What can you do for a newborn with constipation
Symptoms, Treatment and When to Call a Doctor
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Constipation (con-sta-PA-shun) in infants can worry parents. Most of the time, your baby is not really constipated. They may not have developed a routine for pooping yet. Some babies do not develop a bowel movement (BM) pattern for a while.
An infant’s BM pattern can change if their diet changes, like switching from breastmilk to formula, starting solid foods, or drinking less formula than usual. If your baby’s stool (poop) is not soft or easily passed, then they may be constipated.
In rare cases, constipation may be caused by a lack of nerves going to the intestines or by a problem with the way the intestine formed at birth. Your baby can be tested for these conditions if your health care provider feels it is needed.
Signs of Constipation
- less stools than their usual pattern
- straining more than normal to have a bowel movement
- a change in how the stool looks from soft and mushy to:
- small, hard pebbles, or like a large, round golf ball
- loose and watery
- abdomen (belly) bloated or swollen with gas
- painful cramps
Treatment
- If your baby is not eating baby food yet, you may give 1 to 2 ounces of 100% fruit juice (pear, prune, cherry, or apple) once a day.
Stop the juice if their stools become too loose.
- If they are old enough to eat baby foods, feed them pureed pears, peaches, or prunes instead of giving them juice.
- If your baby eats cereal, it may help to give oatmeal, wheat, or barley cereal. Rice cereal can cause constipation in some children.
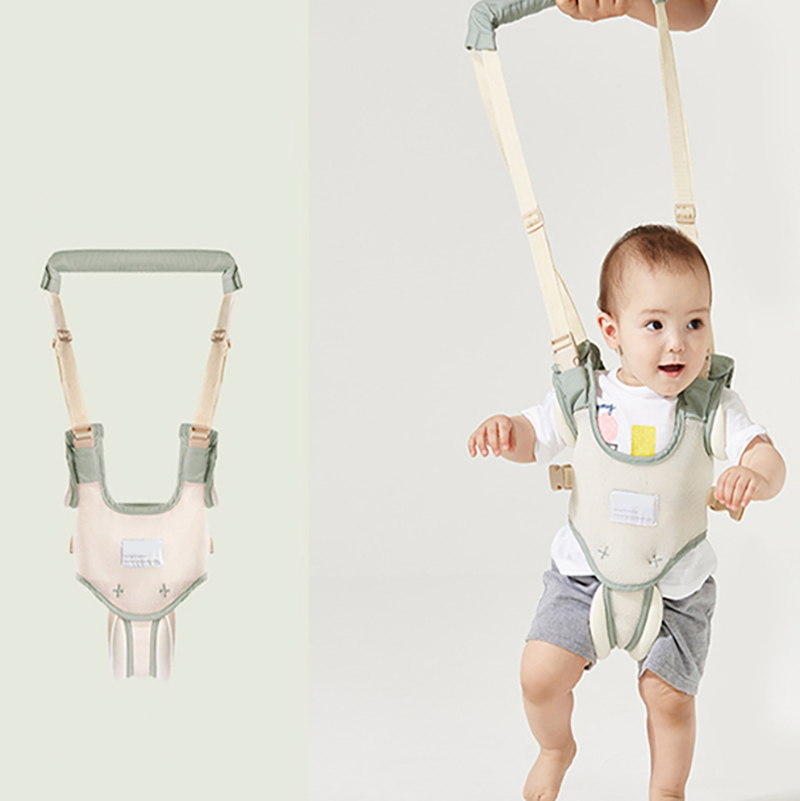
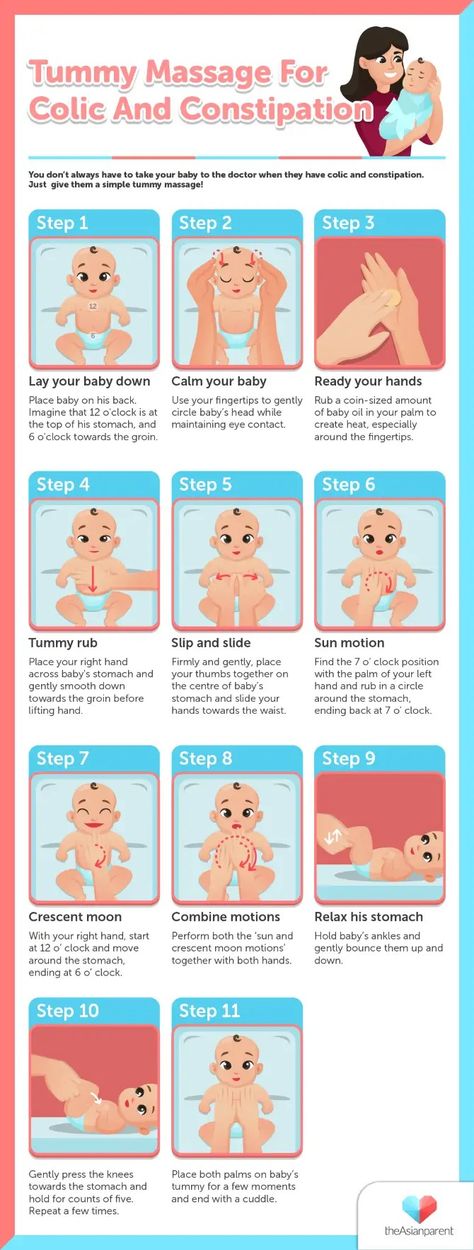
- Sometimes giving your baby a warm bath to relax them or exercising their legs, like riding a bicycle, will help stimulate the bowels to move (Picture 1).
- If it has been a few days since your baby has pooped and the juice or pureed food has not worked, then you can try a glycerin suppository. Place your baby on their back. Gently push the suppository into their anus (bottom). Suppositories are meant for occasional use.
- Contact your baby’s health care provider before giving them laxatives, baby mineral oil, or enemas to treat constipation.
Medical Therapy
Your child’s health care provider may order the following treatments:
- Give your child medication.

- Check your child’s temperature using a digital, rectal thermometer. Put a small amount of petroleum jelly (Vaseline®) on its tip before inserting into the rectum. Taking a rectal temperature may stimulate the baby to pass stool.
When to Call the Health Care Provider
Call the health care provider if any of the following occurs:
- Your baby is irritable and seems to be having stomach pain. Infants will pull their legs up to their stomach and cry when they are in pain.
- Your baby has constipation and develops vomiting, and their belly looks like it is bloated or filled with gas.
- You see blood in their stool.
- Their constipation does not get better with treatment.
If you have any questions or concerns, call your baby’s health care provider.
Constipation: Infant (PDF), Spanish (PDF), Somali (PDF), Arabic (PDF), Nepali (PDF)
HH-I-14 ©Copyright 1984, Revised 2022, Nationwide Children’s Hospital
You Might Also Be Interested In
Blog
Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy: How It Can Help
Podcast
PediaCast 503 Your Childs Stomach Part 1
Blog
Senna-Based Laxatives for Kids’ Constipation: Are They Safe?
Baby constipation: Top 7 home remedies
Babies often go a long time between bowel movements. Most of the time, it is normal for a baby to go days or even more than a week without a bowel movement. However, a baby may sometimes be constipated and need a little help.
Most of the time, it is normal for a baby to go days or even more than a week without a bowel movement. However, a baby may sometimes be constipated and need a little help.
If a baby is constipated, a pediatrician may recommend using home remedies as a first-line treatment for baby constipation.
Home remedies for constipation in a baby include:
1. Exercise
Moving a baby’s legs can help relieve constipation.
As with adults, exercise and movement tend to stimulate a baby’s bowels.
However, as babies may not be walking or even crawling yet, a parent or caregiver may want to help them exercise to relieve constipation.
The parent or caregiver can gently move the baby’s legs while they are lying on their back to mimic the motion of riding a bicycle. Doing this may help the bowels function and relieve constipation.
2. A warm bath
Giving a baby a warm bath can relax their abdominal muscles and help them stop straining. It can also relieve some of the discomfort relating to constipation.
3. Dietary changes
Certain dietary changes may help constipation, but these will vary depending on the baby’s age and diet.
While breastfeeding a baby, a woman could eliminate certain foods, such as dairy, from her diet. It may take some trial and error to identify the dietary changes that help, and it is quite possible that changes in the diet will have no effect on the baby’s constipation.
For formula-fed babies, a parent or caregiver may want to try a different kind of formula. It is best not to switch to a gentle or dairy-free formula without consulting a pediatrician first. If one change does not make a difference, continuing to try different formulas is unlikely to help.
If an infant is eating solid foods, parents or caregivers should look to introduce foods that are good sources of fiber.
Many fruits and vegetables can help stimulate the bowels because of their higher fiber content. Good food choices for babies with constipation include:
- skinless apples
- broccoli
- whole grains, such as oatmeal or whole-grain bread or pasta
- peaches
- pears
- plums
4.
 Hydration
HydrationYoung infants do not typically need supplemental liquids as they get their hydration from breast milk or formula.
However, babies that are constipated may benefit from a small amount of extra liquid.
Pediatricians sometimes recommend adding a small amount of water or, occasionally, fruit juice, to the baby’s diet when they are over 2–4 months old and are constipated.
5. Massage
There are several ways to massage a baby’s stomach to relieve constipation. These include:
- Using the fingertip to make circular motions on the stomach in a clockwise pattern.
- Walking the fingers around the naval in a clockwise pattern.
- Holding the baby’s knees and feet together and gently pushing the feet toward the belly.
- Stroking from the rib cage down past the belly button with the edge of a finger.
6. Fruit juice
A small amount of pure apple juice can help soften stool.
After a baby reaches 2–4 months of age, they can have a small amount of fruit juice, such as 100-percent prune or apple juice. This juice may help treat constipation.
This juice may help treat constipation.
Experts may recommend starting with about 2–4 ounces of fruit juice. The sugar in the juice is hard to digest. As a result, more liquid enters the intestines, which helps soften and break up the stool.
However, a parent or caregiver should not give fruit juice to a baby for the first time without consulting their pediatrician.
7. Taking a rectal temperature
When a baby is constipated, taking the baby’s rectal temperature with a clean, lubricated thermometer may help them pass stool.
It is important not to use this method very often, as it can make constipation worse. The baby may start not wanting to pass a bowel movement without help, or they may begin to associate having a bowel movement with discomfort, leading them to fuss or cry more during the process.
Anyone who feels as though they often need to use this method to help the baby have a bowel movement should talk to the baby’s doctor.
As infants may go for extended periods without a bowel movement, it can be hard to tell if they are constipated. Signs that indicate constipation in a baby include:
Signs that indicate constipation in a baby include:
- infrequent stools that are not soft in consistency
- clay-like stool consistency
- hard pellets of stool
- long periods of straining or crying while trying to have a bowel movement
- streaks of red blood in the stool
- lack of appetite
- a hard belly
Signs of constipation in babies vary depending on their age and diet. A normal bowel movement before a baby begins eating solid food should be very soft, almost like the consistency of peanut butter or even looser.
Hard baby stool prior to solid food is the most obvious indication of constipation in babies.
At first, breastfed babies may pass stool often since breast milk is easy to digest. However, once a baby is between 3 and 6 weeks old, they may only pass a large, soft stool once a week and sometimes even less.
Formula-fed babies tend to pass stool more frequently than breastfed babies. Most formula-fed babies will have a bowel movement at least once a day or every other day. However, some formula-fed babies may go longer between bowel movements without being constipated.
However, some formula-fed babies may go longer between bowel movements without being constipated.
Once a parent introduces solid food to a baby’s diet, a baby may be more likely to experience constipation. A baby may also be more likely to become constipated if a parent or caregiver introduces cow’s milk (other than formula) to their diet.
Share on PinterestA doctor should assess a baby with ongoing constipation.
It is advisable to call a pediatrician if a baby has not passed a stool after a day or two and there are other signs present, such as:
- blood in the stool
- the baby seems to be irritable
- the baby appears to have abdominal pain
- there is no improvement in the baby’s constipation after taking steps to treat it
Treatment typically starts with home remedies. If home remedies do not work, a doctor may examine the baby and, in rare cases, prescribe medications, such as:
- laxatives
- enemas
- suppositories
People should never give these medications to a baby unless a doctor prescribes them.
Constipation can lead to discomfort and irritability in a baby. People can try several at-home methods to help alleviate constipation.
If symptoms do not improve, it is best to speak to the infant’s pediatrician for additional strategies.
Read the article in Spanish.
What to do with constipation in a newborn?
Constipation in a newborn or infant is an extremely unpleasant problem for parents. And it is not always possible to quickly determine what is the cause of constipation in an infant. Most often, problems with bowel movements in babies are functional in nature and are directly related to the nutrition of the child.
Signs of constipation in a child of the first year of life
- Infrequent dry and hard stools
- Sleep disorder
- Troubled state
- Pungent odor of feces and flatus
Causes of constipation in a newborn child
Causes of constipation in newborns and infants, as a rule, are not associated with a serious pathology of the internal organs or the central nervous system. The main cause of constipation in a baby is malnutrition, early transfer of a child to supplementary feeding with infant formula, frequent changes in products during artificial feeding.
The main cause of constipation in a baby is malnutrition, early transfer of a child to supplementary feeding with infant formula, frequent changes in products during artificial feeding.
When breastfeeding, the formation of constipation in children of the first year of life is affected by poor nutrition of the mother, for example, the use of large amounts of animal fats and a lack of fiber in the diet. One possible cause of constipation in newborns is dehydration.
What to do if a child has problems with stool
- If a child under one year old has acute constipation and there is anxiety, straining and arching, we actively massage the abdomen in a clockwise direction so that hand marks remain on the skin (but not bruises!) . We spread it on the stomach, do the exercise - legs to the head, children under one year old can massage the anus, if all this does not help - a children's candle with glycerin from the refrigerator.
- If such situations are repeated often - a mandatory consultation with a pediatrician.

- When introducing complementary foods to a baby with a tendency to constipation, introduce fruits and vegetables into the diet first.
- If the child is older than a year and the process is chronic - evaluate nutrition - whether there are the necessary 5 servings of vegetables and fruits per day (portion - from the palm or fist of the baby). Estimate - how much water does the child drink per day? Is there enough physical activity during the day? What is the psychological climate in the family and the attitude - not to demand a chair from the child, not to swear and not to shout, not to discuss problems with other people in his presence, not to force him to sit on the potty, not to scold him for dirty panties when anointing.
- It is better to choose laxatives based on macrogol or lactulose with the help of a doctor.
- In parallel with laxatives, we conduct psychological work with the child at home and with a specialist - books about defecation, toilet games, etc.
In what case should you be very worried about constipation in a child? Namely:
- if there is no meconium discharge in the first days of life;
- retardation and constipation;
- vomiting and tense abdomen;
- blood in stool;
- changes in hair growth and pigmentation of the sacrum and coccyx,
- violation of the development of the sacrum;
- changes in the anus - fistulas with discharge, hematomas, inflammation;
- change in the muscular skeleton of the anterior abdominal wall - lack of muscles or insufficient development.
If a baby up to a year old is breastfed for several days (3-5 days, but not weeks!) Does not poop and does not worry - if he is cheerful and cheerful, eats well, does not spit up and does not stain the diaper, and farts well, in this no parental intervention required! The stool should be soft and not cause trouble during bowel movements.
In the treatment of constipation, toilet training is important - every day at the same time, preferably after eating and drinking - calmly and kindly go to the potty (if the toilet is, then there should be a support under the feet so that the knees are above the level of the priests) and try to poop. If there was no stool for several days, you can pre-put a glycerin suppository.
If there was no stool for several days, you can pre-put a glycerin suppository.
In the presence of painful defecation, fissures and blood, urgently show the child to a doctor (gastroenterologist or proctologist) and start treatment - local baths, suppositories and laxatives are applied. This is absolutely necessary in order to soften the stool and prevent the formation of persistent fear of defecation, which is then very difficult to remove. Before defecation with a dense stool, you can additionally lubricate the anus with baby oil. 9+7 (423) 267-61-30; +7 (423) 274-32-22; +7 914-704-32-22.
Make an appointment online:
PediatricianGeneral practitionerUltrasound doctorGastroenterologistHematologistGynecologistImmunologist-allergistInfectionistCardiologistNeurologistOtorhinolaryngologist (ENT)Orthopedist-traumatologistOphthalmologistPsychiatristUrologist-andrologistPhysiotherapistPhysiotherapistSurgeonEndocrinologistHouse doctor0003
I agree to the processing of data
Please enable JavaScript to pass the CAPTCHA test
If you have any questions, ask them in the comment form below↓↓↓
Leave This Blank:Leave This Blank Too:Do Not Change This: Your email:
Newborn constipation: what to do | Causes of constipation in a newborn baby | Drinking regimen
Author, editor and medical expert - Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
Pediatrician and medical expert - Arutyunyan Mariam Arutyunovna
Views: 571 335
Last update date: .11.2022.
Average reading time: 6 minutes 6 minutes 3
How to understand that the baby is constipated
When constipation is a temporary problem
Constipation in newborns with diseases
Functional constipation in babies of the first year of life
What to do if a newborn has constipation
Constipation is a pathology that people of all ages face, including newborns and toddlers during the first months of life. And although it is believed that the "debut" of the problem in children occurs at about the age of 2 years, the first "bells" usually appear already in the first year of life 1 . Why constipation occurs in newborns and infants and what to do when they appear?
How to understand that the baby has constipation
Constipation, or constipation, is commonly understood as a violation of the function of the gastrointestinal tract, manifested by rare stools, thickening and fragmentation of feces, and difficulty in defecation 1. 2 . However, for young children there are no strict criteria for the normal frequency of bowel movements 1 . It depends not only on age, but also on the type of feeding of the baby. The consistency of feces is also evaluated depending on the nature of the diet.
2 . However, for young children there are no strict criteria for the normal frequency of bowel movements 1 . It depends not only on age, but also on the type of feeding of the baby. The consistency of feces is also evaluated depending on the nature of the diet.
According to the accepted norms, in children of the first four months of life (before the introduction of complementary foods), who are breastfed , the rectum should be emptied after each feeding, and the feces should have a homogeneous mushy consistency. If the stool is less than 4 times a day, and the feces are thickened, this is a reason to talk about constipation in a newborn or baby 1.2 .
Approximately 4-6 months with the expansion of the diet, the child's stool becomes rarer - 2 times a day. Feces are compacted and formed into a cylinder 1 .
Formula-fed babies normally empty their intestines at least once a day at a certain time 1. 2 . Feces are soft and cylindrical 1.2 . In this case, there should not be any difficulties in defecation.
2 . Feces are soft and cylindrical 1.2 . In this case, there should not be any difficulties in defecation.
Be aware that stool frequency is not the only guide to diagnosing constipation in infants. Even if the frequency of defecation is within the age norms, but the baby's stool is dense, fragmented and scanty, and the emptying of the rectum itself causes him suffering, this is a reason to talk about constipation in the baby or "artificial" 1.2 .
Back to Contents
When Constipation is a Temporary Problem
The main cause of obstructed defecation in infants today is considered functional immaturity of the body 2 , leading to inconsistent work of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and rectal sphincters. Normally, the urge to defecate causes contraction of the abdominal muscles (pulling) and simultaneous relaxation of the muscles that close the anus. If this process is disturbed, and the sphincters of the rectum relax late, defecation is disturbed. Doctors call this condition infantile dyschezia, not constipation
Doctors call this condition infantile dyschezia, not constipation
Diagnostic criteria for dyschezia:
- the baby is less than 9 years oldmonths;
- the baby strains hard (more than 10 minutes) before emptying the intestines;
- stools remain soft, as expected when breastfeeding or bottle-feeding.
Up to content
Constipation in newborns due to illness
The main causes of constipation vary with age. It is believed that a violation of the excretion of feces in the first month of a child's life (the neonatal period) is most often associated with organic pathology, that is, diseases or conditions that affect not only the functions of the intestines.
Constipation in infants and infants can be a manifestation of various pathologies:
- Neuromuscular diseases that disrupt intestinal motility - congenital megacolon, spinal cord lesions, dysplasia of the nervous tissue of the intestine.

- Anatomical defects, such as narrowing and obstruction of the intestine.
- Systemic diseases - rickets, hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis, Down's syndrome, connective tissue diseases, etc.
- Congenital intolerance to cow's milk protein and gluten (cereal protein).
Up to contents
Functional constipation in babies of the first year of life
In the overwhelming majority of cases, constipation in young children is associated with temporary disturbances in intestinal motility as a result of nutritional defects of the nursing mother or the baby himself 1.2 .
| Nutritional causes of constipation in neonates and infants 1 | ||||||
| Underfeeding resulting in decreased volume and hardening of feces | Malnutrition of a nursing mother, in particular the abuse of "fixing" products containing little coarse fibers | Refusal of breastfeeding and transition to artificial feeding | Insufficient fluid intake in the child's body, especially if he is on artificial nutrition or receiving complementary foods | Fast, less than 3 days, change from one mixture to another | Feeding of non-adapted products, e. | Introduction of low-fiber foods such as semolina as complementary foods |
The situation is exacerbated by the baby’s low physical activity, the mother’s excessive insistence and haste in potty training, and, in particular, the frequent irrational use of the gas tube, enemas and irritating laxatives to empty the rectum 1.2 .
Up to contents
What to do if a newborn has constipation
48 hours after baby is born,
All of the above symptoms are a reason for an immediate visit to the doctor and examination of the baby.
With functional constipation, the problem is usually solved by normalizing the nutrition of a nursing mother and baby, laying out after eating on the stomach, tummy massage and special therapeutic exercises.
 g. cow's or goat's milk
g. cow's or goat's milk