Group b strep pcr
Group B strep disease - Symptoms and causes
Overview
Group B strep (streptococcus) is a common bacterium often carried in the intestines or lower genital tract. The bacterium is usually harmless in healthy adults. In newborns, however, it can cause a serious illness known as group B strep disease.
Group B strep can also cause dangerous infections in adults with certain chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or liver disease. Older adults are at increased risk of illness due to group B strep, too.
If you're a healthy adult, there's nothing you need to do about group B strep. If you're pregnant, get a group B strep screening test during your third trimester. If you have group B strep, antibiotic treatment during labor can protect your baby.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Symptoms
Infants
Most babies born to women carrying group B strep are healthy. But the few who are infected by group B strep during labor can become critically ill.
In infants, illness caused by group B strep can be within six hours of birth (early onset) — or weeks or months after birth (late onset).
Signs and symptoms might include:
- Fever
- Low body temperature
- Difficulty feeding
- Sluggishness, limpness or weak muscle tone
- Difficulty breathing
- Irritability
- Jitteriness
- Seizures
- Rash
- Jaundice
Adults
Many adults carry group B strep in their bodies — usually in the bowel, vagina, rectum, bladder or throat — and have no signs or symptoms.
In some cases, however, group B strep can cause a urinary tract infection or other more-serious infections. Signs and symptoms of infections that may be caused by group B strep include the following.
Urinary tract infection
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation or pain when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola colored — a sign of blood in the urine
- Pelvic pain
Blood infection (bacteremia)
- Fever
- Chills
- Confusion or lack of alertness
Pneumonia
- Fever
- Chills
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain when you breathe or cough
Skin or soft-tissue infection
- Swelling, warmth or redness in the area of the infection
- Pain in the area of the infection
- Lesions with pus or drainage
Bone or joint infection
- Fever
- Chills
- Swelling, warmth or redness over the area of the infection
- Pain in the area of the infection
- Stiffness or inability to use a limb or joint
When to see a doctor
If you have signs or symptoms of group B strep infection — particularly if you're pregnant, you have a chronic medical condition or you're older than 65 — contact your doctor right away.
If you notice your infant has signs or symptoms of group B strep disease, contact your baby's doctor immediately.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which
information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with
other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could
include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected
health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health
information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of
privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Causes
Many healthy people carry group B strep bacteria in their bodies. You might carry the bacteria in your body for a short time — it can come and go — or you might always have it. Group B strep bacteria aren't sexually transmitted, and they're not spread through food or water. How the bacteria are spread to anyone other than newborns isn't known.
Group B strep can spread to a baby during a vaginal delivery if the baby is exposed to — or swallows — fluids containing group B strep.
Risk factors
Infants
An infant is at increased risk of developing group B strep disease if:
- The mother carries group B strep in her body
- The baby is born prematurely (earlier than 37 weeks)
- The mother's water breaks 18 hours or more before delivery
- The mother has an infection of the placental tissues and amniotic fluid (chorioamnionitis)
- The mother has a urinary tract infection during the pregnancy
- The mother's temperature is greater than 100.
 4 F (38 C) during labor
4 F (38 C) during labor - The mother previously delivered an infant with group B strep disease
Adults
Adults age 65 and older are at increased risk of group B strep. You're also at increased risk of if you have a condition that impairs your immune system or other serious diseases, including the following:
- Diabetes
- HIV infection
- Liver disease
- Heart disease
- Cancer or history of cancer
Complications
Group B strep infection can lead to life-threatening disease in infants, including:
- Pneumonia
- Inflammation of the membranes and fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meningitis)
- Infection in the bloodstream (bacteremia)
If you're pregnant, group B strep can cause the following:
- Urinary tract infection
- Infection of the placenta and amniotic fluid (chorioamnionitis)
- Infection of the membrane lining the uterus (endometritis)
- Bacteremia
If you're an older adult or you have a chronic health condition, group B strep bacteria can lead to any of the following conditions:
- Skin infection
- Bacteremia
- Urinary tract infection
- Pneumonia
- Bone and joint infections
- Infection of the heart valves (endocarditis)
- Meningitis
Prevention
If you're pregnant, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a group B strep screening during weeks 36 to 37 of pregnancy. Your doctor will take swab samples from your vagina and rectum and send them to a lab for testing.
Your doctor will take swab samples from your vagina and rectum and send them to a lab for testing.
A positive test indicates that you carry group B strep. It doesn't mean that you're ill or that your baby will be affected, but that you're at increased risk of passing the bacteria to your baby.
To prevent group B bacteria from spreading to your baby during labor or delivery, your doctor can give you an IV antibiotic — usually penicillin or a related drug — when labor begins.
If you're allergic to penicillin or related drugs, you might receive clindamycin or vancomycin as an alternative. Because the effectiveness of these alternatives is not well understood, your baby will be monitored for up to 48 hours.
Taking oral antibiotics ahead of time won't help because the bacteria can return before labor begins.
Antibiotic treatment during labor is also recommended if you:
- Have a urinary tract infection
- Delivered a previous baby with group B strep disease
- Develop a fever during labor
- Haven't delivered your baby within 18 hours of your water breaking
- Go into labor before 37 weeks and haven't been tested for group B strep
Vaccine in development
Although it's not available yet, researchers are working on a group B strep vaccine that could help prevent group B strep infections in the future.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Products & Services
Group B Strep and Pregnancy (for Parents)
What Is Group B Strep?
Group B Streptococcus (group B strep, GBS) is a type of
bacteriaoften found in the urinary tract, digestive system, and reproductive tracts. The bacteria come and go from our bodies, so most people who have it don't know that they do. GBS usually doesn't cause health problems.
What Problems Can Group B Strep Cause?
Health problems from GBS are not common. But it can cause illness in some people, such as the elderly and those with some medical conditions. GBS can cause infections in such areas of the body as the blood, lungs, skin, or bones.
About 1 out of every 4 women have GBS. In pregnant women, GBS can cause infection of the urinary tract, placenta, womb, and amniotic fluid.
Even if they haven't had any symptoms of infection, pregnant women can pass the infection to their babies during labor and delivery.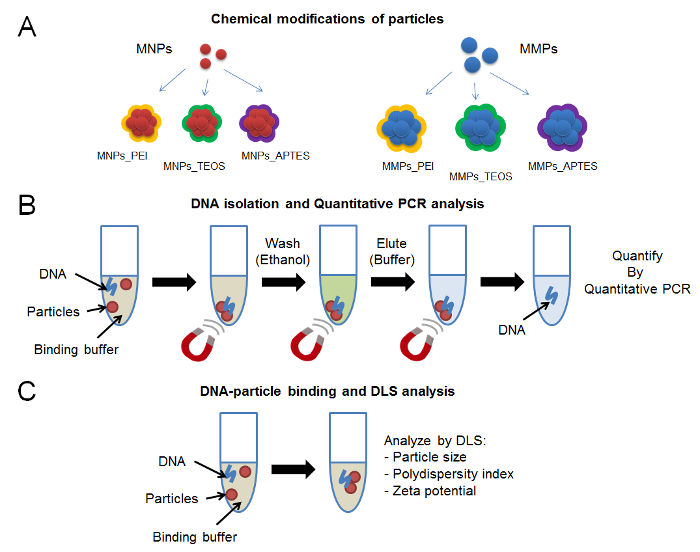
How Does Group B Strep Affect Babies?
When women with GBS are treated with antibiotics during labor, most of their babies do not have any problems. But some babies can become very sick from GBS. Premature babies are more likely to be infected with GBS than full-term babies because their bodies and immune systems are less developed.
The two types of GBS disease in babies are:
- Early-onset infections, which happen during the first week of life. Babies often have symptoms within 24 hours of birth.
- Late-onset infections, which develop weeks to months after birth. This type of GBS disease is not well understood.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of GBS Disease?
Newborns and infants with GBS disease might show these signs:
- a fever
- feeding problems
- breathing problems
- irritability or fussiness
- inactivity or limpness
- trouble keeping a healthy body temperature
Babies with GBS disease can develop serious problems, such as:
- pneumonia
- sepsis
- meningitis (infection of the fluid and lining around the brain).
 Meningitis is more common with late-onset GBS disease and, in some cases, can lead to hearing loss, vision loss, learning disabilities, seizures, and even death.
Meningitis is more common with late-onset GBS disease and, in some cases, can lead to hearing loss, vision loss, learning disabilities, seizures, and even death.
How Is Group B Strep Diagnosed?
Pregnant women are routinely tested for GBS late in the pregnancy, usually between weeks 35 and 37. The test is simple, inexpensive, and painless. Called a culture, it involves using a large cotton swab to collect samples from the vagina and rectum. These samples are tested in a lab to check for GBS. The results are usually available in 1 to 3 days.
If a test finds GBS, the woman is said to be "GBS-positive." This means only that she has the bacteria in her body — not that she or her baby will become sick from it.
GBS infection in babies is diagnosed by testing a sample of blood or spinal fluid. But not all babies born to GBS-positive mothers need testing. Most healthy babies are simply watched to see if they have signs of infection.
How Is Group B Strep Treated?
Doctors will test a pregnant woman to see if she has GBS. If she does, she will get intravenous (IV) antibiotics during labor to kill the bacteria. Doctors usually use penicillin, but can give other medicines if a woman is allergic to it.
If she does, she will get intravenous (IV) antibiotics during labor to kill the bacteria. Doctors usually use penicillin, but can give other medicines if a woman is allergic to it.
It's best for a woman to get antibiotics for at least 4 hours before delivery. This simple step greatly helps to prevent the spread of GBS to the baby.
Doctors also might give antibiotics during labor to a pregnant woman if she:
- goes into labor prematurely, before being tested for GBS
- hasn't been tested for GBS and her water breaks 18 or more hours before delivery
- hasn't been tested for GBS and has a fever during labor
- had a GBS bladder infection during the pregnancy
- had a baby before with GBS disease
Giving antibiotics during labor helps to prevent early-onset GBS disease only. The cause of late-onset disease isn't known, so no method has yet been found to prevent it. Researchers are working to develop a vaccine to prevent GBS infection.
Babies who get GBS disease are treated with antibiotics. These are started as soon as possible to help prevent problems. These babies also may need other treatments, like breathing help and IV fluids.
How Can I Help Prevent Group B Strep Infection?
Because GBS comes and goes from the body, a woman should be tested for it during each pregnancy. Women who are GBS-positive and get antibiotics at the right time during labor do well, and most don't pass the infection to their babies.
If you are GBS-positive and begin to go into labor, go to the hospital rather than laboring at home. By getting IV antibiotics for at least 4 hours before delivery, you can help protect your baby against early-onset GBS disease.
Reviewed by: Thinh Phu Nguyen, MD
Date reviewed: July 2022
Culture for group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus (Streptococcus group B, S. agalactiae)
Method of determination The study is carried out by the method of sowing on dense nutrient media.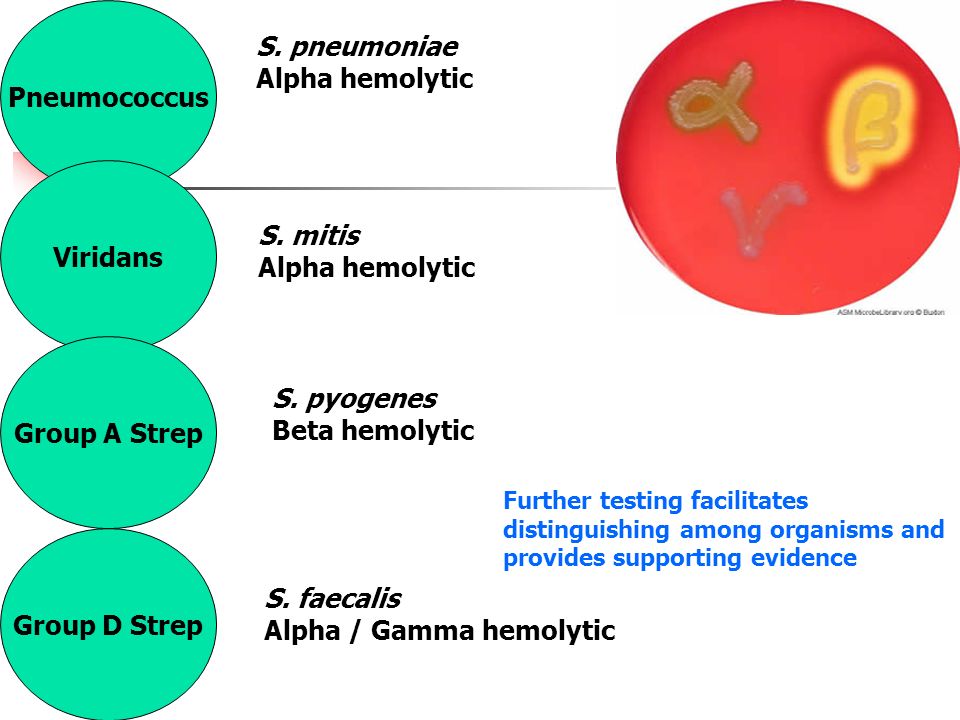 The identification of microorganisms is carried out by mass spectrometry using a Microflex Brucker Daltonik MALDI Biotyper, BRUKER, Germany.
The identification of microorganisms is carried out by mass spectrometry using a Microflex Brucker Daltonik MALDI Biotyper, BRUKER, Germany.
Test material A swab from the entrance to the vagina or anorectal area; vaginal discharge, cervical discharge
Home visit available
Synonyms: Streptococcus group B (S. agalactiae) Culture.
Brief description of the study "Culture for group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus (Streptococcus group B, S. agalactiae)"
Group B streptococcus (GBS, Streptococcus agalactiae) causes severe illness in newborns and is dangerous for certain patients other age groups.
In the vast majority of cases, newborns become infected with GBS during maternal deliveries, with a higher incidence during vaginal delivery. GBS causes early neonatal infections such as sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis, arthritis, and pyelonephritis, with rates ranging from 0.2 to 5 or more per 1,000 live births in different countries. In obstetric practice, group B streptococcus is associated with bacteremia, urinary tract infections, chorioamnionitis, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, preterm labor, postpartum endometritis, etc.
In obstetric practice, group B streptococcus is associated with bacteremia, urinary tract infections, chorioamnionitis, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, preterm labor, postpartum endometritis, etc.
GBS in the human body can colonize the oropharynx, anal area of the rectum, vagina (usually vestibule), urogenital tract, skin.
It has been established that GBS in 5-35% of women can be detected in the vagina and often in the urethra of their sexual partners A significant association of carriage of GBS in the vagina has been shown not only with early septicemia of newborns, but also with spontaneous miscarriages, premature birth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid , urinary infection in pregnant women, the birth of children with low body weight, the development of chorioamnionitis in childbirth, endometritis and sepsis in puerperas. The highest level of colonization in women of reproductive age and pregnant women. In pregnant women, GBS is isolated from the listed areas in 7-30% of cases (more often in young people who have high sexual activity or use intrauterine contraceptives). Of these, 60-75% remain GBS carriers until the end of pregnancy.
Of these, 60-75% remain GBS carriers until the end of pregnancy.
Vaginal-rectal swabs are collected to detect colonization of the vagina of pregnant women with group B streptococcus. In all other cases, the biomaterial is taken only if there are clinical signs of infection.
GBS has a natural sensitivity to beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillins. Determination of sensitivity is necessary in cases where the patient has an individual intolerance to drugs of this group.
Isolateable microorganisms and pathogens:
- Streptococcus agalactiae.
What is the purpose of culture for group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus (Streptococcus group B, S. agalactiae)? in order to identify bacteriocarrier and determine the need for antibiotic prophylaxis during childbirth, to prevent neonatal complications (septicemia, pneumonia and neonatal meningitis).
What can affect the result of the test "Culture for beta-hemolytic streptococcus group B (Streptococcus group B, S.
 agalactiae)"
agalactiae)" Failure to follow the rules for preparing for the study may affect the result of the test.
Strept. Agalactiae (group B streptococci) (determination in the material by PCR method)
Article: 00162
Cost of analysis
in the online store: 7% discount!
Plain
577 rublesLab:
Regular
620 rubles
the price does not include the cost of taking biological material
Add to Basket
Analysis results ready
Regular*: 1-2 working days
Date of passing the analysis:
Date of completion:
*not counting the day of delivery, see rules.
Where and when you can rent
- Buninskaya alley
- Voykovskaya
- Dubrovka
- Maryino
- Novokuznetskaya
- Podolsk
- Weekdays: from 7.
 45 to 21.00
45 to 21.00 - Weekends: from 8.45 to 17.00
Changes in work schedule
Preparation for analysis
General recommendations for testing
For women: Taken after menstruation. Sexual life, douching, vaginal showers, the use of tampons, suppositories and other local preparations are prohibited for 24 hours. It is advisable not to take a bath. Only the external toilet of the genitals is allowed. It is advisable to take smears for infections and crops no earlier than 3 weeks after taking antibiotics (for any reason). This does not apply to the diagnosis of viral infections. For men: Do not urinate for 1.5-2 hours. It is advisable to take smears for infections and crops no earlier than 3 weeks after taking antibiotics (for any reason). This does not apply to the diagnosis of viral infections.
Biomaterial sampling
- Swab sampling
Methods and tests
PCR (polymerase chain reaction). Qualitative
Files
Download a sample of the result of the analysis
What is it for
Group B streptococci (Streptococcus agalactiae) are bacteria found in the lower intestines of 10-35% of healthy men and in the vagina and/or lower intestines of 10-35% of healthy women. These bacteria are a normal part of the human microflora. Although group B streptococcus is generally safe for adults, it can cause serious complications during pregnancy and severe illness in newborns. Also, group B streptococcus can affect people with a weakened immune system, chronic diseases, and the elderly.
These bacteria are a normal part of the human microflora. Although group B streptococcus is generally safe for adults, it can cause serious complications during pregnancy and severe illness in newborns. Also, group B streptococcus can affect people with a weakened immune system, chronic diseases, and the elderly.
How can a newborn become infected with streptococcus
Most infections occur during childbirth. Possible infection with premature rupture of the membranes. It is possible that infection can also occur through intact fetal membranes.
Risk factors for streptococcal infection
- presence of streptococcus on examination in vaginal discharge or urine;
- rupture of membranes;
- fever during labor;
- maternal age less than 20 years;
- streptococcal infection of the newborn in past births.
What can threaten a newborn with streptococcal infection
First of all, infection with streptococcus is dangerous not for the mother, but for the baby.
- Inflammation of the lungs (pneumonia)
- Inflammation of the meninges - meningitis
- Streptococci may cause septic complications
- If infected before delivery, may cause premature birth, miscarriage, stillbirth.
What problems can group B streptococcus cause in a pregnant woman and after childbirth
Usually streptococcus does not affect healthy adults, however, in rare cases, it can cause infectious complications in a pregnant woman:
- Urinary tract infection
- Infection of the placenta and amniotic fluid (chorioamnionitis)
- Bacteremia (circulation of bacteria in the blood)
- Terrible complication - sepsis
- Rarely, after childbirth, streptococcus can cause inflammation and infection of the lining of the uterine cavity - endometritis
- Streptococcus can cause wound infection in women after caesarean section
Should pregnant women be tested?
The first examination is desirable to be done in the first trimester of pregnancy, especially if there have been miscarriages or premature births in the past. It is advisable to re-examine at 35-37 weeks of pregnancy.
It is advisable to re-examine at 35-37 weeks of pregnancy.
Testing is also recommended for elective caesarean section, even though the baby is not in contact with the birth canal.
How to test for streptococcus
Preliminary preparation for the delivery of the analysis is not required. An analysis for group B streptococcus is taken from the vagina with a special swab, which is placed in the environment and then analyzed in the laboratory by PCR.
What to do with the results of the analysis
If the test is negative, no action is required.
If you test positive for group B streptococcus, it does not mean that you or your child will definitely get sick. But the risk of infection in this case is higher. To prevent diseases of the child during childbirth or in case of premature outflow of water, antibiotics are prescribed prophylactically.












