Can you have a pap smear while pregnant
Pap smears are safe – before, during and after pregnancy | Women's Health | Your Pregnancy Matters
×
What can we help you find?Refine your search: Find a Doctor Search Conditions & Treatments Find a Location
Appointment New Patient Appointment
or Call214-645-8300
MedBlog
Women's Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
August 3, 2021
Women's Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
Yetunde Awosemusi, M. D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
Pregnancy induces changes in your body and your mind. Many mothers-to-be experience anxiety, which can lead some to second-guess their most routine medical procedures. While this mindset is understandable, one thing you can definitely cross off your “worry list” is the myth that Pap smears are not safe during pregnancy.
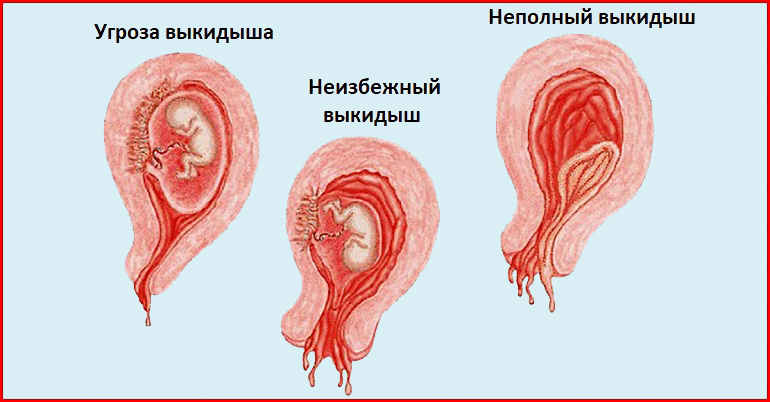
It is normal to experience some spotting after a Pap smear, even when you are pregnant. However, this natural response has caused some misconceptions that the Pap smear, a potentially life-saving procedure, isn’t safe during pregnancy.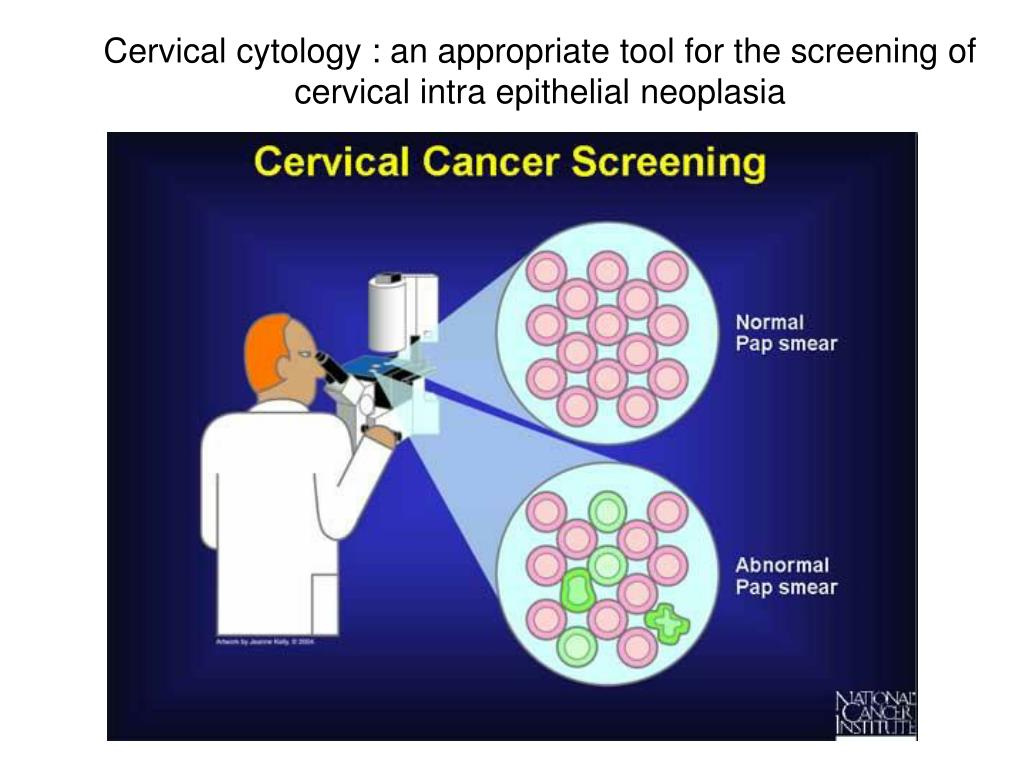
The truth is that getting a Pap smear is safe for you and your baby; it will not cause a miscarriage.
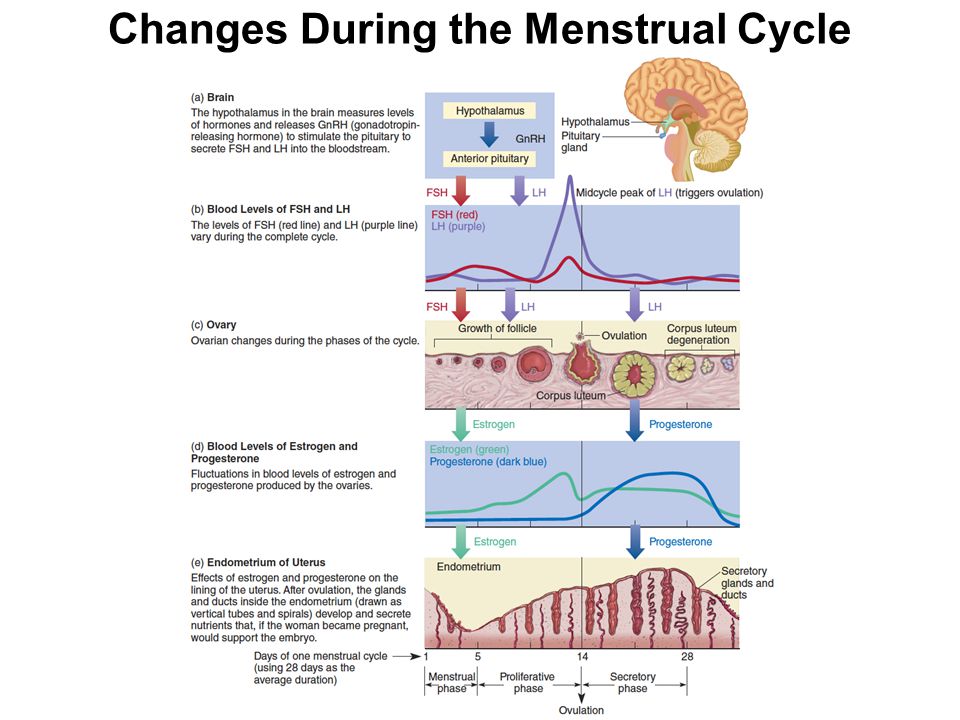
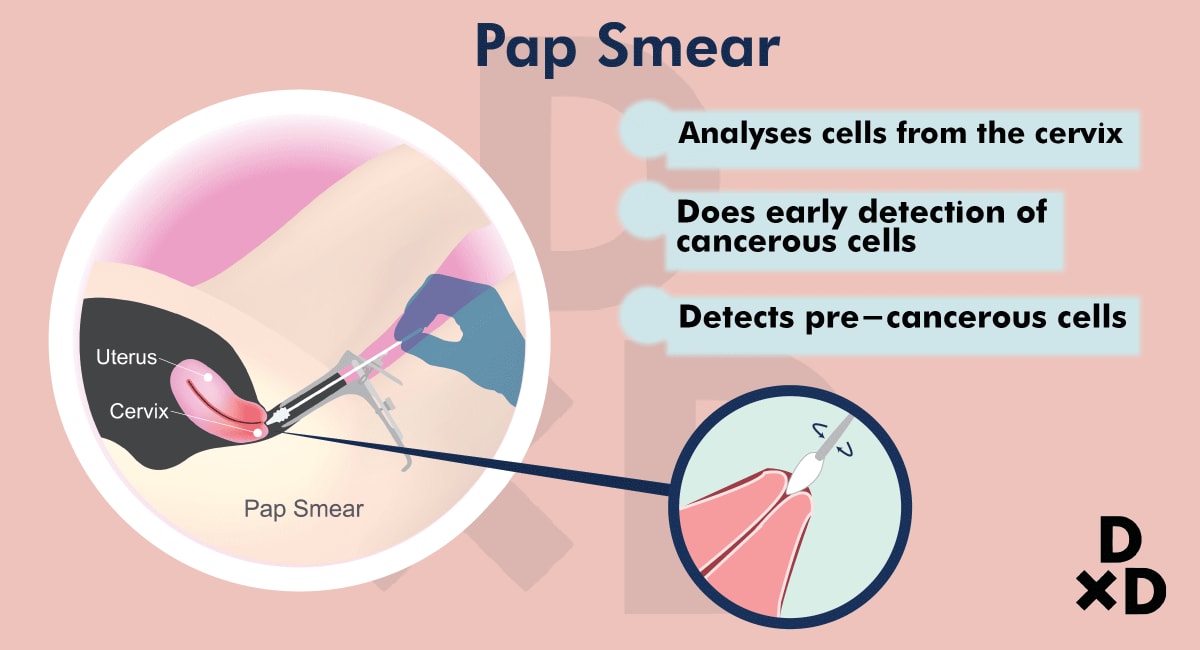
Whether you’re pregnant or not, the Pap smear is the gold standard for screening for cervical cancer. It allows us to collect cells from the surface of the cervix and examine them for abnormalities.
Cervical cancer and abnormal Pap smear results are almost always caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted disease currently infecting around 80 million people in the United States. Though the virus is common, the likelihood of it causing cancer is much less common. In fact, most infections go away on their own. Cancer develops when the infection isn’t detected and managed appropriately, which is why Pap smears are so important.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that cervical cancer deaths have decreased over the last several decades as a result of increased Pap smears. If you follow up on your Pap smear results as recommended by your provider, we almost always will catch the cancer.
What’s even more encouraging is that the HPV vaccine, which the CDC recommends for all children ages 11 or 12, can prevent cervical cancer from developing. We still recommend routine Pap smears for people who receive the vaccine, but we are finding very low rates of abnormal Pap smears within this vaccinated population.
As more people recognize the importance of regular Pap smears, questions about the procedure continue to swirl. We’ve answered the most common ones below.
How often should I get a Pap smear?
We recommend a Pap smear every three years for women between the ages of 21 and 30. If your results are normal and you are negative for HPV, you can extend that to every five years from ages 31 to 65. Higher-risk populations, such as people who have an autoimmune disease, should discuss more frequent testing with their provider.
Do I need a Pap smear when I’m pregnant?
Reviewing your Pap smear history is an early, important step during prenatal care. If you received a normal test result within the last three years, you likely don’t need a Pap smear while pregnant.
If you received a normal test result within the last three years, you likely don’t need a Pap smear while pregnant.
We realize, however, that many newly pregnant people are seeing a doctor for the first time in quite a while – maybe their first time ever as an adult – and haven’t had a Pap smear before, or for several years. To support a healthy pregnancy, we want to rule out the possibility of cervical cancer development as soon as possible.
If I do need one, is it safe?
Pap smears while pregnant are safe for you and your baby. Any suggestion that it might cause a miscarriage is false. It is normal to experience minor bleeding after a Pap smear when you are pregnant because blood flow to the uterus increases, which causes the cervix to bleed more easily when touched.
Any type of bleeding is understandably alarming while pregnant, but in this case the blood is coming from the outside of your cervix – not inside the uterus, where the baby is safe and developing.
What happens if I have an abnormal Pap smear?
The next step may be to perform a colposcopy, which allows us to look more closely at the cervix and take a small tissue sample to test the abnormal cells for cancer. The colposcopy is safe during pregnancy – the only cells we touch are on the outside of the cervix, not the inside near your baby.
Generally, we divide these test results into what we call low-grade or high-grade “dysplasia” – the existence of abnormal cells:
- Low-grade dysplasia doesn’t usually progress to cancer, so we just watch it and will likely encourage you to come back in a year for another Pap smear.
- High-grade dysplasia has an increased chance of progressing to cancer, so we will likely recommend a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) after delivery.
LEEP removes the outside portion of the cervix containing the abnormal cells, and it can increase the risk of pregnancy complications like preterm birth or losing the baby in the second trimester. Because cervical cancer is a slow-growing disease, we can usually postpone the procedure until after delivery and watch the area closely, performing a colposcopy every trimester to monitor the dysplasia’s progress.
Because cervical cancer is a slow-growing disease, we can usually postpone the procedure until after delivery and watch the area closely, performing a colposcopy every trimester to monitor the dysplasia’s progress.
Pregnancy weakens the immune system, which can increase the likelihood of abnormal results, so sometimes the high-grade dysplasia resolves itself after pregnancy. If it does progress to cancer, we will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that incorporates your specific health conditions and needs. As an academic medical center, we can streamline your access to some of the best oncologists in the U.S., right here at UT Southwestern.
If you need a Pap smear, it is safe to get one during pregnancy. Along with the HPV vaccine, Pap smear is a vital tool that helps make cervical cancer preventable – and it will give you one less thing to worry about as you prepare for the healthy birth of your baby.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn or certified nurse-midwife, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
More in: Women's Health, Your Pregnancy Matters
Men's Health; Prevention; Women's Health
- Safia Khan, M.D.
- Zaiba Jetpuri, D.O.
December 28, 2022
Women's Health
- Patrick M.
 Weix, M.D., Ph.D.
Weix, M.D., Ph.D.
December 8, 2022
Plastic Surgery; Women's Health
- Abby Culver, M.D.
- Christine Carman Stiles, M.D.
December 5, 2022
Women's Health
- Maude Carmel, M.
 D.
D.
October 17, 2022
Men's Health; Women's Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Yair Lotan, M.D.
September 6, 2022
Pediatrics; Women's Health
- Nirupama DeSilva, M.
 D.
D. - Jason Jarin, M.D.
August 31, 2022
Women's Health
- Abey Eapen, M.D., Ph.D.
August 18, 2022
Men's Health; Women's Health
July 26, 2022
Prevention; Women's Health
- Andrea Jochim, M.
 D., Ph.D.
D., Ph.D.
July 25, 2022
More Articles
Pap Smear During Pregnancy - Why You Need One, Myths, Side Effects
If you’ve been getting your annual well visits at the gyno (as you should be), you’re likely well familiar with Pap smears, which look for abnormal changes on your cervix and can indicate a human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, pre-cancerous cells, or even cervical cancer.
If you’re pregnant, you may be wondering if it’s safe to get Pap smears during pregnancy as part of your OB visits, especially if you’ve come across conflicting information online. Here are all the facts on Paps during pregnancy.
Current American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologist guidelines recommend women ages between the ages of 21 and 29 have a Pap smear every three years. Women ages 30 to 65 should have a Pap smear and HPV test every five years, or a Pap test alone every three years.
Women ages 30 to 65 should have a Pap smear and HPV test every five years, or a Pap test alone every three years.
If you've previously had an abnormal result from a cervical screening test, or haven't had a screening test in the last three to five years, you may need to have a screening test while pregnant, says Jodie Horton, MD, an ob-gyn in Oakton, Virginia, and chief wellness advisor for Love Wellness. This will usually happen at your first prenatal visit, along with other prenatal labs and blood tests. However, it is otherwise not a standard practice to get one during the first trimester. “Your doctor will follow the same cervical screening test guidelines regardless if you are pregnant or not,” she says.
If needed, the Pap test will normally be done early in pregnancy because it is a way to help detect any abnormal cells and if they are found early on, they can be treated, adds Jessica Shepherd, MD, a minimally invasive gynecologist in Dallas.
“Pap tests don’t cause any harm to a fetus and are a normal part of the gynecological visits for pregnant women,” she says.
How is a Pap smear during pregnancy done?Whether you're pregnant or not, a Pap test is performed when your health care provider puts a metal or plastic instrument called a speculum into your vagina, separating its walls so that they can get to your cervix. They then use a small spatula or brush (also called a sampler) to gently swab cells from your cervix, which are later sent to a lab to be tested. If you’re over 30, your doctor will also sample cells to test for the most common high-risk types of HPV that are responsible for abnormal cell changes and cervical cancer.
Related Stories
- What Is A Doula, And Do You Need One?
- What Is Implantation Bleeding?
- Does Pregnancy Change Your Poop?
“If [you’re found to] have severely abnormal cells of the cervix [beforehand], it is always best to discuss the treatment plan before getting pregnant,” says Dr. Horton. “Some treatments of high-grade abnormalities of the cervix involve removal of part of the cervix but this is generally not recommended during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary.”
Horton. “Some treatments of high-grade abnormalities of the cervix involve removal of part of the cervix but this is generally not recommended during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary.”
The Pap test is not performed any differently in pregnancy, as it is not invasive and only swabs cells from the outside part of the cervix, Dr. Shepherd says. “There may be some extra spotting or light bleeding due to the cervix being a little bit inflamed and fragile in pregnancy, but this is not dangerous,” she says.
Wait, what happens if your Pap smear comes back as abnormal during pregnancy?“If the results of your Pap smear come back abnormal, don’t panic—this does not mean that you have cancer,” says Dr. Horton.
If a pregnant woman has a Pap smear that comes back with abnormal results, the health care provider will recommend further testing options that are safe to perform during pregnancy, says Dr. Shepherd. These options may include repeating the Pap in a year, or getting another test called a colposcopy, which uses a small magnifying instrument to look at the cervix after applying a vinegar solution to highlight any abnormal areas.
Shepherd. These options may include repeating the Pap in a year, or getting another test called a colposcopy, which uses a small magnifying instrument to look at the cervix after applying a vinegar solution to highlight any abnormal areas.
Colposcopies are commonly done with a biopsy to remove a small tissue sample at the same time. While it’s safe to perform a biopsy during pregnancy, your doctor will likely opt to wait until after you deliver, instead monitoring with frequent colposcopies throughout the rest of your pregnancy. Your doctor may opt to do an initial biopsy during your second trimester if a colposcopy showed any abnormalities, says Dr. Horton.
“Cervical cancer is slow-growing and generally will not progress during the pregnancy or affect the pregnancy,” says Dr. Horton. “Based on a biopsy or evaluation during the colposcopy, a follow-up Pap and colposcopy are typically done six weeks or more after giving birth. If cervical cancer is diagnosed at the time of colposcopy, the doctor will discuss treatment options.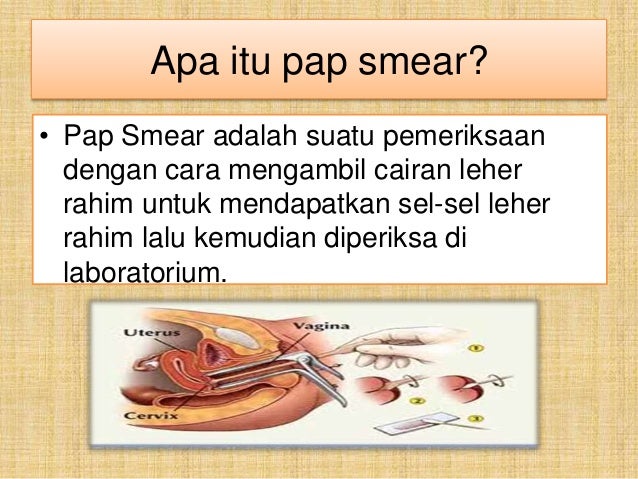 ”
”
You may have come across rampant rumors that Pap smears during pregnancy can cause miscarriage or lead to other complications. Experts want you to know that not only is there *no* truth there, but there are also no risks associated with getting a Pap smear during pregnancy. In fact, there are risks if you don’t catch an infection or health issue that a Pap may help detect.
Fifteen to 20 percent of all pregnancies end in miscarriage, and 80 percent of those miscarriages occur in the first trimester, notes Dr. Horton. “While you may have some light spotting after a Pap smear because of the increased blood flow to the uterus and cervix to support a growing baby, this is not always an indication that a miscarriage is going to happen. If a miscarriage happens, this is just a coincidence and not a consequence of the Pap smear.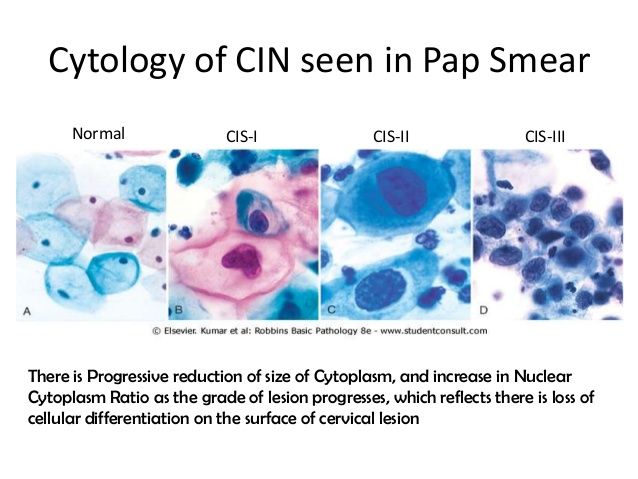 ”
”
The bottom line? If you need a Pap smear during pregnancy, a Pap test is completely safe during pregnancy and will not hurt your baby. "The most important message is that this test saves lives and should be looked at as very crucial to both the health of a mother and her baby," says Dr. Shepherd.
Emilia Benton
Emilia Benton is a Houston-based freelance writer and editor. In addition to Women's Health, she has contributed health, fitness and wellness content to Runner's World, SELF, Prevention, Healthline, and POPSUGAR, among other publications. She is also a 10-time marathoner, frequent traveler and avid amateur baker.
Flora smear during pregnancy - when and why to take it
- When to take a flora smear
- What a flora smear shows
- Flora smear preparation rules
The flora smear is the most common test prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist. To conduct this study, the doctor, while examining a woman in a gynecological chair, takes the contents of the vagina from the posterior fornix (this is the space that is located between the back wall of the vagina and the cervix), the cervical canal and the discharged urethra, applies the material to the glass slide and directs him to the lab. nine0012
nine0012
Smear examination for flora in the laboratory is carried out by a doctor of laboratory diagnostics under a microscope. This study allows you to determine the nature of the microflora (types of microorganisms) of the vagina, cervical canal and urethra, to identify the inflammatory process in the genitals of a woman, in some cases it also allows you to determine the causative agent of this inflammatory process (for example, gonococcus, Trichomonas).
When to take a smear for flora
It is mandatory for all pregnant women to take a swab twice - at registration and at 30 weeks of pregnancy, often another swab for flora is taken at 36-37 weeks to assess the state of the vaginal microflora before childbirth. During these periods, the analysis is given even in cases where the patient is not bothered by anything. This is carried out in order to identify a hidden inflammatory process that can lead to serious complications during pregnancy. During pregnancy, due to changes in hormonal levels and a decrease in immunity, exacerbation of chronic infections, as well as candidiasis (thrush), is much more likely. Any inflammatory process in the vagina during pregnancy can lead to serious complications of pregnancy - premature rupture of amniotic fluid, premature birth, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, intrauterine growth retardation and others. nine0013
Any inflammatory process in the vagina during pregnancy can lead to serious complications of pregnancy - premature rupture of amniotic fluid, premature birth, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, intrauterine growth retardation and others. nine0013
If a pregnant woman has complaints - the appearance of copious discharge from the genital tract, itching, burning or discomfort in the genital area, a swab for flora is also taken. In some pathological conditions, for example, in the presence of past miscarriages associated with infectious complications of pregnancy, cervical incompetence, a smear for flora is taken once a month, and after 30 weeks once every two weeks. Smear sampling is an absolutely safe procedure and does not lead to any complications, therefore it can be performed at any stage of pregnancy. nine0013
Learn more about the services:
- Pregnancy tests
What a flora smear shows
A flora smear is evaluated according to the following indicators:
Epithelium
Squamous epithelium is the cells of the surface layer of the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. The presence of a large amount of squamous epithelium in a smear may indicate an inflammatory process. The absence of epithelium in the smear indicates a violation of the hormonal background. nine0013
The presence of a large amount of squamous epithelium in a smear may indicate an inflammatory process. The absence of epithelium in the smear indicates a violation of the hormonal background. nine0013
Leukocytes
These are blood cells involved in the destruction of pathogenic bacteria. Leukocytes are able to actively penetrate through the wall of blood vessels into the tissues of the body and participate in the fight against infectious agents. Normally, no more than 10 leukocytes are present in a smear for flora from the vagina, no more than 15 leukocytes per field of view from the cervical canal, and up to 2 leukocytes per field of view from the urethra. An increase in the content of leukocytes in a smear is a sign of inflammation, while the higher the content of leukocytes in a smear, the more pronounced the inflammatory process. nine0013
Erythrocytes
These are red blood cells. Normally, single erythrocytes (1-2 in the field of view) can be found in a flora smear. An increase in the number of red blood cells indicates the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, and also be a sign of injury or occult bleeding, for example, in the presence of cervical ectopia (the so-called erosion, when the vaginal part of the cervix is covered with a cylindrical epithelium normally lining the inside of the cervix).
An increase in the number of red blood cells indicates the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, and also be a sign of injury or occult bleeding, for example, in the presence of cervical ectopia (the so-called erosion, when the vaginal part of the cervix is covered with a cylindrical epithelium normally lining the inside of the cervix).
Slime
Normally, there is no mucus in the urethra, a moderate amount of mucus is detected in the vagina, and there may be a large amount of mucus in the cervix. An increase in the amount of mucus may be a sign of an inflammatory process, but this criterion does not have great diagnostic value, and doctors rarely rely on it when making a diagnosis.
Bacteria
Normally, flora should not be detected in the urethra, rod flora is detected in a moderate amount in the vagina and cervix. Rod flora is most often lactobacilli, which are 95% are normal vaginal biocenosis. Lactobacilli actively colonize the vagina and create an acidic environment in it, thereby preventing the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria.
In addition to lactobacilli, other rod bacteria, such as E. coli, bacteroids, and various cocci, may also be present in the vagina. These are bacteria that, under microscopy, have the shape of balls. This group of bacteria includes streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci. In a small amount, they are normally present in the vagina. If their number increases sharply against the background of the death of normal lactobacilli, this can lead to the development of an inflammatory process. Unfortunately, according to the results of a routine smear on the flora, it is impossible to determine which specific bacteria and in what quantity are present in the vagina. Therefore, with a pronounced inflammatory process, as well as when a large amount of coccal flora is found in a smear on the flora, the doctor prescribes an additional analysis to make the correct diagnosis - sowing on the flora with the determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. nine0013
Opportunistic flora
These are micro-organisms that live in the human body in small numbers without causing harm, but under certain conditions can lead to an inflammatory process. Such microorganisms found in a smear on the flora include fungi of the genus Candida and gardnerella.
Such microorganisms found in a smear on the flora include fungi of the genus Candida and gardnerella.
Gardnerella ("key cells")
Gardnerella and other bacteria living in anoxic conditions (so-called anaerobic bacteria) normally live in the vagina in small numbers, without causing symptoms of an inflammatory process. With a decrease in local immunity, which is quite common during pregnancy, there is an increase in the proportion of these bacteria in the vaginal microflora, a disease occurs - bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis). At the same time, “key” cells are found in a smear on the flora - these are cells of the vaginal mucosa, covered with gardnerella and other anaerobic bacteria. The gardnerella themselves are not visible in a normal unstained smear. They can only be detected by staining smears with special dyes. nine0013
Mushrooms
Microorganisms of the genus Candida are part of the normal microflora of the mouth, vagina and colon of most healthy people.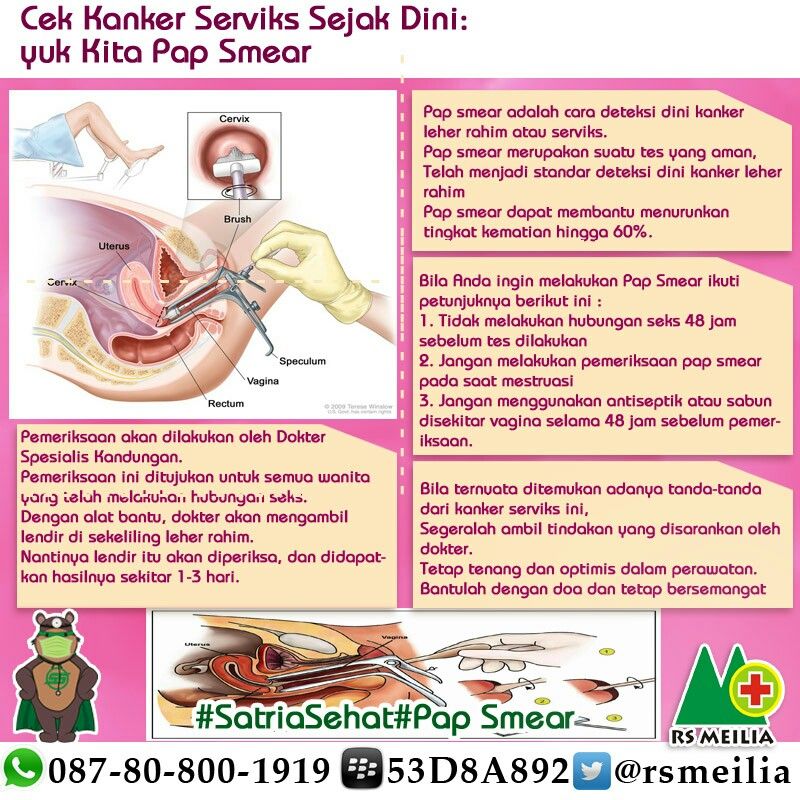 Normally, the number of these microorganisms is small and they do not cause an inflammatory process. Normally, in some women, a small amount of spores of the fungus may be detected in a vaginal smear. In the absence of an inflammatory reaction and complaints of the patient, the treatment of this condition is not carried out. The detection of a large number of spores or mycelium of a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida in a smear on the flora makes it possible to diagnose candidiasis (or thrush)
Normally, the number of these microorganisms is small and they do not cause an inflammatory process. Normally, in some women, a small amount of spores of the fungus may be detected in a vaginal smear. In the absence of an inflammatory reaction and complaints of the patient, the treatment of this condition is not carried out. The detection of a large number of spores or mycelium of a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida in a smear on the flora makes it possible to diagnose candidiasis (or thrush)
Pathogenic flora
There are microorganisms that should not normally be present in the vagina of a healthy woman and the detection of which in a flora smear indicates the presence of a serious sexually transmitted disease. Of these infections in the smear, Trichomonas and gonococci are most often detected.
Trichomonas
These are the simplest microorganisms that have a flagellum and are capable of movement. Detection in a smear on the flora of Trichomonas indicates the presence of a sexually transmitted disease - trichomoniasis. Trichomoniasis in a pregnant woman increases the risk of preterm birth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, intrauterine growth retardation. In addition, there is a risk of infection of the baby when passing through the birth canal, therefore, if Trichomonas is found in a smear, antibacterial treatment is mandatory during pregnancy. nine0013
Trichomoniasis in a pregnant woman increases the risk of preterm birth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, intrauterine growth retardation. In addition, there is a risk of infection of the baby when passing through the birth canal, therefore, if Trichomonas is found in a smear, antibacterial treatment is mandatory during pregnancy. nine0013
Gonococci
These are bacteria that look like double bean-shaped balls in the smear, adjacent to each other with a concave side. Detection of gonococci in a smear allows the doctor to make a diagnosis - gonorrhea. This is a sexually transmitted disease, which must also be cured during pregnancy. The inflammatory process caused by gonococcus significantly complicates the course of pregnancy, can lead to miscarriage, premature birth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, infection of the placenta and membranes, and in addition, when the baby passes through the birth canal, the eyes of the newborn are affected by gonococcus. nine0013
Detection of pathogens of other sexually transmitted infections in a smear on the flora is very difficult.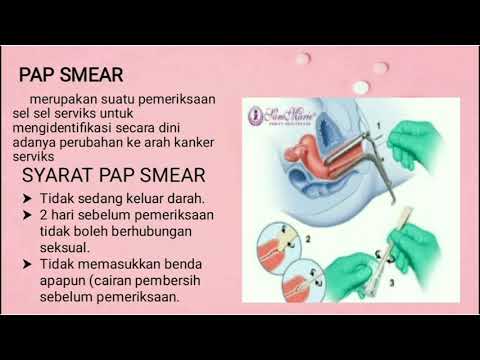 Therefore, in the presence of an inflammatory process according to the smear, the doctor usually recommends testing for sexual infections by another, more sensitive method - a PCR smear.
Therefore, in the presence of an inflammatory process according to the smear, the doctor usually recommends testing for sexual infections by another, more sensitive method - a PCR smear.
Rules for preparation for taking a smear for flora
In order for the result of a smear for flora to be reliable, a number of important conditions must be observed before taking this analysis. Within 2-3 days, you can not use any vaginal suppositories or creams, douching with any solutions is contraindicated, since they change the composition of the vaginal microflora, making it difficult to identify the causative agent of inflammation. In addition, within 2 days it is desirable to refrain from sexual intercourse. This is also due to the fact that spermatozoa and residual semen in the vagina can lead to an incorrect smear result for flora. nine0013
Flora smear during pregnancy
The most informative and most popular test among gynecologists is the flora smear. During this study, the doctor takes material from the urethra, from the walls of the vagina or from the cervical canal. The test sample is applied to glass, which is then sent to the laboratory. A laboratory assistant under a microscope using reagents conducts a qualitative and quantitative analysis. The analysis does not pose a threat and does not cause complications. nine0013
The test sample is applied to glass, which is then sent to the laboratory. A laboratory assistant under a microscope using reagents conducts a qualitative and quantitative analysis. The analysis does not pose a threat and does not cause complications. nine0013
When and how to prepare
Generally pregnancy tests include a vaginal flora swab at registration and at 30 weeks. According to the indications, the doctor may prescribe additional studies of the vaginal microflora later. Monthly, and after the 30th week twice a month, a smear is taken from patients with a history of miscarriages of infectious etiology.
Pregnancy changes the hormonal status, resulting in exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes. In turn, inflammation can cause complications, up to the threat of miscarriage. An extraordinary smear is given in case of heavy discharge that has an unpleasant odor, burning or discomfort in the reproductive organs. Pap smear on vaginal flora after childbirth in Odessa is a prerequisite before discharge.
Pap smear on vaginal flora after childbirth in Odessa is a prerequisite before discharge.
Vaginal flora is 95% lactobacilli (look like rods under a microscope). The remaining 5% are E. coli, bacteroids, streptococci (have the shape of balls). If the balance of rod and ball bacteria is disturbed, an inflammatory process occurs. It is impossible to determine the growth of which "ball" bacteria caused the shift. In this case, the doctor prescribes an additional study - sowing on the flora. nine0013
Where to take tests in Odessa during pregnancy, including a smear for flora? Artmediuz Medical and Diagnostic Center offers a full range of tests. The delivery of a smear is accompanied by several simple requirements that will make the analysis more informative:
- Exclude sexual contact two days before the analysis.
- Do not douche, do not take a bath for a day (shower only).
- Do not use vaginal suppositories and creams for 2-3 days.
 nine0004
nine0004 - When taking material from the urethra, do not urinate for 2-3 hours.
What a smear tells you
In addition to quantitative indicators, a smear tells you about the degree of cleanliness of the vagina (from 1 to 4). Only the first and second are considered the norm. The main indicators by which the doctor evaluates the smear are:
- Squamous epithelium , the norm is 5-10 cells. Exceeding the allowable indicators indicates an inflammatory process. Indicators below the norm indicate hormonal disorders. nine0004
- Leukocytes , normal up to 10 (in the uterus - up to 30). These are white immune cells, they protect the body from pathogens. A slight increase in this indicator is shown by tests after childbirth .
- Red blood cells , acceptable value 1-3. Exceeding the norm indicates the presence of an inflammatory process, hidden bleeding or erosion of the cervix.