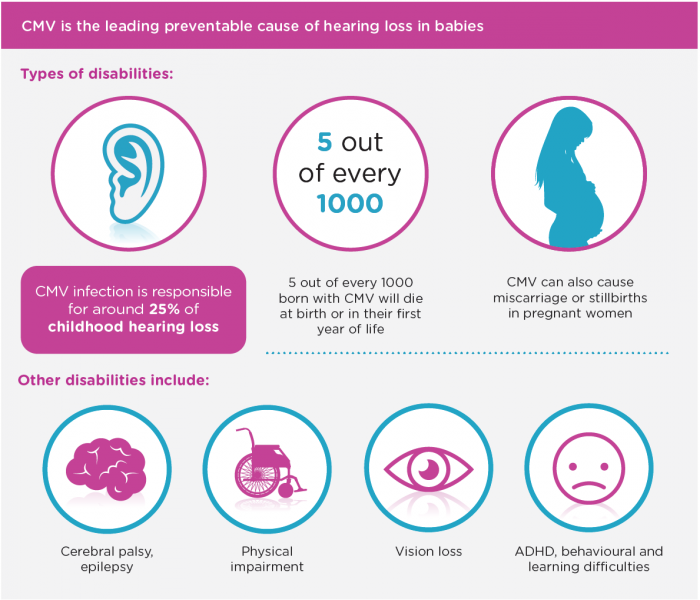
Signs of infection after missed miscarriage
Miscarriage | Sparrow
Overview
Miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week. About 10 to 20 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage. But the actual number is likely higher because many miscarriages occur very early in pregnancy — before you might even know about a pregnancy.
The term "miscarriage" might suggest that something went wrong in the carrying of the pregnancy. But this is rarely true. Most miscarriages occur because the fetus isn't developing as expected.
Miscarriage is a relatively common experience — but that doesn't make it any easier. Take a step toward emotional healing by understanding what can cause a miscarriage, what increases the risk and what medical care might be needed.
Symptoms
Most miscarriages occur before the 12th week of pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage might include:
- Vaginal spotting or bleeding
- Pain or cramping in your abdomen or lower back
- Fluid or tissue passing from your vagina
If you have passed fetal tissue from your vagina, place it in a clean container and bring it to your health care provider's office or the hospital for analysis.
Most women who have vaginal spotting or bleeding in the first trimester go on to have successful pregnancies.
Causes
Problems with the genes or chromosomes
Most miscarriages occur because the fetus isn't developing as expected. About 50 percent of miscarriages are associated with extra or missing chromosomes. Most often, chromosome problems result from errors that occur by chance as the embryo divides and grows — not problems inherited from the parents.
Chromosome problems might lead to:
- Blighted ovum. Blighted ovum occurs when no embryo forms.
- Intrauterine fetal demise. In this situation, an embryo forms but stops developing and dies before any symptoms of pregnancy loss occur.
-
Molar pregnancy and partial molar pregnancy. With a molar pregnancy, both sets of chromosomes come from the father. A molar pregnancy is associated with abnormal growth of the placenta; there is usually no fetal development.

A partial molar pregnancy occurs when the mother's chromosomes remain, but the father provides two sets of chromosomes. A partial molar pregnancy is usually associated with abnormalities of the placenta, and an abnormal fetus.
Molar and partial molar pregnancies are not viable pregnancies. Molar and partial molar pregnancies can sometimes be associated with cancerous changes of the placenta.
Maternal health conditions
In a few cases, a mother's health condition might lead to miscarriage. Examples include:
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Infections
- Hormonal problems
- Uterus or cervix problems
- Thyroid disease
What does NOT cause miscarriage
Routine activities such as these don't provoke a miscarriage:
- Exercise, including high-intensity activities such as jogging and cycling.
- Sexual intercourse.
- Working, provided you're not exposed to harmful chemicals or radiation.
 Talk with your doctor if you are concerned about work-related risks.
Talk with your doctor if you are concerned about work-related risks.
Risk factors
Various factors increase the risk of miscarriage, including:
- Age. Women older than age 35 have a higher risk of miscarriage than do younger women. At age 35, you have about a 20 percent risk. At age 40, the risk is about 40 percent. And at age 45, it's about 80 percent.
- Previous miscarriages. Women who have had two or more consecutive miscarriages are at higher risk of miscarriage.
- Chronic conditions. Women who have a chronic condition, such as uncontrolled diabetes, have a higher risk of miscarriage.
- Uterine or cervical problems. Certain uterine conditions or weak cervical tissues (incompetent cervix) might increase the risk of miscarriage.
- Smoking, alcohol and illicit drugs. Women who smoke during pregnancy have a greater risk of miscarriage than do nonsmokers.
 Heavy alcohol use and illicit drug use also increase the risk of miscarriage.
Heavy alcohol use and illicit drug use also increase the risk of miscarriage. - Weight. Being underweight or being overweight has been linked with an increased risk of miscarriage.
- Invasive prenatal tests. Some invasive prenatal genetic tests, such as chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis, carry a slight risk of miscarriage.
Complications
Some women who miscarry develop an infection in the uterus. This is also called a septic miscarriage. Signs and symptoms of this infection include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Lower abdominal tenderness
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
Prevention
Often, there's nothing you can do to prevent a miscarriage. Simply focus on taking good care of yourself and your baby:
- Seek regular prenatal care.
- Avoid known miscarriage risk factors — such as smoking, drinking alcohol and illicit drug use.
- Take a daily multivitamin.

- Limit your caffeine intake. A recent study found that drinking more than two caffeinated beverages a day appeared to be associated with a higher risk of miscarriage.
If you have a chronic condition, work with your health care team to keep it under control.
Diagnosis
Your health care provider might do a variety of tests:
- Pelvic exam. Your health care provider might check to see if your cervix has begun to dilate.
- Ultrasound. During an ultrasound, your health care provider will check for a fetal heartbeat and determine if the embryo is developing as it should be. If a diagnosis can't be made, you might need to have another ultrasound in about a week.
- Blood tests. Your health care provider might check the level of the pregnancy hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), in your blood and compare it to previous measurements. If the pattern of changes in your HCG level is abnormal, it could indicate a problem.
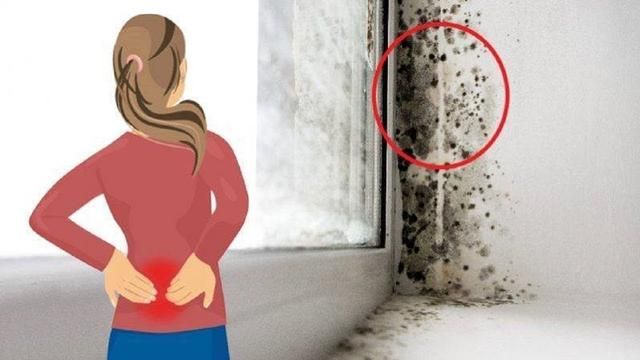 Your health care provider might check to see if you're anemic — which could happen if you've experienced significant bleeding — and may also check your blood type.
Your health care provider might check to see if you're anemic — which could happen if you've experienced significant bleeding — and may also check your blood type. - Tissue tests. If you have passed tissue, it can be sent to a lab to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred — and that your symptoms aren't related to another cause.
- Chromosomal tests. If you've had two or more previous miscarriages, your health care provider may order blood tests for both you and your partner to determine if your chromosomes are a factor.
Possible diagnoses include:
- Threatened miscarriage. If you're bleeding but your cervix hasn't begun to dilate, there is a threat of miscarriage. Such pregnancies often proceed without any further problems.
- Inevitable miscarriage. If you're bleeding, cramping and your cervix is dilated, a miscarriage is considered inevitable.
- Incomplete miscarriage.
 If you pass fetal or placental material but some remains in your uterus, it's considered an incomplete miscarriage.
If you pass fetal or placental material but some remains in your uterus, it's considered an incomplete miscarriage. - Missed miscarriage. In a missed miscarriage, the placental and embryonic tissues remain in the uterus, but the embryo has died or was never formed.
- Complete miscarriage. If you have passed all the pregnancy tissues, it's considered a complete miscarriage. This is common for miscarriages occurring before 12 weeks.
- Septic miscarriage. If you develop an infection in your uterus, it's known as a septic miscarriage. This can be a severe infection and demands immediate care.
Treatment
Threatened miscarriage
For a threatened miscarriage, your health care provider might recommend resting until the bleeding or pain subsides. Bed rest hasn't been proved to prevent miscarriage, but it's sometimes prescribed as a safeguard. You might be asked to avoid exercise and sex, too. Although these steps haven't been proved to reduce the risk of miscarriage, they might improve your comfort.
Although these steps haven't been proved to reduce the risk of miscarriage, they might improve your comfort.
In some cases, it's also a good idea to postpone traveling — especially to areas where it would be difficult to receive prompt medical care. Ask your health care provider if it would be wise to delay any upcoming trips you've planned.
Miscarriage
With ultrasound, it's now much easier to determine whether an embryo has died or was never formed. Either finding means that a miscarriage will definitely occur. In this situation, you might have several choices:
- Expectant management. If you have no signs of infection, you might choose to let the miscarriage progress naturally. Usually this happens within a couple of weeks of determining that the embryo has died. Unfortunately, it might take up to three or four weeks. This can be an emotionally difficult time. If expulsion doesn't happen on its own, medical or surgical treatment will be needed.

- Medical treatment. If, after a diagnosis of certain pregnancy loss, you'd prefer to speed the process, medication can cause your body to expel the pregnancy tissue and placenta. The medication can be taken by mouth or by insertion in the vagina. Your health care provider might recommend inserting the medication vaginally to increase its effectiveness and minimize side effects such as nausea and diarrhea. For about 70 to 90 percent of women, this treatment works within 24 hours.
- Surgical treatment. Another option is a minor surgical procedure called suction dilation and curettage (D&C). During this procedure, your health care provider dilates your cervix and removes tissue from the inside of your uterus. Complications are rare, but they might include damage to the connective tissue of your cervix or the uterine wall. Surgical treatment is needed if you have a miscarriage accompanied by heavy bleeding or signs of an infection.

Physical recovery
In most cases, physical recovery from miscarriage takes only a few hours to a couple of days. In the meantime, call your health care provider if you experience heavy bleeding, fever or abdominal pain.
You may ovulate as soon as two weeks after a miscarriage. Expect your period to return within four to six weeks. You can start using any type of contraception immediately after a miscarriage. However, avoid having sex or putting anything in your vagina — such as a tampon — for two weeks after a miscarriage.
Future pregnancies
It's possible to become pregnant during the menstrual cycle immediately after a miscarriage. But if you and your partner decide to attempt another pregnancy, make sure you're physically and emotionally ready. Ask your health care provider for guidance about when you might try to conceive.
Miscarriage is usually a one-time occurrence. Most women who miscarry go on to have a healthy pregnancy after miscarriage. Less than 5 percent of women have two consecutive miscarriages, and only 1 percent have three or more consecutive miscarriages.
Less than 5 percent of women have two consecutive miscarriages, and only 1 percent have three or more consecutive miscarriages.
If you experience multiple miscarriages, generally two or three in a row, consider testing to identify any underlying causes. Such causes could include problems with the uterus, blood clotting or chromosomes. If the cause of your miscarriages can't be identified, don't lose hope. About 60 to 80 percent of women with unexplained repeated miscarriages go on to have healthy pregnancies.
Coping and support
Emotional healing can take much longer than physical healing. Miscarriage can be a heart-wrenching loss that others around you might not fully understand. Your emotions might range from anger and guilt to despair. Give yourself time to grieve the loss of your pregnancy, and seek help from loved ones.
You'll likely never forget your hopes and dreams surrounding this pregnancy, but in time acceptance might ease your pain. Talk to your health care provider if you're feeling profound sadness or depression.
Preparing for an appointment
If you have signs or symptoms of miscarriage, contact your health care provider right away. Depending on the circumstances, you might need immediate medical care.
Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment, and what to expect from your health care provider.
What you can do
Before your appointment, you might want to:
- Ask about pre-appointment restrictions. In most cases you'll be seen immediately. If that's not the case, ask whether you should restrict your activities while you wait for your appointment.
- Find a loved one or friend who can join you for your appointment. Fear and anxiety might make it difficult to focus on what your health care provider says. Take someone along who can help remember all the information.
- Write down questions to ask your health care provider. That way, you won't forget anything important that you want to ask, and you can make the most of your time with your health care provider.
Below are some basic questions to ask your health care provider about miscarriage:
- What are the treatment options?
- What kinds of tests do I need?
- Can I continue to do my usual activities?
- What signs or symptoms should prompt me to call you or go to the hospital?
- Do you know what caused my miscarriage?
- What are my chances for a successful future pregnancy?
In addition to the questions you've prepared, don't hesitate to ask other questions during your appointment — especially if you need clarification or you don't understand something.
What to expect from your health care provider
Your health care provider is likely to ask you a number of questions, too. For example:
- When was your last menstrual period?
- Were you using any contraceptive methods at the time you likely conceived?
- When did you first notice your signs or symptoms?
- Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?
- Compared with your heaviest days of menstrual flow, is your bleeding more, less or about the same?
- Have you had a miscarriage before?
- Have you had any complications during a previous pregnancy?
- Do you have any other health conditions?
- Do you know your blood type?
Content From Mayo Clinic Updated:
© 1998-2022 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). All rights reserved. Terms of Use
All rights reserved. Terms of Use
1.800.SPARROW
1.517.364.1000
Donate to Sparrow
Unsupported Browser! This website will offer limited functionality in this browser. We only support the recent versions of major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
Recovering from a miscarriage - HSE.ie
While your body is recovering from a miscarriage, you are likely to have:
- bleeding from your vagina
- stomach cramps and pain
When to get urgent medical help
These symptoms could mean that some of the pregnancy tissue is still in your womb.
They could also be signs of an infection, especially if you also:
- feel feverish - a temperatures above 38°C (100.4°F)
- have flu-like symptoms like a sore throat, fever and muscle ache
You should go to the hospital if you are feeling unwell or feverish in the days after your miscarriage
Infection
Infection happens in about 2% of women who have had a miscarriage (2 in every 100 women). Infection can be treated with antibiotics.
Infection can be treated with antibiotics.
Sepsis
If your infection is not treated, sometimes serious complications like sepsis can occur. Sepsis is a very severe infection. It is caused by germs (usually bacteria) getting into your bloodstream.
Sepsis can cause organ damage and even death. It is very important to get medical help urgently if you think you may have an infection.
Do not use tampons
Do not use tampons or moon cups, as these could cause infection. It is safe to use sanitary towels or pads.
Your next period
Your next period will usually be 4 to 6 weeks after a miscarriage.
Emotions after a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be devastating for you and for your partner. The amount of emotional pain you feel is unique to you, and you may find it changes from time to time.
Sometimes, you may feel you are doing fine, but a sudden memory could trigger emotions. Feelings such as guilt, shock and anger are common. There is no right or wrong way to feel after a miscarriage.
Try to be open about your feelings and to communicate with your partner, family or friends.
Talk to your GP if you feel you are not coping. Remember your partner may have different ways of coping with the miscarriage.
Support
The loss of a pregnancy through miscarriage affects people in different ways. It can be a very distressing and emotional experience. You may need lots of support afterwards from your partner, family or friends.
Your GP can give you support during your physical and emotional recovery.
Your maternity hospital may offer support such as:
- chaplaincy or pastoral care
- clinical midwife specialist in bereavement and loss
The Pregnancy and Infant Loss in Ireland website has information and advice for parents.
Returning to work after a miscarriage
Your return to work depends on how you feel physically and emotionally.
If you can, rest for a few days before returning to work. Discuss this with your doctor in the hospital or with your GP.
You can get full maternity leave if you have a stillbirth or miscarriage after week 24 of your pregnancy.
Find out what benefits and entitlements you can get after a miscarriage or stillbirth.
Sex after a miscarriage
You can have sex again as soon as you feel ready. Make sure to wait until you feel well and until the pain and bleeding has reduced.
Remember you could get pregnant in the first month after a miscarriage. This can happen before your period returns. If this is not what you want, talk to your GP about contraception.
Future pregnancies
You can try for another baby as soon as you and your partner feel physically and emotionally ready.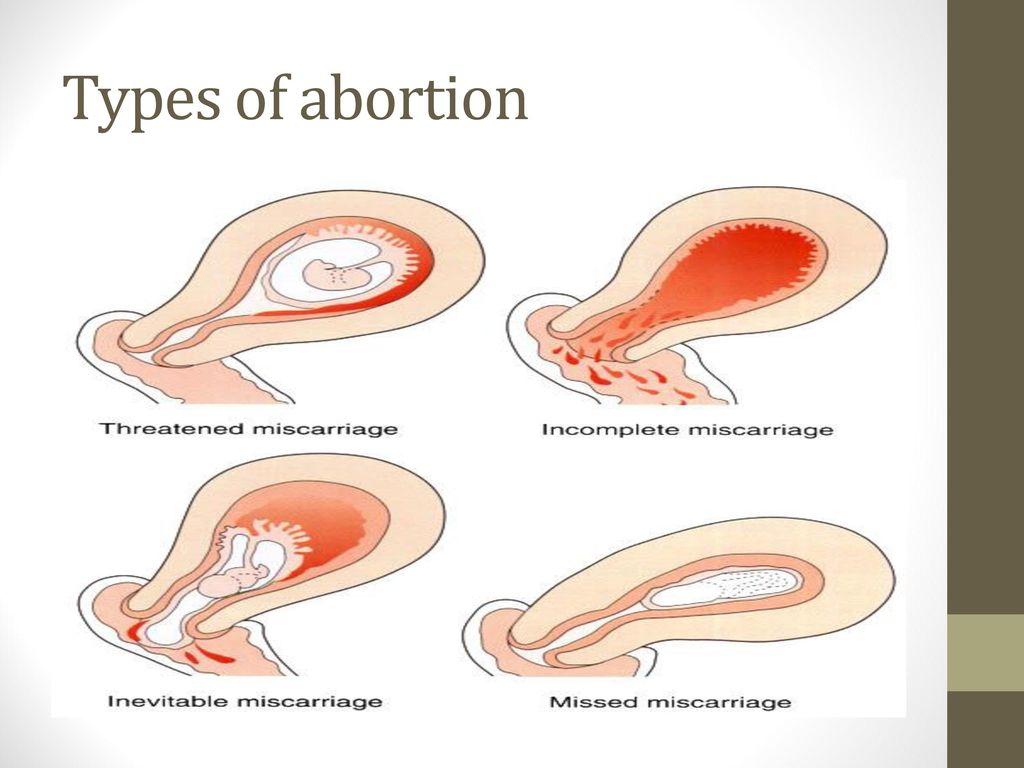
Chances of another miscarriage
Most women will have a successful pregnancy after miscarriage. Having one or two miscarriages does not mean you are at higher risk for miscarriage in the future.
If you have 3 miscarriages, there might be a medical reason. Some medical conditions make it more likely to miscarry. Speak with your GP about treatment options.
Miscarriage - causes timing signs of miscarriage
According to statistics, it is observed in one of 176 women. At the same time, it is difficult to guess which woman will have a fading pregnancy - age, social status and other factors are of secondary importance.
The concept of a missed pregnancy
A missed pregnancy means intrauterine death of the fetus, which occurs due to the development of irreversible processes. Thus, the development of the embryo stops, and its gradual decomposition occurs.
Missed pregnancy does not have severe symptoms that are characteristic of a miscarriage, but it is dangerous in its own way and needs to be diagnosed in a timely manner.
Missed pregnancy should be distinguished from another pathology - an empty fetal egg. This is a fertilized egg attached to the tissues of the uterus, but there is no embryo in it.
Causes
The most common factor in the fading of pregnancy are gene mutations, when the death of the embryo occurs for up to 8 weeks. In addition to chronic and hereditary diseases of future parents, the pathology can be provoked by the consumption of drugs and alcohol in large quantities, potent drugs. The risk of pathology increases when a woman continues to eat, smoke and drink alcoholic beverages.
Sometimes the intake of potent medications that is not coordinated with the doctor becomes a factor in the fading of pregnancy. In this regard, in the first weeks of pregnancy, drug therapy is prescribed with extreme caution and in exceptional situations. After the 10th week, when the placenta is finally formed, the embryo is better protected from destructive external factors. Therefore, in the second trimester, taking the necessary medications can be resumed.
Therefore, in the second trimester, taking the necessary medications can be resumed.
The risk of pregnancy failure is also increased in the following cases :
- Rh conflict between mother and child: this primarily concerns women with multiple miscarriages and a history of abortions. With each termination of pregnancy, the body is more willing to reject the fetus, which gradually reduces the chances of successfully bearing a child.
- Viral and infectious processes: in complicated forms, there is a high risk of infection of the unborn child and its abnormal development, as well as death. When infected with rubella, measles or chickenpox, pregnant women are advised to have an abortion. Otherwise, it will remain to raise a child with developmental disabilities, which doctors must warn about.
- Hormonal disorders: with a deficiency of prolactin or an excess of testosterone, which is often manifested by irregular menstruation, the risk of miscarriage increases.

Multiple abortions, past cases of ectopic pregnancy and anomalies in the structure of the uterus are a reason for the special control of a pregnant woman. Close attention of a doctor is also required by women over 35 years old.
There is a high probability of pathology in women who neglect the management of pregnancy by a doctor. Therefore, for a successful delivery, registration with a specialist is required no later than 7-8 weeks of pregnancy.
It is also very important to undergo tests prescribed by narrow specialists - this is necessary for the early detection of genetic abnormalities and the prevention of serious complications.
Terms of increased risk
Cases of miscarriage are recorded at different terms, including when there are only a few days left before delivery. But, according to statistics, the greatest risks occur at certain times:
- 3-4 weeks after conception;
- 7-11 weeks;
- 16-18 weeks.

The highest percentage of missed pregnancies is determined by doctors before the 14th week, after the 20th week the embryo is already less vulnerable. In the first weeks, the fetus ceases to function due to hormonal surges and due to hereditary causes, after the first trimester, its development is interrupted by infectious and viral diseases.
Symptoms
In the early stages of pregnancy
Miscarriage is not expressed by acute clinical symptoms, so women often notice the pathology too late. However, it is deadly because the decomposition of the fetus causes intoxication of the mother's body. In the future, this has a bad effect on reproductive health and complicates attempts to bear a child in the future.
It is important to pay close attention to your condition in order to notice possible symptoms of a fading pregnancy in time:
- Vaginal discharge: first, about 48 hours, white discharge is noted, then mucus appears with bloody patches, bleeding gradually increases.
 So the body tries to expel the foreign body.
So the body tries to expel the foreign body. - Features of toxicosis: attachment of the fetus to the endometrium provokes the production of the hormone hCG, which causes vomiting. With a frozen pregnancy, the production of hCG stops, the feeling of nausea goes away. However, early diagnosis is not made. It happens that a decrease in the intensity of toxicosis is simply an adaptation of a woman's body to the presence of a fetus.
- Jumps in basal temperature: in the normal state, this figure does not exceed 37 ° C. After the death of the embryo, it decreases to 36.7 ° C, and when it decomposes, it rises sharply to 37.5 ° C.
- Feeling unwell: observed with a long decomposition of the fetus, when the pathology has not yet been identified - a woman regards a woman as feeling unwell as a cold, a general breakdown. Then there are other serious signs: dizziness, fever, abdominal cramps, anxiety.
In late pregnancy
In the second and third trimesters, the fetus gains weight well and grows to a large size.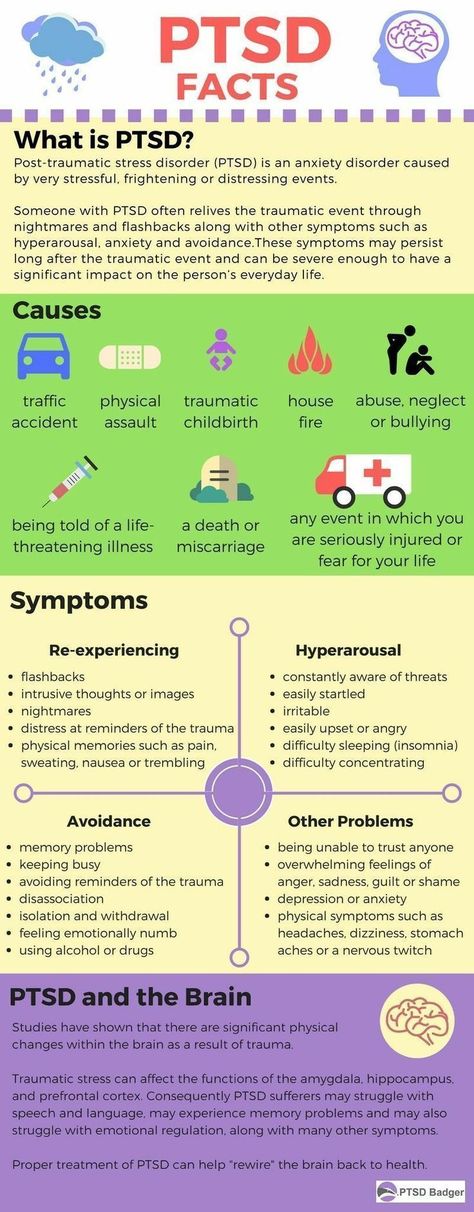 Therefore, in addition to the symptoms characteristic of pathology in the early stages, other manifestations are also observed:
Therefore, in addition to the symptoms characteristic of pathology in the early stages, other manifestations are also observed:
- The fetus does not move for more than 24 hours.
- Stomach hurts and pulls.
- Leaking amniotic fluid with a characteristic putrid odor.
If the fetus does not move for more than 24 hours, another pathology is possible. Similar symptoms are characteristic of a lack of oxygen, which is caused by the umbilical cord wrapping around the neck and torso of the child. But it is also a reason for emergency medical attention, since a child wrapped around the umbilical cord can still be saved.
Regular breast assessments are recommended. With a frozen pregnancy for up to 25 weeks, after a few days, the mammary glands acquire their normal size. In the later stages, colostrum sometimes begins to stand out from the chest after the death of the fetus.
It is also possible to reduce the abdomen, which is caused by leakage of amniotic fluid.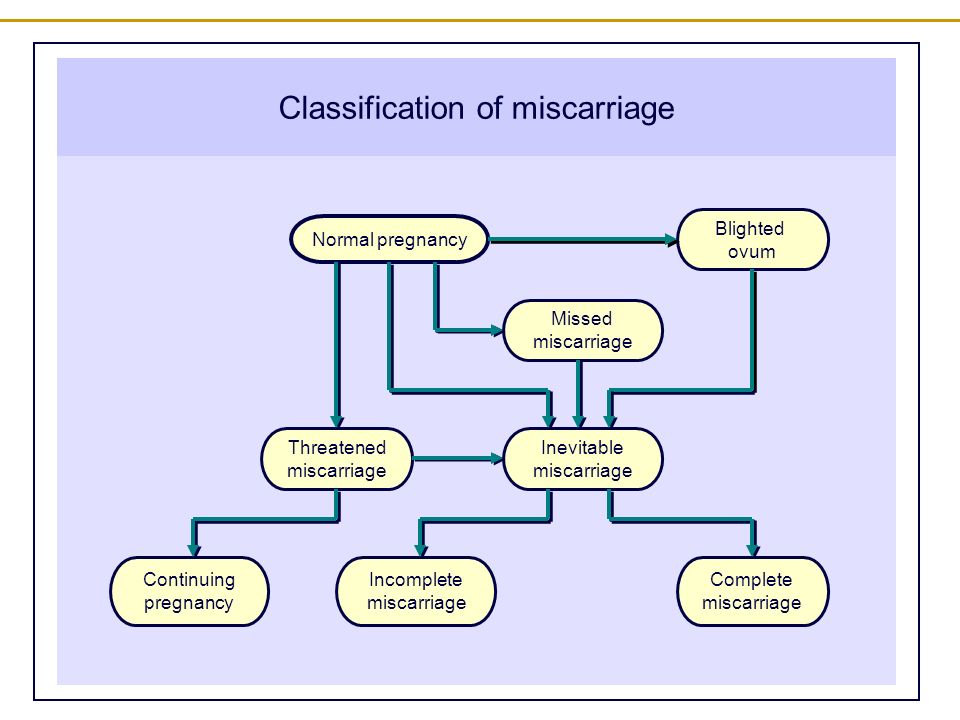 These are attempts by the body to expel the fetus, which has become a foreign body. Symptoms usually start within 2-3 days after the embryo has lost viability.
These are attempts by the body to expel the fetus, which has become a foreign body. Symptoms usually start within 2-3 days after the embryo has lost viability.
Diagnosis
Any of the above symptoms is a serious reason to visit a doctor and undergo the following diagnostic measures:
- visual examination in the gynecologist's office;
- hCG blood test;
- ultrasound;
- measurement of basal temperature.
Medical examination and ultrasound are the main research methods, blood sample and basal temperature measurement are auxiliary.
On ultrasound for up to 7 weeks, the fetus may not yet show signs of vital activity read by the device. Also, the reason for the lack of signs of life often becomes an incorrectly established gestational age. Therefore, abortion is sometimes delayed until a second ultrasound.
The fetus is delayed in development up to 4 weeks in case of stress loads or failures of the hormonal system. If, after a second ultrasound performed after 2 weeks, the fetus remains unchanged in size, this is a sign of its death.
If, after a second ultrasound performed after 2 weeks, the fetus remains unchanged in size, this is a sign of its death.
Ultrasound is usually enough to make a diagnosis. In the first weeks, this is evidenced by the incorrect location and ruptures of the fetal egg. In the later stages, there is no heartbeat, the dimensions do not correspond to the deadline.
Treatment
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the woman is scheduled for an abortion. Each patient has their own method.
First trimester
Medical abortion is usually prescribed to terminate a missed pregnancy up to 9 weeks in Russia and up to 12 weeks in the West. The active ingredients are mifepristone and misoprostol. With high efficiency, this method has the following contraindications:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- severe anemia;
- renal and hepatic insufficiency;
- poor blood clotting.
Curettage is a traditional way of terminating a pregnancy, which is prescribed only when the effectiveness of medications is low and to clean the uterus from embryo fragments. Curettage is indicated until the 12th week of pregnancy. Whenever possible, doctors try to avoid this procedure, since irreversible consequences are possible as a result of trauma to the tissues of the reproductive organs.
Curettage is indicated until the 12th week of pregnancy. Whenever possible, doctors try to avoid this procedure, since irreversible consequences are possible as a result of trauma to the tissues of the reproductive organs.
Before the curettage procedure, a woman must undergo ultrasound, ECG, donate blood, consult an anesthesiologist. The curettage procedure consists of the following steps:
- Intravenous anesthesia (using a fast-acting agent).
- Treatment of the genitals with antiseptics.
- Fixation of the cervix with forceps and dilation of the cervical canal.
- Curettage of the mucous membranes of the uterus and cervical canal with a curette - a gynecological instrument with a loop at the end.
- Treatment of the uterus with drugs to stimulate contractions and a disinfectant iodine solution.
After the procedure is completed, the doctor removes the fixation instruments and applies a cold compress to the woman's abdomen. This helps to tone the uterus due to vasoconstriction. After 6-7 weeks, the menstrual cycle is restored.
This helps to tone the uterus due to vasoconstriction. After 6-7 weeks, the menstrual cycle is restored.
Second trimester
At 13-22 weeks of pregnancy, other methods are used that cause artificial induction of labor:
- Intramial: 20% sodium chloride solution is injected into the water bladder with a special thin needle.
- Isolated: Mifepristone or misoprostol is injected into the genital tract, and one of these drugs is given by mouth.
In case of contraindications or low effectiveness of the above methods, a weight is applied to the pre- posed section of the amniotic sac.
Third trimester
In the third trimester, the only sure way is artificial labor, which is carried out urgently and without anesthesia. Cesarean section is excluded due to the high risk of infection of the woman.
Rehabilitation
In order for the results of treatment to give a positive effect, the woman must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations and continue rehabilitation therapy:
- Hormone therapy for the regeneration of uterine endometrial cells.
- Antibacterial therapy including macrolides or cephalosporins to prevent infection of the endometrium.
- Physiotherapy necessary for the healing of uterine tissues.
- Taking immunostimulating drugs.
Consequences
Termination of pregnancy, even for medical reasons, in any way, is a blow to the reproductive system of a woman. Therefore, a complete rehabilitation of the body is possible no earlier than six months later. All this time, hormone therapy is necessary in accordance with the doctor's recommendations.
If not properly treated, a missed pregnancy has a devastating effect on women's health and causes the following complications:
- Mental disorder: after an abortion, a woman has doubts about the next attempts to become pregnant and bear a child, fear of failure grows. Therefore, treatment must be accompanied by competent psychotherapy.
- Inflammatory processes in the uterus: this common complication occurs after curettage, because during the procedure the mucous membranes are stopped and the tissues of the uterus remain defenseless against bacteria.

- Adhesive processes: adhesion and adhesion of the inner surfaces of the uterus to each other is usually the result of inflammation. This provokes deformation of the uterus, which, if not properly treated, most likely leads to infertility.
Infertility, the most serious complication of a miscarriage, results from non-compliance with medical recommendations and improper treatment. Therefore, it is not enough to terminate a frozen pregnancy. Throughout the rehabilitation period and until a new pregnancy, a woman should be regularly observed by a gynecologist.
Prevention
In order for the pathology not to recur, competent preparation for pregnancy should not be neglected. Future parents must undergo a comprehensive medical examination, including blood samples, genetic tests, ultrasound screening and other procedures. The doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic procedures. You should not conceive a child if one of the spouses had rubella, chickenpox or severe flu less than six months ago. Pregnancy planning also includes the treatment of chronic diseases even before the first attempts at conception.
Pregnancy planning also includes the treatment of chronic diseases even before the first attempts at conception.
Other preventive measures are also recommended:
- healthy lifestyle;
- timely vaccination;
- monitoring the state of the hormonal system;
- genetic counseling;
- refusal of air travel in the first weeks of pregnancy.
High-quality preparation is a proven factor for successful pregnancy and pregnancy. Even if a woman has previously experienced unsuccessful pregnancy attempts with miscarriages and missed pregnancy, competent planning gives a chance to endure and give birth to a healthy child at 90% of cases. After a diagnosed fading, it is necessary to plan a pregnancy with the support of multidisciplinary specialists and quality control over the woman's health.
“The fetus froze”, “The heart of the fetus stopped” - these phrases are heard by about 20% of Russian women during a routine routine examination or after an extended ultrasound. And then - the cruel "You will give birth again."
And then - the cruel "You will give birth again."
It seems that it is impossible to realize and accept: just yesterday you thought up a name for the baby you carried under your heart and managed to fall in love with, but today you have to come to terms with the loss of an unborn child.
“Twice in my life, doctors said the most important words —“ you are pregnant ”— and the most terrible —“ the pregnancy is frozen, we are preparing for hospitalization, ”writes our reader Elena. - The first time it happened during an ultrasound. I looked at the monitor, on which a little man with miniature arms and legs was already looming, the doctor moved the device over my stomach and noted something in the medical record. Everything happened as usual. And suddenly, for some reason, they began to call another gynecologist by phone. After a long deliberation, the doctors came up with a terrible verdict: “We are very sorry, but your fetus is dead.” It is the fetus, not the child. This happened at 24 weeks. Three years later, I managed to get pregnant again, but I stayed in an interesting position for only 7 weeks. My friends don't understand my grief. Everyone repeats like parrots: you will give birth again. I look at the only ultrasound of my first baby and I don't believe I can carry a baby. I am tormented by guilt in front of the baby, which doctors call the embryo.
This happened at 24 weeks. Three years later, I managed to get pregnant again, but I stayed in an interesting position for only 7 weeks. My friends don't understand my grief. Everyone repeats like parrots: you will give birth again. I look at the only ultrasound of my first baby and I don't believe I can carry a baby. I am tormented by guilt in front of the baby, which doctors call the embryo.
Elena Remez
ELENA REMEZ
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, leading specialist of the SM-Clinic holding
The first signs of missed pregnancy
term, - explains Elena Anatolyevna. - From the moment of conception to 8 weeks - the most important and decisive period in the development of the embryo. It is at this time that genetic mutations can occur, leading to severe malformations of the fetus and its death.
A woman may independently suspect a missed pregnancy by indirect signs, for example, a sudden cessation of toxicosis, the appearance of pulling pains in the lower abdomen and spotting from the genital tract, the absence of pain in the chest (women may notice that their mammary glands have ceased to "pour" and abruptly decreased in size).
“If you notice something like this, you should immediately contact a gynecologist to clarify the situation and take timely measures. The doctor will prescribe an ultrasound scan and blood tests to confirm the diagnosis or refute suspicions, ”emphasizes Elena Anatolyevna.
Why does miscarriage occur?
In the first trimester, the main cause of miscarriage is genetic mutations, unfortunately, we cannot influence this. Also during this period, the embryo is more susceptible to the influence of negative external factors, so it is important to plan pregnancy and strictly adhere to a healthy lifestyle: exclude alcohol, do not take medications without consulting a doctor, postpone studies using x-rays, do not come into contact with chemicals.
At the beginning of pregnancy, the expectant mother should try to avoid viral diseases. Even SARS can lead to sad consequences. The presence of problems associated with hormonal imbalance and hemostasis can also cause the death of the embryo, so it is important to find out all the risk factors before pregnancy.
Immune, hormonal and hemostatic system failures; acute and chronic processes in the uterus and appendages, pathological processes in the cervical canal, infections of the genital tract, as well as stress, work overload, an overly active lifestyle can cause fetal loss not only in the early stages, but also in the second and third trimesters .
Miscarriages may be due to past abortions, miscarriages or pelvic surgeries. To avoid this, doctors recommend conducting a pre-gravid examination - a medical examination of the state of the female body, during which various pathologies are detected before conception. History taking, blood tests, genetics consultation, screening for hereditary diseases.
When can I try to get pregnant again?
The period of rehabilitation depends on how long the pregnancy loss occurred. If this happened in the first trimester (the period from the 3rd to the 8th week is especially dangerous, when the internal organs of the child are being formed), then it will take six months to restore the body.
“During the first month, excessive physical activity, visits to baths, saunas, and sexual intercourse are prohibited,” the doctor notes. “It is also recommended to undergo a full examination during this period, consult a psychologist and a geneticist.”
Treatment is individual for every woman. The doctor may prescribe hormone therapy, genetic studies, examinations for sexually transmitted infections, MRI of the pelvic organs, etc. In some cases, laparoscopy or hysteroscopy is necessary.
A missed pregnancy is not a sentence
“If a woman has already had a missed pregnancy in her anamnesis, what should be done to prevent this from happening again?”. This question often worries patients, says the doctor. - I want to immediately reassure expectant mothers: a missed pregnancy is not a sentence, but a serious reason to undergo a full examination, which will help identify the cause of the loss of a child, if possible, eliminate it or correct it with medications. This will allow you to plan a future pregnancy as safely as possible.
This will allow you to plan a future pregnancy as safely as possible.
There is a chance to carry and give birth to a healthy child even after two or more missed pregnancies. There are many happy examples in medical practice when women already despaired of becoming mothers, but fate gave them such an opportunity.
Unfortunately, the loss of a child at an early stage of pregnancy is quite common. After the first miscarriage, a woman lives in constant fear and is afraid that the second attempt to become a mother will turn into a tragedy.
“A miscarriage is a spontaneous termination of pregnancy before the fetus reaches a viable term. A fetus weighing up to 500 g is considered viable, which corresponds to a period of less than 22 weeks of pregnancy. Many women face this diagnosis. About 80 percent of miscarriages occur before 12 weeks of pregnancy."
Causes of miscarriage
Approximately half of early miscarriages occur due to genetic pathologies in the development of the fetus, that is, defects in the number and composition of chromosomes. It is in the first weeks that the formation of the baby's organs begins, which requires 23 normal chromosomes from each of the future parents. When at least one abnormal changes occur, there is a risk of losing a child.
It is in the first weeks that the formation of the baby's organs begins, which requires 23 normal chromosomes from each of the future parents. When at least one abnormal changes occur, there is a risk of losing a child.
At 8-11 weeks the rate of such miscarriages is 41-50%, at 16-19weeks of pregnancy, the frequency of miscarriages caused by chromosomal defects drops to 10 to 20 percent.
There are other causes of miscarriage. Among them:
- Congenital and acquired disorders of the anatomy of the genital organs If there are fibroids, polyps in the uterus, this can cause abnormal development of the embryo. The threat of miscarriage may be in women with an abnormal development of the uterus.
- Infectious causes Numerous studies have shown that the risk of miscarriage increases with sexually transmitted infections. Dangerous for a pregnant woman are measles, rubella, cytomegalovirus, as well as diseases that occur with an increase in body temperature.
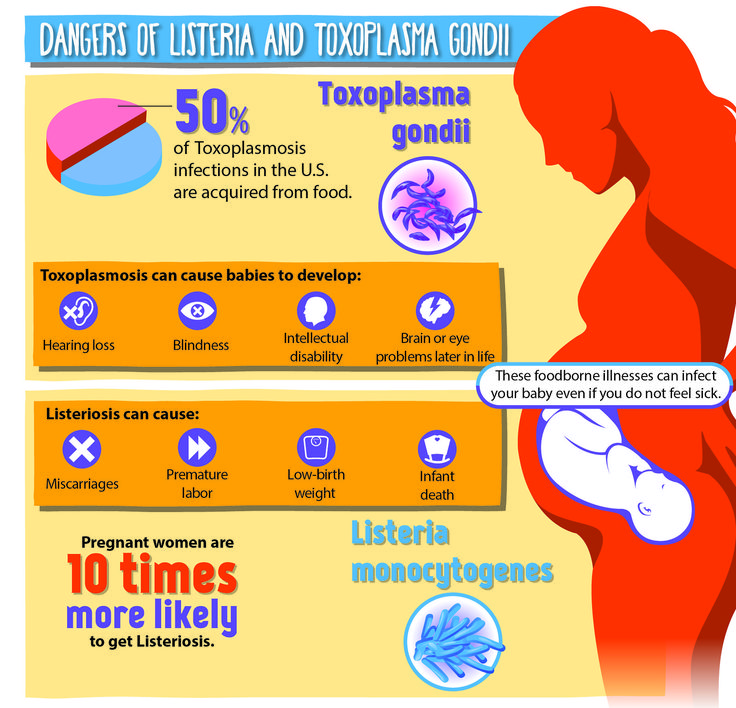 Intoxication of the body often leads to the loss of a child.
Intoxication of the body often leads to the loss of a child. - Endocrine causes Problems with childbearing occur with diabetes, thyroid disease, and adrenal disorders.
- Unfavorable ecology, exposure
- Blood clotting disorders (thrombosis, antiphospholipid syndrome) APS (antiphospholipid syndrome) is a disease in which the human body produces a lot of antibodies to phospholipids - the chemical structures that make up parts of cells. The body mistakenly perceives its own phospholipids as foreign and begins to defend itself against them: it produces antibodies to them that damage blood components. Blood clotting increases, microthrombi appear in small vessels that feed the fetal egg and placenta. Blood circulation in the fetal egg is disturbed. As a result, the pregnancy stops or the growth of the fetus slows down. Both of these lead to miscarriage. All this is due to the hormonal changes during pregnancy.

- Lifestyle and bad habits Nicotine addiction, alcohol use, obesity.
Is it possible to miss a miscarriage
Sometimes women mistake a miscarriage for normal menstruation. This occurs during the so-called biochemical pregnancy, when there is a violation of the implantation of the embryo at a very early stage and menstruation begins. But before the appearance of spotting, the test will show two strips.
The classic variant is when a miscarriage is manifested by bleeding against the background of a long delay in menstruation, which rarely stops on its own. Therefore, even if a woman does not follow the menstrual cycle, the signs of an interrupted pregnancy will be immediately noticed by the doctor during examination and ultrasound.
Alarm
Symptoms of a miscarriage can be completely different, and depending on them, as a rule, you can predict the likelihood of maintaining and successfully continuing this pregnancy.
For the threat of miscarriage is characterized by pulling pains in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, scanty bloody discharge from the genital tract. Ultrasound signs: the tone of the uterus is increased, the cervix is not shortened and closed, the body of the uterus corresponds to the gestational age, the fetal heartbeat is recorded.
Started miscarriage - pain and discharge from the genital tract are more pronounced, the cervix is ajar.
Miscarriage in progress - cramping pains in the lower abdomen, copious bloody discharge from the genital tract. On examination, as a rule, the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age, the cervix is open, the elements of the fetal egg are in the cervix or in the vagina.
Incomplete miscarriage - the pregnancy was interrupted, but there are delayed elements of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity. This is manifested by ongoing bleeding due to the lack of a full contraction of the uterus.
Non-progressive pregnancy - the death of an embryo (up to 9 weeks) or a fetus up to 22 weeks of gestation in the absence of any signs of termination of pregnancy.
Important!
Severe pain in the abdomen and bloody discharge at any stage of pregnancy is a reason for an urgent appeal to an obstetrician-gynecologist with a solution to the issue of hospitalization in a gynecological hospital.
Is it possible to avoid miscarriage
“Today, there are no methods to prevent miscarriages,” says the doctor. “Therefore, it is very important to comprehensively prepare for pregnancy before it occurs by visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist and following all the necessary recommendations for examination and taking the necessary drugs.”
But if, nevertheless, the pregnancy could not be maintained, then the birth of a child can be planned again no earlier than 3-6 months after the miscarriage. This time is needed to figure out, together with the attending physician, what are the causes of miscarriage and whether it is possible to avoid them in the future.
By the way, a common misconception for both women and men is that only the woman is to blame for the loss of pregnancy, but this is far from being the case.
“A man is also responsible, which is why future dads are required to perform a study - a spermogram and be screened for genital infections, since with a pathology of spermatozoa, the likelihood of miscarriage due to genetic abnormalities increases many times,” emphasizes our expert.
There is always a chance
Most women whose first pregnancy ends in miscarriage have a high chance of a successful next pregnancy (about 85 per cent) if they are examined before pregnancy and the causes are eliminated. “A woman who has lost a child needs the support of her family and friends. Sometimes words are unnecessary, just be there. Duty phrases from the series “You will definitely give birth”, “It was just an embryo” hurt very much. The best consolation is to advise you to see a doctor,” says Natalia Kalinina.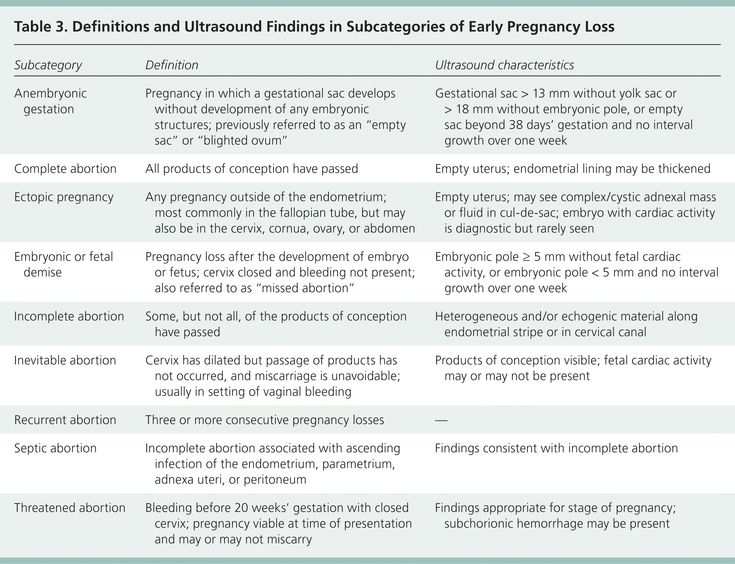
In a non-developing pregnancy, which is also called a "missed pregnancy", the death of the embryo/fetus occurs, but there are no clinical signs of spontaneous miscarriage.
Causes of miscarriage
The causes of miscarriage are very diverse, for example, stopping the development of the embryo/fetus may be due to an inflammatory process as a result of the action of various microorganisms. Most often, the causative agents of inflammation are: streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli, Klebsiella, rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, Coxsackie virus, mycoplasmas, chlamydia, treponema, mycobacteria, toxoplasma, plasmodia, fungi (thrush).
Chronic infectious diseases in a woman most often do not directly lead directly to intrauterine death of the fetus, but cause certain disturbances in its development, which contribute to intrauterine death under the influence of other factors. For example, as a result of direct exposure to an infectious factor, a heart defect is formed in the fetus, which prevents its further normal development. However, not always and not every infection leads to the death of the embryo/fetus. In this case, the influence of the infection depends on the route of its penetration, the involvement of the fetus and amniotic membranes in the infection, the type and activity of the pathogen, the number of penetrating microorganisms, the duration of the mother's disease, the activity of the body's defenses, and other factors.
However, not always and not every infection leads to the death of the embryo/fetus. In this case, the influence of the infection depends on the route of its penetration, the involvement of the fetus and amniotic membranes in the infection, the type and activity of the pathogen, the number of penetrating microorganisms, the duration of the mother's disease, the activity of the body's defenses, and other factors.
Microorganisms can enter the uterus from the lower parts of the reproductive system, infecting the amniotic fluid, which is then swallowed by the fetus. The infection can spread through the amniotic membranes, and further to the fetus, causing damage to its internal organs, which, in turn, is the cause of its death. The infection can also get to the fetus from chronic foci of inflammation in the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
The death of the embryo/fetus may be due to a violation of the immune relationship, given that the fetal egg is half foreign to the mother's body. At the same time, rejection reactions are activated, aimed at defeating the fetal egg and removing it from the uterus. Non-developing pregnancy can be caused by various chromosomal disorders in the first 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, chromosomal changes are present in 60-75% of cases of spontaneous abortion, at 12-17 weeks. - in 20-25%, at 17-28 weeks. at 2-7%. With age, the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities increases. The causes of the development of chromosomal disorders are also unfavorable external factors. The thrombotic complications caused by genetic defects in the blood coagulation system in a pregnant woman can cause an arrest in the growth and development of the embryo/fetus. The most common among them are: factor V Leiden mutation, prothrombin G202110A mutation, methyltetrahydrofolate reductase mutation, plasminogen activator gene polymorphism, platelet receptor polymorphism.
At the same time, rejection reactions are activated, aimed at defeating the fetal egg and removing it from the uterus. Non-developing pregnancy can be caused by various chromosomal disorders in the first 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, chromosomal changes are present in 60-75% of cases of spontaneous abortion, at 12-17 weeks. - in 20-25%, at 17-28 weeks. at 2-7%. With age, the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities increases. The causes of the development of chromosomal disorders are also unfavorable external factors. The thrombotic complications caused by genetic defects in the blood coagulation system in a pregnant woman can cause an arrest in the growth and development of the embryo/fetus. The most common among them are: factor V Leiden mutation, prothrombin G202110A mutation, methyltetrahydrofolate reductase mutation, plasminogen activator gene polymorphism, platelet receptor polymorphism.
Disorders of the blood coagulation system caused by antiphospholipid syndrome also determine the unfavorable development of the embryo/fetus. In the early stages of pregnancy, the role of the direct damaging effect of antiphospholipid antibodies on the structures of the fetal egg, followed by spontaneous abortion, is not excluded. With this pathology, the process of implantation of the fetal egg is disrupted. In addition, with antiphospholipid syndrome, a decrease in the formation of placental vessels and a decrease in its function, which may be the cause of an undeveloped pregnancy. Another cause of impaired development of the embryo / fetus and placenta in antiphospholipid syndrome is thrombosis and damage to the uteroplacental vessels.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the role of the direct damaging effect of antiphospholipid antibodies on the structures of the fetal egg, followed by spontaneous abortion, is not excluded. With this pathology, the process of implantation of the fetal egg is disrupted. In addition, with antiphospholipid syndrome, a decrease in the formation of placental vessels and a decrease in its function, which may be the cause of an undeveloped pregnancy. Another cause of impaired development of the embryo / fetus and placenta in antiphospholipid syndrome is thrombosis and damage to the uteroplacental vessels.
Hormonal changes are also distinguished among the causes of miscarriage. Violation of the formation and decrease in the function of the corpus luteum in the ovary leads to a decrease in progesterone and inadequate preparation of the uterus for implantation of the fetal egg. In this regard, the formation of uteroplacental circulation is disrupted, which entails a decrease in the blood supply to the embryo/fetus, and its death. Often, such disorders occur with excessive accumulation in the body of a woman of male sex hormones (Stein-Leventhal syndrome, adrenogenital syndrome), with reduced or increased thyroid function.
Often, such disorders occur with excessive accumulation in the body of a woman of male sex hormones (Stein-Leventhal syndrome, adrenogenital syndrome), with reduced or increased thyroid function.
The shorter the gestational age, the higher the sensitivity of the embryo/fetus to the action of damaging factors. However, it decreases unevenly throughout fetal development. There are critical periods during pregnancy, in which the ovum, embryo, fetus are especially vulnerable to adverse effects: the implantation period (7-12 days), the embryogenesis period (3-8 weeks), the placenta formation period (up to 12 weeks), the formation period the most important functional systems of the fetus (20-24 weeks).
Clinical signs - symptoms of missed pregnancy
There are a number of consecutive disorders, characteristic of missed pregnancy : decrease and cessation of uteroplacental circulation against the background of damage to the placental structures; cessation of uteroplacental circulation; violation of the structure of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium), caused by the presence of dead elements of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity.
Clinical signs of miscarriage may be extremely poor against the background of the cessation of the increase in the size of the uterus and their inconsistency with the gestational age. However, the uterus can be of normal size, can be reduced, and can even be enlarged if it is filled with blood during detachment of the fetal egg.
For some time after the death of the embryo/fetus, the patient may feel pregnant. However, over time, the subjective signs of pregnancy gradually disappear. Smearing spotting from the genital tract and spastic pains in the abdomen are periodically noted. Chorionic gonadotropin in the blood of a woman, as a rule, is at an extremely low level or even completely absent.
Diagnosis of non-developing pregnancy
0290 ultrasound in the absence of a fetal heartbeat. One of the most common options for non-developing pregnancy is anembryony, i.e. the absence of an embryo in the cavity of the fetal egg after 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. In this case, the fetal egg is smaller than expected, and the embryo is not visualized.
In other cases of non-developing pregnancy, according to ultrasound, the fetal egg matches or lags in size in its development, the embryo can be visualized, but without a heartbeat. Often, a retrochorial hematoma can be detected, which is an accumulation of blood at the site of detachment of the fetal egg from the uterine wall.
With a longer stay of the dead embryo in the uterus, visualization of the embryo is impossible, there are no signs of its vital activity. The size of the uterus lags behind the gestational age, there is a deformation of the fetal egg with fuzzy contours.
Removal of the dead ovum
The death of the embryo/fetus is not always accompanied by its spontaneous expulsion from the uterus. Often there are cases when a dead fetal egg lingers in the uterus for an indefinitely long time. The reason for such a delay may be: primary tight attachment of the fetal egg to the uterine wall during implantation, inferiority of immune rejection reactions of the dead fetal egg, and a decrease in the contractile activity of the uterus.
If a dead embryo is in the uterus for 2-4 weeks or more, the elements of the decay of the dead fetal egg enter the maternal bloodstream, which leads to a violation of the blood coagulation system and can cause massive bleeding when trying to terminate the pregnancy. In this regard, before curettage of the uterus in order to remove the dead fetal egg, it is necessary to perform studies of the state of the blood coagulation system and, if necessary, conduct appropriate treatment.
After a thorough examination and appropriate preparation of the woman (carrying out therapeutic and preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of possible complications), it is necessary to terminate the miscarriage. For this purpose, instrumental or drug-induced dilation of the cervix and instrumental removal of the contents of the uterus are performed. It is also possible to use special medications for non-operative removal of the ovum from the uterus. An ultrasound scan should be performed immediately during the abortion or immediately after it is completed to ensure that parts of the fetus and placenta have been completely removed.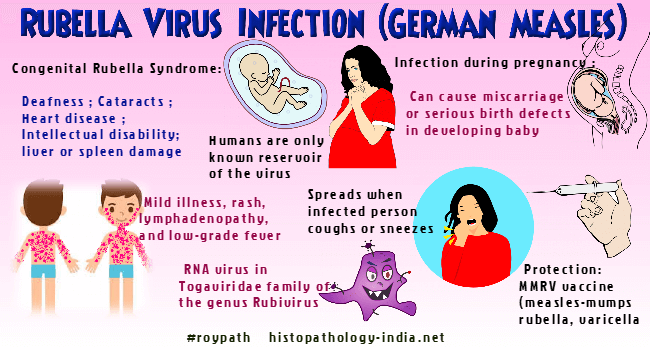 After removal of the fetal egg in non-developing pregnancy, regardless of the method of termination, it is advisable to conduct anti-inflammatory treatment.
After removal of the fetal egg in non-developing pregnancy, regardless of the method of termination, it is advisable to conduct anti-inflammatory treatment.
In each case of a non-developing pregnancy, an in-depth examination is required to identify possible causes of abortion with their subsequent elimination or weakening of the effect.
How to reduce the risk of embryo death?
To reduce the likelihood of possible damaging factors in the course of pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct screening examinations of patients planning pregnancy, as well as women in the early stages of pregnancy for urogenital infection. It is also important to conduct medical genetic counseling in order to identify high-risk groups for congenital and hereditary pathologies. In the presence of endocrine causes of miscarriage, appropriate corrective hormonal therapy should be selected.
It is also important to identify various autoimmune disorders and their correction.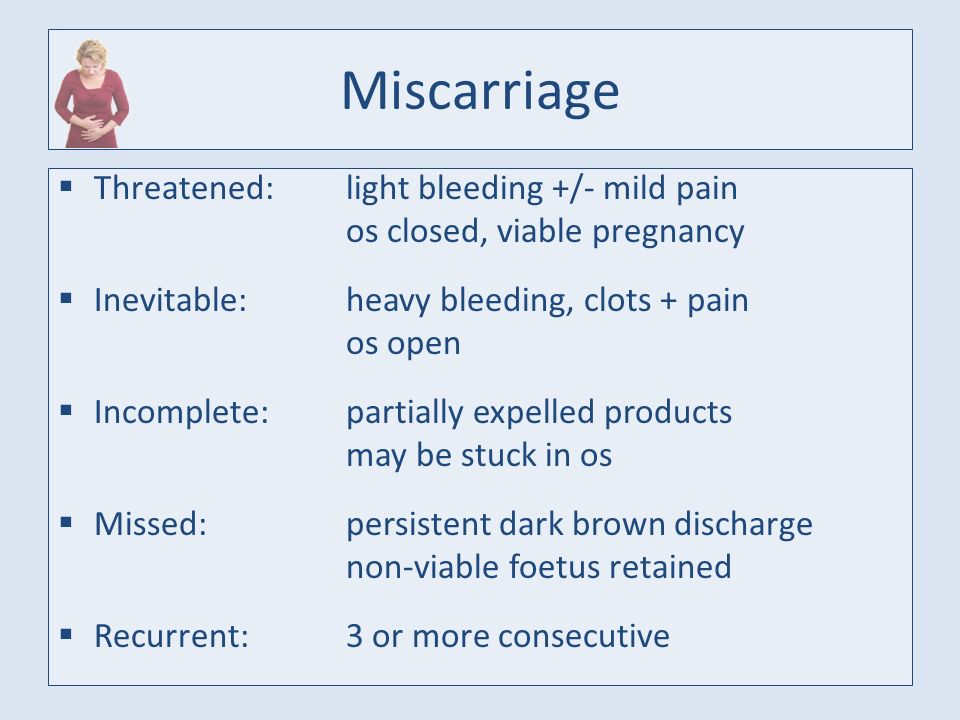 Re-pregnancy is possible when the identified causes of embryo/fetal death are eliminated, and after the necessary treatment has been carried out. In case of a new pregnancy, an ultrasound examination is performed, markers of possible fetal developmental disorders are determined in the blood, including: α - fetoprotein, chorionic gonadotropin, PAPP-A test in the most informative terms. According to indications, invasive prenatal diagnostics is also carried out, including chorion biopsy, amniocentesis or cordocentesis to determine chromosomal and a number of monogenic diseases of the fetus. In addition, they carry out therapeutic and preventive measures aimed at eliminating the infectious process, conduct specific anti-inflammatory therapy in combination with immunocorrectors, correct violations of the blood coagulation system and prevent placental insufficiency from 14-16 weeks of pregnancy.
Re-pregnancy is possible when the identified causes of embryo/fetal death are eliminated, and after the necessary treatment has been carried out. In case of a new pregnancy, an ultrasound examination is performed, markers of possible fetal developmental disorders are determined in the blood, including: α - fetoprotein, chorionic gonadotropin, PAPP-A test in the most informative terms. According to indications, invasive prenatal diagnostics is also carried out, including chorion biopsy, amniocentesis or cordocentesis to determine chromosomal and a number of monogenic diseases of the fetus. In addition, they carry out therapeutic and preventive measures aimed at eliminating the infectious process, conduct specific anti-inflammatory therapy in combination with immunocorrectors, correct violations of the blood coagulation system and prevent placental insufficiency from 14-16 weeks of pregnancy.
Appointment to specialists by phone of a single call center: +7 (495) 636-29-46 (m. "Shchukinskaya" and "Street of 1905 Goda"). You can also make an appointment with a doctor on our website, we will call you back!
"Shchukinskaya" and "Street of 1905 Goda"). You can also make an appointment with a doctor on our website, we will call you back!
signs, symptoms and causes. How to determine a frozen pregnancy. Clinic Ak. Grishchenko
03/15/2021
Not always long-awaited and such a desired pregnancy ends with the birth of a baby. Sometimes women find out that the pregnancy has stopped. Unfortunately, this problem is not rare. According to statistics, in about 15% of cases, the planned babies "freeze" in the womb for one reason or another.
CONTENT:
- What is it?
- Dangerous timing: when can it happen?
- Why is this happening?
- How do doctors determine missed pregnancy?
- Signs and symptoms
- How to recover from a missed pregnancy?
- What tests to pass after?
- Answers from experts on whether ST cleanup is required.
- Frequently asked questions for which go to the forum.

What is it?
A missed pregnancy is a pregnancy that initially met all medical standards, but suddenly stopped developing in a certain period. The cessation of progress in the development of the fetus leads to its death, but it remains in the uterine cavity. For this reason, such a pathology is called a failed miscarriage.
In fact, at the very beginning, everything happens, as in a normal pregnancy - the egg is fertilized, enters the uterus and is implanted for further development, but it stops at one moment. This pathology also includes the syndrome of "empty fetal egg". It is the development of fetal membranes in which there is no embryo. With this syndrome, a pregnancy test is positive, as well as an analysis for hCG.
Dangerous timing: when can it happen?
Fetal development can stop at any time up to 28 weeks (in rare cases, development can stop later), but the greatest probability of such a pathology occurs in the first trimester. There are also several periods with the highest risk of miscarriage, these include the following periods:
There are also several periods with the highest risk of miscarriage, these include the following periods:
- 3-4 weeks;
- 8-10 weeks;
- 16-18 weeks.
It is these terms that most often become critical for pregnancy.
Causes of miscarriage?
Even doctors are not always able to find out exactly why a miscarriage happened. In modern medicine, there are a number of reasons that can cause such a pathology. All of them are divided into several large groups:
- Genetic pathologies . It is these reasons that most often provoke a halt in fetal development. Pathological genes or the presence of an extra chromosome in the embryo can cause the development of many defects that are incompatible with life, leading to termination of pregnancy. Often, genetic pathologies cause a stop in the development of pregnancy in the eighth to tenth week.
- Infections . A missed pregnancy can also often happen due to the presence of infectious diseases, since during the period of bearing a child, a woman experiences a rather serious decline in immune defenses.
 Especially dangerous for this period are TORCH infections, which include rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes and toxoplasmosis. The greatest danger to the fetus is the first "meeting" of the mother with the infection in an already pregnant state. Therefore, when registering, pregnant women are strongly recommended to be screened for these types of infections. Even seemingly simple and familiar diseases such as influenza or SARS can cause pathology, especially in the early stages, when vital organs are formed in the fetus. The infection can affect the fetus directly, causing various types of anomalies, or on the membranes, resulting in a significant lack of oxygen or nutrients to the fetus.
Especially dangerous for this period are TORCH infections, which include rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes and toxoplasmosis. The greatest danger to the fetus is the first "meeting" of the mother with the infection in an already pregnant state. Therefore, when registering, pregnant women are strongly recommended to be screened for these types of infections. Even seemingly simple and familiar diseases such as influenza or SARS can cause pathology, especially in the early stages, when vital organs are formed in the fetus. The infection can affect the fetus directly, causing various types of anomalies, or on the membranes, resulting in a significant lack of oxygen or nutrients to the fetus. - Hormonal disorders . Hormonal balance is extremely important for the normal bearing of a child. Therefore, with a lack of progesterone or an excess of male hormones (androgens), the likelihood of miscarriage significantly increases. Any hormonal disruptions are recommended to be treated before pregnancy.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome . Because of them, the formation of placental vessels or their blockage may also decrease, which leads to a violation of the fetus receiving the necessary nutrition.
- Teratozoospermia . This cause of a missed pregnancy is associated with pathologies in the seminal fluid of a man. With teratozoospermia, spermatozoa have an irregular structure, so fertilization with such a cell leads to abnormalities in the development of the embryo.
- Lifestyle . The presence of bad habits, as well as lifestyle during childbearing (and the planning period) can also adversely affect the development of the embryo, causing it to freeze. Drinking alcohol, smoking, stress, occupational hazards, daily routine, sedentary lifestyle, unbalanced diet - all this is considered negative factors for pregnancy.
- Other factors. Pregnancy fading can also occur due to a sharp change in climate, a history of abortions (especially if there were several).

In some cases, several causes may be found at once, which could lead to a pregnancy fading.
How do doctors determine missed pregnancy?
At each examination of a pregnant woman, the gynecologist determines the size of the uterus, so if they do not correspond to the current period, the specialist may suspect the fetal fading. But such a diagnosis is made only after an ultrasound examination. In rare cases, ultrasound is not performed - if the woman turned to the doctor late and intoxication of the body has already occurred due to the death of the fetus.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of miscarriage are the same in any trimester. The main signs that may indicate such a pathology are:
- vaginal discharge with blood impurities;
- general weakness, chills, fever;
- drawing pains in the lower part of the abdomen;
- cessation of swelling and soreness of the mammary glands;
- abrupt disappearance of manifestations of toxicosis;
- absence of fetal movements (with pathology in the second trimester).
Despite the presence of characteristic symptoms of pathology, often the cessation of fetal development goes unnoticed, since the basal temperature can remain within 37 degrees, and the hCG level remains high for several more weeks. In this case, the woman learns about the problem only at the next appointment with the doctor or a planned ultrasound.
How to recover from a missed pregnancy?
If such a pathology occurs, it is imperative to remove the dead embryo from the uterine cavity, if this did not happen naturally. For this, a cleaning is carried out, with the help of which all particles of the fetal membranes are removed from the uterus. Both scraping and vacuum can be used. If the fading occurred at a very early date, doctors may suggest a medical abortion, which is somewhat more gentle for the woman, including psychologically.
Doctors recommend to refrain from the next pregnancy for six months (according to the recommendation of the World Health Organization). This time is enough for the body to recover after what happened. Therefore, during this time, women are advised to take oral contraceptives, which minimize the likelihood of conception, and also allow you to normalize hormonal levels.
This time is enough for the body to recover after what happened. Therefore, during this time, women are advised to take oral contraceptives, which minimize the likelihood of conception, and also allow you to normalize hormonal levels.
During recovery, it is also recommended to lead the most healthy and active lifestyle, take care of a balanced diet and take vitamin complexes. A woman definitely needs psychological support, and if she endured the incident especially hard, she may need the help of specialists - a psychologist or psychiatrist. This will help you get back to normal and prepare for your next pregnancy.
What tests to take after?
Before becoming pregnant after a missed pregnancy, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a recurrence of what happened. Treatment should be appropriate to the problem that caused the pathology. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo a complete examination, which will help determine the cause of the fetal development fading. According to the results of the examination, doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with the detected diseases.
According to the results of the examination, doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with the detected diseases.
It is recommended to undergo an examination after the restoration of the woman's menstrual cycle (usually it takes about 30 days after cleaning). But both spouses should be tested. The full examination includes:
- genetic testing of spouses;
- tests for TORCH infection;
- study of hormonal levels;
- blood coagulogram;
- Gynecological ultrasound;
- spermogram;
- immunogram.
This examination is usually sufficient to determine the causes of miscarriage, both early and late. The attending physician may prescribe additional studies if necessary. All these examinations can be done at the IVF and infertility treatment clinic of Academician V.I. Grishchenko.
Frozen pregnancy is not a verdict - in 90% of cases, after the occurrence of such a pathology, spouses become happy parents of healthy babies in the near future. The main thing is to undergo a complete examination and eliminate the cause of the pathology. And if necessary, you can go through the procedure of artificial insemination (IVF).
The main thing is to undergo a complete examination and eliminate the cause of the pathology. And if necessary, you can go through the procedure of artificial insemination (IVF).
Answers from specialists in the field of reproduction, fertility, women's health about whether cleaning is mandatory during a missed pregnancy.
On the Internet, the question is often asked: “Is it necessary to do curettage during a missed pregnancy (ZB)?”
We asked this question to our doctors:
Parashchuk Valentin Yuryevich
Head Physician of Academician Grishchenko Clinic, obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist.
Good afternoon. If the pregnancy froze at an early stage and there are no signs that it is going to resolve itself, that is, there is no bleeding, then it is advisable to evacuate the contents of the uterine cavity, that is, to do curettage. If the pregnancy seeks to resolve itself, then it can come out on its own. And then curettage is not required, you can just look at the ultrasound as soon as the discharge ends, that there are no inclusions in the uterine cavity, that there are no elements of the ovum left in the uterine cavity.
If the pregnancy seeks to resolve itself, then it can come out on its own. And then curettage is not required, you can just look at the ultrasound as soon as the discharge ends, that there are no inclusions in the uterine cavity, that there are no elements of the ovum left in the uterine cavity.
Another situation is when the pregnancy has stalled and you really need to evacuate the contents, and then there are alternative methods, sometimes they offer the so-called "medical abortion", that's the term. And it is more correct to do a scraping, or a vacuum, if the time permits. Because, sometimes, after these very medical abortions, you have to do scraping, but already in fact of complications. Because the entire contents of the uterine cavity does not always come out completely, and now inflammation joins, this is a big trauma for the uterus, this is already a conditionally urgent condition, and it is better not to allow it. Therefore, it is better to do a moderate, without severe injury and without complications, curettage on time than to do it as a necessary measure. When it is already clear that this is a frozen pregnancy, tactics can be discussed, but it is important to really understand when it is, which are such dangerous or alarming calls.
When it is already clear that this is a frozen pregnancy, tactics can be discussed, but it is important to really understand when it is, which are such dangerous or alarming calls.
The main complaint is if the uterus is already frozen and the uterus is trying to get rid of the pregnancy, then this is bloody discharge, that is, the pregnancy is already rejected. But it happens that she freezes and the patient knows absolutely nothing about it, and they become a godsend at a later date, when she is told that the fetal egg does not match in size, that she stopped earlier, and this cannot be suspected in any way. Therefore, if there are pains, pulling pains in the lower abdomen, spotting, you should definitely consult a doctor. Firstly, because it is not a fact that it is frozen. Or maybe it’s a threat of pregnancy fading, and you can turn in time, respond in time, stop the process and save the pregnancy. And if she really froze, then react in time and get rid of the fetal egg that has already stopped in development, without allowing any complications.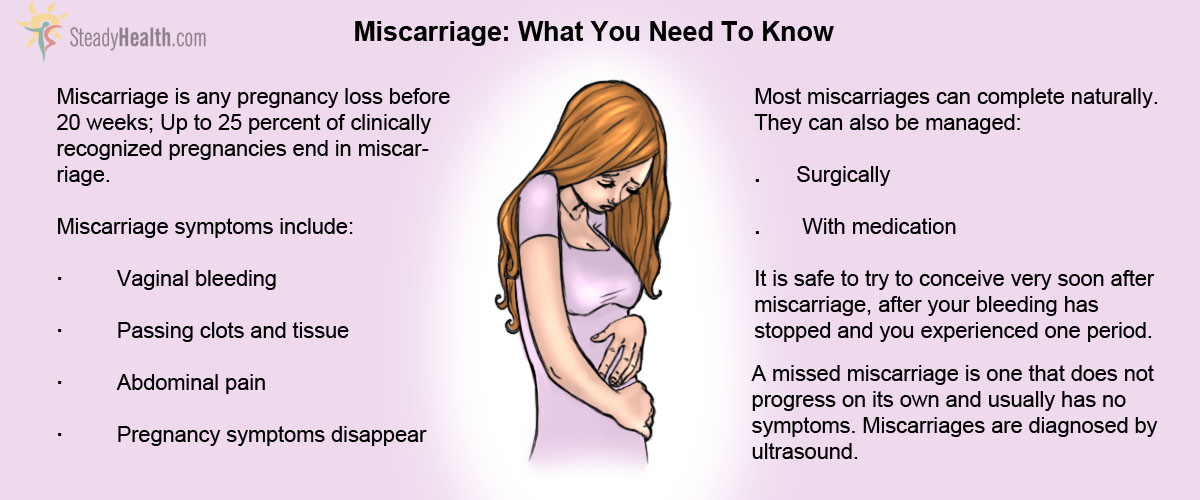 In any case, if pain or spotting occurs during pregnancy, at any time, this is an indication to consult a doctor. There should be no pain, there should be no blood.
In any case, if pain or spotting occurs during pregnancy, at any time, this is an indication to consult a doctor. There should be no pain, there should be no blood.
Alipova Elena Konstantinovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, ultrasound specialist.
The question is unconditional that the miscarriage must be removed from the uterus. That is, non-developing tissues, they are the source of the inflammatory process in the first place, and these tissues should be removed as soon as possible. The best method is still scraping.
As for not deleting at all, this is not even discussed. You can talk a little about medical abortion, but in my opinion, he also has no right to exist with a missed pregnancy. First, because everything needs to be done:
- fast;
- as carefully as possible.

And most the main thing is that scraping products, concept products, as they say now, can be sent in this case for genetic testing . And this, with a frozen pregnancy, is very important because, well, what happened, it happened, and everyone is interested in the question of why it happened. A genetic study of abortive material helps in about 80% of cases to answer the question of what happened after all. If genetics is to blame, this is one conversation, if everything is in order from a genetic point of view, additional examinations will be directed in another direction.
Lutsky Andrey Sergeevich
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist.
Hello. Today we will talk about missed pregnancy. There are surgical methods, such as curettage, vacuum aspiration and hysteroscopic removal of the ovum, and medical methods, the so-called "medical abortion" . Medical methods of abortion are indicated for women who have already had pregnancies in the past and had natural childbirth. This is due to the fact that the cervix of the uterus in such women is ajar and during induction, artificial induction of uterine contractions, a complete spontaneous abortion occurs, no residues remain in the uterine cavity. If the girl is nulliparous, then medical abortion often gives complications. Not everything comes out of the uterine cavity. Parts of the membranes remain, clots, and, let's say, a delay of these parts occurs and there may be an inflammatory process, as a result of which, subsequently, surgical intervention is required - curettage or vacuum aspiration. The method of terminating a missed pregnancy is chosen by the attending physician based on these data. In our clinic, we often encounter missed pregnancy in those women who want to give birth to their child. And to understand the genetics of the fetus, we often recommend hysteroscopic removal or vacuum aspiration of the ovum.
Medical methods of abortion are indicated for women who have already had pregnancies in the past and had natural childbirth. This is due to the fact that the cervix of the uterus in such women is ajar and during induction, artificial induction of uterine contractions, a complete spontaneous abortion occurs, no residues remain in the uterine cavity. If the girl is nulliparous, then medical abortion often gives complications. Not everything comes out of the uterine cavity. Parts of the membranes remain, clots, and, let's say, a delay of these parts occurs and there may be an inflammatory process, as a result of which, subsequently, surgical intervention is required - curettage or vacuum aspiration. The method of terminating a missed pregnancy is chosen by the attending physician based on these data. In our clinic, we often encounter missed pregnancy in those women who want to give birth to their child. And to understand the genetics of the fetus, we often recommend hysteroscopic removal or vacuum aspiration of the ovum.
Yuliya Vladimirovna Labuznaya
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the department of operative gynecology, doctor of the cervical pathology office
Hello. Today I will try to answer the most frequently asked questions regarding non-developing pregnancy. Perhaps I’ll start with such a rink: “Is it necessary to do vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity, that is, the evacuation of a missed pregnancy, if a non-developing pregnancy is diagnosed?” And so let's deal with the concept. Non-developing pregnancy is such a pathological condition in which pregnancy fades, but spontaneous expulsion from the uterine cavity does not occur. At the same time, the woman herself does not immediately understand what happened to her. The first signs of a missed pregnancy can appear 2-3 weeks after the incident. The fetal egg, which is located in the uterine cavity, undergoes various pathological changes, adversely affecting the endometrium, thereby causing an inflammatory process called "endometritis".
The fetal egg, which is located in the uterine cavity, undergoes various pathological changes, adversely affecting the endometrium, thereby causing an inflammatory process called "endometritis".
If a woman decides to wait for the spontaneous expulsion of a missed pregnancy from the uterine cavity, what happens? The endometrium tries to reject the frozen fetal egg, but the inflammatory processes taking place in this endometrium slow down this process, and the process can last from several days to several weeks. Which absolutely negatively affects the endometrium and contributes to the development of the inflammatory process further. There is an act that the fetal egg from the uterine cavity, as it were, came out, but not completely. There is a part of him left. From this part, often, a placental polyp is formed. The presence of a placental polyp in the uterine cavity contributes to the prevention of a subsequent pregnancy. Before the onset, planning a subsequent pregnancy, such a pali must be removed. In addition, the presence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity for four weeks or more significantly increases the risk of bleeding. Therefore, the best solution to such an issue, in the presence of a missed pregnancy in a patient, is vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity with the appointment of subsequent anti-inflammatory therapy.
In addition, the presence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity for four weeks or more significantly increases the risk of bleeding. Therefore, the best solution to such an issue, in the presence of a missed pregnancy in a patient, is vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity with the appointment of subsequent anti-inflammatory therapy.
The second issue is errors in the diagnosis of non-developing pregnancy. For example, at 5-6 weeks, an ultrasound examination, in order to avoid such errors, is carried out by at least two specialists. If there are no clear criteria for non-developing pregnancy, it is recommended for the patient to repeat this study after 3-7 days. Again, to avoid mistakes. In addition, in parallel, the task of such an analysis as an analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood is mandatory. If the pregnancy develops, the hCG will increase accordingly, if the pregnancy is still frozen, then the hCG will either fall or not grow at all. If the gestational age is 7-8 weeks, then according to the ultrasound examination, the heart rate of the embryo will be absent.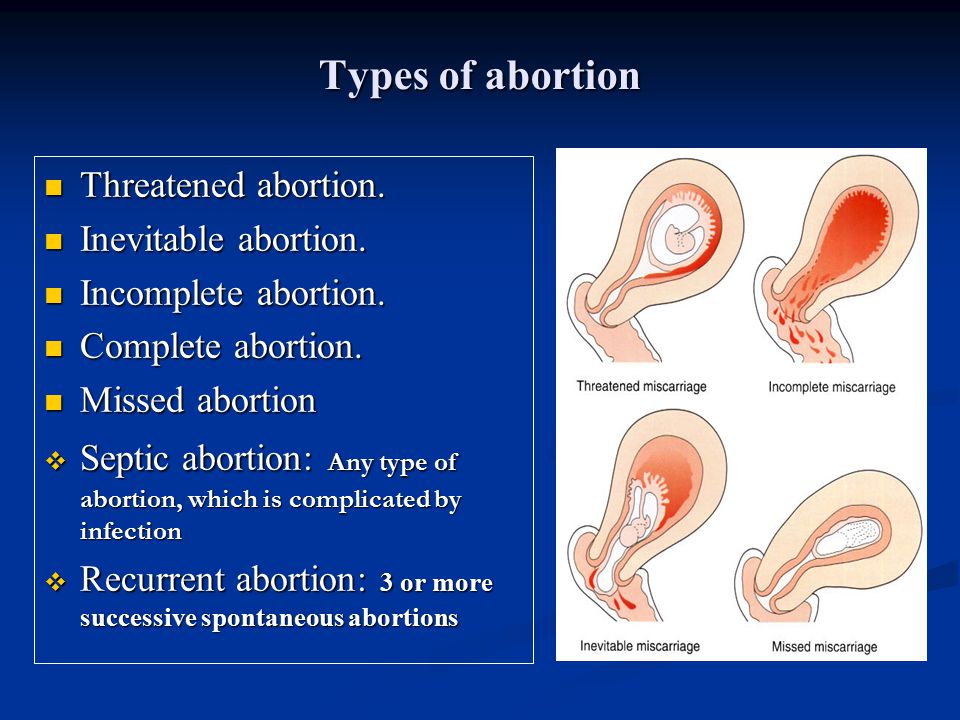 In addition, there will be a discrepancy between the size of the fetal egg and the gestational age. At gestational age 9-12 weeks, in addition to the lack of heart rate and the discrepancy between the gestational age and the size of the fetal egg, there will also be no movement of the embryo. It should always be remembered that every woman has the right to take a closer look at the ultrasound in a few days for an accurate diagnosis, to control the human chorionic gonadotropin, in fact, in order to avoid errors in the diagnosis of "non-developing pregnancy".
In addition, there will be a discrepancy between the size of the fetal egg and the gestational age. At gestational age 9-12 weeks, in addition to the lack of heart rate and the discrepancy between the gestational age and the size of the fetal egg, there will also be no movement of the embryo. It should always be remembered that every woman has the right to take a closer look at the ultrasound in a few days for an accurate diagnosis, to control the human chorionic gonadotropin, in fact, in order to avoid errors in the diagnosis of "non-developing pregnancy".
Answers to frequently asked and discussed questions on the forums:
✅ Can an ultrasound erroneously show a miscarriage?
Misdiagnosis of "non-developing pregnancy" occurs in the early stages. In our clinic, in order to avoid such errors, ultrasound at 5-6 weeks is performed by at least two specialists. If there are no clear criteria for non-developing pregnancy, then the patient is recommended to do a second study after 3-7 days.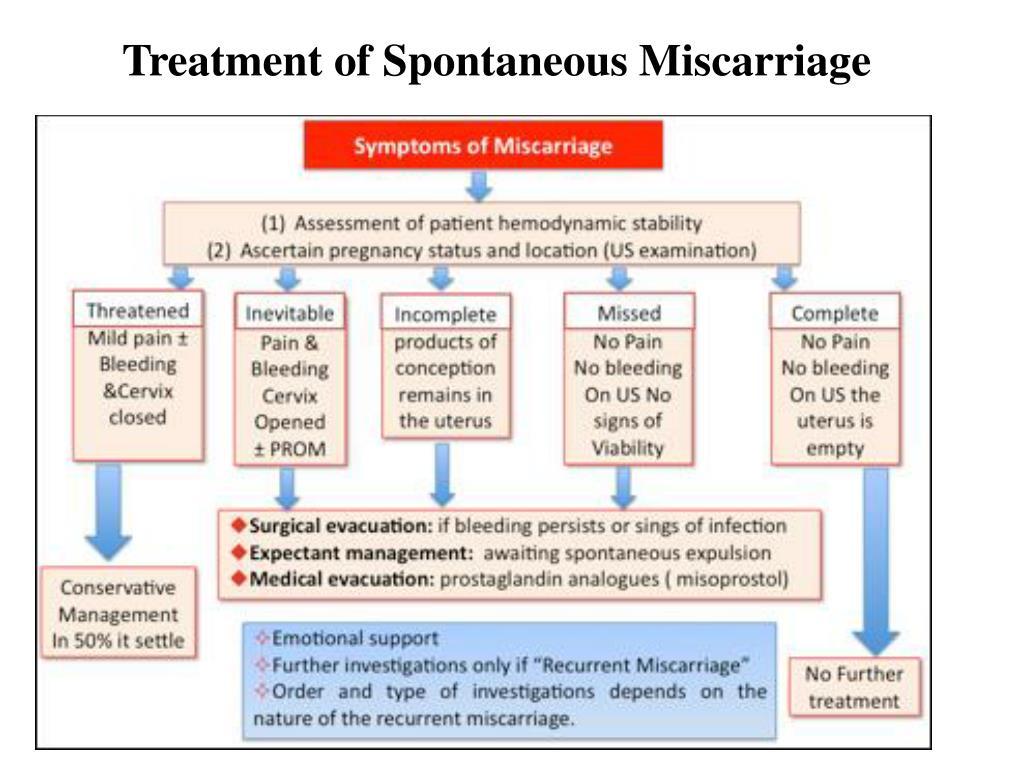 And on re-examination, it may turn out that the missed pregnancy was normal.
And on re-examination, it may turn out that the missed pregnancy was normal.
✅ With a missed pregnancy, is it possible to do without cleaning?
If a frozen pregnancy tends to resolve itself, then it can come out on its own, and then curettage (cleansing) is not required. As soon as the discharge ends, it is necessary to check on an ultrasound scan that there are no elements of the ovum left in the uterine cavity. If the pregnancy froze at an early stage and there are no signs that it is going to resolve itself, that is, there is no bleeding, then it is advisable to do a curettage.
✅ Frozen pregnancy - cleaning or pills?
Medical termination of pregnancy is indicated for women who have had pregnancies in the past and had vaginal delivery. But it is more correct to do a scraping, or a vacuum, if the time permits. Because, sometimes, after medical abortions, you also have to do scraping, but already in fact of complications. Because the contents of the uterine cavity do not always come out completely, and inflammation is added, and this is a big trauma for the uterus and it is better not to allow this.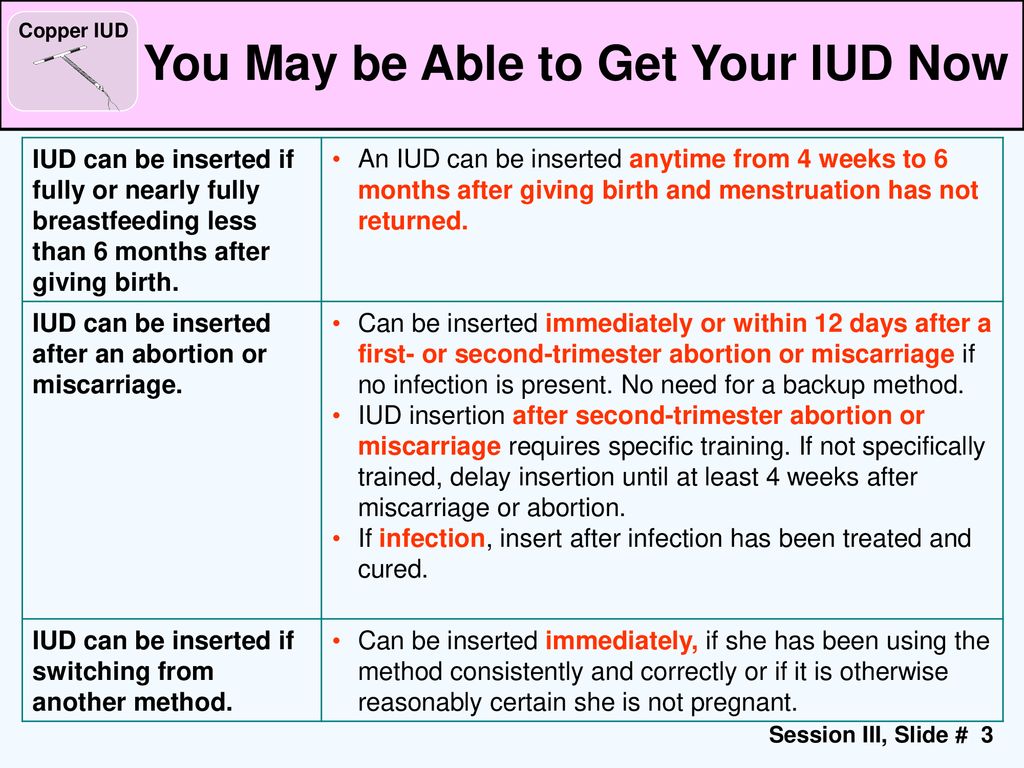 Therefore, it is better to do a moderate, without severe injury and without complications, curettage on time than to do it as a necessary measure. And most importantly, scraping products can be sent for genetic testing to identify the causes of fetal development fading.
Therefore, it is better to do a moderate, without severe injury and without complications, curettage on time than to do it as a necessary measure. And most importantly, scraping products can be sent for genetic testing to identify the causes of fetal development fading.
✅ Can there be a miscarriage without symptoms?
It happens that the pregnancy stops, and the patient knows absolutely nothing about it, and this is discovered at a later date, when she is told that the fetal egg does not correspond in size, that the pregnancy stopped earlier, but this, unfortunately, it is impossible to suspect in advance. The first signs of a non-developing pregnancy can appear 2-3 weeks after the incident. These are spotting or pulling pains in the lower abdomen. With these symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor.
✅ How long does it take to have a miscarriage with a missed pregnancy?
If a woman decides to wait for the spontaneous expulsion of an undeveloped pregnancy, what happens? The endometrium tries to reject the frozen fetal egg, but the inflammatory processes taking place in this endometrium slow down this process, and the process can last from several days to several weeks.