How to give vitamin k injection
Vitamin K Injection: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing
Warnings:
The injectable form of vitamin K can rarely cause severe (sometimes fatal) allergic reactions when given by injection into a muscle or vein. Vitamin K should be injected into a muscle or vein only when it cannot be given by injection under the skin or taken by mouth, or when your doctor has judged that the benefit is greater than the risk. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction such as rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, or trouble breathing.
Warnings:
The injectable form of vitamin K can rarely cause severe (sometimes fatal) allergic reactions when given by injection into a muscle or vein. Vitamin K should be injected into a muscle or vein only when it cannot be given by injection under the skin or taken by mouth, or when your doctor has judged that the benefit is greater than the risk. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction such as rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, or trouble breathing.
... Show More
Uses
Vitamin K is used to treat and prevent low levels of certain substances (blood clotting factors) that your body naturally produces. These substances help your blood to thicken and stop bleeding normally (such as after an accidental cut or injury). Low levels of blood clotting factors increase the risk for unusual bleeding. Low levels may be caused by certain medications (such as warfarin) or medical conditions (such as obstructive jaundice). Vitamin K helps to treat and prevent unusual bleeding by increasing the body's production of blood clotting factors.
How to use Vitamin K1 Ampul
This medication is given by injection under the skin or into a muscle or vein as directed by your doctor. If this medication is given into a vein, it should be injected very slowly (no more than 1 milligram per minute) to reduce the risk of serious side effects.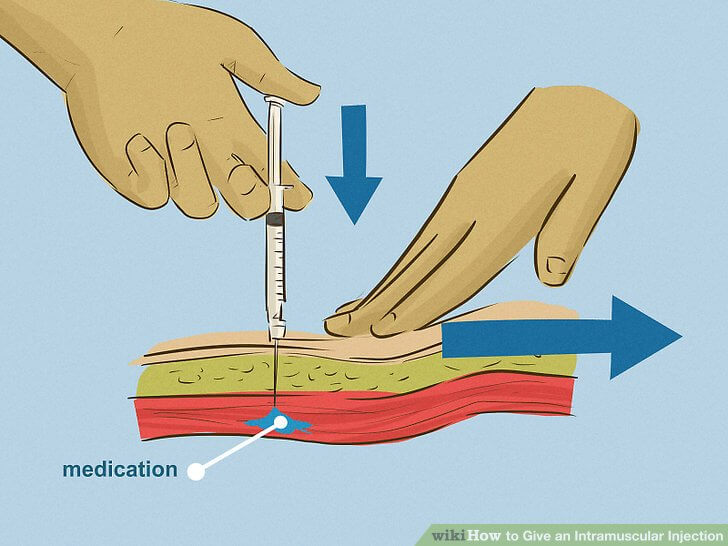 (See also Warning section.)
(See also Warning section.)
Dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment.
If you are giving this medication to yourself at home, learn all preparation and usage instructions from your health care professional. The solution is normally clear and yellow in color. Before using, check this product visually for particles or discoloration. If either is present, do not use the liquid. Learn how to store and discard medical supplies safely.
If you are using a certain "blood thinner" drug (warfarin), vitamin K can decrease the effects of warfarin for up to 2 weeks. Be sure to take your vitamin K and warfarin exactly as directed by your doctor or pharmacist.
If you develop easy bruising or bleeding, seek immediate medical attention. You may need another dose of vitamin K.
Side Effects
Pain, swelling, or soreness at the injection site may occur. Temporary flushing, taste changes, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, sweating, shortness of breath, or bluish lips/skin/nails may also rarely occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
In the US -
In the US - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
Precautions
Before using vitamin K, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: blood disorders, kidney disease, liver disease.
This product may contain aluminum, which can rarely build up to dangerous levels in the body. The risk may be increased if this product is used for an extended time, especially in people with kidney disease. Tell your doctor right away if you notice any symptoms of too much aluminum in the body such as muscle weakness, bone pain, or mental changes.
During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
Vitamin K passes into breast milk, but is unlikely to harm a nursing infant. Consult your doctor before breast-feeding.
Consult your doctor before breast-feeding.
Interactions
Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.
Some products that may interact with this drug include: "blood thinners" (such as warfarin), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, naproxen).
Aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding. However, if your doctor has directed you to take low-dose aspirin for heart attack or stroke prevention (usually 81-162 milligrams a day), you should continue taking it unless your doctor instructs you otherwise. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more details.
Does Vitamin K1 Ampul interact with other drugs you are taking?
Enter your medication into the WebMD interaction checker
Overdose
If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911.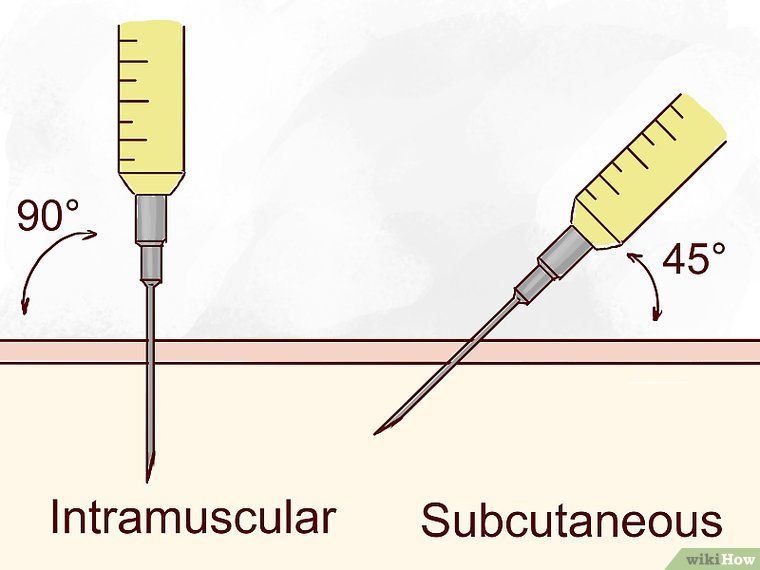 Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
Laboratory and/or medical tests (such as prothrombin time, INR) should be performed to monitor your progress or check for side effects. Consult your doctor for more details.
Vitamin K is commonly found in leafy green vegetables such as spinach, collards, and broccoli. Follow any dietary guidelines recommended by your health care professional.
It is important to get each dose of this medication as scheduled. If you miss a dose, ask your doctor or pharmacist right away for a new dosing schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up.
Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets. Discard any unused portion from single use containers.
Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Images
Next
Related Links
Drug Survey
Are you currently using Vitamin K1 Ampul?
This survey is being conducted by the WebMD marketing sciences department.
Free RX Coupon
Save up to 80% on your prescriptions.
Available coupons
Save up to 80% on your prescription with WebMDRx
Selected from data included with permission and copyrighted by First Databank, Inc. This copyrighted material has been downloaded from a licensed data provider and is not for distribution, except as may be authorized by the applicable terms of use.
CONDITIONS OF USE: The information in this database is intended to supplement, not substitute for, the expertise and judgment of healthcare professionals. The information is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions or adverse effects, nor should it be construed to indicate that use of a particular drug is safe, appropriate or effective for you or anyone else. A healthcare professional should be consulted before taking any drug, changing any diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment.
A healthcare professional should be consulted before taking any drug, changing any diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment.
Protect Your Baby from Bleeds – Talk to Your Healthcare Provider about Vitamin K
Download and print this fact sheet pdf icon[PDF – 473 KB, 2 Pages]
Protect Your Baby from Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding
Before having a baby, most parents don’t give much thought to the vitamin K injection (shot) for their newborn. It’s just not something that is talked about during prenatal checkups, even though babies have been routinely given this important shot at birth since the practice was first recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics in 1961.
Vitamin K is needed for blood to clot normally. Babies are born with very small amounts of vitamin K in their bodies which can lead to serious bleeding problems. Research shows that a single vitamin K shot at birth protects your baby from developing dangerous bleeding which can lead to brain damage and even death.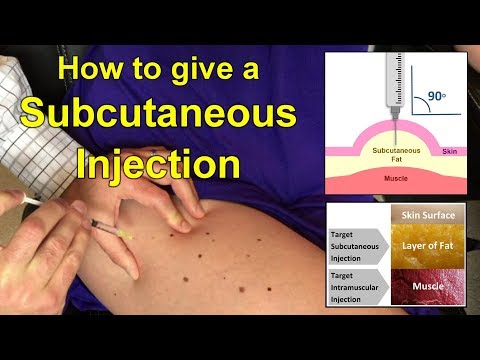 Ask your healthcare provider about the benefits of Vitamin K before your delivery. Protect your newborn by making sure he or she gets the shot after birth.
Ask your healthcare provider about the benefits of Vitamin K before your delivery. Protect your newborn by making sure he or she gets the shot after birth.
What is vitamin K deficiency bleeding (VKDB)?
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding or VKDB, is a condition that occurs when the baby does not have enough Vitamin K.
Without enough vitamin K, your baby has a chance of bleeding into his or her intestines, and brain, which can lead to brain damage and even death. Infants who do not receive the vitamin K shot at birth can develop VKDB up to 6 months of age.
How can I prevent VKDB?
The good news is that VKDB is easily prevented. The easiest and most reliable way to give babies vitamin K is by a shot into a muscle in the leg. One shot given after birth will protect your baby from VKDB.
What is vitamin K?
Vitamin K is a vital nutrient that our body needs for blood to clot and stop bleeding. We get vitamin K from the food we eat. Some vitamin K is also made by the good bacteria that live in our intestines.
Babies have very little vitamin K in their bodies at birth because:
Why does my baby need a vitamin K shot?
- Vitamin K from the mom is not easily shared with the developing baby during the pregnancy
- The intestine of the newborn baby has very little bacteria so they do not make enough vitamin K on their own.
Without enough vitamin K, blood cannot clot well. As a result, bleeding can occur anywhere in the body. This means not only that bleeding from a cut or bruise may continue for a long time, but that uncontrolled bleeding into the brain and other organs may occur.
About half of all babies who develop VKDB bleed into their brains.
Is Vitamin K safe?
A study from the early 1990’s found a possible link between getting vitamin K and developing childhood cancer. Pediatricians became very concerned about this and have done many studies since then, in many different ways, trying to see if this link was true. None of the studies found this link again, even though doctors and scientists looked very hard for it.
Does my baby get vitamin K from breast milk?
Yes, but not enough to prevent VKDB. There is only a little vitamin K in breast milk. Breastfed babies are low in vitamin K for several weeks until they start eating regular foods, usually at 4-6 months, and until the normal intestinal bacteria start making vitamin K.
Should all babies get a vitamin K shot at birth?
Yes. Babies do not have enough vitamin K at birth and are, therefore, at risk for having serious bleeding. Thus, it is very important that all babies get a vitamin K shot to prevent VKDB.
Where can I get more information?
For more information, please visit our website at:
http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/vitamink/index.html
Why are newborns given vitamin K injections?
At Mother and Child clinics, we recommend vitamin K injections for all newborns to prevent hemorrhagic disease.
Hemorrhagic disease (HRD), or vitamin K-deficient hemorrhagic syndrome, is a disease manifested by increased bleeding in newborns and children during the first months of life, due to a deficiency of blood coagulation factors, the activity of which depends directly on vitamin K.
Vitamin K of plant origin, which is called vitamin K 1 or phylloquinone, enters the body with food - green vegetables, vegetable oils, dairy products. Another form of vitamin K, vitamin K2, or menaquinone, is of bacterial origin. Vitamin K 2 is mainly synthesized by the intestinal microflora, which is extremely poor in newborns.
In healthy newborns, the level of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors in blood plasma is 30-60% of that in adults. Their concentration increases gradually and reaches the level of adults by the sixth week of life. In almost all healthy full-term infants in the first five days of life, there is a decrease in the level of procoagulants, physiological anticoagulants and plasminogen.
For the newborn, the only source of vitamin K is mother's milk, formula or medicine. Moreover, the amount of vitamin K received by a child depends on the type of feeding. The level of vitamin K 1 in breast milk ranges from 1 to 10 µg/l, on average 2-2.5 µg/l, which is significantly lower than in artificial milk formulas (about 50 µg/l in mixtures for full-term babies; 60 -100 mcg / l - in mixtures for premature babies). Thus, newborns, due to their physiological characteristics of the coagulation system and vitamin K metabolism, are predisposed to the development of vitamin K-deficient hemorrhagic syndrome.
Thus, newborns, due to their physiological characteristics of the coagulation system and vitamin K metabolism, are predisposed to the development of vitamin K-deficient hemorrhagic syndrome.
PLEASE NOTE! Poor blood clotting is a condition dangerous for the body, in which bleeding or hemorrhage is noted in various organs. This pathology develops in 0.25-0.5% of newborns.
RISK FACTORS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF RHD
• Exclusive breastfeeding
• Lack of prophylactic administration of vitamin K immediately after birth
• Chronic fetal hypoxia and asphyxia at birth
• Giving birth
• Intrauterine development delay
• Giving birth by cesarean section
• Nedness
• The use of a wide range of
• Long -term parenteral nutrition in the conditions of inadequate supply of
• Diseases and condition of the child that contribute impaired synthesis and absorption of vitamin K
• malabsorption syndrome (cystic fibrosis, diarrhea with fat malabsorption lasting more than one week)
• short bowel syndrome;
• cholestasis;
• pre-eclampsia
• maternal diseases (liver and intestinal diseases).
Vitamin B12 ampoules: instructions for use
- home
- »
- Blog
- »
- Vitamin B12 in ampoules: instructions for use
Contents:
- The role of vitamin B12 in the body
- Indications for use of cyanocobalamin
- Treatment regimen with cyanocobalamin
- How to inject
- Storage conditions of vitamin B12 in ampoules
- Dosage of vitamin B12 in ampoules
- Contraindications and side effects
Lack of vitamin B12 leads to a number of diseases. This is an important substance for the functioning of all systems, which reduces susceptibility to infections, increases endurance, physical and mental activity.
This is an important substance for the functioning of all systems, which reduces susceptibility to infections, increases endurance, physical and mental activity.
The role of vitamin B12 in the body
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) was first discovered in 1948. Scientists isolated a new substance from raw liver and prescribed it to treat pernicious anemia.
Over the past 70 years, cyanocobalamin has been well studied by scientists and physicians, as a result of which it was possible to establish its effect on the body:
- blocking the stress hormone;
- improvement of blood clotting;
- synthesis of amino acids;
- decrease in the amount of cholesterol in the blood;
- detoxification of the body with alcoholism;
- improvement of liver function.
Cyanocobalamin helps athletes withstand heavy loads, accelerates weight loss and prevents the development of cardiovascular diseases.
It plays a special role in the functioning of the central nervous system. Vitamin supplements the main therapy for cerebral palsy in children, Down's disease, intercostal neuralgia, etc.
Return to the content of the article
Indications for use of cyanocobalamin
Vitamin B12 in ampoules is used as an adjunct therapy. It enhances the effect of drugs, helps the body to overcome many diseases. In rare cases, it is prescribed as the only remedy for the prevention of anemia.
Indication for vitamin B12:
- chronic migraine;
- Down syndrome;
- cerebral palsy;
- neuralgia;
- radiation sickness;
- alcohol poisoning;
- dystrophy;
- anemia;
- radiculitis;
- diseases of the pancreas and liver;
- gastritis;
- photodermatosis;
- sclerosis.
Reception of cyanocobalamin is indicated for beriberi, frequent respiratory diseases. The lack of a substance in the body leads to a deterioration in the condition of hair, nails and teeth. For this reason, the drug is taken in ampoules not only for medical purposes, but also for cosmetic purposes.
Return to the content of the article
Cyanocobalamin regimen
When Vitamin B12 is prescribed, the Instructions for Use will help calculate the correct dosage. The treatment regimen looks like this:
- For the prevention of anemia and vitamin deficiency - from 200 to 500 mcg per day. The course of treatment is from 7 to 15 days.
- For the treatment of diseases of the central nervous system - 200 mcg per day daily for the first 3 days. Then 300 mcg daily for 4 days.
- If cyanocobalamin is used in complex therapy, then the dosage is from 200 to 500 mcg per day.
Vitamin B12 should only be taken at the dosage recommended by your doctor. It is not recommended to use the drug on its own, since it is rather difficult to determine an individual treatment regimen.
It is not recommended to use the drug on its own, since it is rather difficult to determine an individual treatment regimen.
Return to the content of the article
How to inject
Vitamin B12 shots can be given in different ways:
- subcutaneously;
- intramuscularly;
- intravenously;
- into the spinal cord.
The instructions say that cyanocobalamin cannot be used simultaneously with drugs that increase blood clotting, as well as with vitamins B1 and B6. If there is an allergy to B1, then B12 can exacerbate it.
You can administer the drug intramuscularly and intravenously on your own. For injection into the spinal cord, you should consult an experienced doctor.
Return to the content of the article
Storage conditions for vitamin B12 in ampoules
Vitamin B12 in ampoules should be stored in a dry, dark place, at an air temperature of no more than 25 degrees. Some complex preparations require storage in the refrigerator. This point must be specified in the instructions.
Some complex preparations require storage in the refrigerator. This point must be specified in the instructions.
Do not use the substance after the expiry date stated on the package.
Return to the content of article
Vitamin B12 dosage in ampoules
The dosage of vitamin B12 is determined individually and depends on the age of the patient. The maximum daily dose is:
- children - 400 mcg;
- adults - 1000 mcg.
The dosage increases gradually, you need to start with a small portion of the drug. This is necessary to exclude allergic reactions.
Return to the content of the article
Contraindications and side effects
Subject to the instructions for use and the doctor's recommendations, the drug has no side effects. In exceptional cases, unpleasant symptoms may occur:
- nervous excitement;
- tachycardia;
- headache;
- pain in the region of the heart;
- increased blood pressure;
- dizziness.
If there is an individual intolerance to the drug, then an allergic reaction occurs in the form of skin itching, rash, runny nose. In the event of side effects, the injection is stopped, the treatment method is reviewed together with the doctor.
Before starting injections, you should study the list of contraindications:
- angina;
- erythrocytosis;
- thrombosis;
- varicose veins;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- haemorrhoids;
- oncological diseases.
Another contraindication is individual intolerance to cyanocobalamin.
It is important to follow the instructions for use so that there is no overdose of vitamin B12 . In this case, the following conditions are observed:
- heart failure;
- arrhythmia;
- pulmonary edema;
- rash;
- anaphylactic shock.
Cyanocobalamin makes an invaluable contribution to the functioning of the body.