Bladder infection sign of pregnancy
UTIs During Pregnancy: Symptoms, Treatment, Common Questions
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), also known as bladder infections, are the most common type of bacterial infection diagnosed today, according to research published in the American Journal of Medicine. Roughly 31 percent of pregnant women will have either a symptomatic or an asymptomatic (without symptoms) UTI during pregnancy, research suggests. UTIs occur when bacteria enters into the usually sterile urinary tract and multiplies, causing painful urination and other symptoms. Certain factors during pregnancy make this occurrence more likely to happen. Here’s what you need to know to keep you and your baby healthy.
RELATED: 8 Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Symptoms
Why Are UTIs Common in Pregnant Women?When you’re pregnant, the anatomy of your urinary tract actually changes. For instance, your kidneys become larger and your growing uterus can compress your ureters and bladder. Because of this compression, fully emptying your bladder during pregnancy becomes more difficult. In addition, your progesterone and estrogen levels increase during pregnancy, which can weaken your bladder and ureters. Pregnancy also alters the makeup of your urine, reducing the acidity and increasing the amount of protein, hormones, and sugar in your urine. That excess sugar, for one, can encourage bacterial growth. All of the above contribute to a heightened chance of developing a UTI in pregnancy. And that is why it’s recommended that all pregnant women receive a urinalysis and urine culture at 12 to 16 weeks or during the first prenatal visit.
RELATED: 7 Things an Anesthesiologist Wants You to Know About Pain
UTIs by Pregnancy TrimesterYour risk of UTI goes up beginning at week 6 of your pregnancy; the chances you’ll have a UTI vary by trimester.
First TrimesterAbout 41 percent of UTIs are diagnosed during the first trimester.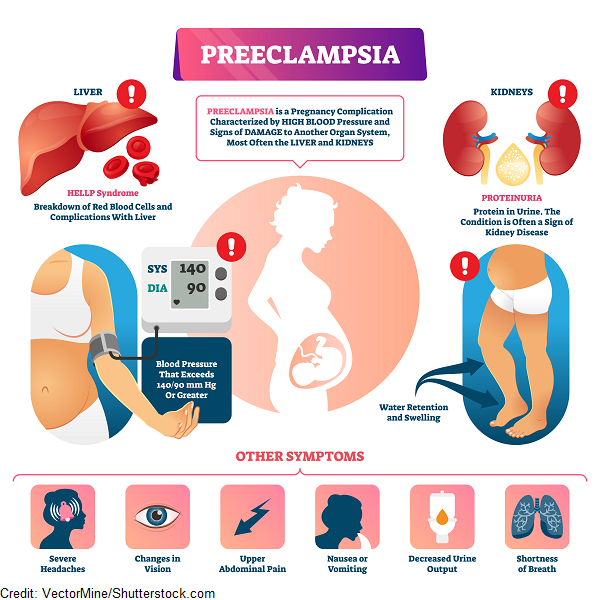 Because getting a UTI during the first trimester is so common, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that your healthcare provider obtain a urinalysis and urine culture at your first prenatal visit. That recommendation holds whether you present with UTI symptoms or not.
Because getting a UTI during the first trimester is so common, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that your healthcare provider obtain a urinalysis and urine culture at your first prenatal visit. That recommendation holds whether you present with UTI symptoms or not.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about half as many pregnant women are diagnosed with a UTI during their second trimester compared with the first trimester.
Third TrimesterCompared with the second trimester, the number of women who experience a UTI during the third trimester is almost halved. However, 80 to 90 percent of acute kidney infections in pregnancy (many caused by the progression of an untreated UTI) occur in the second and third trimesters, according to research published in the Archives of Medical Science. Thus, it’s recommended to do a repeat urine culture during the third trimester, too.
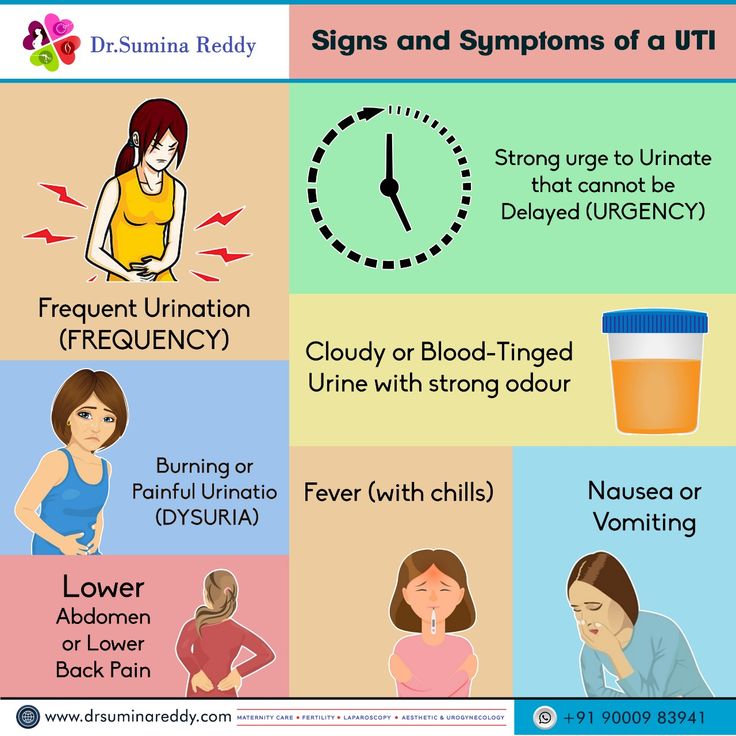
“While mildly painful urination during pregnancy can often mean a yeast infection, not a UTI, it’s always best to see your healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms,” says Heather Bartos, MD, an ob-gyn in Cross Roads, Texas. After all, research suggests that about 18 percent of UTIs that occur during pregnancy are symptomatic UTIs, meaning the telltale UTI signs and symptoms are present:
- Strong and frequent urge to use the bathroom
- Burning while urinating
- Regularly passing only small amounts of urine
- Cloudy, red, pink or cola-colored urine
- Foul-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain, usually in the center of the pelvis
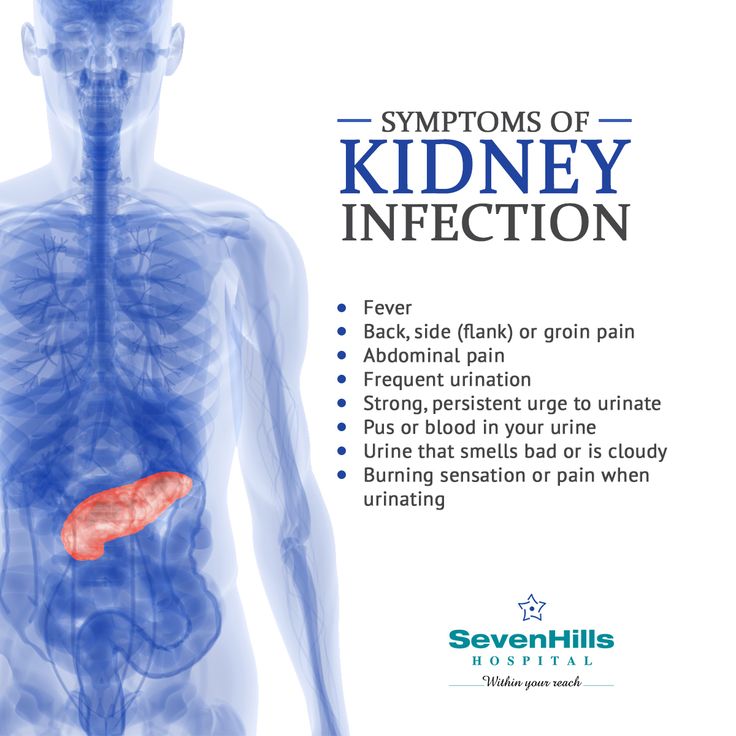
In pregnancy, women are also more susceptible to asymptomatic UTIs, meaning you have significant bacteria in your urine but your urinary tract is free of signs and symptoms. Experiencing no symptoms, however, does not mean that asymptomatic UTIs are benign.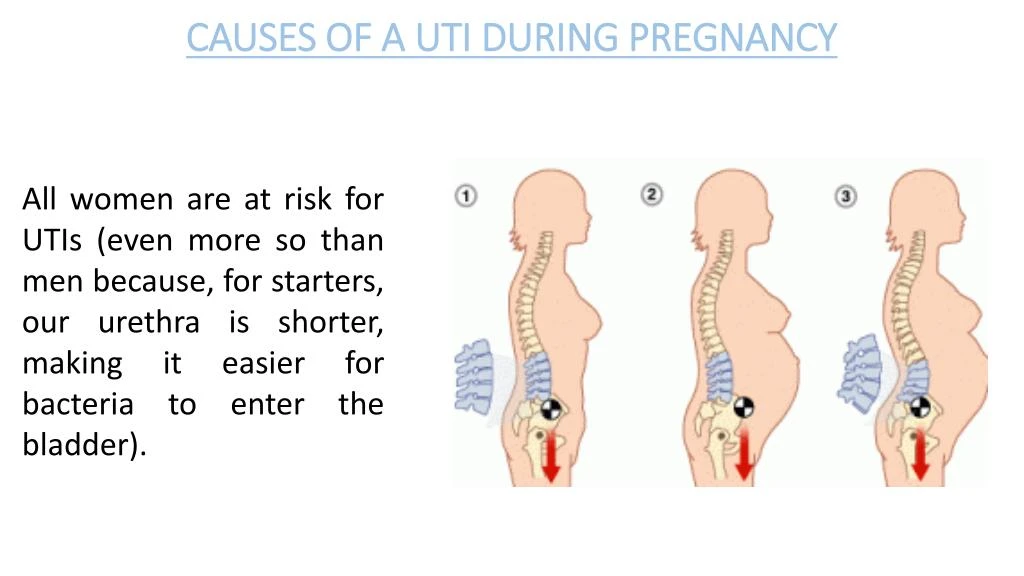 “An asymptomatic UTI can lead to a symptomatic UTI or even a kidney infection,” says Dr. Bartos. In fact, research shows that if asymptomatic UTIs are left untreated, 30 percent of pregnant women will go on to develop a symptomatic UTI, and half of those women will eventually be diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Up to 23 percent will have a kidney infection recurrence during the same pregnancy. It’s important to note that classic UTI signs, like frequent and painful urination, may or may not occur with a kidney infection. Here, some signs to look out for:
“An asymptomatic UTI can lead to a symptomatic UTI or even a kidney infection,” says Dr. Bartos. In fact, research shows that if asymptomatic UTIs are left untreated, 30 percent of pregnant women will go on to develop a symptomatic UTI, and half of those women will eventually be diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Up to 23 percent will have a kidney infection recurrence during the same pregnancy. It’s important to note that classic UTI signs, like frequent and painful urination, may or may not occur with a kidney infection. Here, some signs to look out for:
- High-grade fever
- Chills and rigors (sudden feeling of cold with shivering)
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lower back pain
- Flank pain (often right side)
- Possible reduced urine output
“UTIs can rapidly progress to a kidney infection in pregnancy, which can be much more dangerous than a kidney infection in nonpregnant women,” says Bartos. “Severe infections can lead to respiratory problems and sepsis, which can then lead to preterm labor or even the need to urgently deliver the baby.” Beyond a kidney infection, simply having a UTI during pregnancy appears to possibly be a contributing factor to low birth weight. Women who have a UTI in pregnancy also have a 1.31-fold higher risk of developing preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure, according to a meta-analysis published in September 2018 in the journal Medicine. It’s thought that a UTI may alter a pregnant woman’s inflammatory response, which can spur preeclampsia.
“Severe infections can lead to respiratory problems and sepsis, which can then lead to preterm labor or even the need to urgently deliver the baby.” Beyond a kidney infection, simply having a UTI during pregnancy appears to possibly be a contributing factor to low birth weight. Women who have a UTI in pregnancy also have a 1.31-fold higher risk of developing preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure, according to a meta-analysis published in September 2018 in the journal Medicine. It’s thought that a UTI may alter a pregnant woman’s inflammatory response, which can spur preeclampsia.
RELATED: National Period Day Is October 19
Can Having a UTI While Pregnant Hurt the Baby?Possibly. “A UTI itself doesn’t hurt the baby directly,” says Bartos. “It’s the failure to treat a UTI that can cause things like preterm birth or, rarely, infection of the amniotic sac. ” For example, research published in American Family Physician shows that treating pregnant women who have asymptomatic UTIs decreases the incidence of preterm birth and low-birth-weight infants. That’s why screening and prompt treatment are important.
” For example, research published in American Family Physician shows that treating pregnant women who have asymptomatic UTIs decreases the incidence of preterm birth and low-birth-weight infants. That’s why screening and prompt treatment are important.
Urinary tract infections are not associated with preterm labor, according to research published in the Journal of the Chinese Medical Association. However, if a urinary tract infection is left untreated, it can progress to a kidney infection. And a kidney infection (pyelonephritis) during pregnancy can modestly increase your chances of early contractions and delivery. Research published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology notes that women diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy have a 10.3 percent chance of preterm delivery compared with the 7.9 percent chance among women without a kidney infection during pregnancy.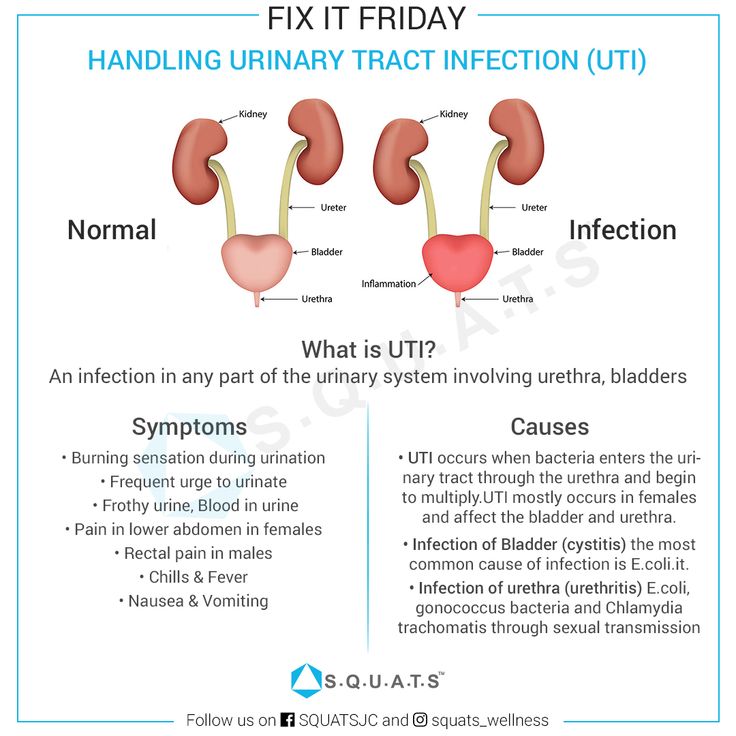
RELATED: Common Types of Vaginal Infections
Do UTIs Differ by Trimester?At week 6, UTI risk starts to go up, with two-fifths of UTIs occurring during the first trimester. Because of the likelihood of getting a UTI during the first trimester, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that pregnant women have a urinalysis and urine culture at their first prenatal visit — whether they have UTI symptoms or not. In the second trimester, about half as many pregnant women are diagnosed with a UTI as in the first trimester, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and that number is almost halved again for the third trimester. However, 80 to 90 percent of acute kidney infections in pregnancy (many caused by the progression of an untreated UTI) occur in the second and third trimesters, according to data published in the Archives of Medical Science, so pregnant women should have a repeat urine culture during the third trimester.
RELATED: March Is Endometriosis Awareness Month
What Are Pregnancy-Safe UTI Treatment Options?How do you treat a UTI when pregnant? It’s similar to how you treat a UTI when not pregnant — with a few key differences. A short-course of antibiotics is the standard treatment for asymptomatic and symptomatic urinary tract infections that occur during pregnancy. There are, however, two important contrasts in treating UTIs in pregnant women versus nonpregnant women. First, asymptomatic UTIs diagnosed during the first trimester are treated with antibiotics, whereas nonpregnant women’s infections are often not treated in this manner. (Outside of pregnancy, asymptomatic bacteriuria is usually not treated with antibiotics.) Also, the preferred antibiotic drugs used to treat UTI in pregnancy often differ than what would be used while not pregnant. For instance, the following antibiotics have not been associated with any birth defects, thus are likely safe to use at any point during pregnancy:
- Penicillins Amoxicillin, ampicillin, and augmentin are in this group.

- Erythromycin Some of the brand names include Ery-Tab, Akne-Mycin, E.E.S. Eryc, and Pediamycin.
- Cephalosporins Keflex (cephalexin) is a cephalosporin.
UTI history and resistance patterns must be considered before prescribing any of these drugs.
Because certain antibiotics pose a potential risk for birth defects (anencephaly, heart defects, and cleft palate) when taken during the first trimester, they are only considered a first-line treatment for UTIs occurring during the second and third trimesters, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Prescribing the antibiotics listed below during the first trimester is considered appropriate only when no other suitable alternative treatments are available:
- Nitrofurantoin Macrobid, Furadantin, and Macrodantin are in this category.
- Sulfonamides Bactrim (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) is part of this class.
Be sure to double-check what your healthcare provider is prescribing, since despite the warnings, nitrofurantoin remains the most frequently prescribed antibiotic during the first trimester.
How to Prevent Urinary Tract Infections, or UTIs
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are the most common type of bacterial infection diagnosed today, with more than half of all women experiencing at least...
By Holly Pevzner
What Is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
By Holly PevznerTreatment for Urinary Tract Infections: Antibiotics, Medication, and Home Remedies
By Holly PevznerSigns and Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections
By Holly PevznerDiagnosing UTI: Tests and Screenings, Early Diagnosis, and Your Doctors
By Holly PevznerCauses and Risk Factors of UTIs
Urinary tract infections occur when harmful bacteria enter the urethra—the tube that carries urine out of the body. Risk factors for UTIs may differ between...
Risk factors for UTIs may differ between...
By Lindsey Konkel
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnancy - symptoms, causes
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnancy - symptoms, causes | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
What is a urinary tract infection?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the urinary system. UTIs are the most common bacterial infection that women develop during pregnancy. They can occur in different parts of the urinary tract, including the bladder (cystitis), urethra (urethritis) or kidneys (pyelonephritis). Sometimes when a UTI develops and bacteria are detected in the urinary tract, you may not have any symptoms of an infection. This is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria.
This is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria.
While anyone can get a UTI, they are much more common in women than men and they are also more likely to occur in the very young and the elderly.
What are the symptoms of UTIs during pregnancy?
Common symptoms of a UTI during pregnancy are similar to those that you might experience at any other time, and include:
- a burning sensation when you pass urine
- feeling the urge to urinate more often than usual
- urinating before you reach the toilet (‘leaking’ or incontinence)
- feeling like your bladder is full, even after you have urinated
- urine that looks cloudy, bloody or is very smelly
- pain above the pubic bone
- fever
Sometimes the first sign of an infection is a faint prickly sensation when you pass urine. If the infection is more advanced and has moved up to the kidneys, you may also experience fever with a particularly high temperature, back pain and vomiting.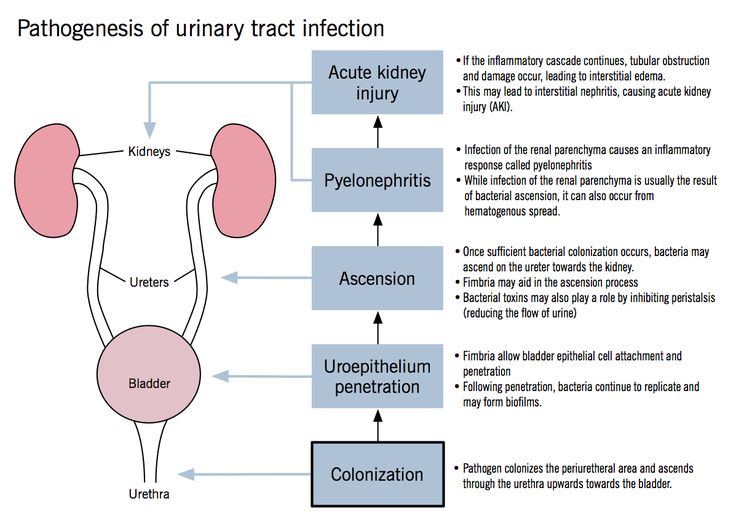
What are the common causes of UTIs?
Your urinary tract is normally free of bacteria. If bacteria enter the tract and multiply, they can cause a UTI. There are several factors that increase the risk of developing an infection:
- Infection with common bacteria in your gut, usually from faeces (poo) can contaminate your urinary tract
- Being sexually active increases the risk of bacteria moving around the genital area and entering the urinary tract
- If you have weak pelvic floor muscles your bladder might not empty completely, which can lead to an infection
- Women with diabetes are at increased risk of developing a UTI since the sugar in their urine may cause bacteria to multiply
Are UTIs a risk during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, many changes occur in your body that increase your risk of developing a UTI, including changes to the make-up of your urine and immune system. As your baby grows, there is also an increase in the pressure on your bladder, which can reduce the flow of your urine and lead to an infection.
UTIs can affect women whether they are pregnant or not. However, pregnant women are more likely to develop repeated or more severe infections. Up to 1 in 10 pregnant women will have a UTI but not have any symptoms at all.
Is there a risk to my baby?
Having a UTI during pregnancy can increase your risk of developing high blood pressure, and your baby may be born early and smaller than usual. For this reason, even if you don’t have any symptoms, it is important to treat a UTI as soon as possible.
How are UTIs diagnosed?
UTIs are diagnosed by taking a urine sample which is checked in a laboratory for bacteria. Your doctor may also perform a physical examination if they think you have an infection.
All pregnant women are offered a urine test, usually at their first antenatal visit or soon after. You may need to repeat the urine test if you have a history of UTIs; have symptoms of a UTI; have a contaminated sample or if your doctor thinks you are at high risk of developing a UTI. If you have frequent UTIs, you may also need additional tests such as an ultrasound of your kidneys.
If you have frequent UTIs, you may also need additional tests such as an ultrasound of your kidneys.
How are UTIs treated during pregnancy?
When you have a UTI, it is important to drink plenty of water to flush out the urinary tract. UTIs are treated with antibiotics that are safe in pregnancy. Your doctor will select the right antibiotic, based on your infection and the type of bacteria found in your urine sample.
Can I prevent UTIs?
You can lower your risk of developing a UTI during pregnancy by:
- drinking plenty of fluids, especially water
- quickly treating any vaginal infection that may occur, including thrush or a sexually transmitted infection
- avoiding becoming constipated
Some women have also found the following tips helpful:
- urinate immediately after sex
- don’t delay going to the toilet — go as soon as you feel the need
- wipe from the front to the back after going to the toilet
- wear cotton underwear
When should I see my doctor?
See your midwife or doctor if you have any symptoms of a UTI. It’s important not to delay treatment since infections develop quickly, and can affect both you and your baby.
It’s important not to delay treatment since infections develop quickly, and can affect both you and your baby.
More information
UTIs are very common during pregnancy, and are best treated early. If you notice the symptoms of an infection, seek medical advice from your doctor, midwife or pharmacist.
For more information on UTIs, visit the Kidney Health Australia page on UTIs.
Sources:
Government of South Australia (Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnancy), Jean Hailes (Urinary Tract Infections), Kidney Health Australia (Factsheet: Urinary Tract Infections), Government of Western Australia North Metropolitan Health Service (Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnant Women)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: August 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Frequent urination during pregnancy
- Incontinence during pregnancy
Need more information?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Urinary tract infection occurs when part of the urinary tract becomes infected. UTIs are usually caused by bacteria and generally clear up with a course of antibiotics.
Read more on myDr website
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) explained - NPS MedicineWise
Learn about the causes & treatments for urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Read more on NPS MedicineWise website
Urinary tract infection (UTI) | SA Health
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the urinary system. Infection may occur in the kidneys, bladder or urethra.
Read more on SA Health website
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) | Jean Hailes
A comprehensive guide to urinary tract infections. Everything you should know about UTIs including causes, symptoms, management and treatment.
Everything you should know about UTIs including causes, symptoms, management and treatment.
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
Incontinence & Bladder Weakness | Jean Hailes
What makes a normal bladder. Types of incontinence. Causes and symptoms. Diagnosis and treatment. Prevention and management.
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
Pyelonephritis
Infection of the kidneys.
Read more on Queensland Health website
Check-ups, tests and scans available during your pregnancy
Antenatal care includes several check-ups, tests and scans, some of which are offered to women as a normal part of antenatal care in Australia.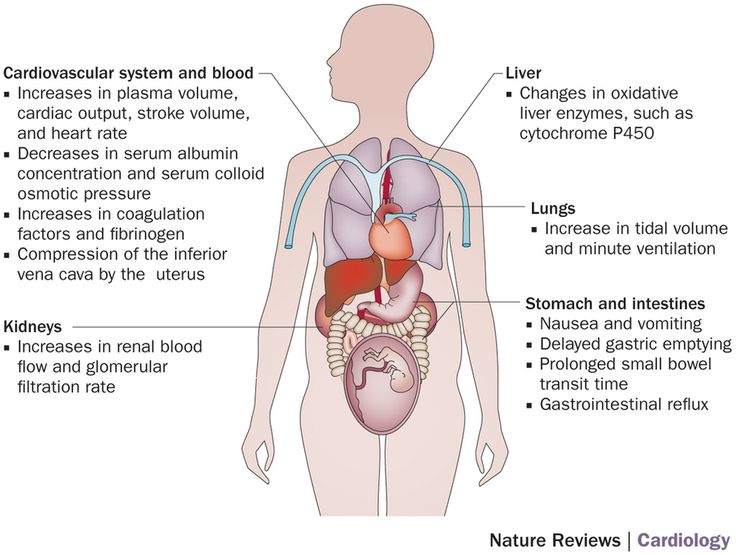 Learn more here.
Learn more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Thrush | SA Health
Thrush or Candidiasis is a common vaginal infection, caused by an overgrowth of yeasts and is not considered to be a sexually transmitted infection
Read more on SA Health website
Pregnancy at week 9
Your baby is now the size of a peanut. You won't be showing just yet, but you may have put on a little weight.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Your first antenatal visit
Find out what will happen and what you can learn during your first antenatal care visit with your GP or midwife.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.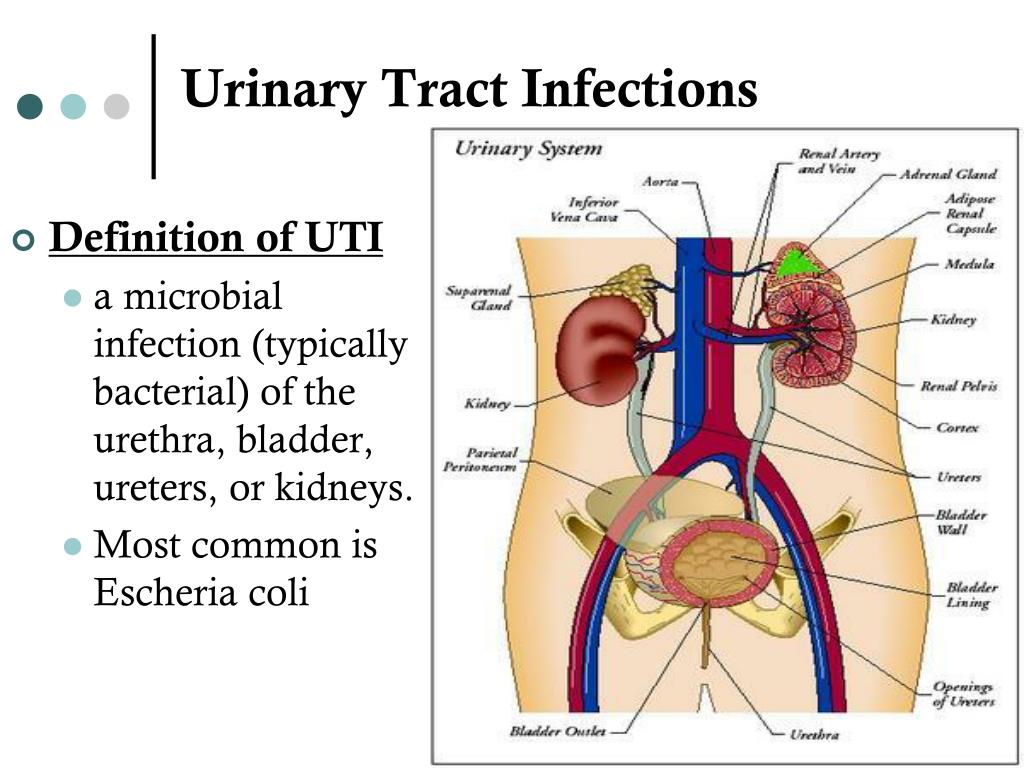
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Urinary tract infections vs pregnancy: treatment and prevention
Summary. Urinary tract infections are one of the most common complications in pregnant women, which can lead to serious consequences not only for the expectant mother, but also for the child. When managing pregnant women with diseases of the urinary system, it is extremely important to choose the right and, most importantly, safe therapeutic tactics. What drugs are safe during pregnancy? What obstetric and therapeutic tactics are most effective for kidney diseases in pregnant women? What diagnostic methods are best used for asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute cystitis and pyelonephritis? Professor 9 spoke about this in her speech0003 Olga Grishchenko , Head of the Department of Perinatology, Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Kharkov Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education during the training workshop for gynecologists "Actual Guidelines of Gynecology, Reproductology, Obstetrics", held on March 29, 2019 in Kharkov. The event was organized by the MedExpert Group of Companies together with the National Medical University named after A.A. Bogomolets and National Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupyk.
The event was organized by the MedExpert Group of Companies together with the National Medical University named after A.A. Bogomolets and National Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupyk.
Urgency of the problem
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the most common bacterial infections in outpatient practice, they take the 2nd place, second only to respiratory tract infections. According to statistics, 50% of women in the world have an episode of UTI at least once in their lives, of which 25–40% experience a relapse of the disease within 6–12 months. Every year, about 10% of women develop acute cystitis, and pyelonephritis remains the leading cause of hospitalization during pregnancy for non-obstetric indications.
In the presence of UTI in pregnant women, the risk of preterm labor and rupture of amniotic fluid, chorioamnionitis increases, premature or functionally immature children are born, and the level of perinatal mortality increases.
In the structure of UTI, asymptomatic bacteriuria is observed in 4-9.5% of pregnant women, acute pyelonephritis - in 12-25%, chronic pyelonephritis - in 33%, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis - in 0.1-0.2%.
Risk factors and pregnancy
As a rule, infections, self-medication or improper treatment, asymptomatic bacteriuria, frequent UTIs in combination with inflammatory diseases (colpitis), lifestyle and nutrition can affect the occurrence of pathology of the urinary system.
Pregnant women have an increased risk of diseases of the urogenital tract. A high level of progesterone leads to the development of hypotension, hypokinesia, dyskinesia of the ureters and pyelocaliceal system. In turn, the uterus compresses the ureter, high intra-abdominal pressure occurs, especially in primiparas. During pregnancy, the renal pelvis enlarges, the growing uterus squeezes the ureter more and more, the outflow of urine from the kidneys becomes difficult, the urine stagnates, bacteria multiply in it, and inflammation easily occurs.
Infectious agents can enter the bladder by ascending (with inflammatory diseases of the urethra), descending (most often with tuberculous kidney damage), hematogenous (if there is a purulent focus in other parts of the body) and lymphogenic (with diseases of the genital organs) by.
Classification of UTIs in pregnant women
UTIs in pregnant women include asymptomatic bacteriuria, lower urinary tract infections (acute and recurrent cystitis) and upper urinary tract infections (acute pyelonephritis, chronic pyelonephritis in remission, exacerbation, latent course).
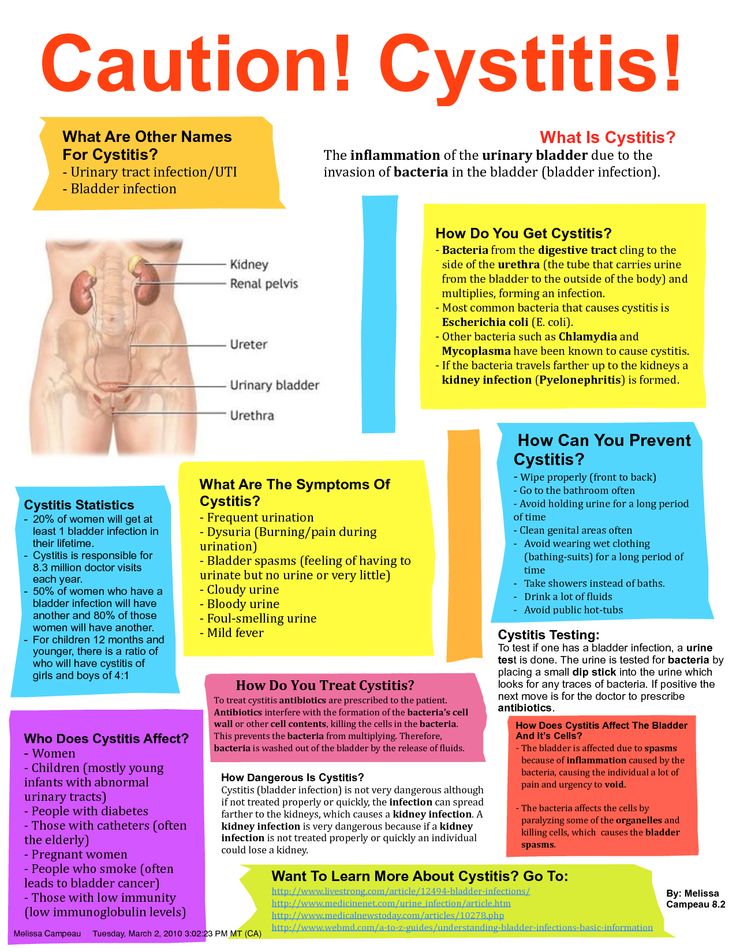
Cystitis in pregnancy: course, diagnosis
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder wall, one of the most common urological diseases, as a rule, its cause is an infection. Symptoms of cystitis in women are manifested in the form of frequent urination, cramps and pain when urinating, pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, weakness, fatigue, irritability, blood in the urine, cloudy urine, pus or yellow spots on the underwear.
Normally, urination is not accompanied by pain. In women, painful urination can be caused by diseases of the bladder, urethra, or vagina. So, pain in the bladder, as a rule, is felt in the area of the womb, it can increase during urination or, conversely, decrease when the bladder is empty. Urethral pain associated with urination is felt by the patient directly in the urethra and is usually aggravated by urination. Urine entering the vaginal opening can cause pain if it is inflamed. Inflammation of the urethra is most often characterized by a bacterial nature and requires additional examination and treatment.
Primary diagnosis of cystitis involves an examination by specialized specialists (urologist, nephrologist, gynecologist), as well as taking an anamnesis and establishing possible causes of the disease (hypothermia, unprotected intercourse, taking medications, the presence of concomitant diseases).
Laboratory tests include a urinalysis for Nechiporenko cultures (helps identify the pathogen), a general urinalysis (allows you to identify erythrocytes, leukocytes, protein in the urine; the urine itself may be cloudy with an admixture of blood or pus), a general blood test (allows you to identify a picture inflammatory process, it is possible to increase the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), leukocytosis).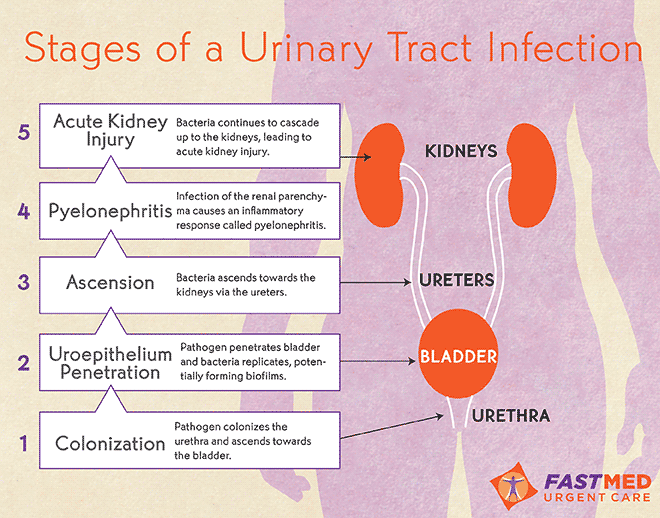 Among instrumental methods, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the bladder, ureteroscopy and cystoscopy (in case of violation of the passage of urine) are used.
Among instrumental methods, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the bladder, ureteroscopy and cystoscopy (in case of violation of the passage of urine) are used.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy
Asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy is dangerous for both mother and fetus, against its background, 25% of women develop acute pyelonephritis. According to the World Health Organization, about 8% of women report asymptomatic bacteriuria, 15-57% of women with untreated asymptomatic bacteriuria develop symptoms of a UTI (acute cystitis or pyelonephritis). Therapy of this disease during pregnancy reduces the risk of developing acute UTIs, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
Diagnosis of asymptomatic bacteriuria can be established by detecting 10 5 CFU/ml of one bacterial strain or 10 2 CFU/ml of uropathogen Escherichia coli field of view in the absence of clinical manifestations of UTI.
It should be remembered that the risk of this pathology is most real from the 9th to the 17th week of pregnancy.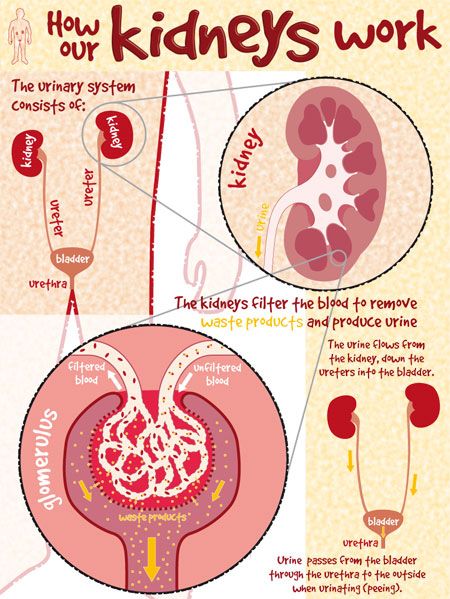 The only reliable method for diagnosing asymptomatic bacteriuria is the method of urine culture.
The only reliable method for diagnosing asymptomatic bacteriuria is the method of urine culture.
In accordance with Ukrainian and international guidelines for asymptomatic bacteriuria, oral antibiotic therapy with a single dose of fosfomycin trometamol is recommended.
Pyelonephritis: diagnosis
Pyelonephritis is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the kidneys of bacterial etiology with a primary and predominant lesion of the interstitium and tubular apparatus. The incidence of pyelonephritis during pregnancy reaches 33%, mortality - 3.5%, maternal mortality from kidney disease in the structure of extragenital pathology is 8-10%, the incidence of gestational pyelonephritis is 11.5%.
Primary pyelonephritis in pregnant women is difficult to treat, may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, pain in the lumbar region, the appearance of pyuria, bacteriuria. As a rule, the right kidney is affected more often than the left one, with expansion of the pelvicalyceal system (according to ultrasound).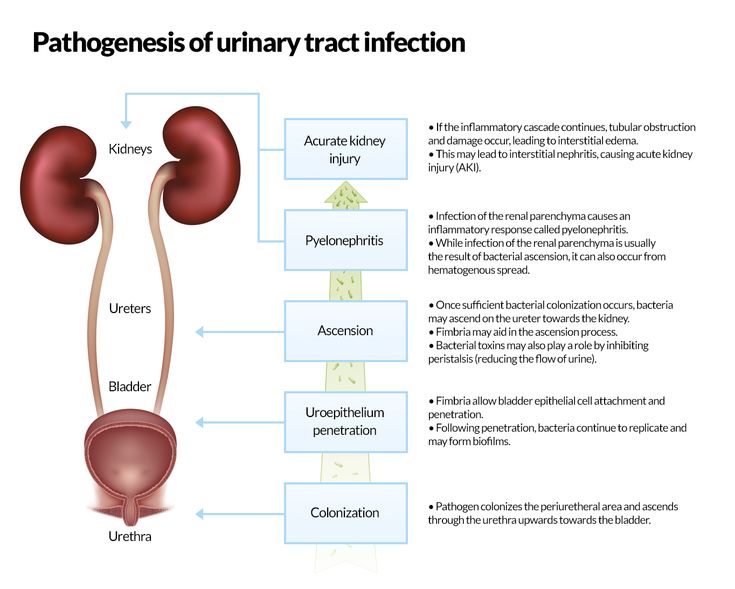
In acute pyelonephritis, the mandatory research methods are a general urinalysis (in 2 portions) 1 time in 7 days, a Nechiporenko urinalysis, a general and biochemical blood test, a bacteriological urinalysis, ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, daily proteinuria, a biochemical blood test , blood pressure monitoring, urologist consultation. Additional research methods - computed tomography without contrast or excretory urogram, nuclear magnetic resonance imaging - are carried out exclusively for strict, sometimes vital, indications.
It should be remembered that dysuria in primary acute cystitis with a body temperature of 38 ° C and chills may indicate acute ascending pyelonephritis. A sharp dysuric syndrome is characteristic of the associated cystitis during exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis. Urinary syndrome (proteinuria, leukocyturia, hematuria, etc.) may periodically disappear with a unilateral process and ureter occlusion; therefore, serial urine tests are necessary.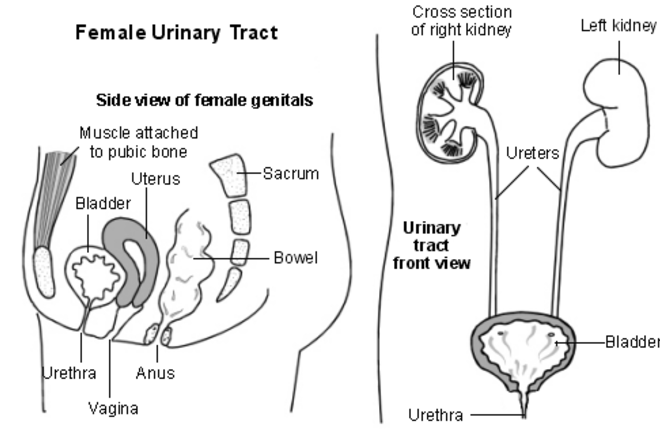 The degree of leukocyturia does not always correspond to the severity of the inflammatory process. A single urine culture gives at least 20% false positive results. Bacteriuria appears and can be detected 2 days earlier than pyuria.
The degree of leukocyturia does not always correspond to the severity of the inflammatory process. A single urine culture gives at least 20% false positive results. Bacteriuria appears and can be detected 2 days earlier than pyuria.
Choice of drugs for the treatment of pregnant women with UTIs
There are certain requirements for antibiotics for the treatment of UTIs in pregnant women. In particular, they must be effective against most pathogenic pathogens, have the ability to create a high concentration in organs - foci of infection, have a long half-life sufficient to maintain a high concentration of the antibiotic in the blood, not have toxic and allergic effects, be well tolerated by patients, be harmless to mother and fetus.
It has been shown that for the treatment of pregnant women with acute cystitis, asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute pyelonephritis, it is advisable to use antibacterial uroseptics. In particular, fosfomycin trometamol has a bactericidal effect associated with blocking the bacterial enzyme involved in the synthesis of the cell wall, as well as an anti-adhesive effect (destroys the fimbria of Escherichia coli, preventing it from fixing on the wall of the urothelium and promoting leaching from the urinary tract). After a single dose of the drug, the therapeutic concentration is observed for 48 hours (this is enough to sterilize urine and recover).
After a single dose of the drug, the therapeutic concentration is observed for 48 hours (this is enough to sterilize urine and recover).
An alternative to antibiotics are phytoneering preparations with anti-adhesive and antibacterial activity, as well as anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, nephroprotective properties.
Organization of care for pregnant women with UTI and prevention
Delivery of pregnant women with UTI (without obstetric pathology) is carried out through the natural birth canal, taking into account the obstetric situation.
There are degrees of risk of pyelonephritis:
- I degree - uncomplicated pyelonephritis that occurred during pregnancy;
- II degree - chronic uncomplicated pyelonephritis, noted before pregnancy;
- III degree - pyelonephritis with hypertension, azotemia, pyelonephritis of a single kidney.
They must be taken into account when managing pregnant women. So, at I-II degree of risk, pregnancy can be prolonged, but at III degree (creatinine> 265 μmol / l, glomerular filtration rate < 30 ml / min), pregnancy should be terminated.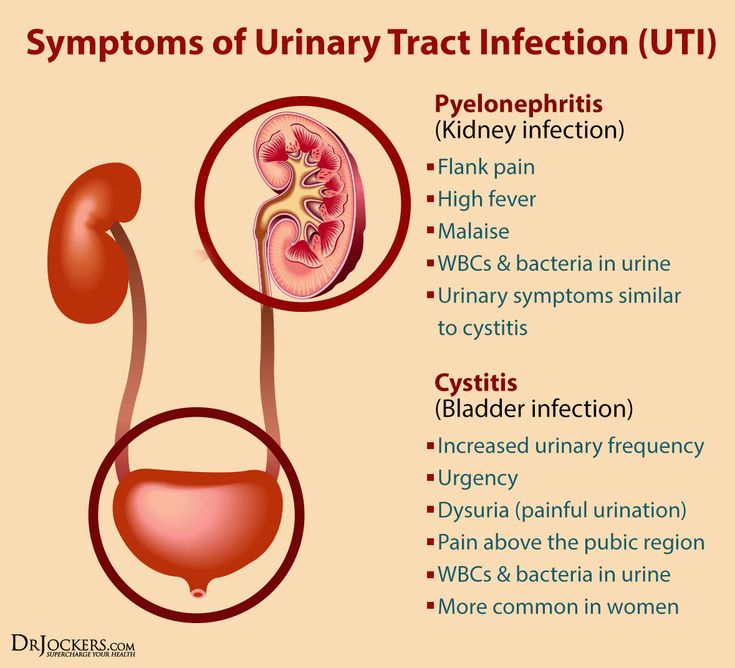
Prevention of UTIs in pregnant women should include sanitation of the vagina in case of violation of its microflora and other sources of infection (teeth, pharynx, etc.), normalization of bowel function, optimal water regime.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel, Viber community, Instagram, Facebook page, and Twitter to be the first to receive the latest and most relevant news from the world of medicine.
Marina Kolesnik,
photo of the author
What not to do with cystitis in early pregnancy
1. Take antibiotics unless prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication can lead to the development of fetal abnormalities. It is especially forbidden to take tetracycline, ofloxacin, norfloxacin, aminoglycosides.
2. Carrying out instillations. This procedure, during which an antibacterial drug is injected into the bladder, can cause an early miscarriage.
3. You can not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. This refers to the intake of nimesil, diclofenac, analgin, etc. Otherwise, the unborn child may experience severe pathologies.
This refers to the intake of nimesil, diclofenac, analgin, etc. Otherwise, the unborn child may experience severe pathologies.
4. Do not carry out physiotherapy procedures, so as not to provoke a miscarriage.
5. Do not take a hot bath, do not visit the sauna, bath. Avoid overheating to avoid uterine hypertonicity.
How does cystitis manifest during pregnancy
The inflammatory process in the bladder in a pregnant woman is manifested:
-
Frequent urination. This symptom does not always signal the appearance of cystitis. This is normal during pregnancy.
-
The appearance of itching and burning in the urethra. An increase in these symptoms is observed after urine has begun to stand out.
-
There is always a feeling that the bladder has not completely emptied.
-
False claims appear. The pregnant woman is in dire need of going to the toilet, but there is no urine output.

-
The stomach hurts, heaviness is felt in the lower part of the abdomen.
-
The color of the urine changes. It is cloudy, reddish in color. This is due to blood impurities.
-
After emptying the bladder, urine still leaks. The spread of the inflammatory process occurred on the sphincter. In this case, there was a violation of its functioning.
-
A woman observes that a purulent and mucous secretion has begun to be released from the urethra.
-
body intoxication. General weakness appears, the head often hurts, body temperature rises, there is no appetite.
Features of the treatment of cystitis in the later stages
Treatment of the disease in the third trimester of pregnancy is very similar to early treatment. However, there is a decrease in the risk of developing pathologies in the unborn child if the gestational age is more than 24 weeks.
At this time, the formation of the main organs, tissues and systems has already taken place. They just mature and develop. But at this stage of pregnancy, the likelihood of developing cystitis increases, which is dangerous for both the child and the pregnant woman with its complications.
They just mature and develop. But at this stage of pregnancy, the likelihood of developing cystitis increases, which is dangerous for both the child and the pregnant woman with its complications.
Those medicines and procedures that were prohibited at an early date may be prescribed at a later date. It must be remembered that only the attending physician can prescribe this. It takes into account all the risks of treatment for the expectant mother and her child.
Exemplary regimen for the treatment of disease in late pregnancy
1. Appointment of antibiotic therapy. They can prescribe amoxicillin, suprax, monural. If the disease is more severe, the doctor prescribes penicillins, macrolipids, and other cephalosporins.
2. Instillation is carried out. During the procedure, an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drug is injected into the bladder. This method can be carried out only in late pregnancy and only in the chronic form of the disease. The procedure is carried out in a hospital.
3. Herbal preparations (canephron, urolesan, cystone) are prescribed.
4. Treatment with antispasmodics.
5. Use of physiotherapy. Pregnant women may be prescribed electrophoresis or galvanophoresis with no-shpa or papaverine, calcium chloride, acetylsalicylic acid, antiseptic and antibiotic. These methods are indicated up to 34 weeks of pregnancy. Physiotherapy is in most cases prescribed for chronic cystitis. Contraindication is increased uterine tone, bleeding, preeclampsia, etc.
6. The use of immunostimulating drugs (flavozid or viferon).
It should be remembered that any therapeutic measures should be prescribed exclusively by a qualified and experienced specialist. With any attempt at self-treatment, the most deplorable consequences for the unborn child can occur.
Types of cystitis during pregnancy
Cystitis in early pregnancy can have a different etiology. This means that there is no single method of treating pathology. Drawing up a treatment regimen and prescribing drugs depends on the results of the diagnosis. The disease may be:
Drawing up a treatment regimen and prescribing drugs depends on the results of the diagnosis. The disease may be:
-
Hemorrhagic. The provoking factor is an infectious agent. They mean Escherichia or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacteria, streptococci. This is the most common form of cystitis. In such a situation, treatment with an antibacterial drug is necessary. The choice of the drug is carried out strictly by the attending physician, since the intake of certain drugs is prohibited in the first trimester of pregnancy.
-
Interstitial. This type of cystitis is characterized by a non-infectious inflammatory process, that is, the cause of the disease is an allergen or medication. To eliminate this form of the disease, an antibiotic is not prescribed. For the treatment of interstitial cystitis, a pregnant woman is shown taking anti-inflammatory, sedative and analgesic drugs.
-
Luchev. Refers to a rarer occurrence during pregnancy.
 This is explained by the fact that the conduct of radiation therapy to a woman is prohibited during the bearing of a child. For the treatment of this form of cystitis, antispasmodics, sedatives and drugs are prescribed that help accelerate regenerative processes.
This is explained by the fact that the conduct of radiation therapy to a woman is prohibited during the bearing of a child. For the treatment of this form of cystitis, antispasmodics, sedatives and drugs are prescribed that help accelerate regenerative processes. -
Sexual. An exacerbation of this form of cystitis during pregnancy occurs due to prior infection. Strengthening of the symptoms of the disease is observed after sexual intercourse, if there are no barrier means of protection. This can be easily explained. After intimacy, the microflora changes. If pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microorganisms have entered the urethra, a woman will notice the appearance of signs of cystitis. Genital inflammation of the bladder needs to take antiseptics, sedatives, diuretics.
Why does cystitis appear
The development of cystitis during pregnancy occurs under the influence of several factors. An important point is the timely determination of the causes that led to the appearance of cystitis.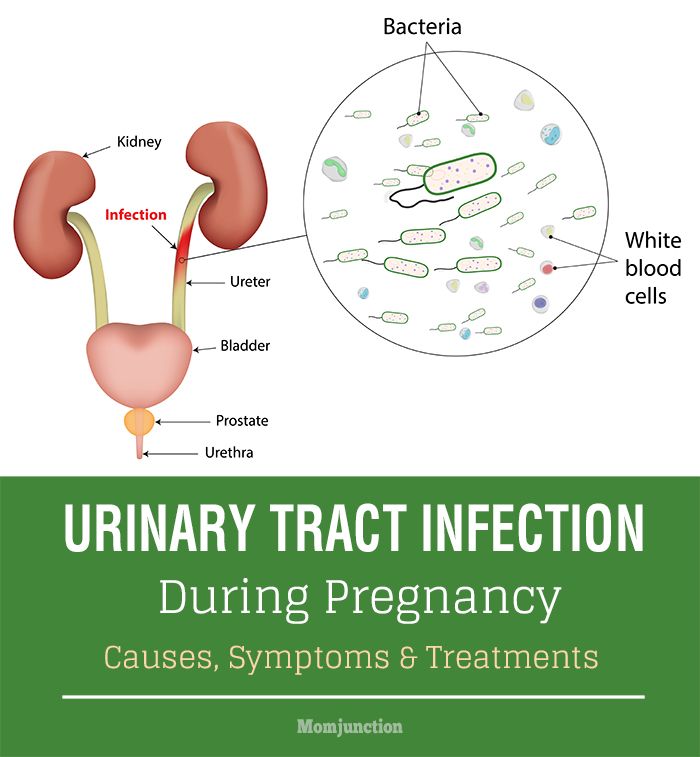 This is necessary so that the doctor can prescribe effective treatment and draw up a list of medical recommendations that will help the pregnant woman avoid a relapse of the disease. Also, it helps to prevent the transition of the disease into a chronic form.
This is necessary so that the doctor can prescribe effective treatment and draw up a list of medical recommendations that will help the pregnant woman avoid a relapse of the disease. Also, it helps to prevent the transition of the disease into a chronic form.
There are a number of factors that lead to cystitis:
-
Promiscuous sexual intercourse. The likelihood of infection during sexual contact increases, since the urethra and vagina are located in close proximity. It should be borne in mind that the penetration of infection into the urinary tract can occur, both from the mucous membrane of the vagina and the external genital organ of a woman.
-
Neglect of hygiene rules. It is necessary to wash the external genital organs daily, to wash after intimacy, to change underwear in a timely manner, to use daily pads. All this helps to reduce the likelihood of infection entering the urinary tract of a woman.
-
Prolonged presence of dysbacteriosis or vaginal candidiasis.
 If the vaginal microflora is disturbed, pathogenic microorganisms multiply much faster. This can cause an inflammatory response.
If the vaginal microflora is disturbed, pathogenic microorganisms multiply much faster. This can cause an inflammatory response. -
Impaired immunity. If immunity is lowered or allergic local pathologies are present, a significant decrease in the protective properties of the body occurs. As a result, pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms enter the bladder without any obstacles.
-
With infrequent urination. It is normal for a woman to empty her bladder at least 4 times a day. During pregnancy, this figure increases. There are various reasons why a timely trip to the toilet is not possible. And if it becomes regular, the structure of the urethra and the sphincter anatomically change. As a result of such changes, the normal emptying of the bladder is disrupted. In addition, if urine is in the bladder for a long time, optimal conditions are created for infectious development.
-
With regular hypothermia. If the body of a pregnant woman is often supercooled, its local protective properties are weakened, as a result of this, the likelihood of unhindered penetration of the infection into the bladder increases.
 Damaging factors contribute to the development of an inflammatory reaction in the walls of the bladder, as a result - the appearance of signs of cystitis.
Damaging factors contribute to the development of an inflammatory reaction in the walls of the bladder, as a result - the appearance of signs of cystitis.
All causes of cystitis are divided into infectious and non-infectious. There are four routes of bladder infection:
1. Descending - the penetration of the infection occurs from the inflamed organ, that is, the kidney.
2. Ascending - the initial localization of the infection that has entered the bladder is the external environment.
3. Lymphogenic - lymphatic vessels are involved in the movement of the infection. Basically, the focus of infection in the inflamed genital organ.
4. Hematogenous - the spread of infection occurs through the bloodstream from a distant purulent focus.
Non-infectious causes of cystitis:
-
An allergic reaction, which manifests itself in the form of an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the bladder.

-
Disturbed work of the immune system, nervous system.
-
If the lower abdomen or pubis is undergoing radiation therapy.
There are factors in the presence of which increases the likelihood of developing cystitis. This happens when:
-
regular hypothermia of the body.
-
Constant use of tight underwear.
-
Non-compliance with hygiene rules.
-
Chronic disease of one or another internal organ.
-
Overwork, hypovitaminosis.
-
Impaired emptying of the bladder.
-
Reduced protective functions of the body.
-
The presence of a foreign body that is located in the bladder.
Despite the fact that the most common cause of cystitis is a bacterial infection, the inflammatory process in the bladder can begin due to some non-infectious factors.
Under the influence of certain drugs, especially chemotherapy drugs, an inflammatory process in the bladder can begin. The cause of drug cystitis is the excretion of the decay products of medicines from the body.
With prolonged use of the catheter, there is an increase in susceptibility to bacterial infection. As a result, the likelihood of an inflammatory process increases. This is called foreign body cystitis.
Some women may be hypersensitive to a particular substance found in personal care or household products. They mean bath foam, feminine hygiene spray, spermicidal gel. In some situations, the inflammatory process is a consequence of the reaction of the body - allergies.
Diagnostic measures
If any signs of cystitis appear, a woman should immediately consult a doctor. At the appointment, the patient is asked about how long ago she noticed the onset of symptoms, whether this happened before, and also what diseases were previously transferred and are present now.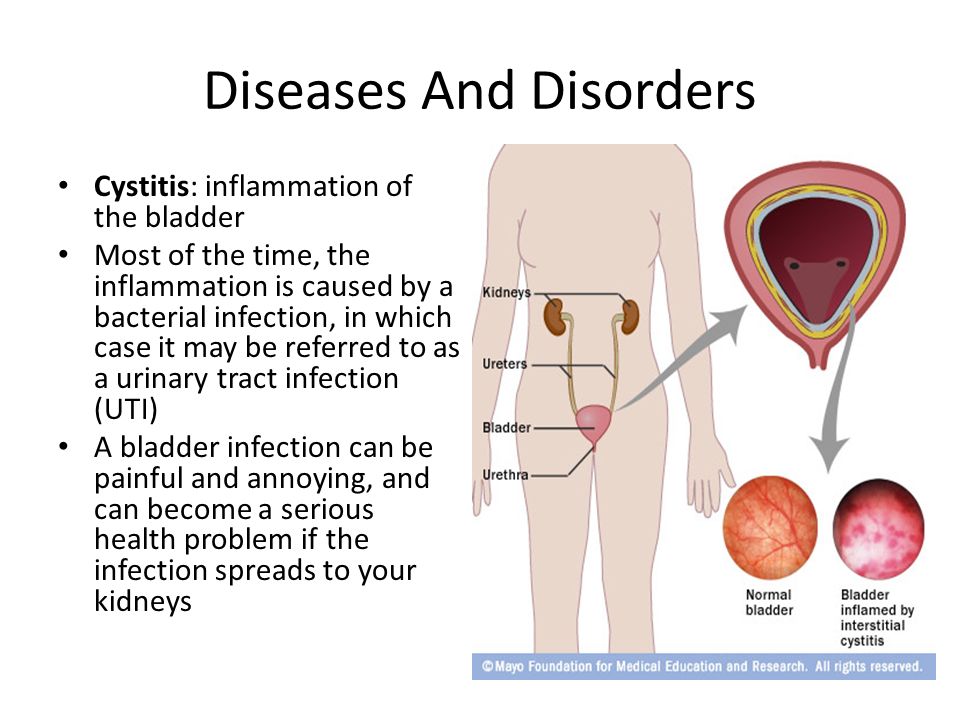 The patient must truthfully answer the questions. Otherwise, the doctor will not get a complete picture of what is happening to her.
The patient must truthfully answer the questions. Otherwise, the doctor will not get a complete picture of what is happening to her.
To detect cystitis, the doctor sends for a laboratory examination. It consists in the delivery of a general analysis of blood and urine. Thanks to such studies, it is possible to detect inflammation, the level of leukocytes and the immature form of neutrophils, the level of erythrocyte sedimentation rate. In addition, protein in the urine, bacteria are detected. If the result of a general urinalysis showed that the content of leukocytes is increased, the patient is prescribed a urine test according to Nechiporenko.
Conducting such a urine test will help determine what was the causative agent of the disease. As a result, more effective treatment is prescribed. With this method of examination, an antibiogram can be performed and the sensitivity of the pathogen to various types of antibacterial drugs can be determined.
Also, special test strips are used, thanks to which nitrites and leukocytes are determined. Such special strips give a reaction if the products of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms are present in the urine.
Such special strips give a reaction if the products of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms are present in the urine.
Ultrasound examination of the bladder helps to exclude stones in the organ, and also, the doctor assesses the condition of the upper urinary tract and the organs adjacent to the bladder. Ultrasound will allow to exclude a volumetric neoplasm.
How to prevent the development of cystitis
There are a number of recommendations, subject to which the likelihood of developing the disease decreases.
1. It is necessary to wash every day once a day. For these purposes, use soap, preferably for children. It does not contain fragrances and dyes.
2. Carefully monitor that the sexual partner observes the basic rules of personal hygiene. He must wash the external genitalia every day.
3. Before and after sexual intercourse, you should thoroughly wash yourself. Use soap. This rule must be respected by both sexual partners.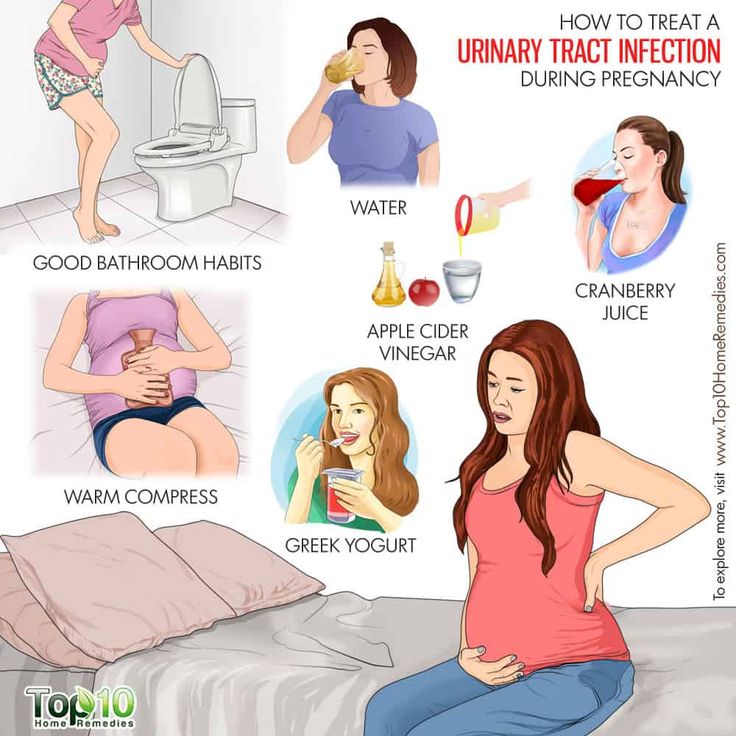
4. With stomatitis, tonsillitis, oral candidiasis and other infections, it is not recommended to have oral sex. This rule is easy to explain - with saliva, the infection is transmitted to the external genital organs, and then to the urethra.
5. Always dress for the weather. Hypothermia can cause chronic recurrent cystitis. It should be noted that cystitis is not the most terrible pathology that hypothermia can cause. In addition to cystitis, an inflammatory process develops in nearby organs, which can provoke a miscarriage.
6. Keep track of the state of your own immunity. If a woman often has a cold, it can be judged that the work of the immune system is reduced. To restore it, you need to contact a qualified specialist.
7. Try as much as possible not to hold back urination. With prolonged retention of urine in the bladder, an infection develops.
8. Drink enough fluids.
9. A man should change his underwear every day.