Breast milk for eye discharge
What Are Blocked Tear Ducts Chicago IL
Categories
- Botox
- Category: Blepharospasm
- Category: Cataracts
- Category: Diabetic Retinopathy
- Category: Droopy Eyelids (Blepharoptosis)
- Category: Eye Conditions
- Amblyopia (Lazy Eye)
- Category: Pterygium
- Chalazion
- Conjunctivitis
- Category: Eyelid Tumors
- Contact Lens Service
- Cornea Procedures
- Cosmetic Procedures
- Double Vision
- Dry Eyes
- Eye Care
- Eye Exam
- Eye Health
- Eye Melanoma
- Glaucoma
- LASIK
- Macular Degeneration
- Macular holes
- Optical Services
- Pediatric Eye Care
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus Surgery
- Retinal Detachment
- Thyroid Eye Disease
- Uncategorized
Archives
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
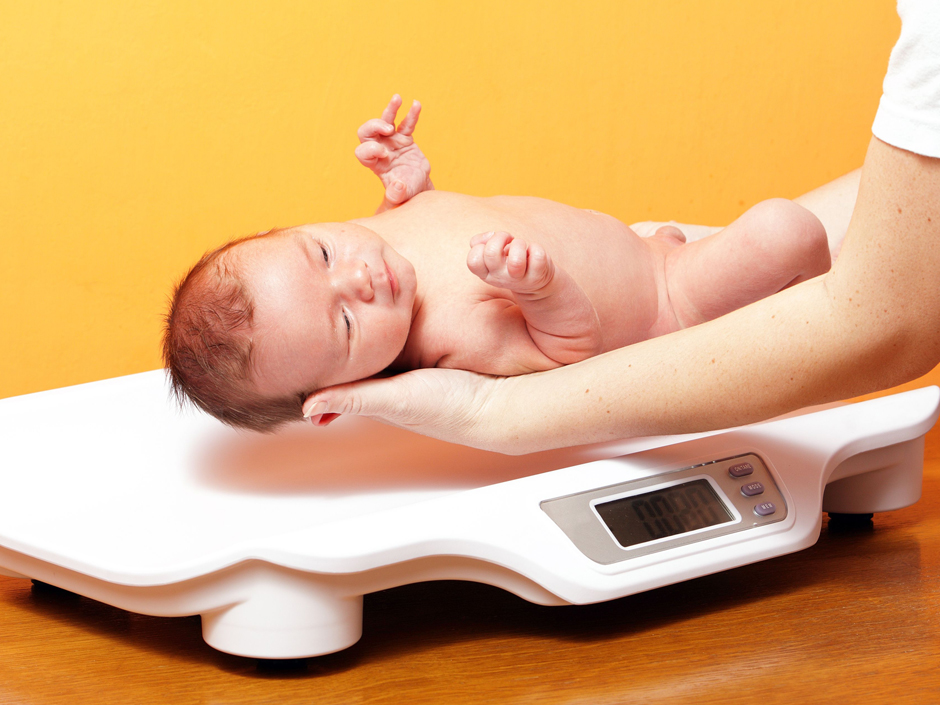
Being a parent to a newborn baby is both exciting and nerve-wracking. At every cough or jolt, your anxieties can get the best of you because you just want to make sure your baby is healthy, happy, and comfortable. As a fairly common condition that can inflict newborn babies clogged tear ducts can cause their eyes to be shut closed or have a residue around the outer edges. If you think your baby has clogged tear ducts, read on to learn more about the causes and treatments.
Causes
The main cause of a clogged tear duct in a newborn baby is simply because their tear ducts didn’t form correctly while in the womb. However, clogged tear ducts can also be caused by infection, so it’s important that you take your baby in to see the pediatrician if the condition persists.
Treatment
When it comes to caring for a newborn baby, the more natural the approach you use, the better. Because newborn baby’s bodies are so fragile, the last thing you want to do is introduce medication to them that will upset their immune system. Luckily, by using the methods listed below, you can help get rid of your child’s blocked tear ducts without the use of medication.
Luckily, by using the methods listed below, you can help get rid of your child’s blocked tear ducts without the use of medication.
- Warm Compress: By applying a warm, wet compress to your child’s eye you can help both remove the gunk that has built up and speed up the production of new tears. To use this method, take a clean, warm, wet washcloth and place it over the inner corner of your baby’s eye for about 10 seconds, then gently wipe away the gunk that has formed.
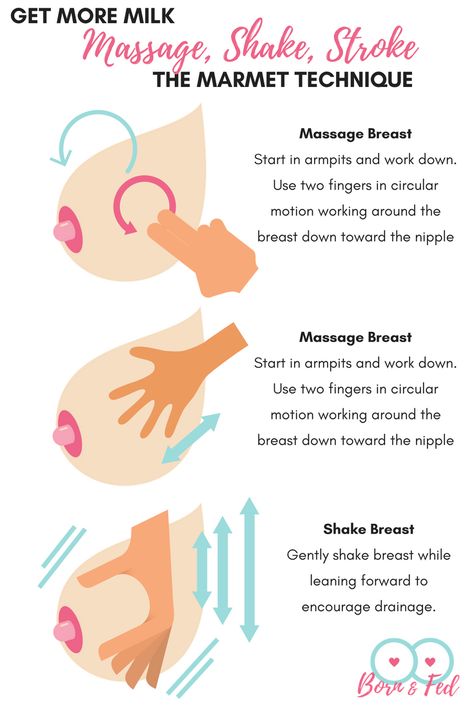
- Breast Milk: This treatment solution may sound a bit like hocus pocus to some people, but the power of breast milk is undeniable. Filled with antibodies, vitamins, and minerals breastmilk can work wonders on your young infant's body. Try placing a drop or two of breast milk directly into the inner portion of your baby’s eyes while they are closed— once they open their eyes, the milk will fall into the eyes and work to clear up any infection. Use this treatment a few times a day for a week or two or until their tear ducts have cleared up.

If your newborn’s tear ducts are clogged, it can make you stressed out and worried. However, by using the tips listed above, you can help them to see better and feel more comfortable. To learn more about these and other pediatric eye treatments, contact Millennium Park Eye Center.
Category:
Leave a Reply
Efficacy and safety of breast milk eye drops in infants with eye discharge
Save citation to file
Format: Summary (text)PubMedPMIDAbstract (text)CSV
Add to Collections
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Name your collection:
Name must be less than 100 characters
Choose a collection:
Unable to load your collection due to an error
Please try again
Add to My Bibliography
- My Bibliography
Unable to load your delegates due to an error
Please try again
Your saved search
Name of saved search:
Search terms:
Test search terms
Email: (change)
Which day? The first SundayThe first MondayThe first TuesdayThe first WednesdayThe first ThursdayThe first FridayThe first SaturdayThe first dayThe first weekday
Which day? SundayMondayTuesdayWednesdayThursdayFridaySaturday
Report format: SummarySummary (text)AbstractAbstract (text)PubMed
Send at most: 1 item5 items10 items20 items50 items100 items200 items
Send even when there aren't any new results
Optional text in email:
Create a file for external citation management software
Full text links
Wiley
Full text links
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2021 Apr;110(4):1322-1329.
2021 Apr;110(4):1322-1329.
doi: 10.1111/apa.15628. Epub 2021 Feb 25.
Tetsu Sugimura 1 , Tomoko Seo 2 , Nami Terasaki 1 , Yukiko Ozaki 3 , Noriko Rikitake 1 , Rumiko Okabe 3 , Masami Matsushita 3
Affiliations
Affiliations
- 1 Department of Pediatrics and Allergology, Sugimura Children's Medical Clinic, Chikugo City, Japan.
- 2 Department of Pediatrics, Green Woods Children's Clinic, Okazaki City, Japan.

- 3 Department of Pediatrics, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume City, Japan.
- PMID: 33098117
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.15628
Randomized Controlled Trial
Tetsu Sugimura et al. Acta Paediatr. 2021 Apr.
. 2021 Apr;110(4):1322-1329.
doi: 10.1111/apa.15628. Epub 2021 Feb 25.
Authors
Tetsu Sugimura 1 , Tomoko Seo 2 , Nami Terasaki 1 , Yukiko Ozaki 3 , Noriko Rikitake 1 , Rumiko Okabe 3 , Masami Matsushita 3
Affiliations
- 1 Department of Pediatrics and Allergology, Sugimura Children's Medical Clinic, Chikugo City, Japan.

- 2 Department of Pediatrics, Green Woods Children's Clinic, Okazaki City, Japan.
- 3 Department of Pediatrics, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume City, Japan.
- PMID: 33098117
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.15628
Abstract
Aim: Breast milk (BM) contains various protective components, such as immunoglobulins, lactoferrin, lysozyme, oligosaccharides and immune cell subsets. We evaluated the effectiveness of BM eye drops in infants with eye discharge in a randomised controlled study.
Methods: Subjects were breastfed infants aged ≤180 days, with eye discharge. We randomly assigned patients to receive eye drops of BM or sodium azulene sulphonate hydrate 0.02% ophthalmic solution (OS). The patients received drop of BM or OS for 7 days. Improvement score of eye discharge in the groups was compared using a non-inferiority test.
Results: The number of patients improved eye discharge was 119/155 (76.8%) and 119/157 (75.8%) in BM and OS groups, respectively. There were no significant differences between groups. The improvement score in eye discharge was 1.76 ± 0.91 in the BM group and 1.71 ± 0.96 in the OS group. The BM group was considered non-inferior to the OS group.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that BM is no less effective than OS in infants with eye discharge aged ≤6 months. The results suggested that the use of breast milk as eye drops could be considered as a first-line treatment for infants aged ≤6 months with eye discharge.
The results suggested that the use of breast milk as eye drops could be considered as a first-line treatment for infants aged ≤6 months with eye discharge.
Keywords: breast milk; eye discharge; eye drops; infant; non-inferiority test.
©2021 Foundation Acta Paediatrica. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Types of Breast Milk Fortification at Discharge from the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Breast Milk Feeding Rates and Growth at 4 Months Corrected Age.
Gehl B, Brownell E, Power K, Feinn R, Haines K, Lussier M, Moore J, Lainwala S. Gehl B, et al. Breastfeed Med. 2020 Oct;15(10):655-661. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2020.0022. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Breastfeed Med. 2020. PMID: 32865432
-
Nutrition, growth, and allergic diseases among very preterm infants after hospital discharge.

Zachariassen G. Zachariassen G. Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4588. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461996 Review.
-
Comparative growth outcome of preterm neonate fed post-discharge formula and breast milk after discharge.
Chotigeat U, Vongpakorn J. Chotigeat U, et al. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014 Jun;97 Suppl 6:S33-9. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014. PMID: 25391170
-
The trends in the usage of breast milk in neonatal intensive care setting.
Çelik K, Asena M, İpek MŞ. Çelik K, et al. Pediatr Int. 2020 Sep;62(9):1064-1072. doi: 10.1111/ped.14263. Pediatr Int. 2020. PMID: 32315473
-
Nutrient-enriched formula milk versus human breast milk for preterm infants following hospital discharge.

Henderson G, Fahey T, McGuire W. Henderson G, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD004862. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004862.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. PMID: 17943829 Review.
See all similar articles
References
REFERENCES
-
- Buznach N, Dagan R, Greenberg D. Clinical and bacterial characteristics of acute bacterial conjunctivitis in children in the antibiotic resistance era. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:823-828.
-
- Patel PB, Diaz MC, Bennett JE, Attia MW. Clinical features of bacterial conjunctivitis in children. Acad Emerg Med. 2007;14:1-5.
-
- Gigliotti F, Williams WT, Hayden FG, et al.
 Etiology of acute conjunctivitis in children. J Pediatr. 1981;9:531-536.
Etiology of acute conjunctivitis in children. J Pediatr. 1981;9:531-536.
- Gigliotti F, Williams WT, Hayden FG, et al.
-
- Japanese Association of Pediatric Ophthalmology. Conjunctivitis. http://www.japo-web.jp/info_ippan_page.php?id=page04. (2020-May-12 accessed).
-
- Everitt H, Little P. How do general practitioners diagnose and manage acute infectious conjunctivitis? A general practitioner survey. Fam Pract. 2002;19:658-660.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Full text links
Wiley
Cite
Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Send To
Breast milk with conjunctivitis - Encyclopedia Ochkov.
 net
net Inflammation of the conjunctiva occurs in infants even with careful care. Conjunctivitis occurs due to infection of the eyes with bacteria or viruses against the background of a lack of tear fluid, which appears in the right amount only by two months of the baby's life. Is it possible to treat such conjunctivitis by washing the baby's eyes with breast milk?
In this article
- Neonatal conjunctivitis: possible causes
- Can breast milk cure conjunctivitis?
- Dacryocystitis vs Conjunctivitis - What's the difference?
- Treatment of conjunctivitis in infants
- Prevention of conjunctivitis in infants
Neonatal conjunctivitis: possible causes
The eyes of newborn babies are extremely sensitive to external influences: wind, dust, bacteria and infections, because they are practically not washed by tear fluid. Tears can appear as early as the first week of a baby's life, and by two or three months, which explains why many newborns cry without tears. Normally, the lacrimal fluid in both children and adults washes away microscopic specks and dust particles from the surface of the eye. It is a reliable barrier against bacteria, as it contains lysozyme, which effectively destroys bacteria and viruses. If a child's eyes remain dry for a long time when crying, you should consult a doctor - you may need massages to help remove the film from the lacrimal canal.
Normally, the lacrimal fluid in both children and adults washes away microscopic specks and dust particles from the surface of the eye. It is a reliable barrier against bacteria, as it contains lysozyme, which effectively destroys bacteria and viruses. If a child's eyes remain dry for a long time when crying, you should consult a doctor - you may need massages to help remove the film from the lacrimal canal.
How does conjunctivitis manifest itself:
- sensitivity to light, swollen eyelids, discharge of clear fluid;
- eyelids stuck together, accumulation of pus in the corners of the eyes;
- inflammation, swelling of the conjunctiva, redness of the eyes.
In that period, while the production of tear fluid is not established, the risks of developing conjunctivitis are high. The cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane, abundant purulent discharge, can be both bacteria and viruses. The allergic nature of conjunctivitis should not be ruled out, since an allergy in a child can occur on pollen, house dust, animal hair, and also on breast milk (lactase deficiency, violation of the diet by the mother, etc.). Determine the cause of conjunctivitis should be a specialist who will prescribe treatment, taking into account the causative agent of the disease.
The allergic nature of conjunctivitis should not be ruled out, since an allergy in a child can occur on pollen, house dust, animal hair, and also on breast milk (lactase deficiency, violation of the diet by the mother, etc.). Determine the cause of conjunctivitis should be a specialist who will prescribe treatment, taking into account the causative agent of the disease.
Self-medication is not worth it, since in children the disease progresses rapidly and quickly leads to complications without adequate therapy.
Can breast milk cure conjunctivitis?
The benefits of mother's milk are enormous, everyone knows this. It is perfectly balanced in composition, contains enzymes, thanks to which it is well absorbed by the child's digestive system. Traditional medicine recipes often contain advice that recommends instilling breast milk into the nose, ears, and eyes of a newborn. Is breast milk treatment effective? Is milk healing, or was it just used before, since there were no effective drugs? Such questions arise for every mother who is advised to use breast milk for the treatment of her baby's eye, and it is very important to be prudent here.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/1459291/original/023410600_1483460950-Cara-Menyimpan-ASI-Perah-yang-Benar.jpg)
Mother's milk is ideal food for an infant, but not a medicine. Its effectiveness with a bacterial or viral infection will be zero, in addition, fatty milk can clog the tear ducts. Only for a while, breast milk can moisturize the mucous membrane and alleviate the condition of the baby, who, for sure, suffers from itching and burning in the eyes. Remember that trying to cure conjunctivitis by only washing your baby's eyes with breast milk without going to a doctor can waste time and make the situation worse.
In children's conjunctivitis, treatment should be monitored by a doctor, since the disease is acute, and the symptoms intensify: severe swelling, redness appear, the amount of purulent discharge increases, and most importantly, it will no longer be possible to quickly cope with such complications. In addition, young mothers may not understand that the child does not have conjunctivitis, but dacryocystitis, a dangerous pathology that requires immediate medical attention.
Dacryocystitis and conjunctivitis - what's the difference?
With conjunctivitis, the mucous membrane of the eye becomes inflamed, and with dacryocystitis, the work of the lacrimal canal is disrupted. As a result of its obstruction, an inflammatory process develops, which is characterized by the appearance of edema of the lower eyelid, redness of the skin at the site of inflammation. With conjunctivitis, both eyes are most often affected, and with dacryocystitis one. The disease can be congenital (narrow nasolacrimal canal, anomalies of the nasal septum) and acquired, resulting from impaired patency of the nasolacrimal canal.
The doctor can determine the patency of the nasolacrimal canal when examining the baby. To do this, use the West test, instilling a safe dye into the eyes and checking the color of a twisted piece of cotton wool, which is previously injected into the child's nose. Dacryocystitis is treated with antibacterial drops, physiotherapy methods. In some cases, surgery is indicated.
In some cases, surgery is indicated.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in infants
Timely treatment of bacterial or viral conjunctivitis in newborns contributes to a quick recovery. It is enough to follow the recommendations of a specialist for several days so that the inflammatory process stops and the baby's eyes become healthy again. It is worth emphasizing that any treatment plan must be strictly agreed with the doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children:
- Careful hygiene of the mother's hands before treating the eyes of the baby. The child's eyes should be cleaned of purulent discharge by soaking cotton wool in a solution of furacilin (use a slightly warm solution to make it easier to remove the discharge from the eyelids).
- Drops "Albucid" - this antimicrobial drug is prescribed to newborns with conjunctivitis, which was caused by microorganisms such as staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci.
- Chloromycetin eye drops (commonly used in young children due to low toxicity) - this treatment of conjunctivitis is recommended if the disease is confirmed to be bacterial, as this antibiotic is effective against various microbes and some viral strains.
- Massage of the bridge of the nose at the inner corner of the eyes should be done with light stroking movements for a minute two or three times a day - this will help restore the lacrimal duct and avoid complications.
Treatment of conjunctivitis using alternative recipes is undesirable, because it is not known how the child's body will react to herbal decoctions or other remedies. To reduce the risk of developing an allergic reaction, use medications prescribed by your doctor to treat conjunctivitis.
Prevention of conjunctivitis in infants
The main preventive measure to help prevent the development of conjunctivitis in young children is careful hand hygiene of adults in contact with the child. You can reduce the likelihood of inflammation of the eyelids and mucous membranes by regularly ventilating the room and doing wet cleaning of the baby’s room. Dust in the air can settle on the mucosa, and due to the fact that the lacrimal fluid in a newborn is not enough to wash it off and remove it, it can become a source of irritation. Long walks in the fresh air are also useful - a sufficient amount of oxygen has a beneficial effect on strengthening the child's immunity, and his body will be less vulnerable to various kinds of viral and bacterial infections.
You can reduce the likelihood of inflammation of the eyelids and mucous membranes by regularly ventilating the room and doing wet cleaning of the baby’s room. Dust in the air can settle on the mucosa, and due to the fact that the lacrimal fluid in a newborn is not enough to wash it off and remove it, it can become a source of irritation. Long walks in the fresh air are also useful - a sufficient amount of oxygen has a beneficial effect on strengthening the child's immunity, and his body will be less vulnerable to various kinds of viral and bacterial infections.
How to prevent the development of conjunctivitis, what to do?
- keep the house clean, organize everything so that the house has a favorable microclimate;
- use air humidifiers in the winter season that maintain the optimal level of humidity in the room - dry, overheated air negatively affects the condition of the mucous membranes of babies, and humidifiers can effectively eliminate this problem;
- air purifiers - such devices often have several options, they can clean the air of dust and humidify it;
- remove all unnecessary items from the children's room so that they do not accumulate dust: souvenirs, vases, soft toys, cosmetics, etc.

With insufficient treatment, the acute form of the disease is transformed into a chronic one, the cornea may become inflamed, turbidity may appear (with a viral disease). You should not rely on the effectiveness of breast milk for bacterial or viral conjunctivitis, because such treatment can not only delay recovery, but also cause complications.
How to cure dacryocystitis in a child? Causes of occurrence. Complications
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac. It is characterized by stagnation of tears, the formation of purulent secretions. It occurs as a result of obstruction of the nasolacrimal canal or its pathological narrowing. It occurs in newborns in the first days of life.
Causes of pathology
Congenital dacryocystitis occurs in newly born babies. During fetal development, the outlets of the nasolacrimal canals are closed with a special thin film. It prevents amniotic fluid from entering the nasal passages. At birth, this film breaks. There are times when it persists. In this case, dacryocystitis develops, since the nasolacrimal duct is closed. Factors in the formation of pathology include:
At birth, this film breaks. There are times when it persists. In this case, dacryocystitis develops, since the nasolacrimal duct is closed. Factors in the formation of pathology include:
- narrowing of the lacrimal sac at the junction with the duct;
- deviated nasal septum;
- nose, eye injuries;
- infectious diseases of the mucous membranes of the nose in a chronic form;
- channel distortion.
The causes may be dropsy of the lacrimal sac, staphylococci, streptococci. If in doubt, please consult our doctors. Doctors will consult remotely on all possible causes of dacryocystitis.
Disease classification
Classification of dacryocystitis according to Cherkunov B.Yu.:
| Name | Description |
| With the flow |
|
| By etiology |
|
Example
Mom turned to the pediatrician with a newborn baby 3 weeks old. The main complaints were purulent discharge from the eyes of a child of a purulent nature. Eye watering. During the examination, the doctor found that the baby had dacryocystitis. It was prescribed: massage, wash the child's eyes from pus with a solution of chamomile.
The main complaints were purulent discharge from the eyes of a child of a purulent nature. Eye watering. During the examination, the doctor found that the baby had dacryocystitis. It was prescribed: massage, wash the child's eyes from pus with a solution of chamomile.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis
The main symptom is lacrimation, accompanied by constant lacrimation. Clinical signs:
- purulent discharge from the affected eye;
- swelling of the lacrimal sac;
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane, skin.
Most of the cases are unilateral dacryocystitis. In cases where there is no outflow of accumulated contents, there is a risk of developing phlegmon. The child's health worsens, body temperature rises, signs of general intoxication appear.
When the first clinical signs appear, it is important to consult our physicians. They will explain how to deal with this pathology, select clinics for examination.
Disease diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on:
- history;
- inspection;
- palpation: purulent contents are released when pressing on the affected area, there may be pain in cases of edema;
- results of the West color test. A special solution is instilled into the affected eye. A swab is inserted into the nasal cavity. Normally, after a few minutes, the tampon will be colored;
- contrast test results. . For this, local anesthesia is performed. The newborn is given a special solution. Ten minutes later, the ophthalmologist conducts an examination under a blue spectrum lamp. Normally, traces of the solution will be visible in the blue glow;
- laboratory studies of purulent discharge for antibiotic resistance.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with conjunctivitis.
Complications of disease
in the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, the following consequences of dacryocystitis in newborns may occur:
- stretching of the lacrimal sac;
- due to a strong inflammatory process, an abscess, phlegmon is formed;
- under the influence of pus, the tissues are melted, the contents are poured into the surrounding tissues and cavities, sepsis, encephalitis, meningitis develop;
- fistula formation;
- persistent conjunctivitis;
- corneal ulcers.

complications can also arise during diagnostic manipulations - when probing the nasolacrimal canal. If the child is not properly restrained, there may be:
- nosebleeds;
- rupture of the wall of the lacrimal canal, lacrimal sac, followed by the spread of purulent contents with the development of sinusitis, ethmoiditis, phlegmon of the orbit.
Important! To avoid complications, it is necessary to perform rhinoscopy before probing the nasolacrimal canal.
Treatment of dacryocystitis
Therapy of pathology can be conservative and operational.
Conservative treatment
Often, in order to get rid of the film, it is enough to properly massage the newborn. It should be point, excluding friction. Pressure is applied to the commissure of the eyelids, behind the anterior crest of the lacrimal fossa, into the depth of the eye orbit. It is necessary to repeat the massage actions three times up to six times a day. It is best to do it while the baby is eating or before each feeding.
It is best to do it while the baby is eating or before each feeding.
Every day, several times a day, you need to wash the eyes of a newborn with a solution of chamomile, green tea. This will remove dried crusts of pus and expiration.
Surgical treatment
This includes the following manipulations:
- probing of the lacrimal ducts with subsequent washing of the channels:
- through the lacrimal points;
- through an incision in the skin;
- through the lower nasal passage;
- dacryocystiodrainage;
- resection of the lacrimal sac;
- external and endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy.
There are no specific measures for the prevention of pathology.
Medical treatment and physiotherapy are ineffective in this pathology. Surgery has age restrictions. Our doctors will remotely advise on possible treatment techniques, explain age restrictions, and select clinics for further treatment.
FAQ
Can the nasolacrimal canal open on its own with dacryocystitis up to a year?
+
In 90 percent of cases, spontaneous opening of the nasolacrimal canal occurs. Many doctors recommend that you first carry out conservative treatment by massage, treat the eyes of a newborn with special preparations, decoctions. If the signs of inflammation are strong, complications have appeared - surgical intervention is indicated.
What to do if the eye of the baby festered?
+
If the eye of a newborn is festering, it is necessary to establish the cause. It can be conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, allergic reactions. It is not worth treating yourself.
Can pus in the eyes of a baby indicate inflammation?
+
Inflammation of the eye is not always accompanied by purulent discharges. Pus in the eyes appears with some diseases, such as conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, with injuries.
Pus in the eyes appears with some diseases, such as conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, with injuries.
How to wipe the eyes of a newborn?
+
It is necessary to treat the baby's eyes as needed. In cases where the eyes stick together from pus, it is necessary to rinse either with special preparations or decoctions. Even in cases of damage to only one eye, it is necessary to wash two at once. For each eye, a cotton pad is taken. Movement from the inner corner to the outer.
Why does a newborn's eye water?
+
The causes may be trauma, birth pathologies of the mucous membranes, anomalies in the structure of the nose, dacryocystitis, conjunctivitis
Expert opinion
Dacryocystitis is a purulent-inflammatory process of the lacrimal sac, which drains the nasolacrimal canal. In this case, the baby's eyes fester, steady lacrimation appears. Usually, the pathology is detected in the first month of a baby's life.