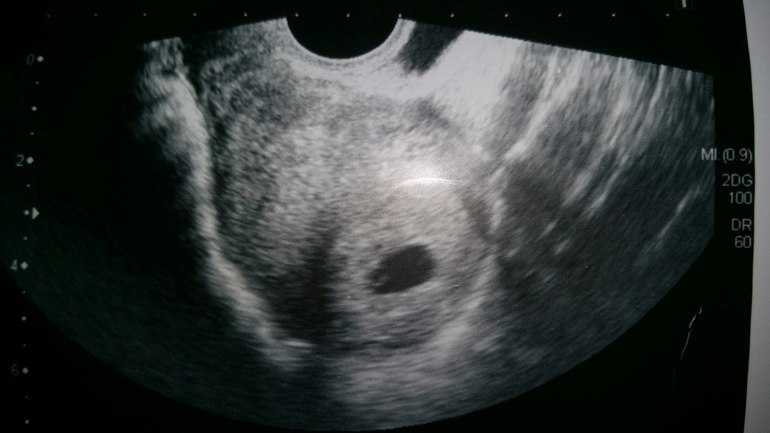
7 weeks empty sac
Blighted Ovum (Anembryonic Pregnancy): Causes & Symptoms
Overview
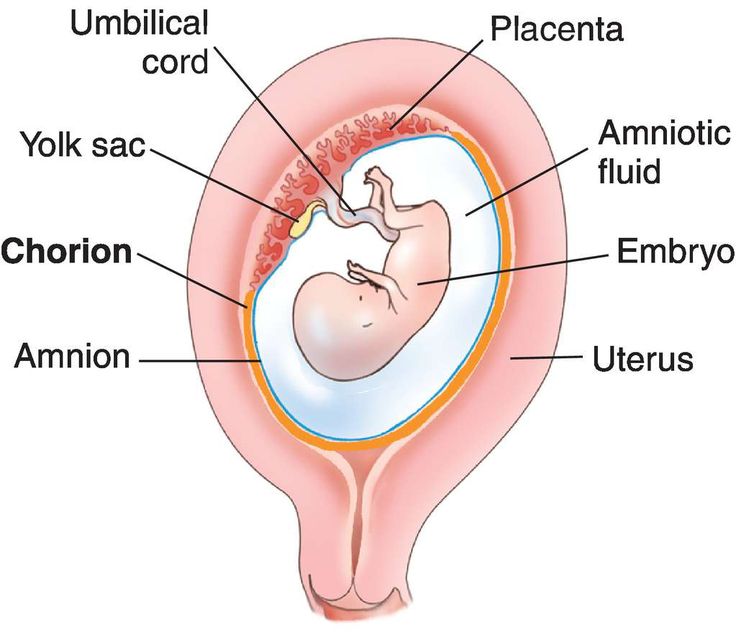
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.What is a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum (also called an anembryonic pregnancy) is a type of early miscarriage that occurs when a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but does not develop into an embryo. The embryo will stop growing, but the gestational sac (where the embryo would develop) continues to grow. The placenta and empty gestational sac will release pregnancy hormones — even without an embryo present. This causes you to have early symptoms of pregnancy or even have a positive pregnancy test. Sometimes it occurs so early in pregnancy that you don't know you're pregnant.
When does a blighted ovum happen?
A blighted ovum causes an early miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. During fetal development, a fertilized egg turns into a blastocyte. At around four weeks of pregnancy, this blastocyte implants in the wall of the uterus and develops into an embryo. When you have a blighted ovum, the gestational sac that would hold the embryo continues to grow, even without an embryo present. The following can occur:
- A blighted ovum happens so early in pregnancy, that you never realize you are pregnant.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy only to discover a blighted ovum at your first ultrasound.
- You have a positive pregnancy test and signs of pregnancy but then experience a miscarriage.
How common is a blighted ovum pregnancy?
A blighted ovum is the number one cause of first trimester miscarriages.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum can occur so early in pregnancy that you never knew you were pregnant. In other cases, you may experience signs of pregnancy such as a missed menstrual period or a positive pregnancy test. You can have symptoms of early pregnancy, such as breast tenderness and morning sickness.
Other times your symptoms will resemble those of a miscarriage:
- Vaginal bleeding: Spotting (light bleeding), bleeding or passing light gray tissue or blood clots.

- Cramping: Mild to moderate cramping in your pelvic and abdominal region.
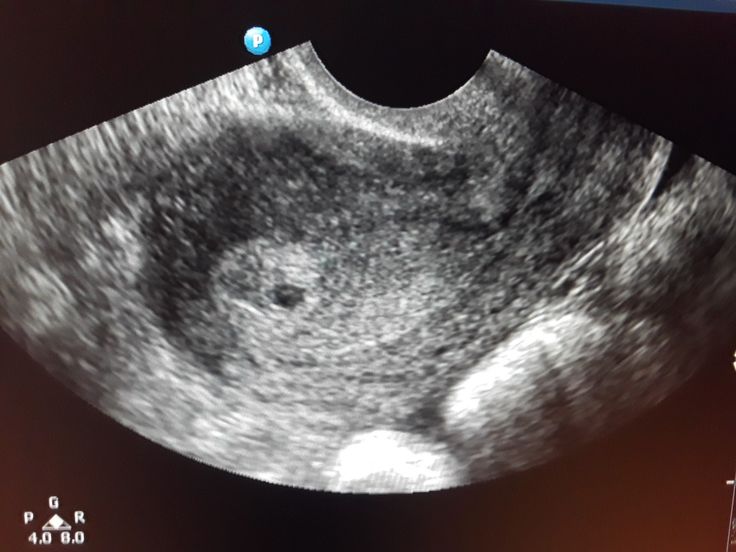
The only way to confirm a blighted ovum is through an ultrasound. It will show a gestational sac that is missing an embryo inside.
What causes a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum is usually caused by chromosomal or genetic problems during cell division. During conception, the egg will begin to divide shortly after being fertilized by sperm. Around ten days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops growing after it’s formed.
How does a blighted ovum miscarriage start?
A blighted ovum miscarriage will cause vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping. A miscarriage usually feels more intense than your regular menstrual period. You can take an over-the-counter medicine like acetaminophen to relieve cramping. Avoid lifting anything heavy or any strenuous exercise as it can increase your bleeding. You may experience spotting for several weeks after a miscarriage.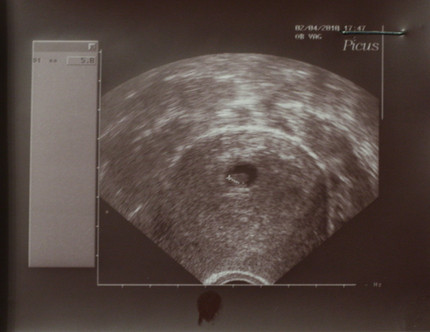
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a blighted ovum diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will diagnose a blighted ovum using transvaginal ultrasound. This happens in the first trimester, usually between seven and nine weeks of pregnancy. An embryo should be visible at this time in pregnancy. With a blighted ovum, the gestational sac will be empty.
- You will lie back on an exam table and place your feet in stirrups like you do for a pelvic exam. Your healthcare provider will put an ultrasound wand into your vagina to see the contents of your uterus.
- A blighted ovum will appear as an empty sac — almost like a bubble.
A blighted ovum is when the gestational sac containing the embryo is empty.
People are often unaware that they have a blighted ovum. This is because your placenta continues to give off hormones, making your body think you are pregnant. This is also why you can still have symptoms of pregnancy, including a positive pregnancy test.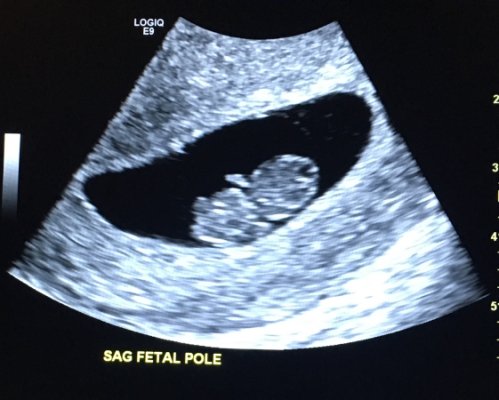
If you’ve already experienced bleeding or signs of a miscarriage, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound to look at the contents of your uterus to diagnose a blighted ovum.
Some healthcare providers will collect a series of blood samples that check the levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your body. HCG is known as the pregnancy hormone because it's only produced if you are pregnant. The level of hCG in your blood increases rapidly in early pregnancy and reaches its peak around weeks eight to ten. If it's not rising quickly, it can indicate a miscarriage or other complication. Your provider may decide to test your hCG levels over the course of several days to evaluate how your hCG levels are rising. This can be an effective tool for diagnosing blighted ovum.
Management and Treatment
How is a blighted ovum treated?
For some people, there may be no treatment needed, because your body passes the embryo through your vagina (a miscarriage). If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
If your body does not miscarry the embryo, there are other options to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will talk you through possible treatments:
- Dilation & Curettage (D&C): This is a surgical procedure to remove the contents of your uterus. Your healthcare provider will dilate, or open, the cervix and use medical tools and suction to remove the pregnancy tissues from your uterus. This is done under sedation or general anesthesia.
- Natural miscarriage: If it's safe, you may be able to watch and wait to see if your body eventually releases the pregnancy tissues. It can sometimes take days or weeks for this to start. Your healthcare provider will let you know if this is an option for you. You will experience cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding once the miscarriage begins.
- Medication-induced miscarriage: You may be given a medication called misoprostol to trigger your body to miscarry.
 This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
This moves the process along and eliminates the time waiting for a miscarriage to start on its own. You will have cramping, abdominal pain and bleeding within 30 minutes to ten hours of taking the medication.
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled four to six weeks after a miscarriage or D&C. You may be given another ultrasound to confirm the uterus is empty. Your healthcare provider will check for signs of infection and make sure there were no complications.
What are the complications of a blighted ovum?
Complications of a blighted ovum are uncommon, but the possible complications could include:
- Excessive bleeding or hemorrhage.
- Infection.
- Scarring (from the D&C procedure).
- Tears in the uterus (from the D&C procedure).
How long does it take to recover from a blighted ovum?
Recovering from a blighted ovum miscarriage or D&C can last from one or two weeks to a month. Cramping generally lasts up to a week, but bleeding can last several weeks. Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
Your bleeding should get lighter until it stops completely.
You can resume normal activities when you feel comfortable. Bleeding can increase with strenuous activity or exercise. Hormones may remain in your body and delay your menstrual cycle. Most people will get their period within four to six weeks after a blighted ovum.
It may take longer to recover emotionally from a blighted ovum miscarriage. You may have feelings of sadness, anger or confusion. It’s OK to take time to grieve. Ask your friends and family for support.
Prevention
Can a blighted ovum be prevented?
A blighted ovum can’t be prevented. Some couples may want to do genetic testing on the tissue inside the uterus. This checks for underlying causes of your miscarriage and can be helpful to couples who have experienced multiple pregnancy losses.
Outlook / Prognosis
How soon after a blighted ovum can I get pregnant again?
Most healthcare providers recommend having one or two regular menstrual cycles before trying to conceive again after any type of miscarriage.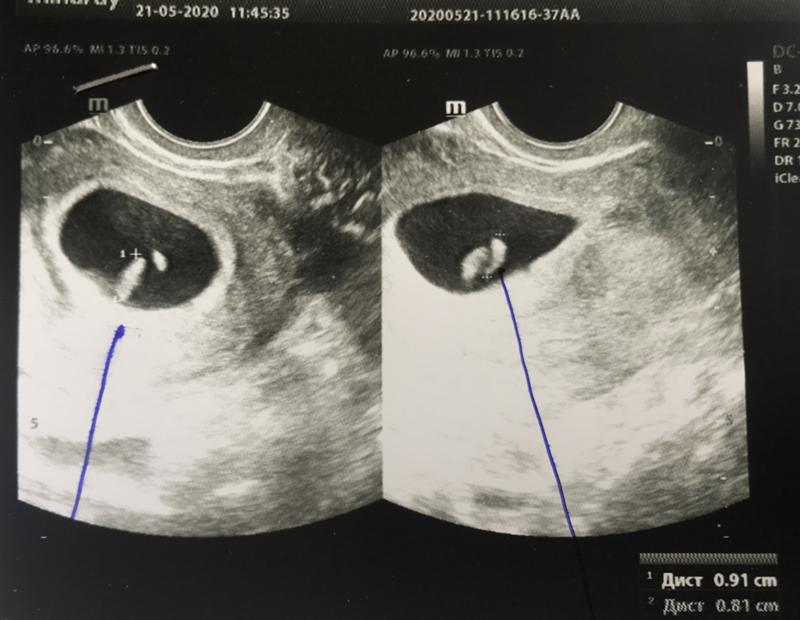
What are my chances of having another blighted ovum?
Your chances of having another blighted ovum are low. Most people go on to have healthy, full-term pregnancies. If you experience more than one blighted ovum, your healthcare provider may suggest testing to determine if there is an underlying cause.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- Excessive bleeding from your vagina.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Fever that does not go away.
- Symptoms that get worse over time.
- Severe pain that isn’t helped with pain medicine.
When should I go to the ER?
Go to the nearest ER If you experience heavy vaginal bleeding — more than two pads per hour for two consecutive hours — or have symptoms of anemia like dizziness, palpitations or paleness.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Losing a pregnancy is upsetting and confusing.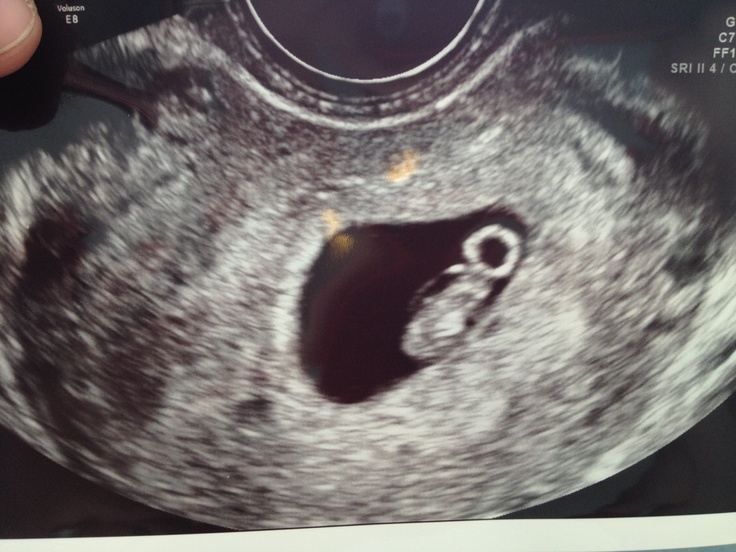 Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
Do not be embarrassed to ask any questions you have. It's completely normal to have questions and feel emotional during this time. Some questions you may ask are:
- Can I let my body miscarry or should I take medication to induce a miscarriage?
- What are the risks of miscarriage?
- Do I have to have a D&C?
- What are the risks of a D&C?
- How long can I expect to bleed or have cramping?
- Is there any indication this will happen again?
- When can I start trying to conceive?
- Do I need to come back for another ultrasound?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a blighted ovum considered a miscarriage?
Yes, a blighted ovum is a miscarriage. A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. A blighted ovum is considered an early miscarriage because it occurs before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
How long can you carry a blighted ovum?
The amount of time you can carry a blighted ovum varies. Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Your placenta will continue to grow and release hormones without an embryo. For some people, a miscarriage can occur within a few days or weeks. Others may still believe they are pregnant only to discover a blighted ovum at their first ultrasound.
Can a blighted ovum turn into a baby?
No, an empty gestational sac will not turn into an embryo. The formation of the embryo occurs within two weeks of conception. By the time the gestational sac is formed, the cells should have already formed the embryo. Your healthcare provider will be able to examine your gestational sac to confirm that no embryo has developed.
Do hCG levels rise with blighted ovum?
Yes, most of the time hCG levels will rise, giving you a positive pregnancy test and symptoms of pregnancy. This is because the placenta continues to give off hCG even if an embryo is not present. The hormone hCG is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone because it is only produced if you are pregnant.
Is a blighted ovum more common with IVF?
A blighted ovum is not more common with IVF (In Vitro Fertilization). Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
Your chances of having a blighted ovum with IVF treatment are about the same as they would be with a natural conception.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Losing a pregnancy is difficult. If you are struggling after a miscarriage, speak with your healthcare provider so they can recommend support groups or counselors. Finding support may help you get through this hard time. Most people who have had a blighted ovum will go on to have a healthy pregnancy.
What You Should See (and Why You May Not)
Your first pregnancy ultrasound is usually an exciting event: You’re 12 or 13 weeks pregnant and looking forward to getting a glimpse of the baby that’s been growing for the last 3 months. You know they’re going to look like an alien, but still — they’ll be your little alien, and you can’t wait.
Sometimes, though, an earlier ultrasound is necessary, and we’ll be honest: It’s weird. Why? Because a ton of gestational development happens between 7 and 12 weeks, making an early ultrasound a completely different experience than the traditional one in your first trimester.
A 7-week ultrasound may not be the bonding experience you’re hoping for, since there’s a lot you may not see. But here’s what you can expect.
Although a 7-week ultrasound isn’t routinely performed, there are actually a bunch of reasons why your doctor might want you to have one — and not all of them fall into the “doom and gloom” category.
In fact, the most common reason doctors order ultrasounds before the 12- or 13-week point is to accurately date your pregnancy.
If your pregnancy symptoms don’t match up with your last menstrual period or there’s any confusion about how old your baby is — gestationally speaking — the measurements taken during an early ultrasound can tell your doctor exactly how far along you are in your pregnancy.
Other reasons for an early ultrasound include:
- Confirming twins or multiples. Especially if you’ve had fertility treatments, this might be something you want to confirm ASAP.
- Confirming fetal heartbeat.
 If you’ve had any concerning symptoms, like spotting or vaginal bleeding, your doctor will want to know if you’re experiencing a miscarriage or what the cause of any unexplained bleeding could be.
If you’ve had any concerning symptoms, like spotting or vaginal bleeding, your doctor will want to know if you’re experiencing a miscarriage or what the cause of any unexplained bleeding could be. - Ruling out an ectopic pregnancy. When an embryo implants outside the uterus, you’ll often have pregnancy symptoms and a positive pregnancy test, even though the embryo isn’t viable. An ectopic pregnancy is a life threatening condition if it’s not treated, so it’s important to diagnose it.
- Checking your reproductive anatomy. Issues with your uterus, cervix, ovaries, or fallopian tubes can cause complications during pregnancy. So, if your doctor suspects you might have a problem — like uterine fibroids, for example — they may want to have that info right away.
Again, it isn’t cause for immediate panic if your doctor orders a 7-week ultrasound. Yes, it could be a worst-case scenario, but it could also just be one where you’re collecting as much info as possible so you can have a healthy pregnancy.
Pop culture has likely taught you that your first ultrasound is a beautiful experience where a technician waves a magic wand over your stomach and you get to stare at a computer screen and see the adorable shape of your baby floating peacefully in your uterus.
But that’s not what happens at a 7-week ultrasound, so let’s just blow that expectation out of the water now. (Sorry!) In most cases, your baby is too small to be seen clearly — or at all — on an external abdominal ultrasound. Instead, you’ll need a transvaginal ultrasound.
It sounds less than fun, we admit, and it is a less-than-fun procedure: A technician inserts an ultrasound wand, called a transducer, a few inches into your vagina until it reaches your cervix.
Then, the technician keeps it in place, adjusting the wand as much as needed to get a good look at the inside of your uterus. It’s not painful, though it may be uncomfortable.
You’ll feel about as much pressure as you do during your annual gynecology exam, for comparison. It does take longer, which can add to the overall unpleasantness, but the technicians are trained to make you comfortable — at least, as comfortable as you can be with an ultrasound wand inside in your vaginal canal.
It does take longer, which can add to the overall unpleasantness, but the technicians are trained to make you comfortable — at least, as comfortable as you can be with an ultrasound wand inside in your vaginal canal.
The good news? There’s no risk to your baby from the procedure and there’s no radiation used. So, while it won’t go down in history as one of your favorite experiences, it can’t cause any harm.
Share on PinterestHave a nice day Photo/Shutterstock
A 7-week ultrasound showing crown rump length of baby, which helps figure out the age of the fetus. Surrounding the fetus is the gestational sac, which is filled with fluid.
You’re not going to be counting fingers and toes at this ultrasound; the embryo is simply too tiny for clear images to be detected. You may see the general shape of your baby or be able to tell something is there, but it’s also normal to not see anything that looks very much like a baby at all.
One thing you will often see in a healthy pregnancy is your baby’s heartbeat.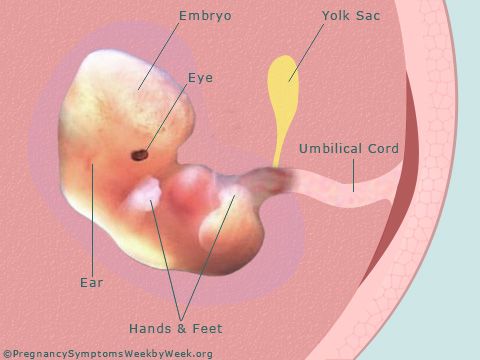 It could be going as fast as 110 beats per minute or more! If your baby is in a visible position on the ultrasound, you’ll probably see a little blinking or pulsing on the screen (and you should be able to hear it briefly, too).
It could be going as fast as 110 beats per minute or more! If your baby is in a visible position on the ultrasound, you’ll probably see a little blinking or pulsing on the screen (and you should be able to hear it briefly, too).
You may see the following anatomical developments on a 7-week ultrasound:
- Gestational sac. This is one of the earliest visible signs of a pregnancy, and it refers to the fluid-filled space surrounding the embryo. It’s usually formed by 5 weeks of gestation, and it can accurately confirm an intrauterine pregnancy the vast majority of the time it’s seen on an ultrasound. It will look like a clear, dark circular or oblong shape, sharply contrasted with the whitish, opaque appearance of the inside of your uterus.
- Yolk sac. Even before you can see an embryo inside the gestational sac, you should spot the yolk sac. It’s the first thing to develop inside the gestational sac, and it provides your baby with nutrients and oxygen until the placenta develops.
 It’ll look like a small white ring or bubble inside the sac.
It’ll look like a small white ring or bubble inside the sac. - Fetal pole. This is the first indication that your baby is forming inside the gestational sac. It will look like a thick, whitish shape attached to the yolk sac. Depending on how far along you are, it may be curved or oblong. It can usually be detected by 6 weeks of gestation on a transvaginal ultrasound. This is where you would see the baby’s heartbeat.
Aside from detecting a heartbeat, the point of a 7-week ultrasound is to take measurements of these fetal developments so your doctor has a better idea of where you are in your pregnancy.
That’s why this is often called a dating ultrasound: The measurements are a good indicator of gestational age.
The technician will measure the size of your gestational sac and also take a crown-to-rump measurement of the embryo, if it’s visible. At 7 weeks, your baby should be about 5 to 9 millimeters (mm) in size and the gestational sac will be about 18 to 24 mm.
At this point, fetal development is on a fast track and making large leaps in size from one week to the next.
A gestational sac measuring well below 18 mm will probably reduce your gestational age — that is, your doctor might tell you you’re only 5 or 6 weeks pregnant, not 7. The opposite is true for a sac that measures much larger than 24 mm.
Keep in mind that ultrasounds aren’t a perfect diagnostic tool, and things like the position of your baby can affect the accuracy of the measurements — or whether your technician is able to take them at all.
If the results are inconclusive, your doctor may ask you to schedule another ultrasound in 1 or 2 weeks to try again.
Considering that most people don’t realize they’re pregnant until they’re at least 3 or 4 weeks in — and the gestational sac is the very first thing to form in your uterus — it’s likely that by the time of your ultrasound, you’ll see at least this initial development with a healthy pregnancy.
But you may not be able to see a yolk sac, the fetal pole, the early shape of your baby, or your baby’s heartbeat yet. And if you don’t, try not to worry.
And if you don’t, try not to worry.
You could be earlier in your pregnancy than you’d first assumed, with a later ovulation window than you’d thought. You could also have a tilted uterus, which can make it harder to see your baby until they’re a little bigger.
That said, the 7-week ultrasound could also reveal a hard truth about the health of your pregnancy.
If there are no signs of pregnancy or inconsistent signs, like a large gestational sac without any yolk sac or fetal pole, it may mean you have a blighted ovum or are otherwise miscarrying. This is very common in the earliest weeks of pregnancy, when the risk is the highest.
If you’re still experiencing early pregnancy symptoms but no fetal growth at all can be found in your uterus, your technician will probably look for signs of an ectopic pregnancy. This may be done along with blood tests and a pelvic exam.
Yes, especially if they’re fraternal. Figuring out how many babies are growing in your uterus is one of the main reasons for having an early ultrasound.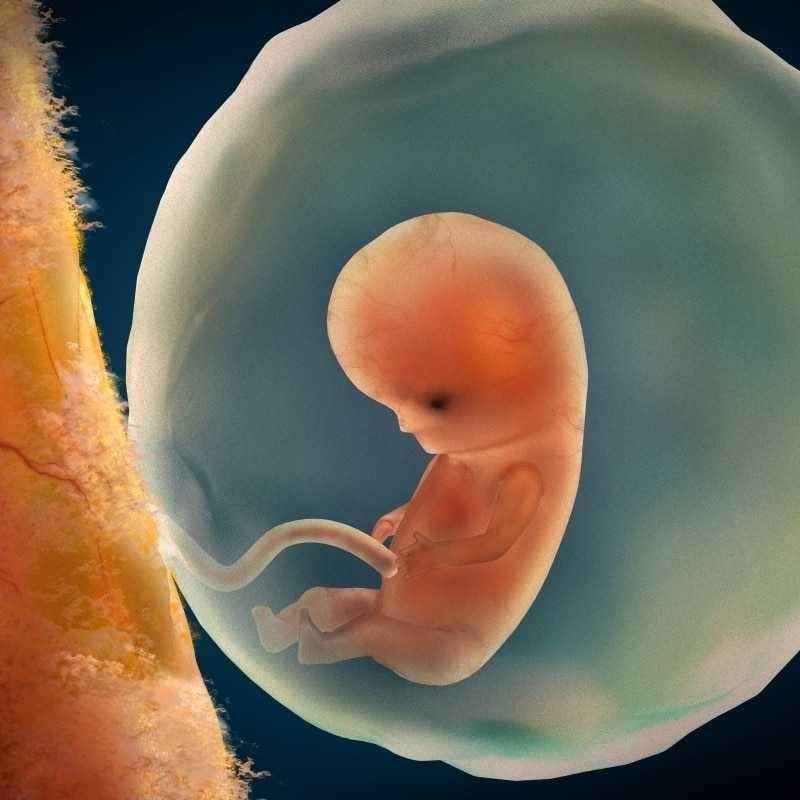
If your twins are fraternal — meaning, two different eggs were fertilized — there will be a separate gestational sac for each baby. If you’re estimating your pregnancy accurately, multiple sacs should be pretty visible on a transvaginal ultrasound at 7 weeks.
If your twins are identical — meaning, one egg was fertilized but then split in two — there’ll only be one gestational sac; however, more than one yolk sac, fetal pole, and heartbeat may be visible.
Again, keep in mind that ultrasounds aren’t foolproof. You may not be far enough along in your pregnancy for all these things to be detected.
And remember that babies like to hide, especially when they have a sibling to hide behind! Multiple gestational sacs may not be visible until a later ultrasound.
Resist the temptation to be alarmed if your doctor orders a 7-week ultrasound; there are several good reasons this test is helpful in the early weeks of pregnancy.
It’s an uncomfortable but harmless procedure that offers important information, including whether your pregnancy is still viable and, if so, exactly how far along you are (and how many babies are growing).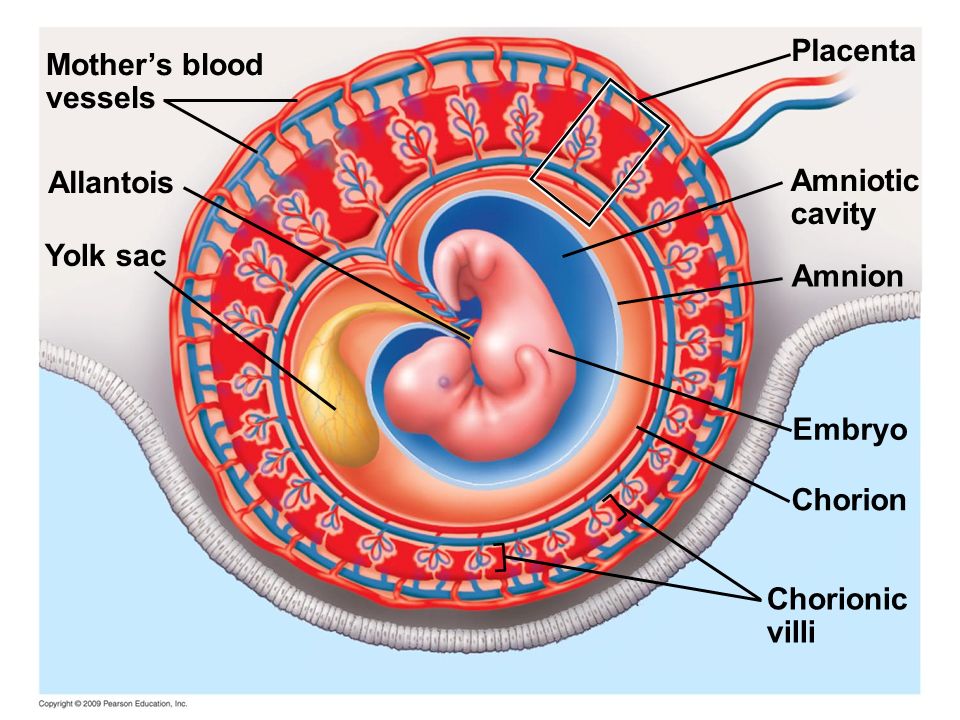
modern methods of diagnostics and treatment
A fertilized egg without an embryo is usually found on ultrasound and is a very common condition. According to some reports, the absence of an embryo is diagnosed in 2 out of 10 women who are faced with a missed pregnancy.
Since there is no fetus as such, symptoms typical of early pregnancy disappear - breast swelling, unstable mood, lethargy and nausea. What to do in this case, the gynecologist decides. The choice of treatment method depends on the duration of pregnancy and the state of health of the woman. nine0003
What is an "empty pregnancy"
If there is a fertilized egg, but there is no embryo, they speak of a non-vesical drift, which is also called anembryony. The embryo could not be in the uterus initially, or it died for up to 5 weeks. In about a quarter of women, such a pregnancy ends in a miscarriage or freezes.
Slightly more than half of the cases are due to spontaneous uterine cleansing: this should occur within 2 weeks after the detection of anembryony. Otherwise, fragments of the fetal egg must be removed medically or surgically. nine0003
Otherwise, fragments of the fetal egg must be removed medically or surgically. nine0003
An empty amniotic egg must be removed no later than 2 weeks after its discovery. If it remains in the uterus after this period, there is a high probability of complications and bleeding. For a more detailed consultation, please contact our doctors - they will give all the necessary recommendations by phone and answer all your questions.
Why the fetal egg is empty: reasons
It is rather difficult to establish the exact cause of anembryonia, it is determined taking into account the existing symptoms and the results of the examination of a pregnant woman. The culprits of this phenomenon can be various factors associated with the characteristics of the mother's body. nine0003
The greatest risk of pregnancy fading occurs in the early stages, when the blastomeres are just beginning to divide, and the embryo is attached to the wall of the uterus.
There are several reasons why an embryo does not develop in a fetal egg:
- gene mutations that do not depend on the genes of the parents;
- endometrial diseases of an atrophic, inflammatory nature;
- defects in the structure of the reproductive organs of the mother; nine0024
- violation of blood clotting;
- too tight fixation of the embryo in the uterus;
- weak local immunity of the myometrium;
- a disorder of the contractile function of the uterus due to improper metabolism and chronic inflammatory processes in the uterine tissues;
- folate deficiency.
Gene mutations
This is the leading reason why the gestational sac is empty. Chromosomal abnormalities can appear at different stages: nine0003
- When an egg is fertilized by two sperm.
- During further cell division.
The risk of gene mutations increases with a woman's age.
Endometrial diseases
The absence of an embryo in the fetal egg may be associated with chronic endometritis and the syndrome of regenerative plastic insufficiency of the endometrium. A chronic inflammatory process leads to changes in the work of local immunity, which reduces the susceptibility of mucous membranes. nine0003
In addition, with sluggish and prolonged inflammation, erythrocytes stick together in the developing chorionic villi, which ultimately leads to the formation of mini-thrombi.
Defects in the structure of the reproductive organs
We are talking about congenital or acquired structural features due to polyps, fibroids or synechiae. Such diseases are accompanied by hormonal imbalance and changes in the receptivity of the endometrium. nine0003
Bleeding disorder
The embryo may die in the early stages of gestation due to lack of nutrition during the formation of blood clots in the intervillous space, when thrombophilia develops for various reasons.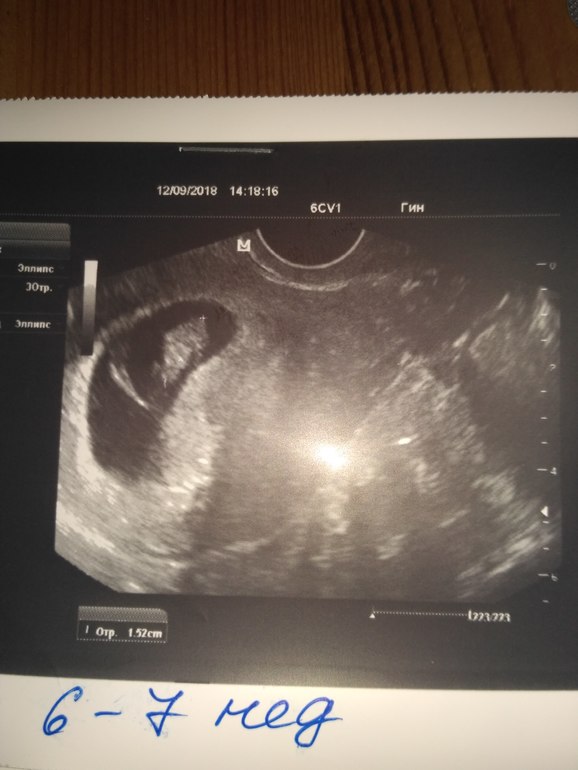
Embryo too tight
Excessively deep implantation of the embryo occurs in 2 cases: if it is actively growing, and the uterine myometrium is not sufficiently prepared for implantation of the embryo, or if the endometrium is functionally immature. nine0003
Weak local immunity
The reactivity of the myometrium is one of the possible reasons that the fetal egg turned out to be without an embryo. It persists in the uterus due to an insufficient immune response, which normally causes the embryo to be rejected as a foreign body.
Contractile function disorder
An empty fetal sac is not rejected in some chronic pathologies of the uterus, accompanied by a violation of the formation of receptors for substances that stimulate uterine contractions (uterotonic). Very often, the contractility of the uterus falls due to improper interstitial metabolism. nine0003
Folic acid deficiency
This acid is a direct participant in the process of division of cellular DNA. If it is not enough in the early stages of gestation, the chromosomes diverge and arrange themselves incorrectly.
If it is not enough in the early stages of gestation, the chromosomes diverge and arrange themselves incorrectly.
Pregnancy without embryo: species
A fetus without an embryo is of 2 types:
- On ultrasound, the embryo is not visible, the fetal sac measures a maximum of 2.5 cm, the volume of the uterus corresponds to 5-7 weeks, which is not consistent with the date of actual conception. Subsequent studies on an ultrasound machine do not record an increase in the uterus. nine0024
- The fetal egg is empty, its size and volume of the uterus correspond to the gestational age. However, the fertilized egg grows, but the embryo does not.
Empty ovum after IVF
Embryo resorption is possible after in vitro fertilization, in which several fetal eggs (PY) are implanted into the woman's uterus. This increases the chances of successful conception.
As a rule, only one embryo takes root, although sometimes 2 or more embryos are implanted in the wall of the uterus. However, not all of them continue to develop, some of the fetal sacs are absorbed or excreted from the body naturally. nine0003
However, not all of them continue to develop, some of the fetal sacs are absorbed or excreted from the body naturally. nine0003
Signs of empty gestational sac without embryo
In the absence of a fetus, there is a regression of symptoms typical of early gestation - nausea, pain in the mammary glands, sleep problems, etc. The woman feels like before pregnancy and ceases to react sharply to smells, and also loses her recent craving for a certain unusual food.
Case study:
The woman had no doubt that she was pregnant, and experienced symptoms typical of her condition - nausea, engorgement of the mammary glands, and tightness of the abdomen. When the symptoms suddenly disappeared, she did not attach any importance to this. On a planned ultrasound, the doctor saw an empty fetal egg at 6 weeks and prescribed the necessary treatment. nine0003
However, the fact that there is no toxicosis and other symptoms does not unequivocally indicate an empty fetal egg or the absence of an embryo.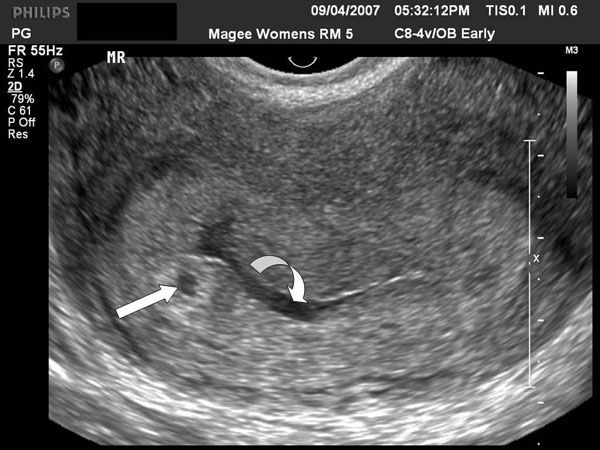 Similar signs can be with a frozen pregnancy.
Similar signs can be with a frozen pregnancy.
But if the decay of the tissues of the embryo begins, then there are pronounced symptoms of intoxication:
- rise in temperature;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- body aches; nine0023 weakness;
- lower abdominal pain;
- bleeding of varying intensity.
The onset of embryo rejection can be suspected by the appearance of vaginal discharge mixed with blood.
Complications
If the uterus does not contract well, or there are problems with blood clotting, bleeding begins. By itself, it is not capable of stopping, the help of a doctor is needed. In addition, bleeding can cause infection of the uterine cavity and anemia. nine0003
In some cases, the fertilized egg decomposes asymptomatically, or the process causes mild discomfort. Empty amniotic membranes spontaneously separate from the endometrium and leave the body naturally.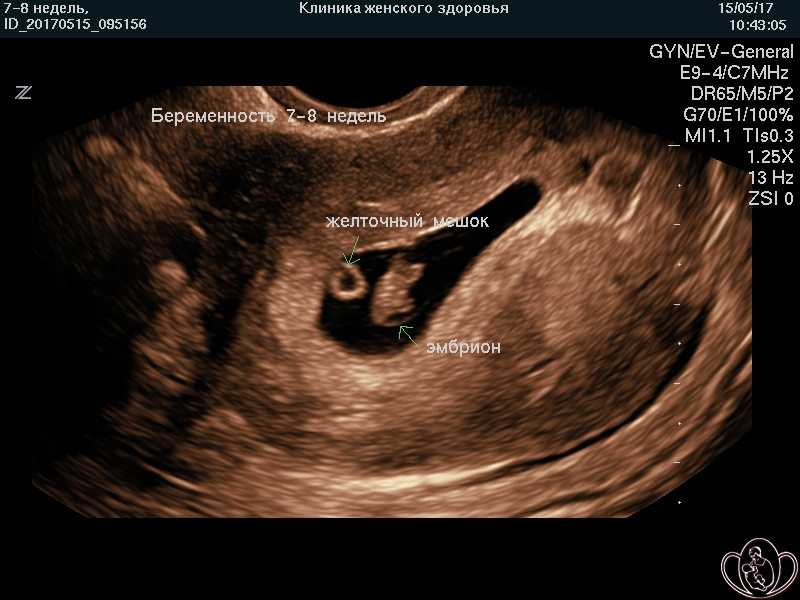
But more often, an amniotic egg without an embryo remains in the uterus and provokes serious complications that often threaten health and even life. If left untreated, chronic endometritis can develop.
Anembryony is sometimes complicated by infertility and miscarriage in the future. nine0003
If the gestational sac continues to grow for 2 weeks or more, the inflammation symptoms described above occur. We advise you to contact our doctors, since the inflammatory process can spread to the entire uterus and nearby tissues. By phone, the doctor will give recommendations and instruct about further actions.
Fetal egg without embryo: diagnosis
An empty egg during pregnancy is detected by ultrasound. Ultrasound allows you to detect the presence of an embryo for a period of 6-7 weeks, before it is not visualized due to its small size and literally merges with neighboring structures. nine0003
Therefore, sonography is performed at 6-7 weeks and confirms (or refutes) the fact of conception. Up to this point, the presence of the embryo is determined by the level of hCG - human chorionic gonadropin.
Up to this point, the presence of the embryo is determined by the level of hCG - human chorionic gonadropin.
Case study:
The woman, suspecting pregnancy, passed the test for hCG. Its level was increased and amounted to 50 mU/ml. However, ultrasound revealed the absence of an embryo in the egg. A re-examination 2 weeks later confirmed the diagnosis of anembryony. nine0003
HCG is called the hormone of pregnancy, its production starts 6-7 days after the attachment of the chorion - the fetal membrane of the embryo - to the uterus. In normal pregnancy, the concentration of hCG increases with the growth of the fetus.
hCG with an empty fetal egg
If there is no embryo in the egg, then the level of hCG, as a rule, grows more slowly or becomes less. This indicator can serve as an indirect confirmation of an undeveloped pregnancy, along with an insufficient content of progesterone in the blood. nine0003
HCG values at the lower limit of the norm are the reason for the appointment of ultrasound, since gonadropin is synthesized even in the absence of an embryo. Moreover, its level is usually within the normal range, in contrast to a missed pregnancy with a dead fetus.
Moreover, its level is usually within the normal range, in contrast to a missed pregnancy with a dead fetus.
Attention! The hCG parameter cannot be considered a reliable diagnostic criterion for anembryony. Therefore, even if hCG is growing, but there is no fetal egg, it is too early to diagnose an empty pregnancy. After all, the growth of the placenta does not stop immediately. nine0003
Why does a fertilized egg grow, but there is no embryo in it
The formation of the body of the embryo and its outer membranes begins at the blastula stage. When it enters the uterine cavity, its outer cells produce specific enzymes that partially dissolve the endometrium and facilitate implantation.
After insertion into the wall of the uterus, the embryo, together with the amniotic membranes, develops synchronously with the gradual formation of the placenta and fetus. nine0003
With anembryony, a fetal egg grows, that is, only the outer shell that produces hCG. And the embryo either does not form at all, or its formation is completed at the initial stages. This is due to incorrect test data showing the development of pregnancy.
And the embryo either does not form at all, or its formation is completed at the initial stages. This is due to incorrect test data showing the development of pregnancy.
However, after some time, hCG still ceases to stand out and decreases.
What to do if there is no embryo in the ovum
If the fertilized egg does not grow due to the absence of an embryo, it is necessary to artificially terminate the pregnancy. Obstetricians and gynecologists do not recommend waiting until the situation resolves itself, and treat with one of three methods: nine0003
| Term | Methodology | Peculiarities | disadvantages |
| 6-8 weeks | medical abortion nine0003 | Taking medications - Mifepraston, Misoprazole | After 8 weeks, incomplete rejection of the fetus is possible with the development of complications |
| Up to 5 weeks | Vacuum aspiration (mini-abortion) | The fertilized egg is pulled out (aspirated) by means of a vacuum pump nine0003 | There is a risk of incomplete abortion, ultrasound control after the procedure is necessary |
| 6-12 weeks | Curettage (curettage) | The uterine cavity at the site of attachment of the fetal egg is mechanically scraped with an iron curette | nine0187
The most effective and safe is medical abortion with the use of drugs that provoke uterine contractions and inhibit endometrial progesterone receptors.
Medical expulsion of the fetus does not damage the mucous membranes of the uterus and does not carry any risks in the future. nine0003
Vacuum aspiration can be performed for up to 12 weeks, according to WHO recommendations. However, in Russia, most often it is done no later than 5 weeks.
Rehabilitation
A single case of anembryony does not raise questions and does not pose a danger. However, if it recurs, or the pregnancy is terminated in the early stages for another reason, it is necessary to establish why the embryo does not develop.
For this, a comprehensive examination and rehabilitation treatment is carried out. Basically, women are diagnosed with chronic endometritis, which can have vivid manifestations or be asymptomatic. Therefore, first of all, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. nine0003
In the treatment of endometrial diseases, drugs of several groups are also used:
- anti-inflammatory;
- immunostimulants;
- enzymes;
- hormones.

Taking combined contraceptives is recommended for 3-6 months in order to restore hormonal levels.
Attention! nine0104 A new conception should be planned only after a full preconception preparation.
FAQ
Can there be a 15 mm PJ?
+
Yes, it is usually seen at 6.5 weeks. The child develops the brain and nervous system. When the fetal egg reaches 15 mm, facial features, eye sockets, and nasolabial folds begin to form.
Can a fertilized egg grow without an embryo? nine0003
+
Yes, this is type 2 anembryony, which can last up to 11 weeks. The size of the egg can reach 5 cm.
What if the fertilized egg is smaller than the embryo? The size of the PY is 2 weeks behind!
+
This is normal, no need to worry. The situation will stabilize after a while, there is no danger to the fetus.
Expert opinion:
A fetal egg without an embryo can be in an absolutely healthy woman. But even in the absence of any pathologies, it is necessary to take a break and resume attempts to conceive a child no earlier than after 2-3 cycles.
Non-developing early pregnancy. / News / RDC
The main unresolved problems in obstetrics and gynecology to date, making a significant negative contribution to reproductive losses, are the lack of a decrease in the number of preterm births (termination of pregnancy after 22 weeks) and an increase in the frequency of spontaneous miscarriages (up to 22 weeks). nine0003
Currently, non-developing pregnancy is usually considered as a polyetiological complication of pregnancy, which is based on a pathological symptom complex: lack of vital activity of the embryo, endometrial dysfunction and disturbances in the hemostasis system of a pregnant woman. As early as 1995, Professor Stuart Campbell stated that: "Early embryonic death should be given the same importance as late fetal death. " Unfortunately, at the present time, this phrase has acquired a special meaning, since we live in an era of an “epidemic” of non-developing pregnancies. Their frequency among cases of spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages has increased over the past 30 years from 10-20% at the end of 90s of the last century to 45-88.6% in recent years. Therefore, the issues of the earliest and most accurate diagnosis of an undeveloped pregnancy become extremely relevant.
" Unfortunately, at the present time, this phrase has acquired a special meaning, since we live in an era of an “epidemic” of non-developing pregnancies. Their frequency among cases of spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages has increased over the past 30 years from 10-20% at the end of 90s of the last century to 45-88.6% in recent years. Therefore, the issues of the earliest and most accurate diagnosis of an undeveloped pregnancy become extremely relevant.
Based on clinical signs, it is very difficult to make this diagnosis in the early stages, since its symptoms are not specific. So, for example, slight spotting from the genital tract may appear after a certain interval after the cessation of its development, or may be absent altogether. Not in every case there are pains in the lower abdomen. General malaise, weakness, dizziness, fever are observed only in 10% of women with a delay of a dead fetus in the uterus for more than 3-4 weeks. The most characteristic and long-known subjective signs of the death of the fetal egg in the first trimester of pregnancy are the disappearance of nausea, vomiting, salivation.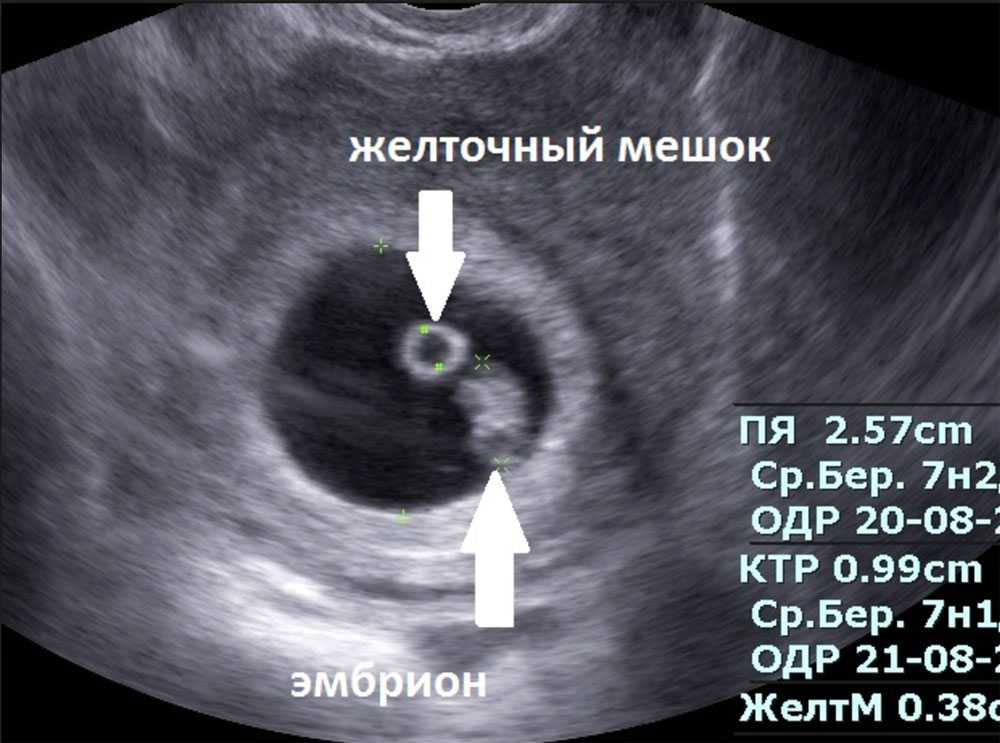 However, all of the above cannot be considered reliable symptoms of a missed pregnancy. The use of biochemical tests, such as serum β-hCG levels, is an aid to differential diagnosis in early pregnancy between conditions such as normal developing uterine pregnancy, non-progressing uterine pregnancy, pregnancy of "unclear localization" and ectopic pregnancy. However, to date, it is recommended to determine the serum level of β-hCG only in the case of "pregnancy of unclear localization". There is no indication for taking serum β-hCG if the gestational sac is clearly visible in the uterine cavity and we need to confirm the diagnosis of an arrested pregnancy. That is why the priority today is given to ultrasound, which allows you to detect non-developing pregnancy long before the onset of clinical symptoms. nine0003
However, all of the above cannot be considered reliable symptoms of a missed pregnancy. The use of biochemical tests, such as serum β-hCG levels, is an aid to differential diagnosis in early pregnancy between conditions such as normal developing uterine pregnancy, non-progressing uterine pregnancy, pregnancy of "unclear localization" and ectopic pregnancy. However, to date, it is recommended to determine the serum level of β-hCG only in the case of "pregnancy of unclear localization". There is no indication for taking serum β-hCG if the gestational sac is clearly visible in the uterine cavity and we need to confirm the diagnosis of an arrested pregnancy. That is why the priority today is given to ultrasound, which allows you to detect non-developing pregnancy long before the onset of clinical symptoms. nine0003
Diagnostic criteria for non-developing pregnancy in the early stages:
- absence of a heart rhythm in the coccyx-parietal size of the embryo 7 mm or more;
- lack of embryonic structure with an average diameter (arithmetic mean of 3 diameters) of the ovum greater than or equal to 25 mm.
If at least one of the indicated signs is present, the diagnosis is considered final. In this case, repeated ultrasound examinations are not required. The probability that in the period of 12 weeks. fetus will be viable is zero. nine0003
There are several other criteria that allow diagnosing a non-developing pregnancy:
- the embryo does not have a heartbeat 14 after the ultrasound examination revealed a fetal egg without a yolk sac at the initial admission;
- the embryo has no heartbeat 11 days after the ultrasound revealed a gestational sac with a yolk sac at the initial intake.
Other signs that are described in the medical literature are prognostic. They do not give a 100% guarantee, but only allow you to suspect a missed pregnancy. In this case, additional ultrasound examinations are required to confirm or refute the diagnosis of non-developing pregnancy. nine0003
Prognostic criteria for non-developing pregnancy include:
- Embryo CTE < 7 mm, no heartbeat;
- the average diameter of the ovum (arithmetic mean of 3 diameters) is 16-24 mm, the embryo is absent;
- Absence of an embryo with a heartbeat 7-10 days after an ultrasound examination revealed a gestational sac without a yolk sac;
- the absence of an embryo with a heartbeat 7-10 days after the discovery of a gestational sac with a yolk sac; nine0024
- no embryo after 6 weeks.
 after the first day of the last menstruation;
after the first day of the last menstruation; - abnormal structure of the yolk sac (irregular shape, hyperechoic structure), dimensions more than 7 mm or less than 3 mm;
- small fetal egg relative to the size of the embryo (the difference in size between the above structures is less than 5 mm), the so-called oligohydramnios of the first trimester;
- abnormal contours of the ovum;
- the appearance of the yolk stalk without registration of cardiac activity in the embryo; nine0024
- modified amniotic cavity;
- increase in CTE less than 0.2 mm/day;
- fetal bradycardia (M-mode heart rate less than 80-90 beats/min.
When conducting early ultrasound examinations, both clear methodological approaches and examination safety principles must be followed. It is necessary to evaluate the following structures: gestational sac, amniotic cavity, yolk sac and embryo with real-time (B-mode) or M-mode cardiac activity. Up to 10 weeks gestation should not use color Doppler mapping (CDM) to record cardiac activity, as this increases the heat index (TI) to 2. 5-4.2, and according to the ALARA principles governing the safety of ultrasound, scan early in pregnancy not recommended for TI greater than the threshold value of 3.0. nine0003
5-4.2, and according to the ALARA principles governing the safety of ultrasound, scan early in pregnancy not recommended for TI greater than the threshold value of 3.0. nine0003
An important issue in the ultrasound diagnosis of non-developing pregnancy is the issue of repeated ultrasound examinations. It is necessary to choose the optimal interval for repeating the study, since unreasonable studies in case of suspected non-developing pregnancy increase the burden on the ultrasound diagnostic rooms and the obstetrician-gynecologist and lead to excessive neuroticism of patients who are faced with this problem. It is wise to adhere to the following recommendations. nine0003
- If an embryo smaller than 7 mm is visualized during the first ultrasound examination and there is no heartbeat, then a second examination is prescribed no earlier than after 7 days. If during the re-examination cardiac activity is not recorded, then the doctor is authorized to make a diagnosis of "non-developing pregnancy".
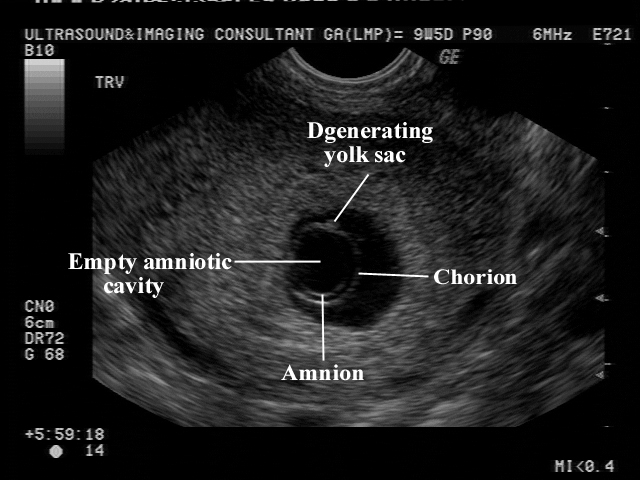
- If the first ultrasound shows an empty fetal egg or a fetal egg with a yolk sac inside and its dimensions are > 12 mm, then a second examination is prescribed no earlier than 7 days later. If during the re-examination the echographic picture does not change, then it is competent to make a diagnosis of “non-developing pregnancy”. nine0024
- If the first ultrasound shows an empty gestational sac or a gestational sac with a yolk sac inside and its size is <12 mm, then a second examination is prescribed no earlier than 14 days later. If the situation does not change during the re-examination, then the doctor is authorized to make a diagnosis of “non-developing pregnancy”.
If the mean ovum diameter (arithmetic mean of 3 diameters) is > 16 mm and no embryo is visualized, there is a 10% chance that we are dealing with a normal developing uterine pregnancy. If an empty gestational sac is detected on the first transvaginal ultrasound, and a yolk sac appears on the second examination, then there is a 27% chance of a developing pregnancy.