Best ways to sleep during pregnancy
How to Sleep Better While Pregnant
Sleep deprivation is an inevitable reality for new parents. Unfortunately for most, sleep troubles start before the baby is even born. Fluctuating hormones, changing body systems, and stress levels fuel a host of physiological shifts that can compromise sleep during pregnancy in unique ways. Research indicates that virtually all pregnant women experience frequent nighttime awakenings, with significant numbers reporting insomnia, poor sleep quality, and excessive daytime fatigue during all three trimesters.
Sufficient shut-eye is critical for both developing babies and mothers. Sleep deprivation during gestation has been associated with longer, more painful labors, higher cesarean rates, and increased levels of inflammation. Inadequate sleep may also increase the risk of preterm birth and postpartum depression, excess pregnancy weight gain, and contribute to elevated body mass index and high blood pressure in the newborn.
There are many strategies for mitigating sleep disruptors and getting the rest that you and your baby need.
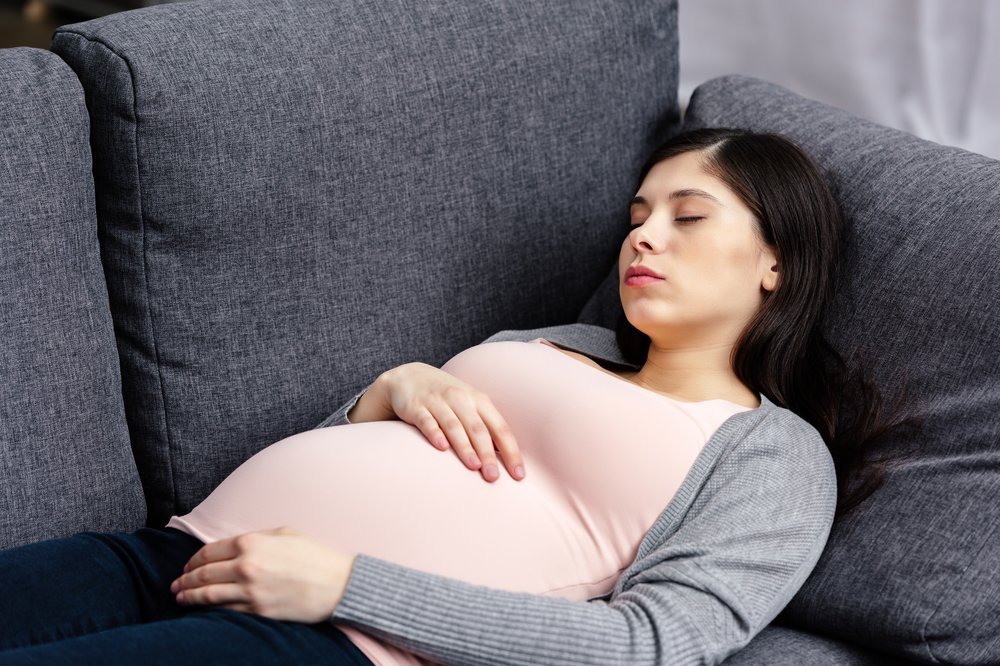
Find a Comfortable Position
As the unborn baby grows larger, a pregnant woman might have difficulty finding a comfortable sleeping position. Expectant mothers should be aware some experts advise to avoid sleeping flat on their back, which can compress the inferior vena cava and decrease oxygen to the placenta.
Pregnant women are frequently most comfortable sleeping on their side with bent knees, which promotes healthy circulation. Most doctors recommend sleeping on the left side specifically, as this position is thought to protect the liver and increase blood flow to the heart, fetus, uterus, and kidneys.
These techniques can make side sleeping more comfortable:
- Place a pillow under your baby bump or between your legs.
- Use a rolled up blanket at the small of your back to relieve pressure.
- Try a foam or egg crate mattress pad to ease sore hips.
- Use extra pillows or a body pillow to support your body.
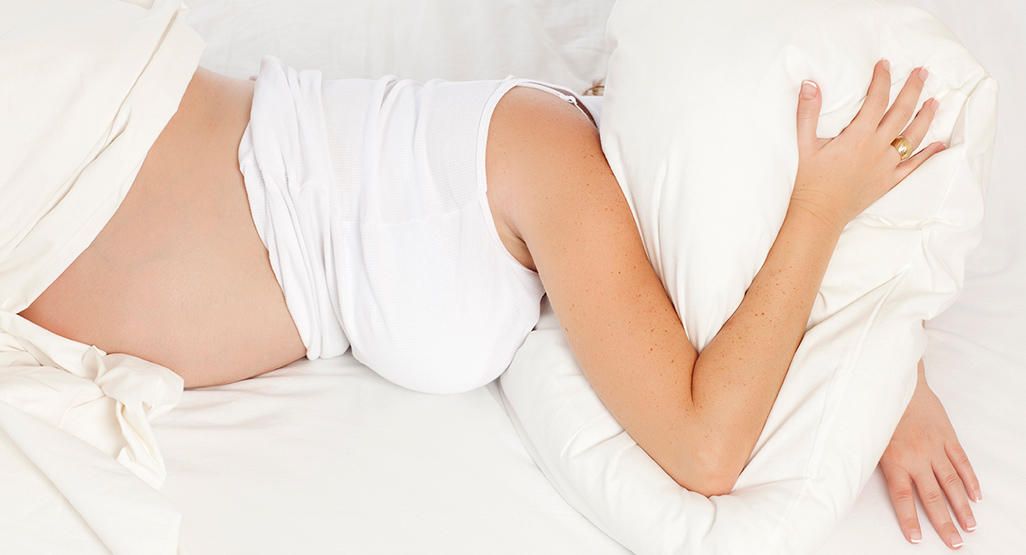

If you revert to sleeping on your back, don’t panic. It’s common for pregnant women to spend at least some time sleeping this way. If you are prone to this position, try placing a wedge pillow behind you when you go to sleep on your side. That way, should you roll back, you’ll at least be at a tilt, thereby lessening the effect of sleeping on your back.
Eat and Drink Strategically
During gestation, hormonal changes combined with an expanding uterus cause the entire digestive system to slow down. This can cause constipation, indigestion, and heartburn, which might become worse at night. At the same time, increased kidney productivity and pressure on the bladder from the growing baby make urination more frequent. Managing the body’s digestive input and output is crucial for a good night’s sleep.
Try these dietary changes to potentially avoid sleep disruptions:
- Avoid carbonated drinks, citrus, peppermint, tomatoes, and spicy or fatty foods.
 These can trigger acid reflux.
These can trigger acid reflux. - Refrain from eating within three to four hours of bedtime.
- Eat small meals throughout the day, instead of three large meals.
- Don’t drink liquid during meals or within two hours of bed.
- Cut out caffeine. This is a stimulant that keeps you awake, and can be harmful for developing babies.
Improve Your Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene is a collection of habits and behaviors that promote reliable, quality sleep. Sleep hygiene is important for everyone, and can make a big difference during pregnancy.
Improve your sleeping habits with these strategies:
- Go to bed and get up at the same time each day.
- Use your bed only for sleeping and sex.
- Don’t exercise within three hours of bedtime.
- Keep electronics out of the bedroom, and avoid screens before bed.
- If you can’t sleep within 30 minutes, get up and do a non-stimulating activity like reading.

Ensure Healthy Breathing
Weight gain, along with hormonal and physiological changes, predispose pregnant women to sleep disordered breathing (SDB). The most common manifestations of SDB during pregnancy include snoring and obstructive sleep apnea, a condition in which the airway becomes repeatedly blocked during sleep.
Getting a handle on SDB is crucial because this condition has been associated with adverse maternal and fetal outcomes, raising the risk of preeclampsia, hypertension, and gestational diabetes. Unchecked SDB can negatively affect overall quality of life, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, and cognitive impairment. Fortunately, evidence suggests that treating even mild SDB improves the health of mother and baby.
To breathe well at night, it may help to:
- Mitigate pregnancy weight gain, with the guidance of your obstetrician. Excess weight is one of the main causes of SDB.
- Consider using a humidifier.
 Nasal congestion, which can increase during pregnancy, worsens SDB. Keeping the room humid may help nasal passageways stay open.
Nasal congestion, which can increase during pregnancy, worsens SDB. Keeping the room humid may help nasal passageways stay open. - Consider raising the head of your bed by using bricks or risers. Because sleeping horizontally exacerbates sleep apnea, even a mild incline can ease SDB.
- Under the guidance of your doctor, consider using a CPAP machine. This device used during sleep is considered to be the gold standard for sleep apnea. It works by pumping air into the lungs and helping keep your airway open, ensuring a healthy supply of oxygen.
If you think you may have sleep disordered breathing, consult your doctor. Proper medical guidance is key for controlling this condition.
Soothe Your Legs
Pregnant women are more likely to experience leg cramping at night, caused by changes in the body’s ability to process calcium. Restless legs syndrome, a condition characterized by strong urges to move your legs, may occur more frequently in pregnancy
Try these techniques to prevent your legs from keeping you awake at night:
- Perform gentle leg stretches before bed.

- Get plenty of daytime exercise.
- Eat a calcium-rich diet.
- For sudden cramps, flex your feet or press them against the foot of the bed.
Ease New Parent Worries
While pregnancy is often an exciting, special time, it can also be filled with stress. Pregnant moms may lie awake ruminating about childbirth, the baby’s health, finances, or a number of other things. They may also experience nightmares and vivid dreams, which are common in pregnancy.
To cope with nighttime worry, try incorporating calming practices into your schedule, like yoga, journaling, and breathing exercises. Consider taking a soothing bath or practicing meditation to wind down in the evenings. You might sign up for a new-parent class to help prepare for the changes ahead. It may also be beneficial to reach out for professional support from a licensed counselor or support group. Many women are experiencing the same feelings, and seeking outside help can make a meaningful difference.
Avoid Sleep Aids
While it’s tempting to reach for a pharmaceutical or herbal supplement to combat sleeplessness, these products are usually not recommended for pregnant women. Sleep aids come with side effects, and they have limited research in pregnant populations. Even an over-the-counter antihistamine like diphenhydramine should not be used without consulting a doctor. Their effectiveness is unreliable, and there’s not enough evidence to be sure that sleep aids don’t adversely affect birth outcomes.
When in Doubt, See the Doctor
Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice for any change in sleep habits, no matter how small. While sleeping troubles can often be managed at home, sometimes a medical expert is needed to guide care or assess for something serious. Staying healthy is especially important during pregnancy, and good health starts with a good night’s sleep.
- Was this article helpful?
- YesNo
References
+16 Sources
-
1.

Mindell, J. A., Cook, R. A., & Nikolovski, J. (2015). Sleep patterns and sleep disturbances across pregnancy. Sleep Medicine, 16(4), 483–488. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25666847/
-
2.
Chang, J. J., Pien, G. W., Duntley, S. P., & Macones, G. A. (2010). Sleep deprivation during pregnancy and maternal and fetal outcomes: Is there a relationship?. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 14(2), 107–114. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19625199/
-
3.
Gay, C. L., Richoux, S. E., Beebe, K. R., & Lee, K. A. (2017). Sleep disruption and duration in late pregnancy is associated with excess gestational weight gain among overweight and obese women. Birth, 44(2), 173–180. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28198036/
-
4.
Harskamp-van Ginkel, M. W., Ierodiakonou, D., Margetaki, K., Vafeiadi, M., Karachaliou, M., Kogevinas, M., Vrijkotte, T., & Chatzi, L. (2020). Gestational sleep deprivation is associated with higher offspring body mass index and blood pressure.
 Sleep, 43(12), zsaa110. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32496519/
Sleep, 43(12), zsaa110. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32496519/ -
5.
Warland, J., Dorrian, J., Kember, A. J., Phillips, C., Borazjani, A., Morrison, J. L., & O'Brien, L. M. (2018). Modifying maternal sleep position in late pregnancy through positional therapy: A feasibility study. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 14(8), 1387–1397. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30092890/
-
6.
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. (2020, June 2). Problems sleeping during pregnancy. MedlinePlus. Retrieved April 1, 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000559.htm
-
7.
O'Brien, L. M., & Warland, J. (2014). Typical sleep positions in pregnant women. Early Human Development, 90(6), 315–317. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24661447/
-
8.
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. (2019, January 19). Heartburn. MedlinePlus. Retrieved April 1, 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003114.htm
-
9.

Rhee, J., Kim, R., Kim, Y., Tam, M., Lai, Y., Keum, N., & Oldenburg, C. E. (2015). Maternal caffeine consumption during pregnancy and risk of low birth weight: A dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies. PloS One, 10(7), e0132334. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26193706/
-
10.
Izci Balserak B. (2015). Sleep disordered breathing in pregnancy. Breathe, 11(4), 268–277. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27064321/
-
11.
Artal-Mittelmark, R. (2019, July). Physiology of pregnancy. Merck Manual Professional Version. Retrieved April 1, 2021, from https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/approach-to-the-pregnant-woman-and-prenatal-care/physiology-of-pregnancy
-
12.
Souza, F., Genta, P. R., de Souza Filho, A. J., Wellman, A., & Lorenzi-Filho, G. (2017). The influence of head-of-bed elevation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep & breathing = Schlaf & Atmung, 21(4), 815–820.
 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28647854/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28647854/ -
13.
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. (2020, January 29). Obstructive sleep apnea - adults. MedlinePlus. Retrieved April 1, 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000811.htm
-
14.
Office on Women’s Health. (2019, January 30). Body changes and discomforts. Womenshealth.gov. https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/body-changes-and-discomforts
-
15.
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. (2019, June 23). Restless legs syndrome. MedlinePlus. Retrieved April 1, 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000807.htm
-
16.
Okun, M. L., Ebert, R., & Saini, B. (2015). A review of sleep-promoting medications used in pregnancy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 212(4), 428–441. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25448509/
See More
Best Sleeping Positions While Pregnant
The best sleep position during pregnancy is “SOS” (sleep on side) because it provides the best circulation for you and your baby. It also places the least pressure on your veins and internal organs. Sleeping on your left side will increase the amount of blood and nutrients that reach the placenta and your baby. Plus good circulation helps reduce potential swelling, varicose veins in your legs and hemorrhoids.
It also places the least pressure on your veins and internal organs. Sleeping on your left side will increase the amount of blood and nutrients that reach the placenta and your baby. Plus good circulation helps reduce potential swelling, varicose veins in your legs and hemorrhoids.
How Can I Sleep More Comfortably During Pregnancy?
Keep your legs and knees bent, and put a pillow between your legs to relieve the stress on your back.
- If you find that you are having problems with back pain, use the “SOS” position, and try placing a pillow under your abdomen as well.
- If you are experiencing heartburn during the night, you may want to try propping your upper body with pillows.
- In late pregnancy, you may experience shortness of breath. Try lying on your side or propped up with pillows.
These suggestions may not sound completely comfortable, especially if you are used to sleeping on your back or stomach, but try them out. You may find that they work. Keep in mind that you may not stay in one position all night, and rotating positions is fine.
Keep in mind that you may not stay in one position all night, and rotating positions is fine.
What Sleep Positions During Pregnancy Should I Avoid?
Sleeping on your back: This can cause problems with backaches, breathing, the digestive system, hemorrhoids, low blood pressure and cause a decrease in circulation to your heart and your baby. This is a result of your growing abdomen resting on your intestines and major blood vessels (the aorta and vena cava). You can also develop sleep apnea as you put on weight.
Sleeping on your stomach: When you are farther along in your pregnancy, your breasts become more tender and your abdomen continues to grow, both making sleeping on your tummy uncomfortable. Using a donut-shaped pillow (with a hole in the middle) may help you sleep comfortably on your stomach.
Reasons for your discomfort may include:
During pregnancy, you may find yourself wrestling in bed trying to get comfortable before falling asleep. When you are pregnant your body goes through a variety of changes causing your regular sleeping positions to no longer work for you.
When you are pregnant your body goes through a variety of changes causing your regular sleeping positions to no longer work for you.
- Increased size of the abdomen
- Back pain
- Heartburn
- Shortness of breath
- Insomnia
More Steps to Sleeping Better While Pregnant
- Limit caffeine. Try not to drink coffee or caffeinated tea after 3 p.m.
- Brink plenty of water. Drink lot of water through out the day, but limit intake a couple of hours before bedtime so you don’t have to wake up and go to the bathroom.
- Exercise for 30 minutes. Exercise helps you sleep better, but don’t exercise within four hours of bedtime.
- Relaxing activities. A warm bath, foot or shoulder massage will help you relax.
- Peaceful bedroom. Keeping your bedroom dark, quiet and cool at night will help to drift off to sleep and stay asleep.
- 7 Discomforts of Pregnancy
- Nighfood Nighttime Ice Cream
- Pregnancy Week 15
Compiled using information from the following sources:
1. Nemours Foundation
Nemours Foundation
https://www.kidshealth.org
1. Your Pregnancy Week by Week Fifth Ed. Curtis, Glade B., OB/GYN, et al. Week 16
Insomnia during pregnancy
Insomnia during pregnancy is a fairly common occurrence that affects many women.
Causes of insomnia during pregnancy
Causes of insomnia during pregnancy can be physical or psychological.
Physiological causes of insomnia:
- back and back pain;
- manifestation of urge to urinate due to the expansion of the uterus and its oppression of the bladder;
- fetal movement inside the uterus;
- occurrence of heartburn;
- occurrence of convulsions;
- the appearance of shortness of breath.
Psychological causes of insomnia
During pregnancy, insomnia can also occur for psychological reasons, such as:
- stress;
- fatigue;
- the occurrence of frequent nightmares.

Types of insomnia
There are primary and secondary types of insomnia. Secondary insomnia usually resolves without treatment, while primary insomnia requires medical attention.
Treatment for insomnia during pregnancy
There is no one-size-fits-all cure for insomnia during pregnancy, so you will need to carefully monitor your nervous system, diet and exercise levels.
How to deal with her insomnia pregnant woman expecting a baby, what rules to follow and what to follow?
Diet for insomnia (advice)
- drink less before bed;
- Before going to bed, drink a cup of warm milk, or non-energizing tea;
- you can also use folk remedies of herbal origin;
- Eat turkey meat containing the soothing substance tryptophan;
- do not eat heavy meals before going to bed;
Preparing the bedroom (tips)
- ventilate the room at least half an hour before going to bed;
- sleep on your side, not on your stomach and not on your back, which often hurts during this period;
- sleep on a comfortable, not too soft, but not hard surface.

Bed ritual
- avoid stress and overexertion;
- take warm baths or showers before bed;
- If you are concerned about itchy abdomen, lubricate it with lotion.
Sleeping pills: to use or not?
Do not use sleeping pills during pregnancy. It can harm the baby in the same way as any other medicines, which are best avoided during pregnancy.
Morning preparation
Morning preparation for the day ahead during pregnancy begins with breathing exercises and light routine exercises. You can also apply the so-called acupuncture - massage points on the palms and soles of the feet. As you know, it is on the palms and feet that there are nerve endings, through which you can influence your entire body as a whole, as well as the level of activity of the brain and nervous system.
And don't forget to be positive before you get out of bed. The reason for this can be even such a trifle as the first morning and most delicious cup of coffee.
Also distribute your daily load in such a way that in the evening there are no noisy gatherings, physical exertion. Limit TV viewing before bed. And no thrillers, horror films, detective stories and tragedies - this will unsettle your nervous system.
Hormonal changes in a woman's body: what is important to know?
Hormonal changes in the body entail not too pleasant consequences, as a result of which the body simply refuses to rest.
The sleep of a pregnant woman is extremely important not only for herself, but also for her baby. You need to sleep as much as you want. At the same time, it is necessary to be very careful in terms of choosing positions for sleeping and not to allow the state of the so-called oversleeping, which usually occurs if a woman, having gone to bed during the day or in the evening, wakes up only in the morning of the next day. In general, early evening is not the best time for sleep in general, this leads to a failure of the woman's biological clock and chronic insomnia at night.
If it is simply impossible to get enough sleep due to some physical reasons, a woman may accidentally fall into a state of drowsiness somewhere on the street. It is much better when sudden drowsiness occurs to enter into a state of REM sleep - fall asleep for fifteen to twenty minutes in a comfortable position and in a relaxed state. During this time, the body, as a rule, has time to recover to a large extent. The same effect of REM sleep gives rapid blinking of the eyes for thirty seconds, this action will bring the brain into a state of wakefulness for two to three hours.
If there are no bouts of drowsiness during the day, but there is no sleep either, it is better to contact your doctor, as well as a narrowly specialized specialist, because although insomnia is a natural phenomenon during pregnancy, it causes a lot of problems for both the mother and fetus. And there is no need to hope that the body itself knows how much it needs to sleep. The body of a woman in labor is constantly in a suspended, nervous state of the deepest stress and simply cannot independently feel how much sleep she needs.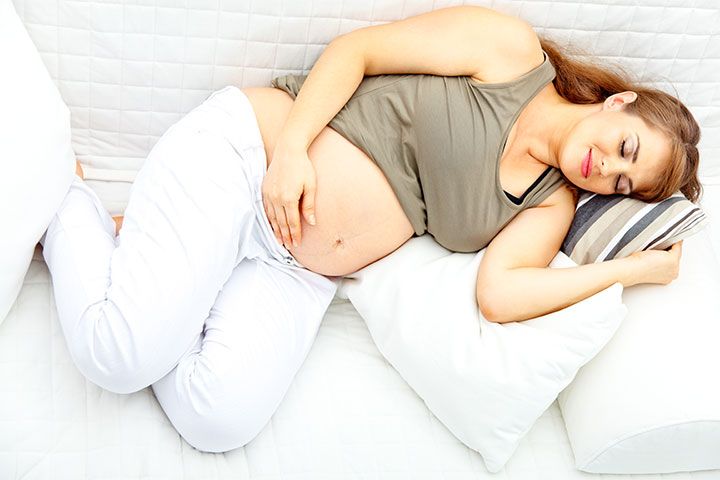
Correct physical activity for insomnia
Hiking in the park and trips to the country are suitable. We do not advise for the sake of unity with nature to go, for example, to the mountains and in general, to be exposed to any kind of physical or psychological danger. Do not forget: all your stresses are the stresses of the unborn baby!
Aroma and aqua therapy
Use aroma and aqua therapy, phytotherapy - this will also help to cope with insomnia during pregnancy. But before using it, do not forget to consult a doctor and take a test to detect your individual intolerance. You can also use proven methods of traditional medicine, but we remind you once again: no chemistry during pregnancy!
Orthopedic subtleties for insomnia
Use an orthopedic mattress that is custom made for your body shape. It is also recommended to put pillows under the lower back, between the legs and under the stomach, although sleeping on the stomach during pregnancy is highly discouraged - this can harm the baby.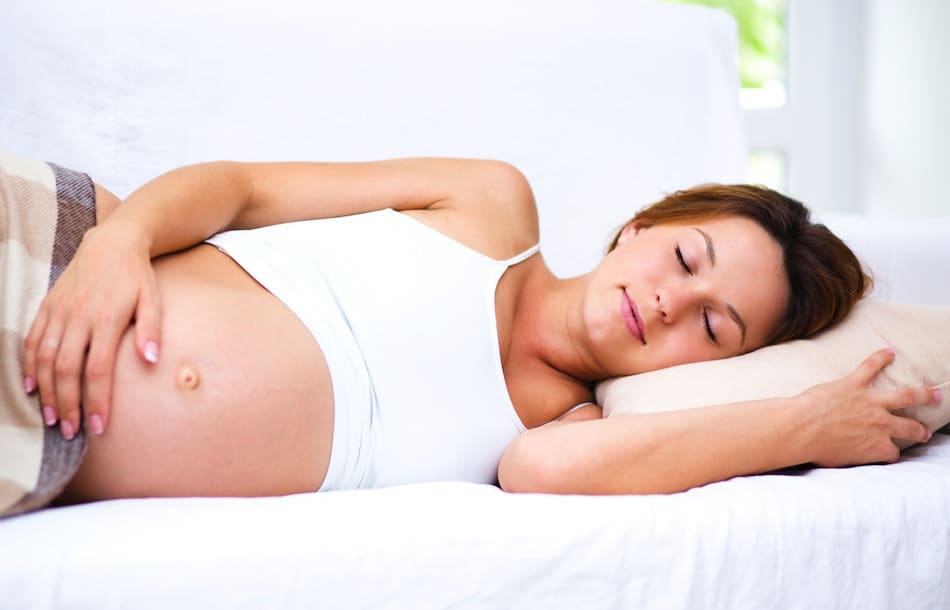
Homeopathy for insomnia
Homeopathic medicines can help you, but the chances are about 50/50, so you'd better go to a highly qualified narrow-profile homeopathic doctor. These medicines must necessarily be selected in full accordance with the existing individual symptoms.
Does the brain simply refuse to "switch off"? Are you constantly in an incomprehensibly cheerful, excited state, similar to euphoria, and therefore you can’t fall asleep in any way? Put three grains of coffee under your tongue.
Folk remedies
Today, there are quite conflicting opinions about the use of sleeping pills made on the basis of various herbs, such as, for example, valerian and passionflower.
You would be better off avoiding them completely during pregnancy.
Scutellaria broadleaf can be used during pregnancy, but with the greatest care. It should not be used for a long period of time. It is not suitable for those who have liver problems.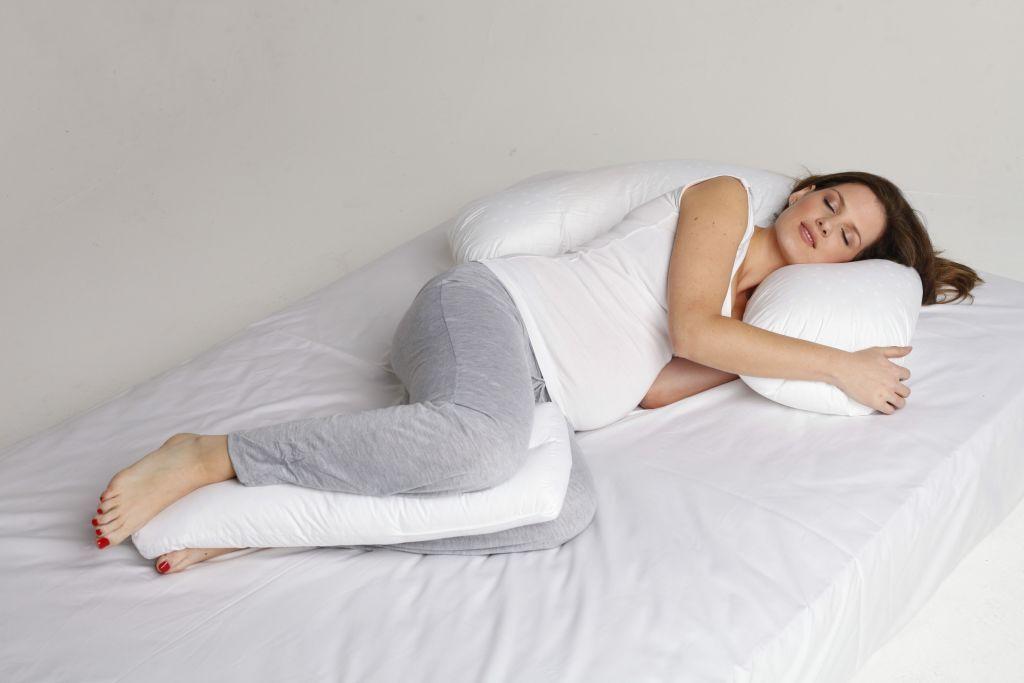
You can sleep on a specially made pillow filled with hops. However, do not drink tea infused with hops unless it is prescribed to you by a qualified specialist.
Medicines for insomnia
It is better not to start taking medicines, as already mentioned in passing. The effect may be and will be, but it is not clear what effect this or that substance will have on the unborn baby, so we do not recommend taking risks.
By applying the above methods, you will most likely soon get rid of your insomnia forever and sleep peacefully with your baby. Do not forget that the fetus constantly feels our mood, stress and tension. Have you ever noticed that, for example, if you quarreled with someone while pregnant, the baby inside you invariably began to push, kick, in general, get nervous in every possible way? Noticed? Exactly! So first of all, if insomnia occurs during pregnancy, you must:
Stop being nervous!
In general, although insomnia is a natural phenomenon during pregnancy, it, in fact, is only a consequence of a combination of a wide range of concomitant factors, and not an independent phenomenon. So it is not only possible to fight it, but, undoubtedly, it is necessary. So do not give up and stubbornly win back your healthy sleep from your nervous system, exhausted by shaking and stress! If you work hard on yourself, you will succeed!
So it is not only possible to fight it, but, undoubtedly, it is necessary. So do not give up and stubbornly win back your healthy sleep from your nervous system, exhausted by shaking and stress! If you work hard on yourself, you will succeed!
What position should I sleep in during pregnancy?
A Harvard University study found that women who drank three glasses of apple juice every day were 15% more likely to develop type II diabetes. In the case of orange juice, the likelihood of illness increases by 25%, plus there is a risk of obesity.
Sleep during pregnancy brings a lot of inconvenience to a woman. Heartburn, frequent urge to urinate, shortness of breath, bouts of insomnia, back pain.
To get the most comfortable sleep in the upcoming months of pregnancy, read our guide.
Sleep on your back.
When you sleep on your back it is safe during the 1st trimester. When the body is on the back, the stomach and uterus put pressure on the main vein, which returns blood from the lower body to the heart. Thus, while lying on your back, you may feel dizzy, nauseous, and it is more difficult for blood and nutrients to reach the placenta.
When the body is on the back, the stomach and uterus put pressure on the main vein, which returns blood from the lower body to the heart. Thus, while lying on your back, you may feel dizzy, nauseous, and it is more difficult for blood and nutrients to reach the placenta.
In addition, back pain, shortness of breath, problems with the digestive system, hemorrhoids, and low blood pressure may occur.
Sleep on stomach.
After 20 ti weeks to sleep on a stomach it is simply not convenient. Imagine that you are sleeping on a huge watermelon! By the way, do not be afraid to sleep in this position, you can not hurt the child. Even at nine months, the walls of the uterus provide sufficient protection for the baby. From a medical point of view, sleeping in this position is safe but uncomfortable.
Sleep on the side.
The best way to sleep comfortably through the night is to sleep on your side, especially on your left side. So you provide maximum blood flow for the baby and does not put pressure on the liver. Place a pillow between your legs for comfort. This position will also help the kidneys work, which in turn will reduce swelling.
So you provide maximum blood flow for the baby and does not put pressure on the liver. Place a pillow between your legs for comfort. This position will also help the kidneys work, which in turn will reduce swelling.
What to do if you periodically wake up on your back?
If you wake up on your back in the middle of the night, don't worry. You would begin to feel dizzy and nauseous before the child was in real danger and could not get enough oxygen.
If you wake up and find yourself on your back, don't be alarmed. Just roll over on your side and go back to sleep. If you have restless sleep and cannot sleep. Consult your doctor.
You can make an appointment with a gynecologist by calling 8 (843) 207-18-00
Articles
Return to the list
Multidisciplinary Clinic MEdel
We are waiting for you at the following addresses:
Kazan, st. Siberian tract, 34, bldg.