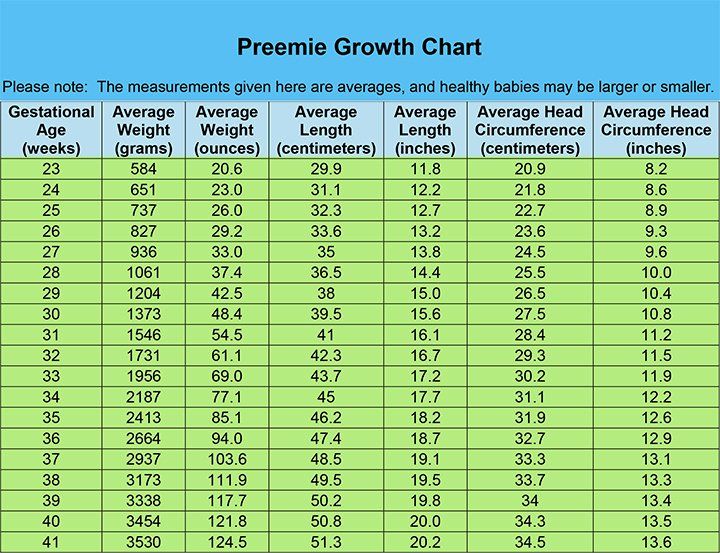
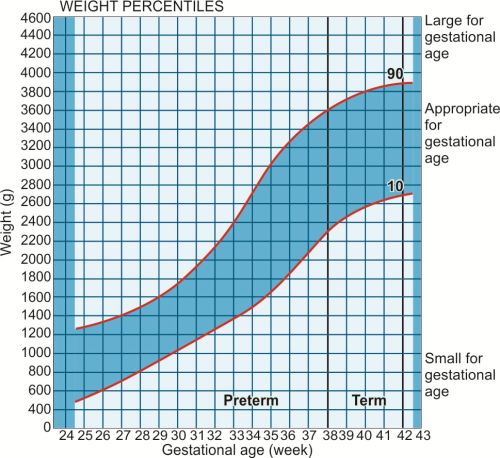
Baby weight at birth chart
Average baby weight: Chart and development
Weight is one indicator of good nutrition and physical development. It can therefore be helpful to know about babies’ average weight month by month.
First, it is worth noting that average weight is not “normal” weight. Just like adults, babies come in all shapes and sizes. If a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, this does not necessarily signal a problem with their growth or physical development. With this in mind, using a weight chart can help a person generally track their baby’s growth.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend using the World Health Organization (WHO) weight chart for babies up to 2 years of age.
This article describes the average weight of a baby month by month from birth. It also explores what can affect a baby’s weight.
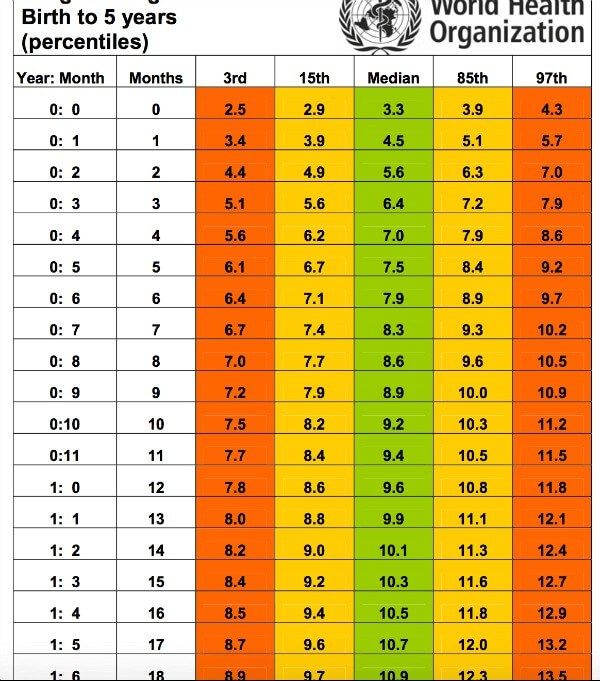
According to the WHO, the average birth weight of a full-term male baby is 7 pounds (lb) 6 ounces (oz), or 3.3 kilograms (kg). The average birth weight of a full-term female is 7 lb 2 oz, or 3. 2 kg.
The average weight of a baby born at 37–40 weeks ranges from 5 lb 8 oz to 8 lb 13 oz. This is 2.5 to 4 kg.
At delivery, experts consider a low birth weight to be less than 5 lb 8 oz, or 2.5 kg.
It is common for babies to lose around 10% of their weight shortly after birth. This decrease is mostly due to fluid loss and usually nothing to worry about. Most babies gain back this weight within 1 week.
Weight charts can help a person tell what percentile their baby’s weight falls into. For example, if their weight is in the 60th percentile, it means that 40% of babies of the same age and sex weigh more, and 60% of these babies weigh less.
This does not necessarily mean that any baby weighs too much or too little. It can simply indicate where a baby’s weight falls on a spectrum.
The chart below shows baby weights in the 50th percentile. This is the average weight. Male babies tend to weigh a little more than female babies, so the chart is divided by sex.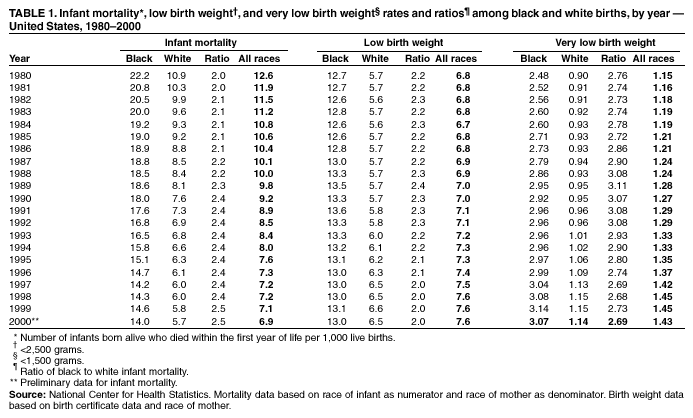
| Baby age | Female 50th percentile weight | Male 50th percentile weight |
| Birth | 7 lb 2 oz (3.2 kg) | 7 lb 6 oz (3.3 kg) |
| 1 month | 9 lb 4 oz (4.2 kg) | 9 lb 14 oz (4.5 kg) |
| 2 months | 11 lb 5 oz (5.1 kg) | 12 lb 4 oz (5.6 kg) |
| 3 months | 12 lb 14 oz (5.8 kg) | 14 lb 1 oz (6.4 kg) |
| 4 months | 14 lb 3 oz (6.4 kg) | 15 lb 7 oz (7.0 kg) |
| 5 months | 15 lb 3 oz (6.9 kg) | 16 lb 9 oz (7.5 kg) |
| 6 months | 16 lb 1 oz (7.3 kg) | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) |
| 7 months | 16 lb 14 oz (7.6 kg) | 18 lb 5 oz (8.3 kg) |
| 8 months | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) | 18 lb 15 oz (8.6 kg) |
| 9 months | 18 lb 2 oz (8.2 kg) | 19 lb 10 oz (8.9 kg) |
| 10 months | 18 lb 11 oz (8.5 kg) | 20 lb 3 oz (9.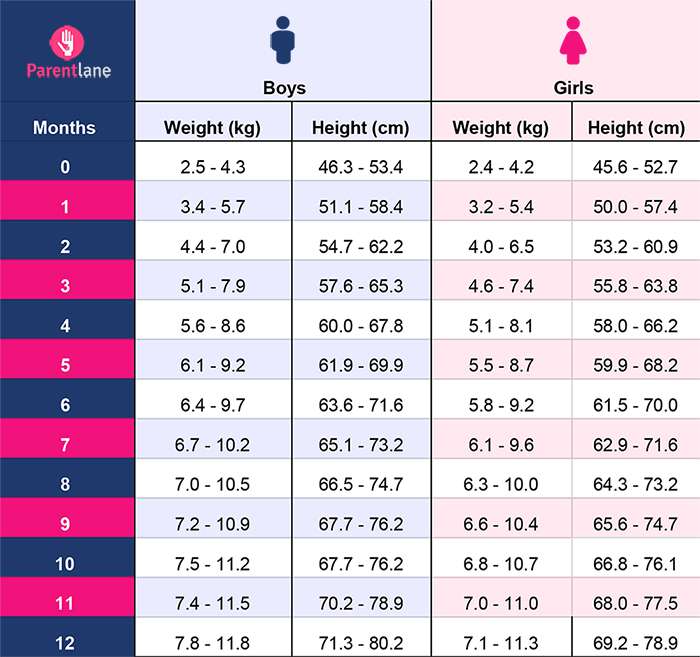 2 kg) 2 kg) |
| 11 months | 19 lb 4 oz (8.7 kg) | 20 lb 12 oz (9.4 kg) |
| 12 months | 19 lb 12 oz (8.9 kg) | 21 lb 4 oz (9.6 kg) |
Babies grow and gain weight the fastest within the first 6 months of life. Although this can vary, babies tend to gain around 4–7 oz, or 113–200 grams (g), per week in the first 4–6 months.
Weight gain then slows slightly, with an average gain of around 3–5 oz (about 85–140 g) per week when the baby is 6–18 months. On average, babies triple their birth weight by their first birthday.
Growth patterns do not follow a clear schedule, however.
Some babies gain weight steadily and stay in the same percentile, or close to it, for several months. Others gain weight rapidly, signalling a growth spurt, which can happen at any time. This may move a baby into a new weight percentile.
It is important not to focus on weight as the only indicator of physical development. Other measurements of this development include the baby’s length and head circumference.
Considering all three measurements gives doctors an idea about how the baby is growing, compared with other babies of the same age and sex.
Meanwhile, it is also important to keep other developmental milestones in mind. Various checklists of milestones by age are available, including one from Pathways.org, which is endorsed by organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners.
For anyone looking for more information about what influences the weight of a baby, several factors can be involved, including:
Sex
Male newborns tend to be bigger than female newborns, and they typically gain weight a little faster during infancy.
Nutrition
Weight gain and growth rates can also depend on whether the baby consumes breast milk or formula.
The American Academy of Pediatrics notes that breastfed babies gain weight and grow faster than formula-fed babies during the first 6 months.
However, that rate can shift during the next 6 months. Breastfed babies may gain weight and grow more slowly than formula-fed babies when they are aged 6 months to 1 year.
Breastfed babies may gain weight and grow more slowly than formula-fed babies when they are aged 6 months to 1 year.
Medical conditions
Underlying health issues can cause a baby to gain weight more slowly. For example, babies with congenital heart irregularities may gain weight at a slower rate than babies without this condition.
Health issues that affect nutrient absorption or digestion, such as celiac disease, may also lead to slow weight gain.
Prematurity
Babies born prematurely may grow and gain weight more slowly during their first year than babies born at full term.
However, many babies born prematurely gain weight rapidly and “catch up” by about their first birthday.
The average birth weight for full-term male babies is 7 lb 6 oz, or 3.3 kg. For female babies born full-term, the average birth weight is 7 lb 2 oz, or 3.2 kg.
Baby weight charts can help a healthcare team track a baby’s physical development by comparing the baby’s weight with the weights of others of the same age and sex.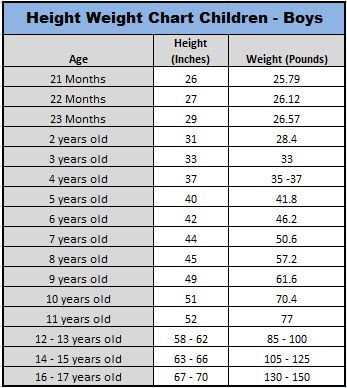
Still, a doctor usually looks for steady growth, rather than a target percentile, when assessing a baby’s physical development. And even if a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, they will not necessarily be a small adult — just as longer babies do not necessarily become tall adults.
Knowing about average weights by month can help people gauge their babies’ physical development, but doctors also look for other important indicators, such as length and head circumference.
Healthcare professionals also take into account whether a baby is generally hitting other milestones on time. And by taking a detailed medical history, they can rule out any medical conditions or nutritional considerations that may be preventing a baby from gaining weight appropriately.
Average baby weight: Chart and development
Weight is one indicator of good nutrition and physical development. It can therefore be helpful to know about babies’ average weight month by month.
First, it is worth noting that average weight is not “normal” weight.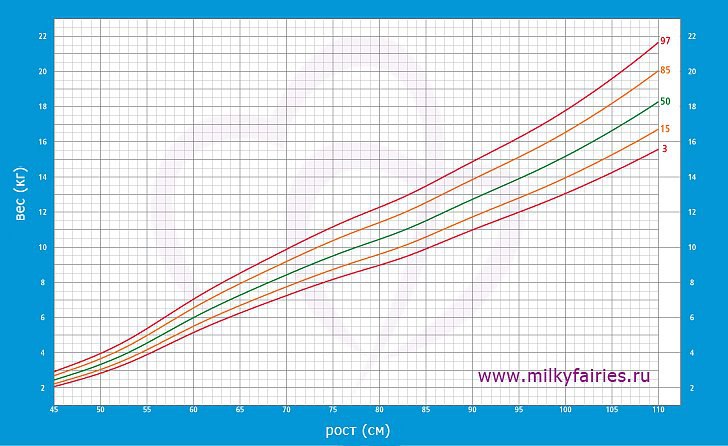 Just like adults, babies come in all shapes and sizes. If a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, this does not necessarily signal a problem with their growth or physical development. With this in mind, using a weight chart can help a person generally track their baby’s growth.
Just like adults, babies come in all shapes and sizes. If a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, this does not necessarily signal a problem with their growth or physical development. With this in mind, using a weight chart can help a person generally track their baby’s growth.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend using the World Health Organization (WHO) weight chart for babies up to 2 years of age.
This article describes the average weight of a baby month by month from birth. It also explores what can affect a baby’s weight.
According to the WHO, the average birth weight of a full-term male baby is 7 pounds (lb) 6 ounces (oz), or 3.3 kilograms (kg). The average birth weight of a full-term female is 7 lb 2 oz, or 3.2 kg.
The average weight of a baby born at 37–40 weeks ranges from 5 lb 8 oz to 8 lb 13 oz. This is 2.5 to 4 kg.
At delivery, experts consider a low birth weight to be less than 5 lb 8 oz, or 2.5 kg.
It is common for babies to lose around 10% of their weight shortly after birth.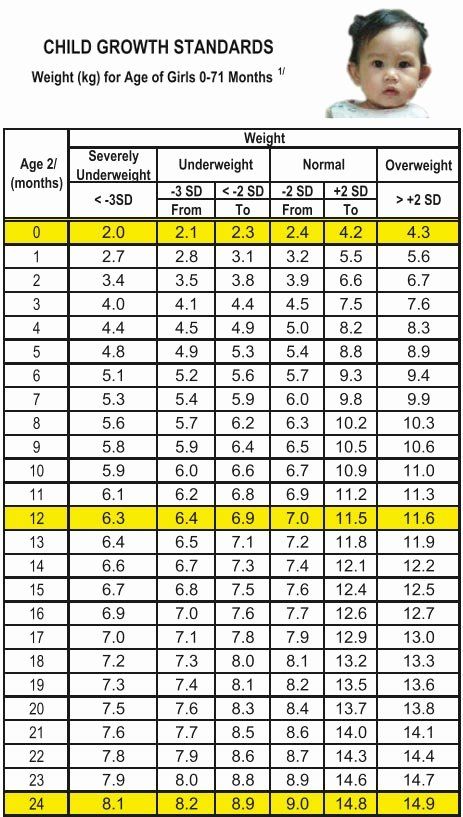 This decrease is mostly due to fluid loss and usually nothing to worry about. Most babies gain back this weight within 1 week.
This decrease is mostly due to fluid loss and usually nothing to worry about. Most babies gain back this weight within 1 week.
Weight charts can help a person tell what percentile their baby’s weight falls into. For example, if their weight is in the 60th percentile, it means that 40% of babies of the same age and sex weigh more, and 60% of these babies weigh less.
This does not necessarily mean that any baby weighs too much or too little. It can simply indicate where a baby’s weight falls on a spectrum.
The chart below shows baby weights in the 50th percentile. This is the average weight. Male babies tend to weigh a little more than female babies, so the chart is divided by sex.
| Baby age | Female 50th percentile weight | Male 50th percentile weight |
| Birth | 7 lb 2 oz (3.2 kg) | 7 lb 6 oz (3.3 kg) |
| 1 month | 9 lb 4 oz (4.2 kg) | 9 lb 14 oz (4.5 kg) |
| 2 months | 11 lb 5 oz (5.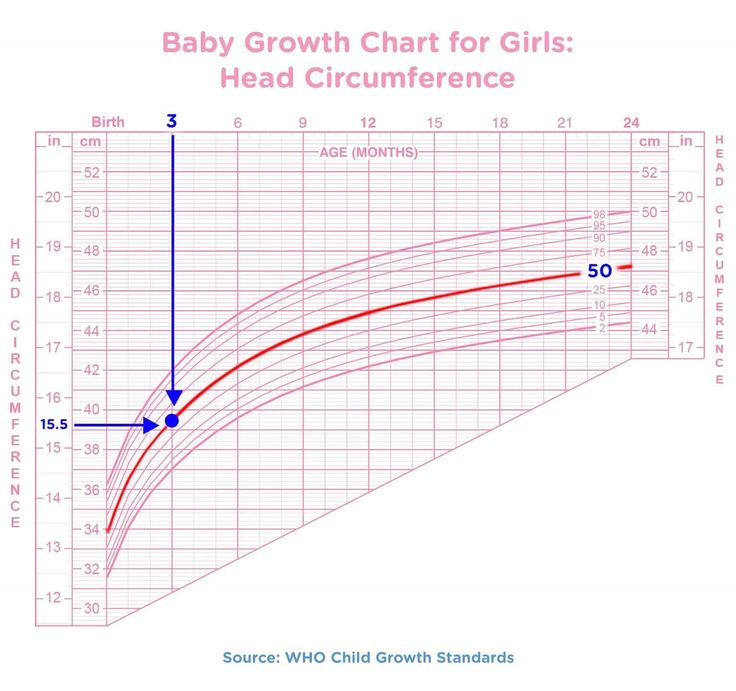 1 kg) 1 kg) | 12 lb 4 oz (5.6 kg) |
| 3 months | 12 lb 14 oz (5.8 kg) | 14 lb 1 oz (6.4 kg) |
| 4 months | 14 lb 3 oz (6.4 kg) | 15 lb 7 oz (7.0 kg) |
| 5 months | 15 lb 3 oz (6.9 kg) | 16 lb 9 oz (7.5 kg) |
| 6 months | 16 lb 1 oz (7.3 kg) | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) |
| 7 months | 16 lb 14 oz (7.6 kg) | 18 lb 5 oz (8.3 kg) |
| 8 months | 17 lb 8 oz (7.9 kg) | 18 lb 15 oz (8.6 kg) |
| 9 months | 18 lb 2 oz (8.2 kg) | 19 lb 10 oz (8.9 kg) |
| 10 months | 18 lb 11 oz (8.5 kg) | 20 lb 3 oz (9.2 kg) |
| 11 months | 19 lb 4 oz (8.7 kg) | 20 lb 12 oz (9.4 kg) |
| 12 months | 19 lb 12 oz (8.9 kg) | 21 lb 4 oz (9.6 kg) |
Babies grow and gain weight the fastest within the first 6 months of life. Although this can vary, babies tend to gain around 4–7 oz, or 113–200 grams (g), per week in the first 4–6 months.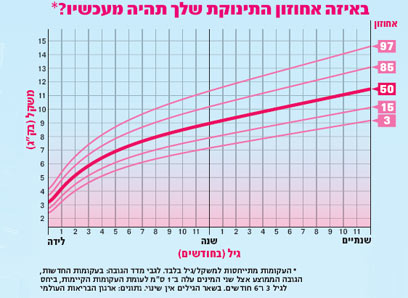
Weight gain then slows slightly, with an average gain of around 3–5 oz (about 85–140 g) per week when the baby is 6–18 months. On average, babies triple their birth weight by their first birthday.
Growth patterns do not follow a clear schedule, however.
Some babies gain weight steadily and stay in the same percentile, or close to it, for several months. Others gain weight rapidly, signalling a growth spurt, which can happen at any time. This may move a baby into a new weight percentile.
It is important not to focus on weight as the only indicator of physical development. Other measurements of this development include the baby’s length and head circumference.
Considering all three measurements gives doctors an idea about how the baby is growing, compared with other babies of the same age and sex.
Meanwhile, it is also important to keep other developmental milestones in mind. Various checklists of milestones by age are available, including one from Pathways. org, which is endorsed by organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners.
org, which is endorsed by organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners.
For anyone looking for more information about what influences the weight of a baby, several factors can be involved, including:
Sex
Male newborns tend to be bigger than female newborns, and they typically gain weight a little faster during infancy.
Nutrition
Weight gain and growth rates can also depend on whether the baby consumes breast milk or formula.
The American Academy of Pediatrics notes that breastfed babies gain weight and grow faster than formula-fed babies during the first 6 months.
However, that rate can shift during the next 6 months. Breastfed babies may gain weight and grow more slowly than formula-fed babies when they are aged 6 months to 1 year.
Medical conditions
Underlying health issues can cause a baby to gain weight more slowly. For example, babies with congenital heart irregularities may gain weight at a slower rate than babies without this condition.
Health issues that affect nutrient absorption or digestion, such as celiac disease, may also lead to slow weight gain.
Prematurity
Babies born prematurely may grow and gain weight more slowly during their first year than babies born at full term.
However, many babies born prematurely gain weight rapidly and “catch up” by about their first birthday.
The average birth weight for full-term male babies is 7 lb 6 oz, or 3.3 kg. For female babies born full-term, the average birth weight is 7 lb 2 oz, or 3.2 kg.
Baby weight charts can help a healthcare team track a baby’s physical development by comparing the baby’s weight with the weights of others of the same age and sex.
Still, a doctor usually looks for steady growth, rather than a target percentile, when assessing a baby’s physical development. And even if a baby’s weight is in a lower percentile, they will not necessarily be a small adult — just as longer babies do not necessarily become tall adults.
Knowing about average weights by month can help people gauge their babies’ physical development, but doctors also look for other important indicators, such as length and head circumference.
Healthcare professionals also take into account whether a baby is generally hitting other milestones on time. And by taking a detailed medical history, they can rule out any medical conditions or nutritional considerations that may be preventing a baby from gaining weight appropriately.
Tables of weight and height of the child by months and by years. For boys and for girls.
The height and weight of a child are the main indicators of his physical development. That is why immediately after the birth of the baby, it is imperative to measure the weight of his body and the length of the body and continue to weigh himself daily at the same time until discharge from the hospital.
There are many factors that affect the physical development of a child, for example:0010
How to understand what is the norm?
The All-Russian Health Organization recommended special tables for matching the height and weight of children, or as they are called, centile tables. At each examination, the pediatrician measures the height and weight of the child, compares the obtained values \u200b\u200bwith the standard indicators. Such tables allow you to identify obvious pathologies, for a more accurate analysis, the doctor calculates additional indicators using special formulas.
Monthly infant weight and height chart (up to 1 year)
The table shows the average height and weight of infants (under 1 year of age) by month for boys and girls.
| Age | Girls | Boys | ||||||
| , kg | 9000 9000, KG, KG | 9000 9000, KG, KG 9000 9000, KG, KG 9,000|||||||
| Newborns | 3. 33 ± 0.44 33 ± 0.44 | 49.50 ± 1.63 | 3.53 ± 0.45 | 50.43 ± 1.89 | 1 month | 4.15 ± 0.54 | 53.51 ± 2.13 | 4.32 ± 0.64 | 54.53 ± 2.32 |
| 2 months | 5.01 ± 0.56 | 56.95 ± 2.18 | 5 .29 ± 0.76 | 57.71 ± 2.48 | ||||
| 3 months | 6.07 ± 0.58 | 60.29 ± 2.08 903 | 61.30 ± 2.41 | |||||
| 4 months | 6.55 ± 0.79 | 62.15 ± 2.49 | 6.87 ± 0.74 | 63.79 ± 2.68 | ||||
| 9000 3 months | 7.38 ± 0.96 | 63.98 ± 2.49 | 7.82 ± 0.80 | 66.92 ± 1.99 | ||||
| 6 months | 7.97 ± 0.92 | 66.60 ± 2.44 | 8.77 ± 0.78 | 67.995 ± 2.24 80049 7 months | 8.25 ± 0.95 | 67.44 ± 2.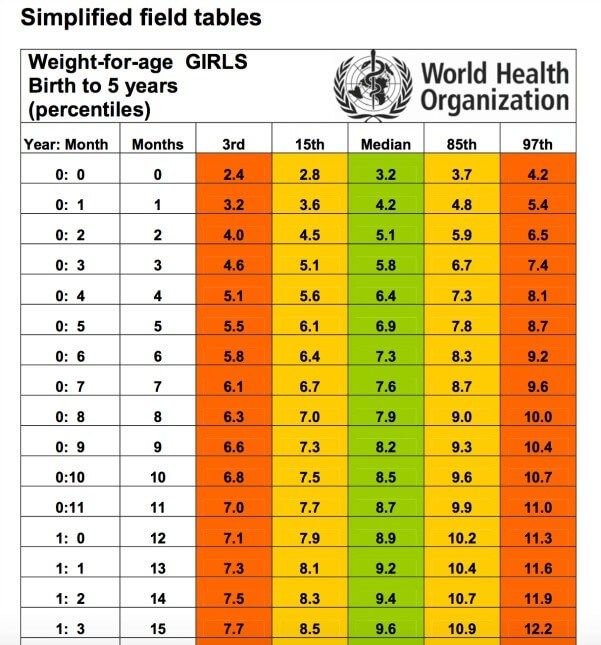 64 64 | 8.92 ± 1.11 | 69.56 ± 2.61 |
| 9000 3 months 9000 | 8.35 ± 1.10 | 69.84 ± 2.07 | 9.46 ± 0.98 | 71.17 ± 2.24 | ||||
| 9000 9 months | 9.28 ± 1 .01 | 70.69 ± 2.21 | 9.89 ± 1.18 | 72.84 ± 2.71 | ||||
| 10 months | 9.52 ± 1.3572.11 ± 2.86 | 10.35 ± 1.12 | 73.91 ± 2.65 | |||||
| 11 months | 9.80 ± 0, 0, 80 | 73.60 ± 2.73 | 10.47 ± 0.98 | 74.90 ± 2.55 | ||||
| 10.04 ± 1.16 | 74.78 ± 2.54 | 10.66 ± 1.21 | 75.78 ± 2.79 | |||||
Table of weight and height of the child by years (from 1 to 18 years)
weight of the child by years aged 1 to 18 years for boys and girls.
| Age | Girls | Boys | |||||
| , kg | | 9000 9000, KG, KG | 9000 9000, KG, KG | 9000 9000, KG, KG 9000, KG |||||
| 1 year 3 months | 10.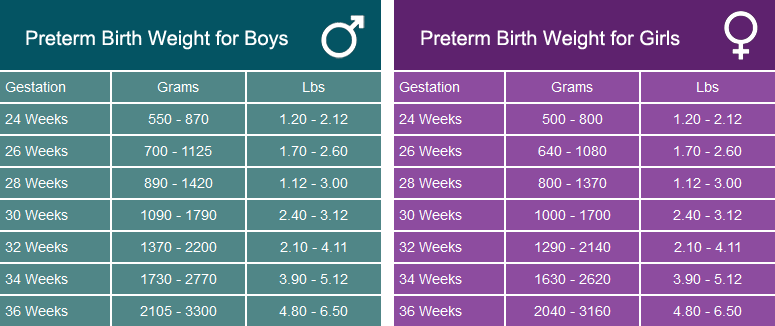 52 ± 1.27 52 ± 1.27 | 76.97 ± 3.00 | 11.40 ± 1.30 | 79.45 ± 3.56 | |||
| 1 year 6 months | 11.40 ± 1.12 | 80.80 ± 2.98 | 11.80 ± 1.18 | 81.73 ± 3.34 | |||
| 9000. 1 year | 12.27 ± 1.37 | 83.75 ± 3.57 | 12.67 ± 1.41 | 84.51 ± 2.85 | |||
| 12.6.63 ± 1.76 | 86.13 ± 3.87 | 13.04 ± 1.23 | 88.27 ± 3.70 | ||||
| 2 years 6 months | 13.93 ± 1.60 | 91.20 ± 4,28 | 13.96 ± 1.27 | 81.85 ± 3.78 | |||
| 3 years old | 14.85 ± 1.53 | 97.27 ± 3 , 78 | 14.95 ± 1.68 | 95.72 ± 3.68 | |||
| 4 years | 16.02 ± 2.30 | 100.56 ± 5.76 | 17, 14 ± 2.18 | 102.44 ± 4.74 | |||
| 5 years | 18.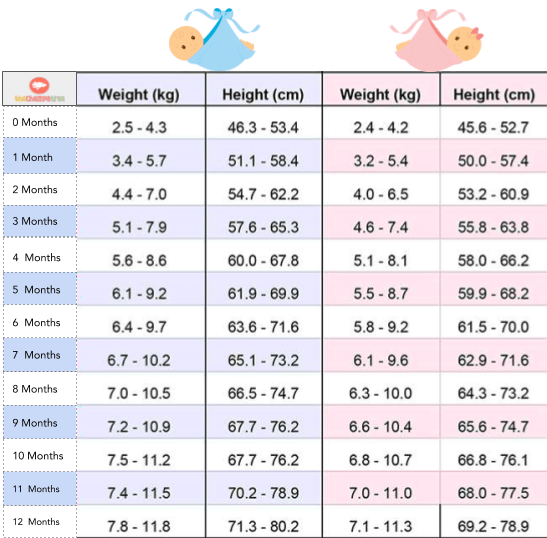 48 ± 2.44 48 ± 2.44 | 109.00 ± 4.72 038 | 110.40 ± 5.14 | | ||||
| 6 years | 21.34 ± 3.14 | 115.70 ± 4.32 | 21.20 | 115.98 ± 5.51 | |||
| 7 years old | 24.66 ± 4.08 | 123.60 ± 5.50 | 24.92 ± 4.44 | 123.88 ± 5.40 | |||
| 8 years | 27.48 ± 4.92 | 129.00 ± 5.48 | 27.86 ± 4.72 | 129.94 ± 5.70 | 0049 9 years old31.02 ± 5,92 | 136.96 ± 6.10 | 30.60 ± 5.86 | 9004.64 ± 6.12
| 10 years 10 years old | 888888888834.32 ± 6.40 | 140.30 ± 6.30 | 33.76 ± 5.26 | 140.33 ± 5.60 | |||
| years 11 years | 37.40 ± 7 06 | 144.58 ± 7.08 | 35.44 ± 6.64 | 143.38 ± 5.72 | |||
| 12 years 9004 038 | 152. 81 ± 7.01 81 ± 7.01 | 41.25 ± 7.40 | 150.05 ± 6.40 | ||||
| 48.70 ± 9.16 | 156.85 ± 6.20 | 45.85 ± 8.26 | 156.65 ± 8.00 | ||||
| 14 years old | 51.32 ± 7.30 | 160.86 ± 6.36 | 51 , 18 ± 7.34 | 162.62 ± 7.34 | |||
| 15 years old | 56.65 ± 9.85 | 161.80 ± 7.40 | 56.50 ± 13.50 ± 13.50 | 168.10 ± 9.50 | |||
| 16 years old | 58.00 ± 9.60 | 162.70 ± 7.50 | 62.40 ± 14.10 | 172.60 ± 9.40 | |||
| 17 years old | 58.60 ± 9.40 | 163.10 ± 7,30 | 67.35 ± 12.75 | 176.30 | |||
Deviations of weight or height from tabular values
There is no need to panic if there is a minimal discrepancy with the indicated values in the table, and here's why:
- First of all, the child's height and weight charts contain reference indicators , what should ideally be the weight and height of the child, without taking into account many other factors .
 Sometimes parents of premature babies mistakenly use a standard table for comparison, while there are special tables for assessing the development of children born prematurely.
Sometimes parents of premature babies mistakenly use a standard table for comparison, while there are special tables for assessing the development of children born prematurely. - The rate of growth and weight gain for each child is unique . In the first year of life, babies develop in leaps and bounds. For example, during the period of introducing complementary foods, the weight of the baby may not reach the “norm” due to adaptation to a new type of food, and not because of pathology.
This does not mean that deviations from the norm should be ignored , but it is better to regard them as an occasion to pay attention and consult a specialist in order to identify possible health problems, or to make sure that they are not present.
What can cause obvious deviations from the norm?
Earlier we talked about minor deviations from the norm and that there is no need to be scared if your child is not growing and gaining weight strictly according to the chart. But what to do if the values of the essential have gone beyond the limits of the permissible parameters , or are they at the intersection of norm and pathology?
But what to do if the values of the essential have gone beyond the limits of the permissible parameters , or are they at the intersection of norm and pathology?
Reasons for possible deviations can be divided into two groups:
1. Non-endocrine:
- Constitutional growth retardation . Or in another way, the syndrome of late puberty. One of the variants of the norm, when the puberty jump occurs later than in other children.
- Family stunting . It has a hereditary predisposition, in the family of such children there are relatives with short stature. Growth retardation manifests itself from early childhood.
- Prematurity, intrauterine and postnatal injuries.
- Genetic syndromes . As a rule, they have many clinical manifestations, one of which is growth retardation.
- Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular, bronchopulmonary systems, gastrointestinal tract, as well as anemia.
- Fasting .
- Taking certain medications .
2. Endocrine:
- Growth hormone deficiency . Biologically active substance, which is the main regulator of the growth process after 2 years.
- Deficiency of thyroid hormones . More often of a congenital nature, it is clinically characterized by a delay in physical and intellectual development from birth.
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus . A disease in which, due to insulin deficiency, the flow of glucose into the cells of the body is impaired, the so-called. "starvation" of cells, as a result, growth rates slow down.
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease (or syndrome) . At the same time, the production of hormones of the adrenal cortex, glucocorticoids, is increased, which in large doses leads to a violation of the secretion of growth hormone.
- Rickets .
 A lack of vitamin D leads to bone destruction and skeletal deformities, which in turn is manifested, among other things, by a decrease in growth.
A lack of vitamin D leads to bone destruction and skeletal deformities, which in turn is manifested, among other things, by a decrease in growth. - Other rare disorders of the endocrine system.
As you can see, there are a lot of reasons.
If the child's growth is stunted, parents should consult a doctor to identify the causes of short stature and correct it in a timely manner.
Which specialist should I contact? First, you should make an appointment with a pediatrician. Also, in most cases, consultation with a pediatric endocrinologist is required.
Remember that for the normal growth of the child you need a complete, balanced diet with enough vitamins and minerals, as well as dosed physical activity.
Growth and weight standards for children and adolescents
The physical development of a child as a combination of various indicators (length, weight, shape, strength, etc.) characterizing his growth and development is due to a complex of hereditary and social factors.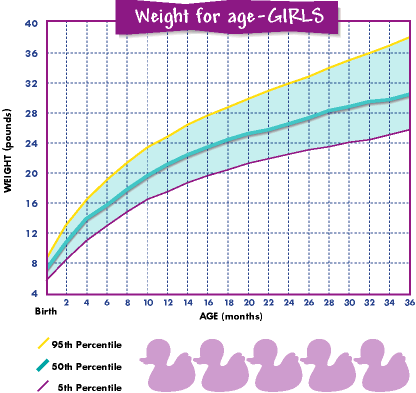 To study the physical development of children and adolescents, a unified method for measuring the human body and its parts has been developed. All anthropometric indicators can be divided into two groups: basic (body length, body weight, chest and head circumference) and additional (other anthropometric indicators, for example, leg length, head height, etc.). Analysis of the main anthropometric indicators at the time of the examination makes it possible to assess the physical condition of the child, in dynamics - the pace of physical development. At the same time, the features of the physique, the state of the musculoskeletal system, the degree of puberty, etc. are taken into account. Physical development is analyzed by comparing individual or group indicators with average data (standards) characteristic of the corresponding age and gender of the child.
To study the physical development of children and adolescents, a unified method for measuring the human body and its parts has been developed. All anthropometric indicators can be divided into two groups: basic (body length, body weight, chest and head circumference) and additional (other anthropometric indicators, for example, leg length, head height, etc.). Analysis of the main anthropometric indicators at the time of the examination makes it possible to assess the physical condition of the child, in dynamics - the pace of physical development. At the same time, the features of the physique, the state of the musculoskeletal system, the degree of puberty, etc. are taken into account. Physical development is analyzed by comparing individual or group indicators with average data (standards) characteristic of the corresponding age and gender of the child.
The value of indicators of a child's physical development can be explained by a number of arguments. For many chronic diseases of childhood, there are no specific symptoms related to the early stage of the development of the disease, therefore, a violation of physical development is one of the first signs of trouble and serves as an indication for an in-depth examination of the child. Violations of the physical development of children and adolescents may be the result of malnutrition, lack of necessary care, improper or harsh treatment of the child, etc. Violations of physical development can cause constitutional features, congenital or hereditary pathology of the developmental apparatus. Such children have imperfect mechanisms of adaptation and anti-infective protection, for example, a lack of body weight in a child may be accompanied by a higher frequency of minor developmental anomalies. Any deviations of anthropometric parameters from the norm at the birth of a child can become one of the reasons for the decrease in immunological resistance, increasing the likelihood of a disease in the first year of life by half, and the probability of death by 4 times. All factors characterizing the growth and development of the child's body can be divided into genetic and environmental factors. The influence of heredity affects the growth of the child after 2 years of life.
Violations of the physical development of children and adolescents may be the result of malnutrition, lack of necessary care, improper or harsh treatment of the child, etc. Violations of physical development can cause constitutional features, congenital or hereditary pathology of the developmental apparatus. Such children have imperfect mechanisms of adaptation and anti-infective protection, for example, a lack of body weight in a child may be accompanied by a higher frequency of minor developmental anomalies. Any deviations of anthropometric parameters from the norm at the birth of a child can become one of the reasons for the decrease in immunological resistance, increasing the likelihood of a disease in the first year of life by half, and the probability of death by 4 times. All factors characterizing the growth and development of the child's body can be divided into genetic and environmental factors. The influence of heredity affects the growth of the child after 2 years of life.
Hereditary factors mainly determine the rate and possible limit of a child's growth under optimal environmental conditions.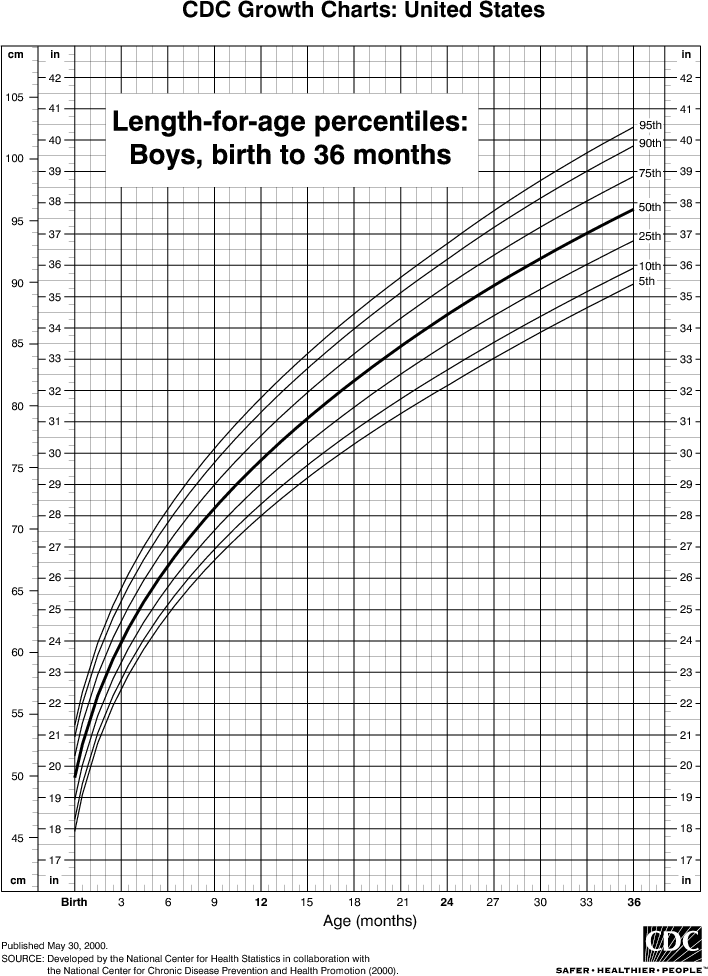
The influence of environmental factors on the growth rate of the child's body can be traced very clearly. Among these factors, nutrition and vitamin sufficiency, motor mode and emotional stress, acute and chronic diseases, the influence of climatic and geographical conditions, etc. are distinguished. At the same time, environmental factors can slow down or accelerate growth processes, but in general the growth trend is quite stable, it obeys the conservation law growth. A variety of adverse influences that disrupt the individual growth rate of a child can subsequently be neutralized by the phenomenon of "catch-up or compensatory growth." What happens to the physical development of your baby from the moment of birth to its full maturity? We observe the growth and development of a child in the first year of life: How can we understand if he is healthy, is everything okay with him? Remember: the health of a child is judged primarily by its weight, height and head circumference. On average, a newborn's body weight is 3.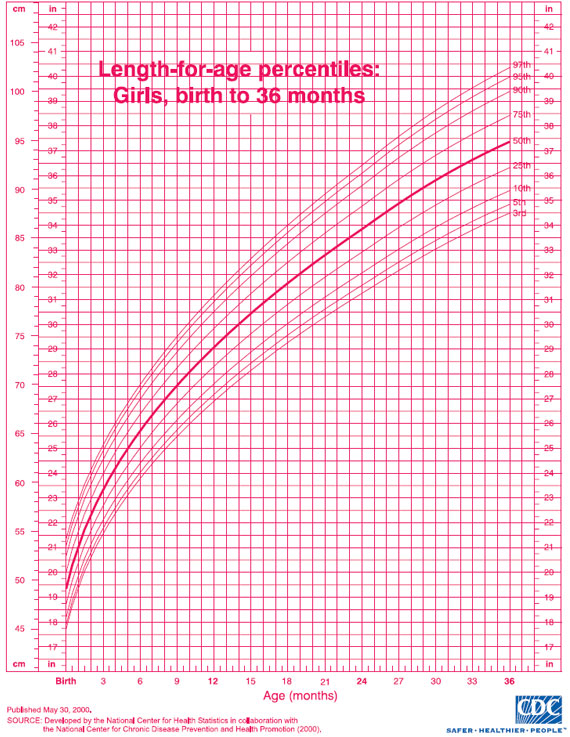 0-3.5 kg, body length 50 cm, head circumference 35 cm. But do not expect your baby to necessarily meet this standard. Children are considered normal if their indicators are within the following limits: body weight 2.5-4.5 kg, length 45-55 cm, head circumference 33-37 cm. Immediately after birth, babies lose some weight, and then regain it and start adding. Further weight gain as well as height and head circumference are important indicators of your child's condition. By the end of the 1st year of life, body length increases by 47% in relation to body length at birth.
0-3.5 kg, body length 50 cm, head circumference 35 cm. But do not expect your baby to necessarily meet this standard. Children are considered normal if their indicators are within the following limits: body weight 2.5-4.5 kg, length 45-55 cm, head circumference 33-37 cm. Immediately after birth, babies lose some weight, and then regain it and start adding. Further weight gain as well as height and head circumference are important indicators of your child's condition. By the end of the 1st year of life, body length increases by 47% in relation to body length at birth.
Weight gain of a child in the first year of life: by 4-5 months, body weight doubles, by the 1st year it increases 3 times. The head circumference of a child in the first 6 months of life increases by approximately 1 cm per month, but if the father of the child is large and the mother is small, the growth rate of the head circumference may be above the norm, and in the opposite ratio - below the norm. The circumference of the chest of newborns is less than the circumference of the head, these dimensions are equalized only by the age of one.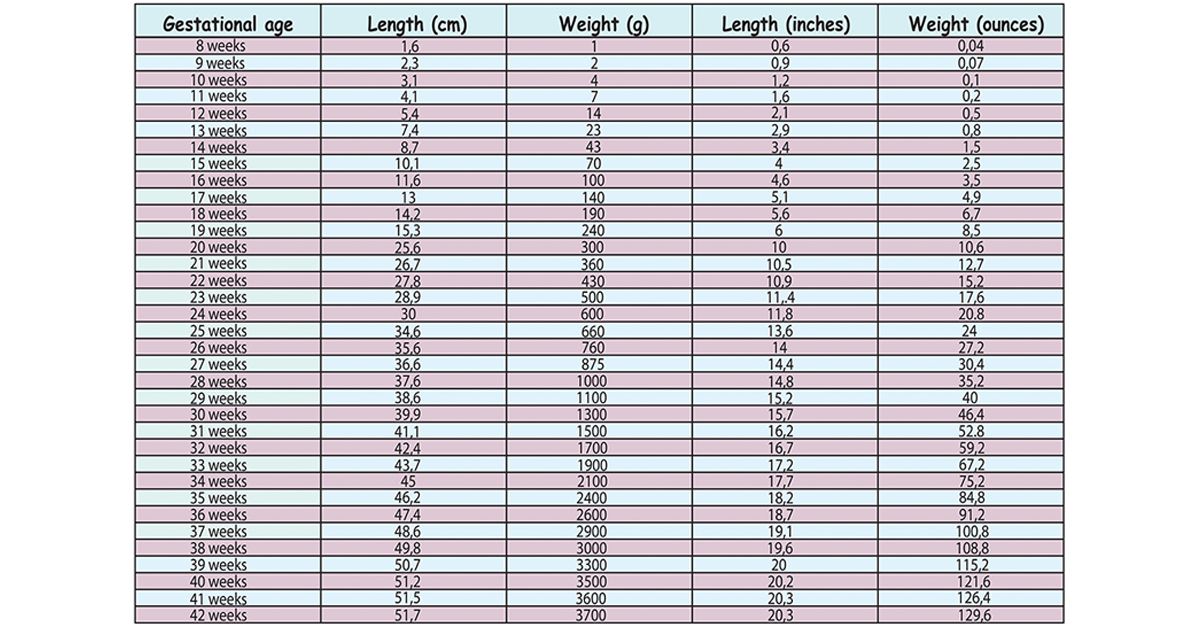 In the first month of life, the child must be weighed daily. Thus, you monitor the development of lactation and fix the daily weight gain. Body weight is the most sensitive indicator of a child's health: whether he fell ill, whether his appetite worsened, whether his sleep was disturbed, whether you made any errors in care - all this will immediately be reflected in grams. A sign of nutritional adequacy is normotrophy - the correspondence of body weight due to a given body length of a child. If the weight of the baby has decreased by more than 10%, this is already a sign of malnutrition (malnutrition). Equally alarming is excess weight - parotrophy (excess nutrition). But the increase in the growth of the child is a more stable indicator, and its violations often indicate the presence of the disease.
In the first month of life, the child must be weighed daily. Thus, you monitor the development of lactation and fix the daily weight gain. Body weight is the most sensitive indicator of a child's health: whether he fell ill, whether his appetite worsened, whether his sleep was disturbed, whether you made any errors in care - all this will immediately be reflected in grams. A sign of nutritional adequacy is normotrophy - the correspondence of body weight due to a given body length of a child. If the weight of the baby has decreased by more than 10%, this is already a sign of malnutrition (malnutrition). Equally alarming is excess weight - parotrophy (excess nutrition). But the increase in the growth of the child is a more stable indicator, and its violations often indicate the presence of the disease.
Assess the rate of development of your child in the first year of life, prescribe additional examinations in case of violations of the rate of weight gain, body length, head and chest circumference, correct nutrition, if necessary, a pediatrician will be able to, therefore the cooperation of parents is so important with a doctor from the very first year of a baby's life.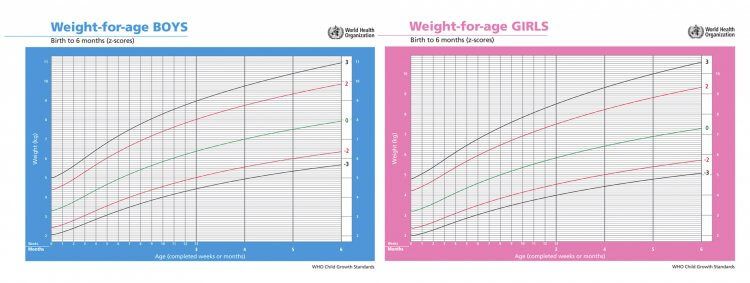
It must be remembered that during the first month the pediatrician examines the child weekly, then, if the development of the baby corresponds to normal indicators, monthly. Assessment of the physical development of a child from one to 10 years. After your baby is one year old, he begins to grow by leaps and bounds. In the second year of life, he adds about 2.5-4.0 kg, and growth increases by 10-15 cm. At the age of 3 to 5 years, the baby adds 2 kg and 3 kg per year.
The head circumference of a child from 51 cm at the age of 5 increases to 53-54 cm at the age of 12. At 5-8 years old, the first traction occurs. But not all children grow in the same way - depending on a variety of factors, such as genetic ones. Children of undersized parents are usually smaller than their peers, but their puberty processes still occur on time. Faster growth than that of peers, with normal body proportions, is characteristic of children of tall parents. In some babies, the growth rate slows down from the second year of life, but after 2-3 years it accelerates again to normal.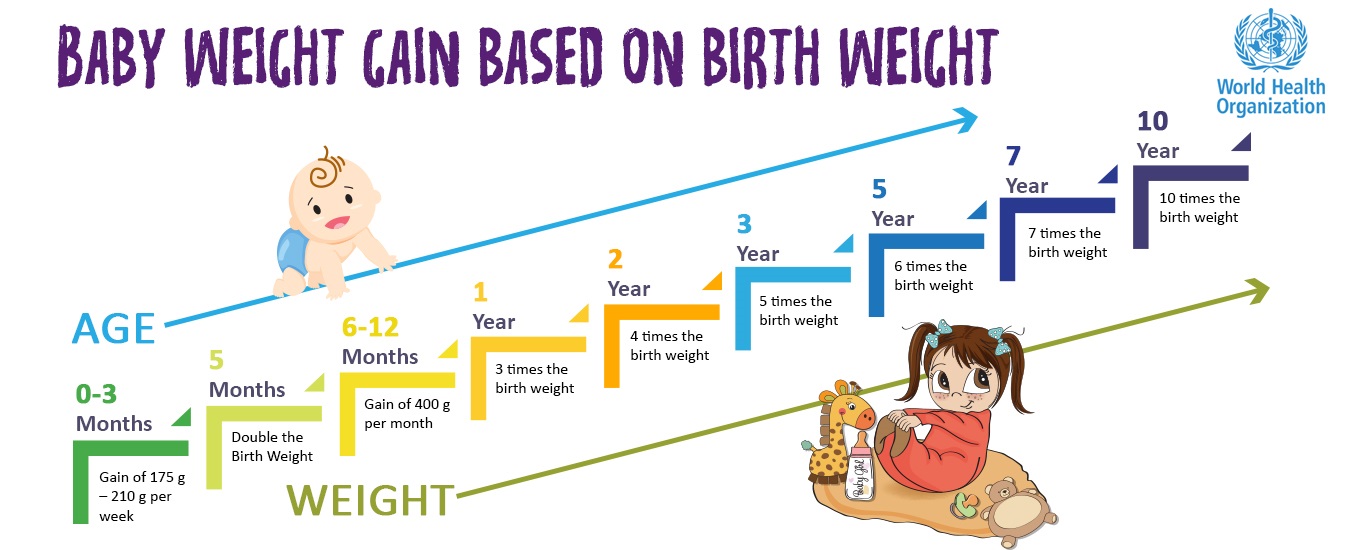 They have both growth and the onset of puberty delayed by a period during which growth was retarded, but final growth is in line with genetic potential. You must understand: the growth rate of the child should not correspond to any exact parameters, the criteria for “normality” are not at all rigid, but nevertheless, deviations in the growth rate of the child can also be pathological: for example, grossly out of proportion to age or accompanied by a violation of proportions body. Such cases require expert advice. It is also necessary to control body weight. As mentioned above, the lack and excess of body weight requires close monitoring of pediatricians, endocrinologists. In children with reduced body weight, there is a decrease in the immunological reactivity of the body, which leads to frequent colds. And excess everything is a risk factor for acquiring obesity in the future and all the serious diseases associated with it: atherosclerosis, heart disease, colon cancer, etc.
They have both growth and the onset of puberty delayed by a period during which growth was retarded, but final growth is in line with genetic potential. You must understand: the growth rate of the child should not correspond to any exact parameters, the criteria for “normality” are not at all rigid, but nevertheless, deviations in the growth rate of the child can also be pathological: for example, grossly out of proportion to age or accompanied by a violation of proportions body. Such cases require expert advice. It is also necessary to control body weight. As mentioned above, the lack and excess of body weight requires close monitoring of pediatricians, endocrinologists. In children with reduced body weight, there is a decrease in the immunological reactivity of the body, which leads to frequent colds. And excess everything is a risk factor for acquiring obesity in the future and all the serious diseases associated with it: atherosclerosis, heart disease, colon cancer, etc.
- Increase in the recommended amount of food;
- Satisfying a child's thirst with milk, sugary drinks or formula;
- Excessive (more than 50-100 ml per day) consumption of sweet fruit juices and nectars;
- Use of excess high-calorie foods - fat, sweets, baked cottage cheese;
- Calming the child with food;
- Familial overeating, which distorts the child's development of a real sense of the need for food;
- Force-feeding, inculcating the habit of eating everything on the plate.

Your pediatrician and endocrinologist will be able to establish the correct diet, give recommendations on the daily diet. Please remember that in the second year of life, the pediatrician examines the child once a quarter, from the third year of life once every six months, in the fourth year and then once a year. Your child is between 10 and 15 years old. A uniform increase in the growth of preschoolers is replaced by its sharp acceleration in adolescence. At 10-13 years old (for girls) and at 12-15 years old (for boys) there is a second traction and at the same time an increase in body weight. The maximum growth rate in girls usually occurs at 12 years of age. The increase in height at this age is approximately 8 cm per year. The maximum increase in body weight in girls usually occurs later at 13 years of age. In boys, the maximum growth rate usually occurs at 14-15 years of age and is approximately 10 cm per year. The maximum increase in the body of a boy usually occurs with a maximum increase in height. The probable final height depends on the height of the parents. It can be calculated using the following formula: Boy's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) + 6.5 cm Girl's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) - 6.5 cm. Possible error must be taken into account - the final height can be 8.5 cm more or less.
The probable final height depends on the height of the parents. It can be calculated using the following formula: Boy's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) + 6.5 cm Girl's height = 1/2 x (father's height + mother's height) - 6.5 cm. Possible error must be taken into account - the final height can be 8.5 cm more or less.
Boys themselves and their parents are often worried about delays in growth acceleration, while girls, on the contrary, are worried about excessive growth. However, you need to worry only if the child's growth parameters differ significantly from the parameters indicated in special tables and graphs. In such a situation, it is necessary to contact an endocrinologist.
Remember - there are methods that can influence these processes. One of the most important features of the physical development of children and adolescents is the uneven change in growth rate. In children, the distal segments of the body grow at a faster rate and in a shorter time than the upper and proximal segments.