Newborn puffy eyes how long
Eyes | Newborn Nursery | Stanford Medicine
-
Eyelid Edema
-
Dysconjugate Eye Movements
-
Dacrocystoceles
-
Dacrocystocele
-
Dacrostenosis
-
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
-
Iris Cyst
-
Normal Eye
-
Injected Eye
-
Peripupillary Vascularity
-
Gonococcal Conjunctivitis
-
Congenital Glaucoma
-
Peter's Anomaly
-
Congenital Cataract
Eyelid Edema
Most infants exhibit some degree of eyelid edema after birth. The puffiness may make it seem that the infant has difficulty opening one or both eyes, but with a gentle examination, the eye can be easily evaluated. Edema resolves over the first few days of life.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Dysconjugate Eye Movements
During the first few months of life, newborns will frequently have dysconjugate eye movements, where the eyes appear to move independently. Eyes may transiently appear crossed or divergent. This phenomena is particularly noticeable when the infant is falling asleep or being woken from sleep. If the dysconjugate movement is fixed (one eye is always out, or always in, relative to the other), a pediatric ophthalmologist should be consulted. But if the movements are transient, it is a normal finding and will spontaneously resolve.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Dysconjugate Eye Movements
Here is another example of dysconjugate eye movements. This infant was sound asleep when the lids were gently opened for the photo. When awake, the infant could easily fix and focus on the mother's face.
When awake, the infant could easily fix and focus on the mother's face.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Dacrocystoceles
This infant was noted at birth to have some bluish nodules inferior to the medial canthi of both eyes, widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), and a flat nasal bridge. The nodules are dacrocystoceles. They are caused by obstructions at both superior and inferior ends of the nasolacrimal duct. Though relatively small externally, these lesions almost completely obstructed the nasal passages. For this reason, internal nasal evaluation is recommended when the dacrocystoceles are bilateral, even when the patient is otherwise asymptomatic (as this child was).
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Dacrocystocele
An intra-operative photo shows the degree of obstruction of the nasal passage on the right side. The pink structure on the upper left is the turbinate, and the bluish mass at the bottom of the photo is the dacrocystocele. The small dark spot in the center was the area available for breathing.
photo by Anna Messner, MD
Dacrostenosis
Here is an example of dacrostenosis. In this case, both eyes are affected, although there is slightly more discharge around the left eye than the right. The sclera of both eyes are clear, and there are no other signs of infection. For about half of affected patients, this will resolve within the first week of life. For the other half, spontaneous resolution is expected in several weeks to a few months.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
Subconjunctival hemorrhage is a frequent finding in normal newborns. It results from the breakage of small vessels during the pressure of delivery. The red area may be large or small but is always confined to the limits of the sclera. It is asymptomatic, does not affect vision, and spontaneously resolves in several days. Note also the numerous petechiae on the forehead. This infant had significant facial bruising as well as the eye finding.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Iris Cyst
This infant had a normal physical exam at birth. By about 20 hours of life, there was a reddish/blue discoloration of the eyelid and redness in the left eye, the sclera was markedly injected, there was a small amount of discharge in the upper lashes, and the retinal light reflex was not visible. With careful inspection, a reddish discoloration over the iris (which gives the normally bluish iris a brown tint), and an opacity within the pupil can be seen. These findings were believed to be due to an iris cyst, an extremely rare finding. Interestingly, the cyst spontaneously resoved over a few months.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Normal Eye
For comparison, this is the completely normal right eye of the same infant. Note the lack of injection in the sclera, the normal greyish blue iris and the clear pupil. A retinal reflex was easily obtained in this eye.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Injected Eye
This is another newborn with unilateral conjunctival injection. On initial examination, the right pupil was about 2mm in diameter and the normal left pupil was 5-6mm. A retinal reflex was not present on the right side. This photo was taken after dilating drops were placed. Some dilation of the right pupil is noted, but it was not equal with the left, and still the retina could not be well seen. The differential diagnosis includes tumor and vascular abnormalities. An ultrasound of the eye was done to evaluate this finding further.
On initial examination, the right pupil was about 2mm in diameter and the normal left pupil was 5-6mm. A retinal reflex was not present on the right side. This photo was taken after dilating drops were placed. Some dilation of the right pupil is noted, but it was not equal with the left, and still the retina could not be well seen. The differential diagnosis includes tumor and vascular abnormalities. An ultrasound of the eye was done to evaluate this finding further.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Peripupillary Vascularity
This is the same infant shown in the previous photo. Here the light from the ophthalmoscope is shining obliquely across the front of the eye. Without any special equipment, a red tinge (described by the ophthalmologist as a lacy network of peripupillary vessels) can be appreciated at the rim of the pupil. When the other eye was evaluated in this way, no red color was seen.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Gonococcal Conjunctivitis
When gonococcal conjunctivitis occurs, it typically presents in the first few days of life with copius, purulent discharge in the eyes. In this infant, the marked edema of the eyelids was the first symptom noted, but with just slight pressure on the lids, purulent material oozed out (seen here). Unlike the typical "pink eye" conjuncitivitis that occurs in older children, gonococcal conjunctivitis is an ophthalmologic emergency. Because the bacteria can erode through an intact cornea, treatment is very aggressive and includes systemic intravenous antibiotics, frequent eye washes, and monitoring in a neonatal intensive care unit. Fortunately, this diagnosis is very uncommon in places where prophylactic antibiotic eye ointment is used at birth.
In this infant, the marked edema of the eyelids was the first symptom noted, but with just slight pressure on the lids, purulent material oozed out (seen here). Unlike the typical "pink eye" conjuncitivitis that occurs in older children, gonococcal conjunctivitis is an ophthalmologic emergency. Because the bacteria can erode through an intact cornea, treatment is very aggressive and includes systemic intravenous antibiotics, frequent eye washes, and monitoring in a neonatal intensive care unit. Fortunately, this diagnosis is very uncommon in places where prophylactic antibiotic eye ointment is used at birth.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Congenital Glaucoma
This infant presented with hazy bilateral corneal opacities on the initial newborn exam. Congenital glaucoma was the underlying cause.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Peter's Anomaly
This infant has haziness of the central cornea visible without special equipment. On evaluation with an ophthalmoscope, retinal reflexes could not be seen due to this opacity. Although the opacity is central and could be mistaken for opacity of the lens, a view from a more oblique angle showed that the cloudiness extended over parts of the iris as well.
Although the opacity is central and could be mistaken for opacity of the lens, a view from a more oblique angle showed that the cloudiness extended over parts of the iris as well.
photo by Randall Young, MD
Congenital Cataract
In contrast to the previous photo, the opacities here occur behind the pupil, as the pupil is easily and clearly seen along its entire circumference. Again, the opacity can be appreciated without any special equipment (a good reminder to assess the eyes visually even if an ophthalmoscope is not readily available). A retinal light reflex could not be obtained. Congenital cataracts require early intervention to preserve sight, so immediate referral to a pediatric ophthalmologist is indicated. It is important to remember that cataracts that are less dense may not be visibly cloudy, so any time retinal reflexes cannot be obtained on exam, even if the eye appears grossly normal, referral is required.
photo by Janelle Aby, MD
Neonatal Physical Findings Atlas
Decoding your newborn’s appearance, from a large head to puffy eyes
November 7, 2019 8:05:11 pm
By Dr Vanshika Gupta Adukia
Dimpled cheeks, rosy lips, buttoned nose and all things perfect is what one imagines their newborn bundle of joy to ‘look’ like. Contrary to this, in the real world freshly delivered babies look far “different” than what we had pictured.
Contrary to this, in the real world freshly delivered babies look far “different” than what we had pictured.
The little baby has spent a long time cramped in what would be the tiniest of spaces that he/she would ever live in (water filled uterus), and then probably spent a tedious couple of hours trying to push through the narrowest space (birth canal) that it would ever have to wriggle and squeeze its way through.
Subscriber Only Stories
View All
Get New Year offer with promo code ED10
This and a lot more truly attribute to your newborn’s temporary but immediate post-birth appearance.
Disproportionately big and long, pointed head
Newborns arrive with their heads looking quite large for the size of their bodies. Additionally their oversized head looks long and pointy. All of these are characteristics, babies owe to the long hours spent in the birth canal pushing their way out into the world with the help of their heads (vaginal delivery). Eventually, the shape of the head will even out and the head proportion too will soon match that of the body.
Diamond-shaped space at the top of baby’s head
The ‘fontanelle’ or soft spot, as it is commonly known, is a space present both anteriorly and posteriorly in the baby’s head. These regions don’t have the bone fused together at birth so as to aid with gently pushing the baby’s way through the birth canal. The spaces are covered and protected by a tough membrane. Normally, the soft spot closes between 12-18 months as the rapid brain growth development is also occurring.
Choose eco-friendly products for your baby
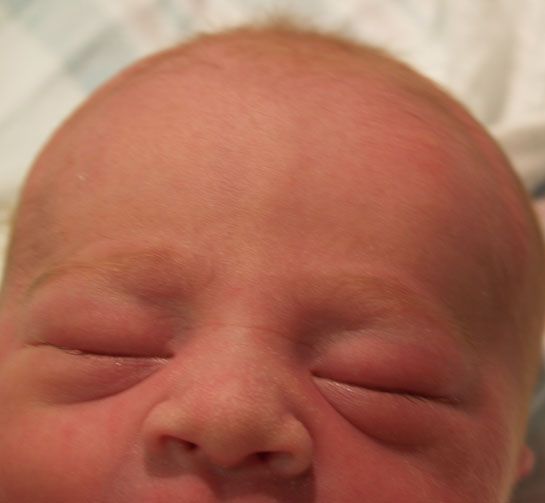
Puffy swollen eyes
Right after birth, the baby’s eyes appear swollen and puffy. This too has to do with the endless hours spent in the amniotic fluid filled uterus and then later having to push their way through a ‘rocky’ path of the vaginal canal.
Advertisement
Gradually in a couple of days this will subside and in no way would it have any effect on your little one’s vision.
Skin
Newborn skin is thin, may appear to have a pale pinkish casting from the blood vessels running right underneath or in the initial couple of seconds right after birth appear to be bluish due to the temporary decrease in oxygen at birth.
Their skin may also have a cheesy white coating known as the vernix. This vernix is believed to protect and moisturise the baby’s skin from the amniotic fluid in the womb. Babies born early may have more of the cheesy looking substance on their skin, while those born a little late may appear to have their skin peeling off and wrinkled as the vernix has already begun to peel off. Some babies may be born with bluish or slate coloured pigmentation known as mongolion spots. These are harmless even though they may look like bruises and eventually fade away with time.
Advertisement
White, pimple-like bumps across your baby’s nose and cheeks
Known as milia, these are harmless sebaceous cysts that will subside gradually and must not be squeezed or picked on.
Genitals
Newborn genitals, irrespective of their gender, may appear to be swollen and that is normal. Pregnancy hormones play a role in this and due to their effect this maybe a temporary situation at birth. There may even be a milky discharge from the nipples and, in girls, a vaginal discharge (sometimes bloody).
These temporary, yet unique newborn characteristics are something that every parent must witness after birth. Each of these characteristics is absolutely normal and must not be looked upon as a baby’s “cuteness” dampener as the effects will subside with time. Remember, your new little one is beyond precious.
(The writer is pregnancy, childbirth, lactation specialist and pelvic floor physiotherapist.)
© IE Online Media Services Pvt Ltd
First published on: 07-11-2019 at 08:05:11 pm
Next Story
Satwik-Chirag continue juggernaut, keep Indian flag flying in China Open
- Tags:
- newborn babies
- parenting tips
what are the reasons and what to do if the upper or lower eyelid of the baby is swollen?
The postpartum period is stressful for a baby, his body can react differently, which will surely frighten parents. One such factor is swollen eyelids.
One such factor is swollen eyelids.
Is this normal, is there any reason to be wary? Why a baby (month-old or older) has swollen eyelids from above or there is swelling under the eyes, how to help a newborn, what are the first actions of parents in this situation - we will talk about everything in detail in this article. nine0005
Do not self-medicate! Be sure to consult a qualified physician. The information is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice.
- The lower and upper eyelids are swollen - why this occurs
- What to do to parents of the baby
- Assistance to the baby
- Recommendations and warning
The lower and upper eyelids are swollen - why this occurs
Eye of the eyes in the first 5-7 days are normal. If they persist longer, then this should alert. Consider the causes that can lead to swollen eyelids in a baby. nine0003
Possible stye, an infection caused by staphylococcus aureus. Inflammation affects the hair follicles, inflammation appears. Initially, it will be point, but in the absence of therapy measures, it can spread to the entire eyelid.
Inflammation affects the hair follicles, inflammation appears. Initially, it will be point, but in the absence of therapy measures, it can spread to the entire eyelid.
The appearance of barley is possible due to the following factors or conditions :
When a child has barley, the eyelid increases, begins to turn red, and the temperature may rise. Affected follicles fill with pus, swell, and then burst. After that, the baby usually feels better, swelling and temperature go away. nine0003
Do not try to squeeze the stye out on your child. You can damage his eye, bring an infection. With professional treatment, the disease usually resolves quickly, so parents need to call a doctor as soon as possible. With barley, the essence of therapy is to instill Albucid into the affected eye and treat the affected eyelid with dry heat.
Another common cause of swollen eyes in a newborn is conjunctivitis. This is an infectious disease, manifested by profuse lacrimation, redness, high fever. Conjunctivitis is treated simply, but if the process is started, then serious complications are possible, up to blindness. nine0003
Conjunctivitis is treated simply, but if the process is started, then serious complications are possible, up to blindness. nine0003
It is usually recommended to regularly wash the child's eyes with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and furacilin, instillation of sulfonamides, and the use of antibiotic ointments.
If the films are not removed from the eyes, we can talk about diphtheria conjunctivitis, a serious disease. The child needs urgent hospitalization. Conjunctivitis with bloody discharge is a consequence of infection in the birth canal with gonococcus. The disease is usually treated easily if the right measures are taken in a timely manner.
The next phenomenon is dacryocystitis, in which the thin film of the nasolacrimal canal does not break. There is an accumulation of tears, an environment favorable for the development of bacteria is created, inflammation occurs.
In addition to cleansing the eyes from pus with potassium permanganate, it is recommended to use a clean finger to make gentle movements from the inner to the outer edge of the eyelid (as if you are trying to wipe away tears). Such a massage contributes to the rupture of the film, the disappearance of pus. The swelling goes away soon. Read more about massage for dacryocystitis here. nine0003
Such a massage contributes to the rupture of the film, the disappearance of pus. The swelling goes away soon. Read more about massage for dacryocystitis here. nine0003
Puffy eyes in a baby may be due to allergies. There can be a lot of factors that provoke it: food, medicines, animal hair, dust.
More often than not, babies "outgrow" allergies - after some time it disappears on its own.
But it's important to take steps to help your child feel better, otherwise an allergic reaction can turn into a more serious problem. You need to see a dermatologist. He usually prescribes antihistamines, a special hypoallergenic diet for a nursing mother. nine0003
The following causes of swelling of the eyelids in a newborn are possible :
- Furunculosis. Usually accompanied by elevated body temperature. Needs treatment in stationary conditions, sometimes surgery is required.
- Respiratory diseases. Swelling of the eyelids is possible with a cold.
 Be sure to call your child's pediatrician.
Be sure to call your child's pediatrician. - Insect bite. A harmless cause, but in the fragile body of the baby, it can cause allergies. More often, doctors recommend the use of antihistamines, the use of ointments that relieve swelling. nine0012
- Ptosis is the defective development of the muscle responsible for lifting the upper eyelid. The condition causes discomfort to the baby, requires the intervention of a doctor.
- Edema of the eyelids may be the result of acute or chronic cardiac decompensation, renal, hepatic, venous, lymphatic insufficiency, hormonal disorders.
These conditions threaten the child's life and require urgent hospitalization.
What to do for parents of a baby
When passing through the birth canal, the baby encounters compression, pressure, discomfort, therefore, at first, swelling of the eyelids and narrowing of the eye lumen to one degree or another are possible. nine0003
It is normal if it goes away in 5-7 days. But if eyelid edema lasts longer, and especially if lacrimation, fever, pus, redness are additionally noted, then it is important to contact a pediatrician as soon as possible .
But if eyelid edema lasts longer, and especially if lacrimation, fever, pus, redness are additionally noted, then it is important to contact a pediatrician as soon as possible .
The human eye is a very fragile mechanism. It is important that its treatment be timely and professional - otherwise, consequences are possible, up to complete blindness. The doctor will diagnose, prescribe the necessary tests and adequate measures. You cannot self-medicate. nine0003
Help for the baby
The necessary measures will depend on what caused the problem. With barley, eye drops, ointments and physiotherapy are prescribed.
In case of conjunctivitis, instillations, tetracycline ointment are indicated.
If you have an allergy, you need to visit a doctor and undergo the appropriate tests to identify the allergen. Then treatment will be given. Edema can be the result of various conditions: it is better to consult a specialist immediately. nine0003
Advice and warnings
Do not self-medicate. If you are alerted by the swollen eyelids of the baby, then consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If you are alerted by the swollen eyelids of the baby, then consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Do not blindfold . If the child has barley, do not squeeze out the pus yourself, as the infection can spread and provoke meningitis and other complications.
There are many reasons for swollen eyes in a baby. In any case, contacting a professional will help to avoid a number of negative consequences. nine0003
Neonatal eyes (oedema, strabismus, blue) | Baby health
So. You have a child, you take care of him, take care of him, and then, purely by chance, you noticed that he has blue eyes. Why's that? After all, neither you nor your husband have blue eyes. But do not be so surprised, because almost all children have sea-colored eyes. The child's own eye color will appear within 3-6 months, but sometimes this period can be delayed up to 2 years. Then the young mother will be able to accurately determine “whose” eyes they are. nine0003
According to ophthalmologists, children lack some pigment in the iris, which appears after a while. And scientists believe that the blue color of the eyes in children is an illusion, and it all depends on the lighting, in one light the eyes may appear blue, in another - gray, etc. Who to believe in this case is not known.
And scientists believe that the blue color of the eyes in children is an illusion, and it all depends on the lighting, in one light the eyes may appear blue, in another - gray, etc. Who to believe in this case is not known.
Yes, and why go into these details, because the color of the eyes does not play any role, blue is blue, gray means gray.
But sometimes it is impossible to determine the color of a child, because it is impossible to see the eyes, the baby does not open them. This condition is called eye swelling. Edema is an increased content of water and fat in the tissues. With edema, the size of the eyelids increases, sometimes several times. During edema, the skin usually shines, if an inflammatory process has begun in the eyelid, the skin becomes red. Often, swelling of the eyelids appears due to other diseases - conjunctivitis, a cold. Sometimes swelling appears due to lack of sleep of the child, in such cases, everything must be done to make him fall asleep. If the factor in the origin of eye swelling is an infection, then use eye drops that the doctor will prescribe during a thorough examination of the baby. The use of eye drops will save the newborn from swelling for 4-7 days. But sometimes swelling of the eyelids can be congenital and will not go away when using drops. But over time, in most cases, eye swelling goes away on its own, without anyone's intervention. nine0003
The use of eye drops will save the newborn from swelling for 4-7 days. But sometimes swelling of the eyelids can be congenital and will not go away when using drops. But over time, in most cases, eye swelling goes away on its own, without anyone's intervention. nine0003
What else can surprise the eyes of a newborn?
Also, strabismus in children is not uncommon, and this is one of the main causes of concern for father and mother. Strabismus is a disease in which the eyes look in different directions, that is, the eyeballs are not parallel. Usually in children under the age of one year, strabismus is not a disease, but only a cosmetic problem that will go away with time. This strabismus is caused by a weakening of the eye muscle.
True strabismus is not a cosmetic problem, but a real disease. The main cause of strabismus is a disorder of the muscular system of the eye, which is caused by disturbances in the nervous regulation. This strabismus will not go away without the use of medicine or surgery. If strabismus is not associated with nervous disorders, then a pediatric ophthalmologist will treat your child. He will determine the usefulness of binocular vision and try to solve the problem of strabismus with glasses to improve visual acuity for each eye. If this method does not help, there is another effective method. The essence of this method is to bandage the healthy eye in order to improve the functionality of the muscles and visual acuity of the diseased eye. nine0003
If strabismus is not associated with nervous disorders, then a pediatric ophthalmologist will treat your child. He will determine the usefulness of binocular vision and try to solve the problem of strabismus with glasses to improve visual acuity for each eye. If this method does not help, there is another effective method. The essence of this method is to bandage the healthy eye in order to improve the functionality of the muscles and visual acuity of the diseased eye. nine0003
It takes several years to cure strabismus, because it requires a lot of effort on the part of the child, parents, and the ophthalmologist. Wearing a bandage or glasses is often replaced by surgery, which is necessary to correct the work of the muscle. After the operation, the child is prescribed the same exercises as before.
In order to avoid various diseases and defects associated with the eyes of newborns, examination and diagnosis is necessary. Only in such cases can you avoid eye diseases in a child, or cure the disease at the earliest stages.