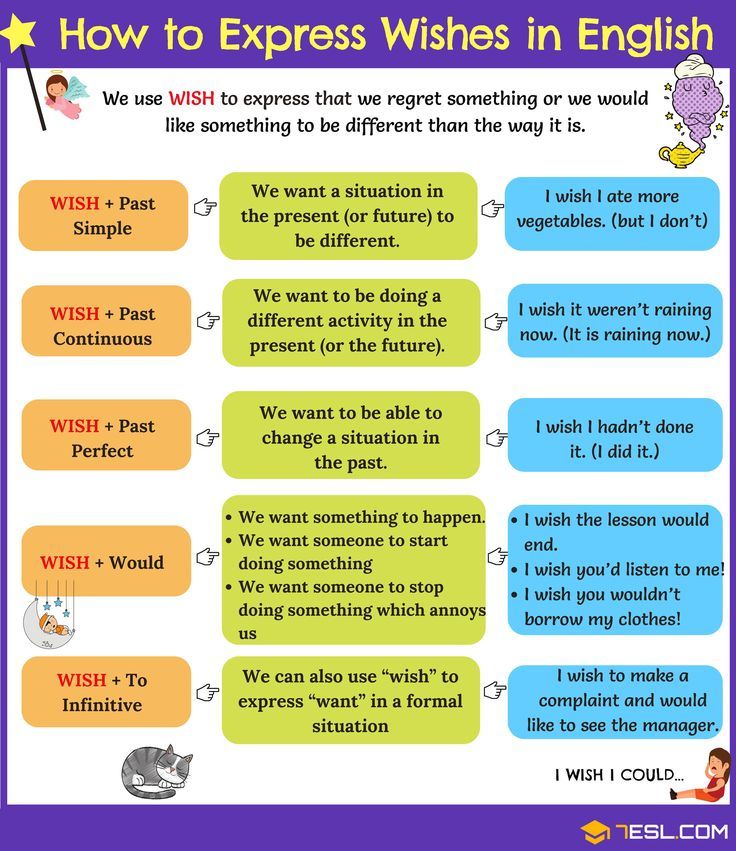
White patches on 2 month old baby skin
Tinea Versicolor in Babies and Children
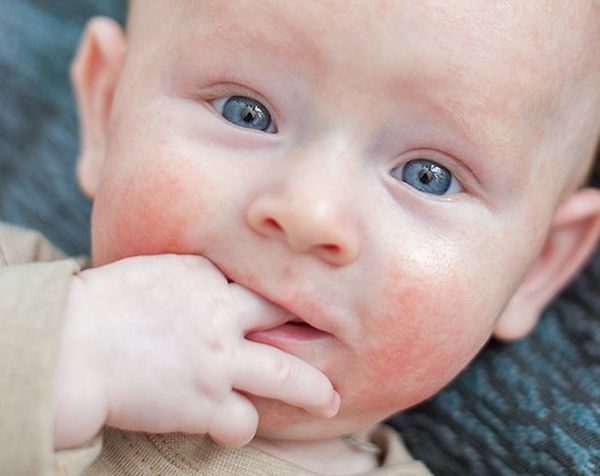
Tinea versicolor is a fungal condition that shows up as flat patches of discoloration on the skin. You may notice the patches on your child's chest, on his back, under his arms, on his upper arms, or even on his neck and face. The patches can range from white to pink and from tan to dark.
Have you noticed small patches of discolored skin on your baby or child? If the patches are spreading (and possibly slightly itchy) it could be tinea versicolor skin infection. It’s unusual for babies and children to have tinea versicolor as it typically occurs after puberty, but it can happen.
Tinea versicolor isn’t contagious. It also can’t be fully cured. However, there are ways you can help your child manage the symptoms.
© Dr. P. Marazzi / Science Source
What is tinea versicolor?
Tinea versicolor (also called pityriasis versicolor) is a non-contagious skin condition that shows up as patches of discoloration on the skin. The word “versicolor” actually refers to the variable color of the spots or patches; they can be either hyperpigmented (dark) or hypopigmented (light). Most often they appear pink or tan on lighter skin, and as light patches on darker skin.
A normal skin yeast may overgrow and cause the uneven skin color to appear. Anyone can get tinea versicolor. However, it is most common in teenagers and young adults. The yeast, called Malassezia furfur, may also cause skin conditions like dandruff.
(See what tinea versicolor and other skin rashes look like in BabyCenter’s visual guide to children's rashes and skin conditions).
Tinea versicolor symptoms
The rash typically begins on the upper arms, back, chest, or even on his neck and face. The discolored patches can range from white to pink and from tan to dark; if you look closely, you may be able to see very fine scales on their surface. It’s more noticeable in the warm, summer months, as the yeast prevents the skin from tanning in the areas of infection.
People with light-colored skin tend to get darker spots, while those with dark-colored skin seem to have lighter spots. In some cases, the skin turns white.
The patches can flake (like dandruff) and sometimes cause mild itchiness.
How do I treat tinea versicolor at home?
If the spots are small and mild and your child doesn't seem uncomfortable, look for an over-the-counter dandruff shampoo with the active ingredients selenium sulfide or ketoconazole on the label. These ingredients kill the yeast.
- Wash your child’s hair with the shampoo and put a thin layer on all the affected patches, spreading it a couple of inches beyond their borders.
- Leave the shampoo on for 10 to 15 minutes before rinsing it off.
- Repeat every night for a few weeks, and the yeast should improve.
Unfortunately, it can take months for the skin color to return to normal. And the condition can come back again. If it does return, call your child’s doctor.
What if the home remedy for tinea versicolor doesn't work?
If shampoo doesn't work, call your child’s doctor. A provider can typically diagnose tinea versicolor just by looking at your child's skin with a special lamp (called a Wood's lamp). Sometimes, doctors scrape a small sample of skin from one of the discolored patches and look at it under a microscope – a procedure that is completely painless.
If it is tinea versicolor, the doctor will probably prescribe a topical antifungal medicine. If the case is severe, or the topical treatment doesn't work, the doctor may prescribe an oral antifungal medication.
To prevent tinea versicolor from spreading further:
- Keep the skin cool and dry.
- Dress your child in loose clothing and avoid hot, humid air.
- Apply sunscreen whenever your child is exposed to the sun.
Will my child always have tinea versicolor?
Possibly. Once diagnosed with tinea versicolor, the yeast remains in your child’s skin. It may seem to disappear in the winter months, and then reappear in the summer. Typically, tinea versicolor peaks during adolescence.
It may seem to disappear in the winter months, and then reappear in the summer. Typically, tinea versicolor peaks during adolescence.
As your child ages, she may become more self-conscious about her skin’s appearance. It will be important to remind her how common tinea versicolor is. She’ll also need to stay away from tanning beds, as they will make it appear worse.
Books to help your child cope:
- Malcolm Finney Medical Detective – The Case of… Itch and Rash by Erika Kimble (August 2011)
- Wonder by RJ Palacio (Jan 2014)
- Connect the Dots: Discovering Self-love with Skin Imperfections by Dahnisha Adams (February 2019)
9 Common Baby Skin Discolorations & Birthmarks (With Pictures)
Have you noticed changes in your baby’s skin? Maybe they were born with a discolored patch, or you’re beginning to see a weird-looking spot.
Birthmarks are normal. They’re part of what makes each of us unique.
Some skin discoloration could be completely harmless and vanish as quickly as it appeared. It may be the after-effect of an infection, or in rare circumstances, it could be caused by a serious condition.
It may be the after-effect of an infection, or in rare circumstances, it could be caused by a serious condition.
You or your partner might have a special birthmark, but does that mean your little one will also have one? Let’s look at baby skin discoloration and birthmarks in more detail.
Table of Contents
- Baby’s Skin Color
- Brown Spots and Discoloration
- White Patches
- Yellow Discoloration (Jaundice)
- Birthmarks
- What Causes Birthmarks?
Baby’s Skin Color
In our heads, we usually picture our newborn to be a chubby-cheeked wonder with perfect skin. But that’s not always how it is.
The reality is a newborn baby, fresh from the womb, will likely be purple and slimy. They may also be covered in white goo, called vernix caseosa.
A baby’s skin is paper thin. Therefore, environmental changes play a huge role in the skin’s color. You’ll likely notice straight away if your baby is cold — their feet will probably be a bluish color. Conversely, their cheeks will be red and flushed if they are hot.
Conversely, their cheeks will be red and flushed if they are hot.
Newborns will sometimes have a lighter skin complexion than you expected. Their skin tone can change over time. Some babies take up to six months or longer to develop their permanent skin color.
Pro Tip
Birthmarks or skin discoloration may be noticeable on babies when they are first born. But some may appear after birth or as your baby grows older.
Brown Spots and Discoloration
Brown spots could be more than just freckles. It’s not uncommon to find a few when bathing your baby (and you try to rub it off but realize it’s on the skin). Don’t worry; most baby spots are harmless.
Here’s what might be causing them:
Cafe Au Lait Macules
Cafe au lait macules (CALMs) are brown spots or patches. They can appear anywhere on a baby’s body and are usually present from birth. These spots are found in about 3% of infants.
They’re typically randomly and unevenly shaped and can range from one-fifth of an inch to one inch in size. They can be dark or light brown and may darken with sun exposure.
They can be dark or light brown and may darken with sun exposure.
The spots can be slightly raised, although they are usually smooth. CALMs are relatively common, and there’s no reason for concern if you find a couple of these spots on your infant. But if you find six or more, you should consult your doctor so they can check for NF1.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Warning
Having more than six CALMs, particularly if you also find freckles around the armpit or groin, could be a sign of a genetic disorder called neurofibromatosis type 1(NF1).
There are three variations of neurofibromatosis, with Von Recklinghausen’s disease (VRD) being the most common.
NF1 affects about 1 in 3,000 babies. It causes tumors to form on the tissues and nerves in the body and on the skin, and the growths can trigger many different health issues. Symptoms vary widely, even within members of the same family.
The tumors are usually not cancerous. However, it is necessary to monitor them in case they do become malignant, especially if they multiply (1).
White Patches
Many things can cause white patches on a child’s skin. The most common is likely to be a sore or scratch, where the surface has been broken. This produces new skin not yet exposed to the sun, which makes it lighter.
Many of us moms have worried when white spots suddenly appeared on our baby’s skin to later realize it was just a scratched mosquito bite or a healing wound.
However, white patches or discoloration of the skin can also be a sign of vitiligo.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a condition that causes white spots and patches to develop on the skin. It can be a long-term condition that often doesn’t go away completely.
The condition results from a loss of pigment, or melanin, in the skin. It can affect people of all ages and ethnicities.
The patches can be any shade, from light to white with a pale pink center. It usually starts around the face, neck, or hands but can occur anywhere on the body.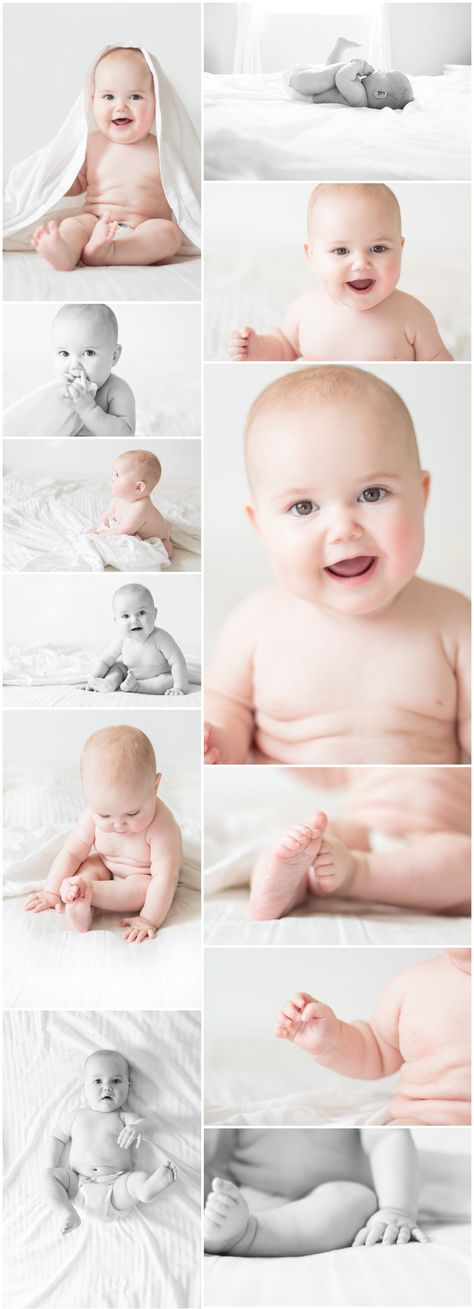
If your child has vitiligo, it is crucial to use a strong sunscreen on the patches. The loss of pigment makes the skin much more vulnerable to sunburn.
Different types of vitiligo include segmental, focal, and generalized.
Segmental vitiligo only affects one side of the body, and focal affects just a couple of spots in one area. Generalized vitiligo shows up as symmetrical patches on both sides of the body. Some experts consider vitiligo to be an autoimmune disorder, while others refer to it as a genetic disorder (2).
Tinea Versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection of the skin. It shows up as patches ranging from white to dark, depending on your child’s skin color. If you look closely, you may see tiny scales on the skin’s surface.
This condition is very common in children and young adults. The fungus prevents the affected skin from tanning, which means the patch will be even more obvious when exposed to the sun.
Pityrosporum ovale is a type of fungus that lives in the pores. As the condition progresses, the fungus overgrows, causing discoloration.
As the condition progresses, the fungus overgrows, causing discoloration.
The patches are harmless and shouldn’t bother your little one aside from minor itching.
This condition should resolve itself, but if you’re concerned, contact your child’s pediatrician for further advice (3).
Yellow Discoloration (Jaundice)
While white or brown spots or patches may seem more normal, seeing your baby turn yellow can be alarming. But don’t panic; your little bundle of joy probably just has a touch of jaundice.
Jaundice is a prevalent condition in infants, generally appearing two to three days after birth. It typically turns the baby’s skin yellow and can also affect the whites of the eyes.
Neonatal jaundice occurs due to a buildup of bilirubin in the blood. When red blood cells break down, bilirubin is produced, and it has a yellow color.
Take Note
Jaundice is common in newborns because they have more red blood cells. Their liver is also not fully developed, which makes it harder to remove the bilirubin. The condition is more likely in premature babies or those with low birth weight.
Their liver is also not fully developed, which makes it harder to remove the bilirubin. The condition is more likely in premature babies or those with low birth weight.
Jaundice is mostly harmless and usually disappears within one or two weeks.
However, if the condition is apparent within 24 hours of delivery, it could signify a more severe problem. In this case, you should consult your doctor.
Treatment for jaundice is usually not necessary. A simple treatment you can do at home is exposing your baby to controlled sunlight for a few minutes each day.
Never place your newborn in direct sunlight, though. Instead, use a thin fabric or curtain to cover a sunlit window. Sit there with your baby for 10 to 15 minutes every day.
The sun will provide your baby with much-needed vitamin D, which helps to break down the bilirubin. As a mother of babies who both had slight jaundice, I can assure you this method is very effective.
As a mother of babies who both had slight jaundice, I can assure you this method is very effective.
Severe cases may require medical intervention in the form of one of the following:
- Phototherapy: Your baby will be exposed to a particular light that changes the form of bilirubin, making it easy for the liver to break it down.
- Exchange transfusion: If phototherapy does not work, a complete blood transfusion might be necessary to reduce the amount of bilirubin in your baby’s blood.
It is vital to diagnose and treat severe cases of jaundice correctly. If jaundice is left untreated and bilirubin levels become too high, it can lead to seizures or permanent brain damage (4).
Birthmarks
A birthmark is skin discoloration either present at birth or appearing within the first month of a baby’s life. They come in various colors, shapes, and sizes and can occur anywhere on the body. Let’s look at the most common.
1. Salmon Patch
A salmon patch is a red or pink flat patch that often occurs on the baby’s eyelids, forehead, or neck.
They usually fade entirely within the first few months, although patches on the forehead can take up to a year or more. My baby looked like a mini Harry Potter for a couple of months with a little lightning-shaped pink mark on his forehead.
These patches can become more visible when the baby cries as they fill with blood. Salmon patches are benign and are no cause for concern.
2. Infantile Hemangioma
These are also known as strawberry birthmarks. Unsurprisingly, they look like strawberries. Infantile hemangiomas can appear anywhere on the body and may also develop deeper in the skin, making it look blue or purple.
Strawberry marks are strangely more common among girls than boys. They usually grow rapidly in the first few months. They then decrease in size, and most disappear eventually, although this could take several years.
These birthmarks are not harmful. However, if they interfere with feeding, vision, or other vital functions, consult a specialist for advice (5).
3. Mongolian Spots
A Mongolian spot is a blue-gray, bruise-looking birthmark that is present at birth. It is also known as a slate grey nevi. The formal term for slate grey nevi is congenital dermal melanocytosis.
These strange-looking spots are quite common in darker-skinned people. They are mostly found on the lower back or buttocks but can occur anywhere.
Mongolian spots can last for months or even years, but they usually disappear as the child ages (6). The marks are often mistaken for bruises, so it’s a good idea to ensure your baby’s doctor has a record of any spots on their skin.
4. Capillary Malformation
Capillary malformation, also known as a port-wine stain, is a flat red or purple mark.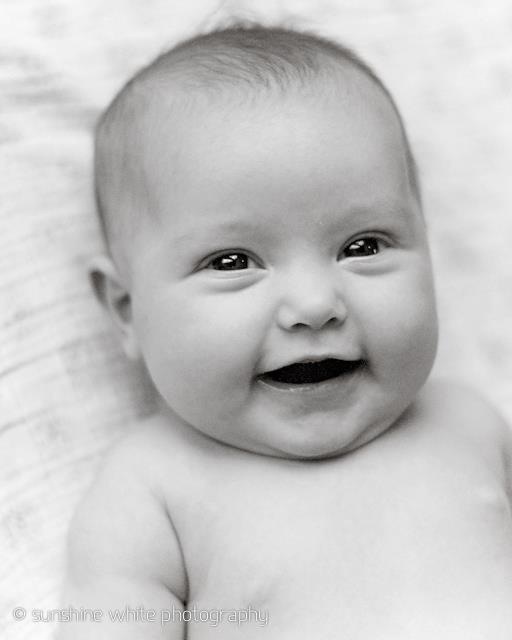 These marks vary in size. Some are only a fraction of an inch, while others cover large areas.
These marks vary in size. Some are only a fraction of an inch, while others cover large areas.
A port-wine stain may darken over time, and your child will likely be affected by it for life. However, there are ways to lighten it with laser technology.
These marks also tend to flare up and become more visible with changes in hormone levels. Flare-ups could happen around puberty, pregnancy, or menopause (7).
What Causes Birthmarks?
It’s not completely clear why birthmarks appear. There are two kinds of birthmarks (8).
1. Vascular Birthmarks
These marks are caused by abnormal blood vessels in or under the skin. They include port-wine stains and strawberry marks.
Vascular birthmarks get their size and color because of the nerves that control the size of the vessels.
Because these nerves don’t function properly, they constantly allow blood to be supplied to the area. This results in the bright red or purple color you see.
2. Pigmented Birthmarks
These are caused by a cluster of pigmented cells in the skin. Pigmented birthmarks are usually flat, but some can be a little raised. They include Mongolian spots and CALMs.
Feedback: Was This Article Helpful?
Thank You For Your Feedback!
Thank You For Your Feedback!
What Did You Like?
What Went Wrong?
White spots on the body of a child
Advertising
Content:
- Varieties and main causes of white spots
- What is Vitiligo?
- Treatments for Vitiligo
Discoloration of the skin is a problem that has recently become common in both adults and children. Very often, white spots appear on the body of newborns, which cause concern. Should I worry about white spots in newborns, what is the reason for their appearance and what to do about it? Let's figure it out together.
The main causes
Any of the diseases is collectively called hypopigmentation - discoloration of the skin, nails and hair, which occurs due to a lack of a pigment called melanin. One of the most common diseases that is accompanied by the appearance of white spots on the skin of the baby is Vitiligo (loss of melanin). The causes of the origin of this disease are unknown, the ways of its treatment also do not give the proper result. The only thing that can be done is to try to improve the appearance of the skin in various ways, which we will discuss next.
One of the most common diseases that is accompanied by the appearance of white spots on the skin of the baby is Vitiligo (loss of melanin). The causes of the origin of this disease are unknown, the ways of its treatment also do not give the proper result. The only thing that can be done is to try to improve the appearance of the skin in various ways, which we will discuss next.
Pityriasis versicolor
The second most common cause of white spots is fungi, which are found in the body of every person. However, under favorable conditions (moisture and heat), the number of fungi begins to increase, resulting in red-brown or white spots on the skin. The causes of infection are excessive sweating, a warm, humid climate. For treatment, you can use antifungal drugs, for example, Clotrimazole or Terbinafine.
Important! A correct diagnosis can only be made by a professional dermatologist, so you should not experiment on a child and his health by self-medicating.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Symptoms:
- Small white patches exposed to the sun.
- The skin becomes smooth, but is able to peel off.
Important! This disease is more common among women with fair skin, the cause of its occurrence is unknown, doctors suggest that this is one of the symptoms of aging.
White lichen
With this disease, the skin also begins to change its color. White lichen is most often seen in adolescents and children living in warm climates. Whitish spots become dry and scaly, the causes of the occurrence are still unknown.
Pigmented nevus
In simple terms, a pigmentless nevus is a birthmark that poses a threat to human life and health, since the development of melanoma is a severe malignant tumor that occurs on the skin.
Other causes
It is worth noting that white spots may appear on the child's body due to improper or poorly balanced nutrition. Due to the lack of vitamins and certain pigments, white marks may appear on the human body, which are not dangerous and disappear with the right diet or taking bioactive supplements. In addition, the reasons for the appearance of white spots can be:
Due to the lack of vitamins and certain pigments, white marks may appear on the human body, which are not dangerous and disappear with the right diet or taking bioactive supplements. In addition, the reasons for the appearance of white spots can be:
- Psoriasis is a chronic non-communicable disease.
- Leucoderma is a disease that may appear after syphilis.
Important! The diseases mentioned earlier are extremely rare in infants, but it is necessary and important to know about them, as it concerns health.
Manifestations in children
As for the skin of newborns, white spots on it may appear due to one of these diseases:
- Tumorous sclerosis - white spots, the radius of which reaches 1.5 centimeters. The result of the disease can be more serious pathologies, such as epilepsy, mental retardation, or damage to internal organs.
- Hypomelanosis - may appear after suffering a serious infectious disease, occurs due to dyschromia of the upper layer of the skin.

What is Vitiligo?
As mentioned earlier, the most common disease that is accompanied by the appearance of white spots on the skin is Vitiligo. As a result of this disease, spots of various shapes and sizes appear on the skin of adults and children, the cause of which is the absence of melanin. As a result, the skin is not protected from the effects of the sun and there is a possibility of getting burned.
Manifestation of Vitiligo:
- On the arms and face, in the elbows and groin.
- Spots appear in separate areas or create groups that merge into a single spot, occupying most of the body.
- The disease does not appear on the feet and hands.
- If spots appear on the head, the hairline also loses color.
Causes of the disease:
- Heredity.
- Impaired liver function.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland and endocrine system.
- Incorrect work of the pituitary gland.

- Disease of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Disease of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Stress and infectious diseases.
- Malfunctions of the immune system.
- Disturbed balance of vitamins and microelements.
Very often Vitiligo is confused with other diseases, namely:
- Leucoderma.
- Ringworm.
- Pityriasis versicolor.
Important! Only a dermatologist can determine the cause of stains and how to treat them, so do not put off your visit to the doctor.
Precautions:
- Do not sunbathe with a sweaty body.
- It is forbidden to stay in drafts for a long time.
- The use of air conditioners and fans is not recommended.
- Avoid exposure to high humidity for long periods of time.
Important! In general, any violation of the skin is a health problem, however, Vitiligo is not an infectious disease, so it does not pose a danger to others.
Treatment methods for Vitiligo
Our ancestors found several ways to combat Vitiligo, however, it is impossible to completely cure this disease, since the cause of its occurrence remains unclear. At the same time, spots can be easily masked, so that the feeling of discomfort will disappear. Means for the treatment of the disease:
- Duckweed.
- Parsley.
- Dill herb.
- St. John's wort.
It is enough to choose one of the plants and apply its extract to depigmented areas. These plants contain furocoumarins, which increase the production of melanin and restore normal skin color.
Important! At the same time, there is an opinion that these procedures increase the likelihood of skin cancer. What to believe and what not - everyone decides for himself.
causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment - Articles - ON CLINIC Baby
Light spots on the skin are signs of such a little-studied disease as vitiligo.
According to WHO, around 30 million people worldwide suffer from vitiligo, some of them children.
The discolored areas do not lend themselves to tanning and contrast sharply with the main skin color. Most often, this disease affects girls.
Very often, children are embarrassed by the manifestations of vitiligo and are afraid of peer ridicule in kindergarten and school. Psychological stress adversely affects the health of the child, becomes the cause of constant stress. The task of parents is to turn to a professional pediatric dermatologist in a timely manner, who will not only help solve the problem, but also support the child, teach him to cope with the disease and not be embarrassed by its manifestations.
Pediatric dermatologist at ON CLINIC
Experienced pediatric dermatologists work at the On Clinic Baby International Medical Center, who can find a language with absolutely any child. They understand parents perfectly and support the desire of mothers and fathers to give the baby all the best, including medical care.
Pediatric dermatologists of our clinic constantly participate in scientific conferences and seminars, and also cooperate with pediatricians and other doctors from the best clinics in Russia and around the world. In addition, we have our own clinical diagnostic laboratory, so small patients receive the results of research in the shortest possible time.
Diagnosis and treatment of vitiligo in children
Diagnosis of vitiligo in infants and older children is based on a clinical examination of the child, the use of special lamps and anamnesis analysis. Other research methods, including laboratory ones, may also be required.
The main goal of vitiligo therapy is to rid the child of a cosmetic defect and restore skin pigmentation.
To date, there are no methods of treatment for this disease that are suitable for absolutely everyone. Therefore, for effective and complete therapy, the qualification of a pediatric dermatologist and an individual approach to a small patient are very important. In many cases, the child needs not only a course of treatment in the clinic, but also the selection of a special diet that will help the body overcome the disease.
In many cases, the child needs not only a course of treatment in the clinic, but also the selection of a special diet that will help the body overcome the disease.
To combat vitiligo, both physiotherapeutic methods of treatment that stimulate the synthesis of melanin and medications are used, including the use of drugs inside and local therapy in the form of applying ointments, alcohol extracts and tinctures to the foci of the disease.
What you need to know about vitiligo?
Vitiligo symptoms in children
Vitiligo disease is manifested by the formation on the skin of a child of clearly defined spots with smooth or torn edges. Their color is most often milky white. The skin in the foci of the development of the disease may remain unchanged. In some cases (most often when exposed to ultraviolet light), hyperemia (redness), peeling and thickening of the skin may appear.
Vitiligo can appear as one or more patches on any part of the body - the face (including the lips and skin around the mouth), trunk, hands, feet. When the lesions are located on the head, poliosis is observed - premature depigmentation and graying of the hair.
When the lesions are located on the head, poliosis is observed - premature depigmentation and graying of the hair.
Spots can either remain unchanged for several years, or increase in size and cover new areas. In the process of development of vitiligo, old foci of the disease merge and new ones form.
Causes of vitiligo
Vitiligo is characterized by the slowdown or death of melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Scientists have not yet been able to establish the main reasons leading to a failure in the production of melanin. Among the most popular causes put forward by various experts are frequent nervous stress, trauma, excessive sun exposure and exposure to chemical agents.
According to some hypotheses, diseases of the endocrinological system, liver disease and helminthic invasion can also lead to the development of vitiligo. As for the hereditary transmission of the disease, it has been established that predisposing factors can be transmitted from parents to children, which nevertheless do not always lead to the development of vitiligo and the appearance of white spots on the skin.