your favorite pizza cheese. As long as it’s made from pasteurized milk, mozzarella (even the softer fresh variety) is almost universally safe for you to eat while pregnant.
Keep reading for the lowdown on including it in your diet during pregnancy.
Remember your science lesson about pasteurization from way back when? Pasteurization is a process of heating foods — dairy products in particular — to temperatures high enough to kill pathogens.
Because pasteurization virtually eliminates harmful bacteria, mozzarella made from pasteurized milk is fine to consume during pregnancy, both cooked and in its fresh, uncooked form.
Read food labels carefully to be sure any mozzarella you purchase is made with pasteurized milk. Or, if dining out, don’t be afraid to ask questions about the origins of the cheese in your pasta or salad.
If it’s been pasteurized, you’re good to dig in.
Choosing pasteurized mozzarella is critical because the risks of eating soft cheese in pregnancy come down to one offending bacteria in particular: listeria. When unpasteurized or raw milk is used to make soft cheeses, listeria has more opportunity to grow and potentially cause infection.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), listeriosis (the bacterial infection caused by listeria) is especially serious in pregnancy.
When you’re pregnant, you’re 10 times more likely than other people to get a listeria infection, and the infection can spread to babies in utero. Serious complications can result, including miscarriage, stillbirth, preterm labor, and even death in newborns.
Beyond concerns of pasteurization, use your senses to assess the safety of any questionable cheese (you know, the hunk that’s been sitting in your fridge for ages).
If the mozzarella has a foul odor or any visible mold, don’t eat it. Especially during pregnancy, it’s smart to follow the old food spoilage adage: When in doubt, throw it out.
Believe it or not, the list of soft cheese to avoid during pregnancy is actually pretty short.
As long as cheese isn’t mold-ripened and is made with pasteurized milk, you’re in the clear to enjoy tons of delicious cheeses, including the following:
- feta
- ricotta and cottage cheese
- cream cheese
- paneer
- havarti
- halloumi
- Parmesan
- pecorino
- Romano
- cheddar
- Swiss
We don’t typically think of cheese as a health food, but mozzarella actually provides a number of nutritional benefits.
For one thing, its star nutrient, calcium, is a key player in bone health. Your body also funnels calcium to your unborn baby, helping them grow bones and teeth.
It’s recommended that if you’re over the age of 18, you should consume 1,000 milligrams (mg) of calcium per day during pregnancy.
Teens who are pregnant need 1,300 mg per day. With 200 mg per 1-ounce serving, mozzarella can provide a substantial chunk of this mineral.
Mozzarella also shines in its high protein content of 7 grams (g) per 1-ounce serving.
While the current recommended dietary allowance for protein is just 0.8 g per kilogram (kg) body weight (0.35 grams per pound or g/lb), you need more protein when pregnant.
Researchers suggest about 1.2 g of protein per 1 kg body weight (0.54 g/lb) during early pregnancy and about 1.5 g/kg (0.68 g/lb) during the later stages of pregnancy.
A serving of mozz will contribute to protein’s many functions during pregnancy, including creating breast and uterine tissue, increasing your blood supply, and promoting the growth of your baby’s brain.
As cheeses go, mozzarella is a relatively low-sodium option, with approximately 7 percent of your daily value per ounce. If you’re on a low-sodium diet due to preeclampsia or other concerns, a bit of the stretchy stuff can be a smart choice for satisfying that cheese craving.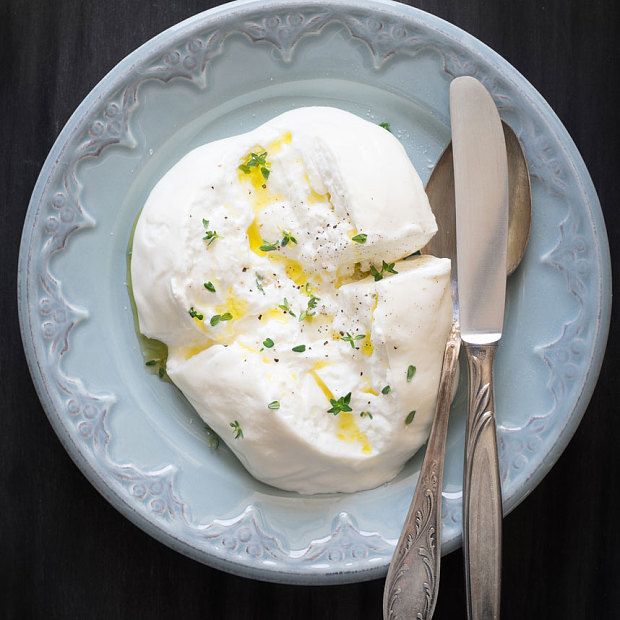
Meanwhile, as a nutrient-dense food, mozzarella is an easy go-to for fulfilling your extra calorie allotment during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
And as that stick of string cheese fuels your own healthy weight gain, it might help your baby’s, too.
Studies from 2012 and 2019 showed a positive association between milk and dairy consumption during pregnancy and greater infant birth weight and length.
Like all full-fat dairy, cheese does have more than its fair share of saturated fat.
Whole milk mozzarella contains 4 g of saturated fat per ounce (about 20 percent of the daily value), and even part-skim mozzarella contains 3 g (16 percent of the daily value) per 1-oz serving.
Since saturated fat has been associated with health issues like heart disease and weight gain, you may have concerns about this cheese’s healthfulness. But keep in mind that you need healthy fat sources like cheese during pregnancy.
And intriguingly, some studies have indicated that not all saturated fat is created equal. Recent research indicates that whole foods like cheese may have protective health effects, despite their saturated fat content.
Recent research indicates that whole foods like cheese may have protective health effects, despite their saturated fat content.
One 3-week study found that full-fat dairy foods didn’t adversely affect blood cholesterol, glucose, or insulin levels. (Note that this study was funded by the Danish Dairy Research Foundation.)
Another study even showed that eating more cheese led to reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
As always, talk to your doctor if you have concerns about your diet during pregnancy.
Adding a bit of mozzarella to your pregnancy diet is simple! Try these healthy, low-prep snacks:
- Pair mozzarella slices with a handful of whole wheat crackers or a piece of fresh fruit.
- Make a caprese salad by drizzling balsamic vinegar over sliced mozzarella, tomatoes, and basil leaves.
- Spread marinara sauce on a whole wheat English muffin half. Sprinkle with shredded mozzarella and bake at 400 degrees for 8–10 minutes — you have yourself an easy pizza!
With all the foods off the menu during pregnancy, isn’t it nice to know you can still enjoy the gooey stretch and salty flavor of mozzarella?
Opt for cheese made with pasteurized milk and you’re in the clear to enjoy this savory favorite in pizza, pasta, and cheesy dips.
Can You Eat Mozzarella in Pregnancy? Isn’t It a Soft Cheese?
If you’re a cheese lover, the recommendation to avoid certain soft cheeses during pregnancy may feel downright demoralizing. No mold-ripened Roquefort, no fresh Camembert, no imported gorgonzola? What’s a cheese-ophile to do?
With some soft cheeses a no-go for 9 months, you may wonder if you can drown your sorrows in some stretchy mozzarella — only to hear buzz that fresh mozz might also be unsafe in pregnancy.
Fortunately, there’s good news about your favorite pizza cheese. As long as it’s made from pasteurized milk, mozzarella (even the softer fresh variety) is almost universally safe for you to eat while pregnant.
Keep reading for the lowdown on including it in your diet during pregnancy.
Remember your science lesson about pasteurization from way back when? Pasteurization is a process of heating foods — dairy products in particular — to temperatures high enough to kill pathogens.
Because pasteurization virtually eliminates harmful bacteria, mozzarella made from pasteurized milk is fine to consume during pregnancy, both cooked and in its fresh, uncooked form.
Read food labels carefully to be sure any mozzarella you purchase is made with pasteurized milk. Or, if dining out, don’t be afraid to ask questions about the origins of the cheese in your pasta or salad.
If it’s been pasteurized, you’re good to dig in.
Choosing pasteurized mozzarella is critical because the risks of eating soft cheese in pregnancy come down to one offending bacteria in particular: listeria. When unpasteurized or raw milk is used to make soft cheeses, listeria has more opportunity to grow and potentially cause infection.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), listeriosis (the bacterial infection caused by listeria) is especially serious in pregnancy.
When you’re pregnant, you’re 10 times more likely than other people to get a listeria infection, and the infection can spread to babies in utero. Serious complications can result, including miscarriage, stillbirth, preterm labor, and even death in newborns.
Beyond concerns of pasteurization, use your senses to assess the safety of any questionable cheese (you know, the hunk that’s been sitting in your fridge for ages).
If the mozzarella has a foul odor or any visible mold, don’t eat it. Especially during pregnancy, it’s smart to follow the old food spoilage adage: When in doubt, throw it out.
Believe it or not, the list of soft cheese to avoid during pregnancy is actually pretty short.
As long as cheese isn’t mold-ripened and is made with pasteurized milk, you’re in the clear to enjoy tons of delicious cheeses, including the following:
- feta
- ricotta and cottage cheese
- cream cheese
- paneer
- havarti
- halloumi
- Parmesan
- pecorino
- Romano
- cheddar
- Swiss
We don’t typically think of cheese as a health food, but mozzarella actually provides a number of nutritional benefits.
For one thing, its star nutrient, calcium, is a key player in bone health. Your body also funnels calcium to your unborn baby, helping them grow bones and teeth.
It’s recommended that if you’re over the age of 18, you should consume 1,000 milligrams (mg) of calcium per day during pregnancy.
Teens who are pregnant need 1,300 mg per day. With 200 mg per 1-ounce serving, mozzarella can provide a substantial chunk of this mineral.
Mozzarella also shines in its high protein content of 7 grams (g) per 1-ounce serving.
While the current recommended dietary allowance for protein is just 0.8 g per kilogram (kg) body weight (0.35 grams per pound or g/lb), you need more protein when pregnant.
Researchers suggest about 1.2 g of protein per 1 kg body weight (0.54 g/lb) during early pregnancy and about 1.5 g/kg (0.68 g/lb) during the later stages of pregnancy.
A serving of mozz will contribute to protein’s many functions during pregnancy, including creating breast and uterine tissue, increasing your blood supply, and promoting the growth of your baby’s brain.
As cheeses go, mozzarella is a relatively low-sodium option, with approximately 7 percent of your daily value per ounce. If you’re on a low-sodium diet due to preeclampsia or other concerns, a bit of the stretchy stuff can be a smart choice for satisfying that cheese craving.
Meanwhile, as a nutrient-dense food, mozzarella is an easy go-to for fulfilling your extra calorie allotment during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
And as that stick of string cheese fuels your own healthy weight gain, it might help your baby’s, too.
Studies from 2012 and 2019 showed a positive association between milk and dairy consumption during pregnancy and greater infant birth weight and length.
Like all full-fat dairy, cheese does have more than its fair share of saturated fat.
Whole milk mozzarella contains 4 g of saturated fat per ounce (about 20 percent of the daily value), and even part-skim mozzarella contains 3 g (16 percent of the daily value) per 1-oz serving.
Since saturated fat has been associated with health issues like heart disease and weight gain, you may have concerns about this cheese’s healthfulness. But keep in mind that you need healthy fat sources like cheese during pregnancy.
And intriguingly, some studies have indicated that not all saturated fat is created equal. Recent research indicates that whole foods like cheese may have protective health effects, despite their saturated fat content.
Recent research indicates that whole foods like cheese may have protective health effects, despite their saturated fat content.
One 3-week study found that full-fat dairy foods didn’t adversely affect blood cholesterol, glucose, or insulin levels. (Note that this study was funded by the Danish Dairy Research Foundation.)
Another study even showed that eating more cheese led to reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
As always, talk to your doctor if you have concerns about your diet during pregnancy.
Adding a bit of mozzarella to your pregnancy diet is simple! Try these healthy, low-prep snacks:
- Pair mozzarella slices with a handful of whole wheat crackers or a piece of fresh fruit.
- Make a caprese salad by drizzling balsamic vinegar over sliced mozzarella, tomatoes, and basil leaves.
- Spread marinara sauce on a whole wheat English muffin half. Sprinkle with shredded mozzarella and bake at 400 degrees for 8–10 minutes — you have yourself an easy pizza!
With all the foods off the menu during pregnancy, isn’t it nice to know you can still enjoy the gooey stretch and salty flavor of mozzarella?
Opt for cheese made with pasteurized milk and you’re in the clear to enjoy this savory favorite in pizza, pasta, and cheesy dips.
Is it possible to eat mozzarella cheese during pregnancy? – Drink-Drink
If you are a cheese lover, the recommendation to avoid certain soft cheeses during pregnancy can seem downright demoralizing. No ripe Roquefort mold, no fresh Camembert, no imported Gorgonzola? What should a syrophila do?
Since some soft cheeses are banned for 9 months, you may wonder if you can drown your sorrows in some stretchy mozzarella — only to hear rumors that fresh mozzar might also be unsafe during pregnancy.
Luckily, there is good news about your favorite pizza cheese. If mozzarella (even the softer fresh variety) is made from pasteurized milk, it is almost always safe for pregnant women.
Continue reading to find out how to include it in your diet during pregnancy.
What's safe when it comes to mozzarella during pregnancy
Remember your science lesson about pasteurization? Pasteurization is the process of heating food, particularly dairy products, to a temperature high enough to kill pathogens.
Since pasteurization virtually destroys harmful bacteria, mozzarella made from pasteurized milk can be consumed during pregnancy both cooked and fresh, raw.
Read food labels carefully to make sure the mozzarella you buy is made from pasteurized milk. Or, if you're dining out, don't be afraid to ask questions about the origin of the cheese in your pasta or salad.
If it's been pasteurized, you can dig.
What to avoid when eating mozzarella during pregnancy
The choice of pasteurized mozzarella is critical because the risk of eating soft cheese during pregnancy comes down to one harmful bacterium in particular: Listeria. When unpasteurized or raw milk is used to make soft cheeses, Listeria have more room to grow and potentially cause infection.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), listeriosis (a bacterial infection caused by listeria) is especially dangerous during pregnancy.
When you are pregnant, you are 10 times more likely to get listeria than other people, and the infection can spread to your children in utero. This can lead to serious complications, including miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth, and even death of the newborn.
This can lead to serious complications, including miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth, and even death of the newborn.
Pasteurization issues aside, use your senses to assess the safety of any questionable cheese (you know, the piece that's been sitting in your fridge for ages).
If the mozzarella has an unpleasant odor or any visible mold, do not eat it. Especially during pregnancy, it's wise to follow the old adage about food spoilage: when in doubt, throw it away.
Similar cheeses to avoid during pregnancy
Believe it or not, the list of soft cheeses to avoid during pregnancy is actually quite short.
As long as the cheese is not moldy and made from pasteurized milk, you can enjoy a variety of delicious cheeses, including the following:0040
Health benefits of mozzarella cheese for you and your baby during pregnancy .
First, its main nutrient, calcium, plays a key role in bone health.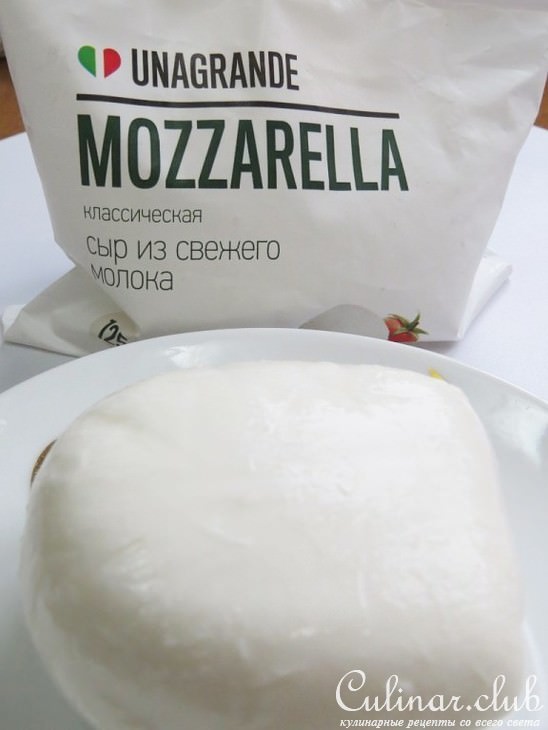 Your body also sends calcium to your unborn child, helping him grow bones and teeth.
Your body also sends calcium to your unborn child, helping him grow bones and teeth.
If you are over 18, it is recommended that you consume 1,000 milligrams (mg) of calcium per day during pregnancy.
Pregnant teenagers need 1,300 mg per day. With 200 mg per 1 ounce serving, mozzarella can provide a significant portion of this mineral.
Mozzarella is also high in protein, with 7 grams (g) per 1 ounce serving.
While the current recommended dietary allowance for protein is only 0.8 g per kilogram (kg) of body weight (0.35 g per pound or g/lb), you need more protein during pregnancy.
Researchers suggest about 1.2 g of protein per kg of body weight (0.54 g/lb) in early pregnancy and about 1.5 g/kg (0.68 g/lb) in later pregnancy.
A serving of mozza will contribute to many of the functions of protein during pregnancy, including building breast and uterine tissue, increasing blood supply, and stimulating the growth of your baby's brain.
When it comes to cheeses, mozzarella is a relatively low sodium option, around 7 percent of your daily value per ounce. If you're on a low-sodium diet due to preeclampsia or other issues, some stretchy foods may be a smart choice to satisfy those cheese cravings.
If you're on a low-sodium diet due to preeclampsia or other issues, some stretchy foods may be a smart choice to satisfy those cheese cravings.
Meanwhile, mozzarella, as a nutritious food, easily replenishes your extra calories in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
And because this cheese stick helps you increase your own healthy weight, it can help your baby too.
Studies from 2012 and 2019 showed a positive association between milk and dairy consumption during pregnancy and higher birth weight and height.
Other Considerations When Eating Mozzarella Cheese During Pregnancy
As with all full-fat dairy products, cheese is higher in saturated fat.
Whole milk mozzarella contains 4 grams of saturated fat per ounce (about 20 percent DV), and even partially skimmed mozzarella contains 3 g (16 percent DV) per 1 ounce serving.
Since saturated fat has been linked to health problems such as heart disease and weight gain, you may have concerns about the health benefits of this cheese. But keep in mind that during pregnancy you eat healthy sources of fat like cheese.
But keep in mind that during pregnancy you eat healthy sources of fat like cheese.
And interestingly, some studies have shown that not all saturated fats are the same. Recent research suggests that whole foods like cheese may have a protective effect on health despite their saturated fat content.
one 3-week study found that high-fat dairy products did not adversely affect blood cholesterol, glucose, or insulin levels. (Please note that this study was funded by the Danish Dairy Research Foundation.)
Another study even showed that eating more cheese leads to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
As always, talk to your doctor if you have concerns about diet during pregnancy.
Mozzarella Maternity Healthy Snacks
Adding some mozzarella to your maternity diet is easy! Try these healthy, minimal-prep snacks:
- Pair mozzarella slices with a handful of whole grain crackers or a piece of fresh fruit.
- Make a caprese salad by drizzling chopped mozzarella, tomatoes and basil leaves with balsamic vinegar.

- Spread half a whole wheat English muffin with the marinara sauce. Sprinkle with grated mozzarella and bake at 400 degrees for 8-10 minutes - light pizza is ready!
Bottom line
With all the foods off the menu during pregnancy, isn't it nice to know that you can still enjoy the sticky and salty taste of mozzarella?
Opt for cheese made from pasteurized milk and you can enjoy this savory favorite on pizza, pasta and cheese sauces.
What kind of cheese can you eat during pregnancy?
Mozzarella, brie, goat cheese, mascarpone. Sometimes cheeses are a tasty and healthy substitute for pickles during pregnancy. But how useful?
Experts advise against cheese made from raw milk, as it may contain listeria monocytogenes, which is dangerous for the baby. In the worst case, infection leads to premature birth, miscarriage, or intrauterine death before birth. Fortunately, this doesn't happen often.
Why is cheese good for pregnancy?
Cheese is rich in calcium, vitamins B12 and D. Calcium is essential for the formation of a child's bone mass. Vitamin D ensures proper absorption of calcium. Most types of cheese contain 25% of the daily value of calcium for a serving of 200 grams.
Calcium is essential for the formation of a child's bone mass. Vitamin D ensures proper absorption of calcium. Most types of cheese contain 25% of the daily value of calcium for a serving of 200 grams.
Which cheese is forbidden during pregnancy: raw milk cheese
As a rule, such cheeses are not found on store shelves, but if there is any doubt about the origin of the product, consult the seller. Be wary of softer varieties such as Brie, Roquefort and Camembert, as well as blue cheeses.
When you can't refuse cheese made from raw milk, consumption after heat treatment is acceptable, bacteria die when heated from 85 degrees Celsius.
Did you accidentally eat this cheese? The chance of being infected with the Listeria bacterium is very small. The first signs of infection are similar to the manifestations of the flu, consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and receive timely treatment.
Which cheese to choose during pregnancy: pasteurized
Pasteurized milk undergoes a rapid heat treatment at the factory, this is enough to deprive the product of all harmful bacteria. Thus, during pregnancy, you can eat mature hard cheeses, such as parmesan, cheddar, dutch. Other cheeses safe during pregnancy:
Thus, during pregnancy, you can eat mature hard cheeses, such as parmesan, cheddar, dutch. Other cheeses safe during pregnancy:
- Pasteurized soft cheeses: camembert, brie, cream brie, mozzarella.
- All pasteurized blue cheeses.
- Goat cheese. Listeria is rarely found in goat cheese, probably due to a certain substance in the composition. Hard goat cheese is safer than soft goat cheese. Reheating goat cheese in the oven certainly makes it safe.
If the cheese is made from raw milk, this must be stated on the packaging.
Mozzarella during pregnancy
Mozzarella is officially a raw milk cheese. Therefore, many women wonder if it is possible to eat it during pregnancy. Usually supermarket mozzarella is safe.
This cheese is warm enough that there is no risk of listeria infection. Please check the packaging before purchasing. If the product is pasteurized, it can be eaten as usual.
Would you like a mozzarella salad? Specify what milk it is based on: pasteurized or cheese. If it is a heated form, such as for pizza, you can eat it without worry.
If it is a heated form, such as for pizza, you can eat it without worry.
Is it possible to eat goat cheese
There are different types of goat cheese: hard and soft. The solid version is made from pasteurized milk. Soft goat cheese is not always safe during pregnancy as it contains raw milk where bacteria can breed.
Cheese fondue during pregnancy
Would you like a delicious cheese fondue? It's possible. The cheese is heated, which kills the bacteria. Just in case, go to a cheese shop and indicate that you are pregnant, the sellers will make sure that the grated cheese is safe for you. Remember the dangers of alcohol, which should not be on your menu.
Hard cheeses
For reference, 95 percent of all hard cheeses - whether made from pasteurized milk or not - can be considered safe to eat during pregnancy. According to nutrition experts, hard cheeses don't contain as much water as soft cheeses, making it harder for bacteria to survive. The following hard cheeses are safe to eat:
The following hard cheeses are safe to eat:
- Parmesan cheeses
- Pecorino but hard look
- Gruyere
- Cheddar
- Gouda Cheese
- Emmental
- Edam
- Dutch Farm Cheese
- Manchego.
All soft pasteurized cheeses
Below is a list of soft cheeses made from pasteurized milk.
- feta
- Cream cheese
- Ricotta
- Soft cheese
- Specially prepared cheese spread.
Cheesecake during pregnancy
Can I eat cheesecake while pregnant? Cheesecake is usually made with monchou or cream cheese. This cheese is pasteurized and can be eaten as usual, but be aware of the amount of sugar so as not to harm your health.
Cheese consumption during pregnancy: table
| Which cheese is unsafe? | Raw milk hard and soft cheeses such as camembert, brie, gorgonzola, mozzarella, soft goat cheese, roquefort Other dairy products made from raw milk, such as yogurt or cottage cheese. |
| Why not? | Listeria monocytogenes may be present because raw milk is not heated. |
| How can you eat these foods? | Raw milk is safe after boiling. You can also eat raw milk cheeses after they have been properly heated, for example in a baking dish. |
| What is generally safe? | All pasteurized cheeses not containing raw milk. Pasteurized milk, any milk in the supermarket. |
Share with your friends in any way convenient for you!
Related posts
Threatened miscarriage in early pregnancy: symptoms and causes
Miscarriage is a spontaneous spontaneous abortion due to natural causes before the 20th week of fetal development. There are many factors leading to pregnancy loss, sometimes the cause remains unknown even to specialists. Miscarriage before 12 weeks…
Share with your friends in any way convenient for you!
How to count fetal movements and when to worry
What should you know about movements? What should alert or, on the contrary, reassure? Before counting the movements of the fetus, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the basic concepts, this information will help you avoid unnecessary worries.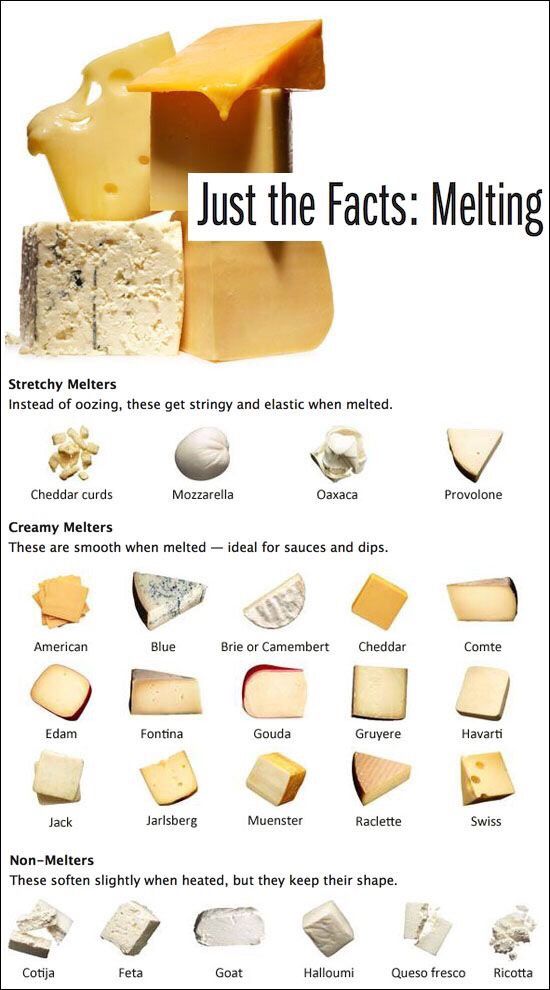 When a baby…
When a baby…
Share with your friends in any way convenient for you!
Pregnancy after 30: what expectant mothers need to know
The age when a woman first becomes a mother is getting closer and closer to 30-35 years, this is due to a number of reasons - career, starting a family after 25, lack of own housing ....
Share with your friends in any way convenient for you!
Amnioscopy during pregnancy: how to do it, indications
Amnioscopy is a study to assess the color and amount of amniotic fluid. For this purpose, an amnioscope is inserted into the woman's cervical canal and the doctor makes a diagnosis based on his observations. How amnioscopy is done ...
Share with your friends in any way convenient for you!
Weekly rate of amniotic fluid, value for the fetus
Amniotic fluid is involved in the metabolism of the child and protects him from injury, and their study helps to identify deviations from the norm.